ural1519插头DP
1519. Formula 1
Time limit: 1.0 second
Memory limit: 64 MB BackgroundRegardless of the fact, that Vologda could not get rights to hold the Winter Olympic games of 20**, it is well-known, that the city will conduct one of the Formula 1 events. Surely, for such an important
thing a new race circuit should be built as well as hotels, restaurants, international airport - everything for Formula 1 fans, who will flood the city soon. But when all the hotels and a half of the restaurants were built, it appeared, that at the site for the future circuit a lot of gophers lived in their holes. Since we like animals very much, ecologists will never allow to build the race circuit over the holes. So now the mayor is sitting sadly in his office and looking at the map of the circuit with all the holes plotted on it. ProblemWho will be smart enough to draw a plan of the circuit and keep the city from inevitable disgrace?
Of course, only true professionals - battle-hardened programmers from the first team of local technical It should be said, that the circuit in Vologda is going to be rather simple. It will be a rectangleN*M cells in size with a single circuit segment built through each
cell. Each segment should be parallel to one of rectangle's sides, so only right-angled bends may be on the circuit. At the picture below two samples are given for N = M = 4 (gray squares mean gopher holes, and the bold black line means the race circuit). There are no other ways to build the circuit here. 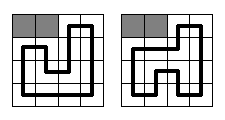 InputThe first line contains the integer numbers N and M (2 ≤ N, M ≤ 12). Each of the next N lines contains M characters,
which are the corresponding cells of the rectangle. Character "." (full stop) means a cell, where a segment of the race circuit should be built, and character "*" (asterisk) - a cell, where a gopher hole is located. OutputYou should output the desired number of ways. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 263-1.
Samples
|
分析看这(转):http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_51cea4040100gmky.html
依照上面链接分析就非常明白了,情况分清楚了就好写了
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#define INF 99999999
typedef long long LL;
using namespace std; const int MAX=300000+10;//最多的有效状态
const int N=10+10;
int n,m,size,index;
int mp[N][N],total[2],bit[N],ex,ey;//ex,ey记录最后一个非限制点,total记录有多少状态
int head[MAX],Next[MAX],Hash[MAX];//Hash用哈希查询状态,才用邻接表查询
//对于第i,j格仅仅须要用到第i,j-1格到达,所以才用滚动数组节省内存
LL dp[2][MAX],state[2][MAX],sum;//state记录对应状态,dp记录对应状态可到达的数量 void Init(){
memset(mp,0,sizeof mp);
sum=size=index=0;
total[index]=1;
state[index][1]=0;//初始化仅仅有一种可到达状态:没有不论什么插头
dp[index][1]=1;
} void HashCalState(LL s,LL num){
int pos=s%MAX;
for(int i=head[pos];i != -1;i=Next[i]){
if(state[index][Hash[i]] == s){
dp[index][Hash[i]]+=num;
return;
}
}
++total[index];
state[index][total[index]]=s;
dp[index][total[index]]=num;
//头插法
Hash[size]=total[index];
Next[size]=head[pos];
head[pos]=size++;
