Rest-Framework组件源码之认证、频率、权限
一:使用RestFramwork,定义一个视图
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet class BookView(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
认证、频率和权限组件都由继承的ModelViewSet支持,所以要了解这三个组件的具体如何实现
对认证、频率、权限的管理就需要进入到其中查看
二:首先来了解组件认证

由上图可以看到ModelViewSet继承了六个类,前面的五个并没有组件的内容,不去管,接下来进入GenericViewSet类中看看
GenericViewSet这个类没有具体的代码,但是可以看到它继承了两个类ViewSetMixin,和generics.GenericAPIView
ViewSetMixin
这个类中主要需要了解的是as_view这个在url中使用的方法,这个类只是重写了as_view中的view方法,具体的核心代码如下
for method, action in actions.items():
handler = getattr(self, action)
setattr(self, method, handler)
简单来说,就是把url中传入的字典for循环,利用反射找到对应的方法重新设置get请求对应的函数
url(r'^authors/$', views.AuthorModelView.as_view({"get":"list","post":"create"})),
如上:在Django启动后,views.AuthorModelView.as_view({"get":"list","post":"create"})的执行结果是一个闭包函数view
请求发送进来,根据闭包函数外的actions:{"get":"list","post":"create"}设置self.get = list或者设置 self.post= create等等
由上可知,这个函数也与要找的组件关系不大。
generics.GenericAPIView
def get_queryset(self):
def get_object(self):
def get_serializer(self, *args, **kwargs):
def get_serializer_class(self):
def get_serializer_context(self):
def filter_queryset(self, queryset):
@property
def paginator(self):
def paginate_queryset(self, queryset):
def get_paginated_response(self, data):
类中方法与要找组件无关,继续进入其父类中找
在父类APIView中的dispach方法中
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)这一段代码负责所有的认证、权限和频率管理
因为视图的继承复杂,现在需要搞清楚类的继承关系和代码具体运行步骤,才好往下走
继承关系图
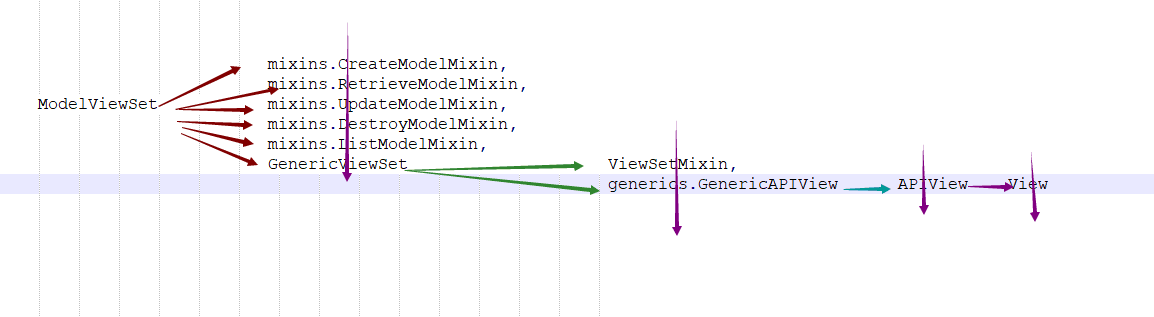
请求执行流程
Django启动
url(r'^authors/$', views.AuthorModelView.as_view({"get":"list","post":"create"})) 在Django启动时就执行,as_view的执行结果是一个闭包函数
view,由actions = {"get":"list","post":"create"}等参数包裹:
实际路由为:url(r'^authors/$', view)
请求到来:
根据继承关系:请求到来执行的view函数是类ViewSetMixin中的闭包函数view
view源代码
def view(request, *args, **kwargs):
self = cls(**initkwargs)
# We also store the mapping of request methods to actions,
# so that we can later set the action attribute.
# eg. `self.action = 'list'` on an incoming GET request.
self.action_map = actions # Bind methods to actions
# This is the bit that's different to a standard view
for method, action in actions.items():
handler = getattr(self, action)
setattr(self, method, handler) if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'):
self.head = self.get self.request = request
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs # And continue as usual
return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
可以看到,在将self.get,self.post等方法映射之后,view方法最终返回了self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)的执行结果
根据对象的属性和方法查找原则,self.dispatchfan方法调用的是类APIView中的dispatch方法
dispatch源码
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try:
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # 认证、频率、权限相关 # Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc) self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response
dispatch的核心功能就是根据请求的方法不同,分发执行不同的代码,并最终返回结果。
在这里我注意到,每次请求分发之前都会执行self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) 这段代码,也就是说每次请求都会进入这里执行。
initial源代码
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
self.perform_authentication(request) # 认证
self.check_permissions(request) # 权限
self.check_throttles(request) # 频率
initial中的核心代码是依次执行:
self.perform_authentication(request) # 认证
self.check_permissions(request) # 权限
self.check_throttles(request) # 频率
也就是:认证之后才会验证权限,权限验证之后才会验证频率
perform_authentication源代码
def perform_authentication(self, request):
request.user
perform_authentication中返回了request.user,首先要明白这个request来自于哪里?