} void DP(){//才用4进制进行DP,x*4^y=x*2^(2*y)
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
for(int k=1;k<=total[index];++k)state[index][k]<<=2;//由上移一行到达这一行(i,0格)在上一行的0号插头前面再加一个插头,去掉最后一个插头(最后一个插头肯定为0)
for(int j=1;j<=m;++j){//求由i,j-1到达i,j的状态以及状态数
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
size=0;
index=index^1;
total[index]=0;
for(int k=1;k<=total[index^1];++k){//枚举上一格的状态,用来到达i,j某个状态
LL s=state[index^1][k];//取状态
LL num=dp[index^1][k];//取到达对应状态个数
int p=(s>>bit[j-1])%4;//取第j位
int q=(s>>bit[j])%4;//取第j+1位
if(!mp[i][j]){//i,j有限制不能通过,必须绕过
if(p+q == 0)HashCalState(s,num);//仅仅有p=q=0才干到达p'=q'=0的状态,才用哈希计算到达的状态以及个数
}else if(p+q == 0){//i,j无限制则必须有两个插头通过(一进一出)
if(!mp[i+1][j] || !mp[i][j+1])continue;
s=s+(1<<bit[j-1])+2*(1<<bit[j]);//创建新的连通块(添加第j,j+1个插头)
HashCalState(s,num);
}else if(!p && q){//p无插头,q有插头,则新状态须要添加一个插头
if(mp[i][j+1])HashCalState(s,num);//状态不变,连通块不变
if(mp[i+1][j]){
s=s+q*(1<<bit[j-1])-q*(1<<bit[j]);
HashCalState(s,num);
}
}else if(p && !q){//同上
if(mp[i+1][j])HashCalState(s,num);
if(mp[i][j+1]){
s=s-p*(1<<bit[j-1])+p*(1<<bit[j]);
HashCalState(s,num);
}
}else if(p+q == 2){//p=q=1,合并连通块
int b=1;
for(int t=j+1;t<=m;++t){//寻找近期的匹配的括号
int v=(s>>bit[t])%4;
if(v == 1)++b;
if(v == 2)--b;
if(b == 0){
s=s+(1<<bit[t])-2*(1<<bit[t]);//将右括号变为左括号
break;
}
}
s=s-(1<<bit[j-1])-(1<<bit[j]);
HashCalState(s,num);
}else if(p+q == 4){//p=q=2,同上
int b=1;
for(int t=j-2;t>=0;--t){//寻找近期的匹配括号
int v=(s>>bit[t])%4;
if(v == 2)++b;
if(v == 1)--b;
if(b == 0){
s=s-(1<<bit[t])+2*(1<<bit[t]);//将左括号变为右括号
break;
}
}
s=s-2*(1<<bit[j-1])-2*(1<<bit[j]);
HashCalState(s,num);
}else if(p == 1 && q == 2){//合并连通块,仅仅有最后一格的时候才连成整个回路
if(i == ex && j == ey)sum+=num;
}else if(p == 2 && q == 1){
s=s-2*(1<<bit[j-1])-(1<<bit[j]);
HashCalState(s,num);
}
}
}
}
} int main(){
char ch;
for(int i=0;i<N;++i)bit[i]=i<<1;//求4进制的某位用2进制求须要右移的位数*2
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){
Init();
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
getchar();
for(int j=1;j<=m;++j){
scanf("%c",&ch);
mp[i][j]=(ch == '.');
if(ch == '.')ex=i,ey=j;
}
}
DP();//插头DP
printf("%lld\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}
/*
12 12
............
............
............
............
............
............
............
............
............
............
............
............
9 10
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
..........
*/
版权声明:本文博客原创文章,博客,未经同意,不得转载。
ural1519插头DP的更多相关文章
- URAL1519 Formula 1 【插头dp】
题目链接 URAL1519 题解 看题型显然插头\(dp\) 考虑如何设计状态 有这样一个方案 当我们决策到某个位置 轮廓线长这样 你会发现插头一定是相互匹配的 所以我们实际上可以把状态用括号序列表示 ...
- URAL1519 Formula 1 —— 插头DP
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/URAL-1519 1519. Formula 1 Time limit: 1.0 secondMemory limit: 64 MB ...
- [URAL1519] Formula 1 [插头dp入门]
题面: 传送门 思路: 插头dp基础教程 先理解一下题意:实际上就是要你求这个棋盘中的哈密顿回路个数,障碍不能走 看到这个数据范围,还有回路处理,就想到使用插头dp来做了 观察一下发现,这道题因为都是 ...
- 模板:插头dp
前言: 严格来讲有关dp的都不应该叫做模板,因为dp太活了,但是一是为了整理插头dp的知识,二是插头dp有良好的套路性,所以姑且还叫做模板吧. 这里先推荐一波CDQ的论文和这篇博客http://www ...
- 省选算法学习-插头dp
插头dp?你说的是这个吗? 好吧显然不是...... 所谓插头dp,实际上是“基于连通性的状态压缩dp”的简称,最先出现在cdq的论文里面 本篇博客致力于通过几道小小的例题(大部分都比较浅显)来介绍一 ...
- [HNOI2007][bzoj1187] 神奇游乐园 [插头dp]
题面: 传送门 给定一个四联通棋盘图,每个格子有权值,求一条总权值最大的回路 思路: 插头dp基础教程 棋盘? 回路? n,m<=10? 当然是插头dp啦~\(≧▽≦)/~ 然后发现这道题并不是 ...
- ural 1519 fomular 1 既插头DP学习笔记
直接看CDQ在2008年的论文吧. 个人认为她的论文有两个不明确的地方, 这里补充一下: 首先是轮廓的概念. 我们在进行插头DP时, 是从上往下, 从左往右逐个格子进行的, 已经处理的格子与未经处理的 ...
- 插头dp
插头dp 感受: 我觉得重点是理解,算法并不是直接想出怎样由一种方案变成另一种方案.而是方案本来就在那里,我们只是枚举状态统计了答案. 看看cdq的讲义什么的,一开始可能觉得状态很多,但其实灰常简单 ...
- HDU 4113 Construct the Great Wall(插头dp)
好久没做插头dp的样子,一开始以为这题是插头,状压,插头,状压,插头,状压,插头,状压,无限对又错. 昨天看到的这题. 百度之后发现没有人发题解,hust也没,hdu也没discuss...在acm- ...
随机推荐
- atcoder它A Mountaineer
Time limit : 2sec / Stack limit : 256MB / Memory limit : 256MB Problem Dave is a mountaineer. He is ...
- C语言文件操作函数大全
http://blog.csdn.net/mu0206mu/article/details/18980913 clearerr(清除文件流的错误旗标) 相关函数 feof表头文件 #include&l ...
- SSH深度历险(三) EJB Session Bean有状态和无状态的差别与联系
刚開始对两种sessionbean存在误解.觉得有状态是实例一直存在,保存每次调用后的状态,并对下一次调用起作用.而觉得无状态是每次调用实例化一次,不保留用户信息.细致分析并用实践检验后,会发现,事实 ...
- 仿jQuery之链式调用
链式调用的形式其实就是对象调用一连串的方法.为什么能连续调用这么多的方法?因为调用方法返回调用的对象,于是乎就可以一如既往,一往无前地调用下去.链式调用的原理就是在方法中返回执行上下文this,每次调 ...
- C#从SQL server数据库中读取l图片和存入图片
原文:C#从SQL server数据库中读取l图片和存入图片 本实例主要介绍如何将图片存入数据库.将图片存入数据库,首先要在数据库中建立一张表,将存储图片的字段类型设为Image类型,用FileStr ...
- POJ 1743 Musical Theme Hash+二分法
标题效果:有一个美丽的旋律,它们是由一些不大于88音调.如果计为五个音调的量度,问:是否有相同的节奏的多个部分(相同的差,以及两者之间的相同的节奏不能重叠),并寻求最长长度. 思考:这个问题是八人中的 ...
- iframe参数
iframe参数: <iframe src="test.jsp" width="100″ height="50″ frameborder="no ...
- STUN协议简介
STUN简要 STUN(Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs,NAT 的UDP简单穿越)是一种网络协议.它同意位于NAT(或多重NAT)后的client找出自己的公网地址 ...
- Nyoj 三国志(dijkstra+01背包)
描述 <三国志>是一款很经典的经营策略类游戏.我们的小白同学是这款游戏的忠实玩家.现在他把游戏简化一下,地图上只有他一方势力,现在他只有一个城池,而他周边有一些无人占的空城,但是这些空城中 ...
- 面向对象三大特征之封装与static——(Java学习笔记四)
面向对象 编程本质:以类的方式组织代码,以对象的方式组织(封装)数据 对象:具体的事物,某个类的对象(实例) 类:是对对象的抽象,用于描述同一类型的对象的一个抽象概念 对象和类的关系:特殊到一 ...