从dispatch中一路过来,request一直没做处理,说明request至少来自于dispatch,APIView中dispatch的源码中有一行代码可以解释request的来源
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
initialize_request源码
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the initial request object.
"""
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
)
initialize_request代码中返回了一个Request类的对象,传入了
request
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
def __init__(self, request, parsers=None, authenticators=None,
negotiator=None, parser_context=None):
assert isinstance(request, HttpRequest), (
'The `request` argument must be an instance of '
'`django.http.HttpRequest`, not `{}.{}`.'
.format(request.__class__.__module__, request.__class__.__name__)
) self._request = request @property
def user(self):
"""
Returns the user associated with the current request, as authenticated
by the authentication classes provided to the request.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate()
return self._user
perform_authentication代码中执行的request.user就是执行的Request类的user方法
user方法中的代码代码表示如果没有_user属性就执行self._authenticate()
_authenticate源代码
def _authenticate(self):
"""
Attempt to authenticate the request using each authentication instance
in turn.
"""
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return self._not_authenticated()
_authenticate:for循环self.authenticators并赋值给authenticator,然后执行authenticate方法
首先要知道self.authenticators来自于哪里?
回溯代码:
_authenticate中调用了self.authenticators。
self对象来自于user方法
user方法中的self对象Request的实例化对象
Request的实例化对象的实例化对象有一个属性:
self.authenticators= authenticators or ()
authenticators 是一个Request类的实例化参数,默认为None,如果有传入参数则为传入的值
在initialize_request源代码中实例化时:authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
)
这时的self来自于调用initialize_request的对象
initialize_request在dispatch中被调用,dispatch的调用对象即是自定义的视图类的实例化对象
也即使说self.get_authenticators()是视图类调用的get_authenticators方法
get_authenticators源代码
def get_authenticators(self):
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]
get_authenticators中for循环视图类的authentication_classes的属性,加括号实例化组成一个列表返回
于是查找对象的属性,首先从对象自己找,然后从视图类中找,如果找不到,在依照继承关系从被继承的类中找
在被视图类所继承的类APIView中找到authentication_classes属性的定义
class APIView(View):
# The following policies may be set at either globally, or per-view.
renderer_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES
parser_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
permission_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES
content_negotiation_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS
metadata_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS
versioning_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS
# Allow dependency injection of other settings to make testing easier.
settings = api_settings
api_settings = APISettings(None, DEFAULTS, IMPORT_STRINGS)
APISettings类中并没有DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES属性,自动触发__getattr__方法
APISettings源码
class APISettings(object):
def __init__(self, user_settings=None, defaults=None, import_strings=None):
if user_settings: # 如果user_settings有值执行下列代码
self._user_settings = self.__check_user_settings(user_settings)
self.defaults = defaults or DEFAULTS
# defaults有值则赋给self.defaults,没有则把DEFAULTS赋值给self.defaults
self.import_strings = import_strings or IMPORT_STRINGS
self._cached_attrs = set()
@property
def user_settings(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_user_settings'): # 如果_user_settings没有定义
self._user_settings = getattr(settings, 'REST_FRAMEWORK', {})
# 从Django项目的settings文件中利用反射取出'REST_FRAMEWORK'的值赋给self._user_settings
return self._user_settings
def __getattr__(self, attr): # 对象用.attr的方法查找不到属性时自动触发
if attr not in self.defaults: # 如果self.defaults中没有查找的属性则报错
raise AttributeError("Invalid API setting: '%s'" % attr)
try:
# Check if present in user settings
val = self.user_settings[attr]
# 从self.user_settings执行返回的值中取出属性attr的的值赋给val
except KeyError:
# Fall back to defaults
val = self.defaults[attr]
# Coerce import strings into classes
if attr in self.import_strings:
# 如果属性attr在self.import_strings中通过反射取出对应的相应的方法或属性做进一步处理
val = perform_import(val, attr)
# Cache the result
self._cached_attrs.add(attr)
setattr(self, attr, val) # 利用反射给视图类对象设置一个属性attr值为val
return val
DEFAULTS = {
# Base API policies
'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer',
'rest_framework.renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer',
),
'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser',
'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser',
'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser'
),
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
),
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny',
),
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': (),
'DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.negotiation.DefaultContentNegotiation',
'DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.metadata.SimpleMetadata',
'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS': None,
# Generic view behavior
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': None,
'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS': (),
# Schema
'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.schemas.AutoSchema',
# Throttling
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'user': None,
'anon': None,
},
'NUM_PROXIES': None,
# Pagination
'PAGE_SIZE': None,
# Filtering
'SEARCH_PARAM': 'search',
'ORDERING_PARAM': 'ordering',
# Versioning
'DEFAULT_VERSION': None,
'ALLOWED_VERSIONS': None,
'VERSION_PARAM': 'version',
# Authentication
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': 'django.contrib.auth.models.AnonymousUser',
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
# View configuration
'VIEW_NAME_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_name',
'VIEW_DESCRIPTION_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_description',
# Exception handling
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler',
'NON_FIELD_ERRORS_KEY': 'non_field_errors',
# Testing
'TEST_REQUEST_RENDERER_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.renderers.MultiPartRenderer',
'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer'
),
'TEST_REQUEST_DEFAULT_FORMAT': 'multipart',
# Hyperlink settings
'URL_FORMAT_OVERRIDE': 'format',
'FORMAT_SUFFIX_KWARG': 'format',
'URL_FIELD_NAME': 'url',
# Input and output formats
'DATE_FORMAT': ISO_8601,
'DATE_INPUT_FORMATS': (ISO_8601,),
'DATETIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601,
'DATETIME_INPUT_FORMATS': (ISO_8601,),
'TIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601,
'TIME_INPUT_FORMATS': (ISO_8601,),
# Encoding
'UNICODE_JSON': True,
'COMPACT_JSON': True,
'STRICT_JSON': True,
'COERCE_DECIMAL_TO_STRING': True,
'UPLOADED_FILES_USE_URL': True,
# Browseable API
'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF': 1000,
'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF_TEXT': "More than {count} items...",
# Schemas
'SCHEMA_COERCE_PATH_PK': True,
'SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES': {
'retrieve': 'read',
'destroy': 'delete'
},
}
DEFAULTS
在本例中视图类中并没有重写authentication_classes,因此根据APISettings中的代码可知,程序首先在Django的settings文件中查找,由于settins文件中没有定义,因此抛出异常,最终从DEFAULTS中取得了authentication_classes的值
最终APIView中authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES的执行结果是
authentication_classes =
(
SessionAuthentication,
BasicAuthentication
),
于是
authenticators = [SessionAuthentication(),BasicAuthentication()]
最终在 _authenticate源代码中执行的是SessionAuthentication,BasicAuthentication这两个方法中的authenticate(self, request)方法
class SessionAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
"""
Use Django's session framework for authentication.
""" def authenticate(self, request):
"""
Returns a `User` if the request session currently has a logged in user.
Otherwise returns `None`.
""" # Get the session-based user from the underlying HttpRequest object
user = getattr(request._request, 'user', None) # Unauthenticated, CSRF validation not required
if not user or not user.is_active:
return None self.enforce_csrf(request) # CSRF passed with authenticated user
return (user, None) def enforce_csrf(self, request):
"""
Enforce CSRF validation for session based authentication.
"""
reason = CSRFCheck().process_view(request, None, (), {})
if reason:
# CSRF failed, bail with explicit error message
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied('CSRF Failed: %s' % reason)
authenticate方法的逻辑就是就是认证组件的实际逻辑
根据整个源码的思路,可以在重新写一个认证类,而其中必定有authenticate方法来控制验证逻辑
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication class TokenAuth(BaseAuthentication): def authenticate(self,request): token=request.GET.get("token",None) token_obj=UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if token_obj:
return token_obj.user.user,token_obj
else:
raise AuthenticationFailed("认证失败!")
Rest-Framework组件源码之认证、频率、权限的更多相关文章
- Django框架之DRF 认证组件源码分析、权限组件源码分析、频率组件源码分析
认证组件 权限组件 频率组件
- Rest_Framework之认证、权限、频率组件源码剖析
一:使用RestFramwork,定义一个视图 from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet class BookView(ModelViewSet ...
- Django-restframework 源码之认证组件源码分析
Django-restframework 源码之认证组件源码分析 一 前言 之前在 Django-restframework 的流程分析博客中,把最重要的关于认证.权限和频率的方法找到了.该方法是 A ...
- Django REST framework —— 权限组件源码分析
在上一篇文章中我们已经分析了认证组件源码,我们再来看看权限组件的源码,权限组件相对容易,因为只需要返回True 和False即可 代码 class ShoppingCarView(ViewSetMix ...
- .NET开发邮件发送功能的全面教程(含邮件组件源码)
今天,给大家分享的是如何在.NET平台中开发“邮件发送”功能.在网上搜的到的各种资料一般都介绍的比较简单,那今天我想比较细的整理介绍下: 1) 邮件基础理论知识 2) ...
- 浅探element-ui2组件源码之upload
最近不小心更新了element-ui的版本,已经到了2.1.0,以前修改的源码都失效了. 于是重新尝试下面的指令重新修改: git clone https://github.com/ElemeFE/e ...
- element-ui 组件源码分析整理笔记目录
element-ui button组件 radio组件源码分析整理笔记(一) element-ui switch组件源码分析整理笔记(二) element-ui inputNumber.Card .B ...
- element-ui input组件源码分析整理笔记(六)
input 输入框组件 源码: <template> <div :class="[ type === 'textarea' ? 'el-textarea' : 'el-in ...
- element-ui Message组件源码分析整理笔记(八)
Message组件源码: main.js import Vue from 'vue'; import Main from './main.vue'; import { PopupManager } f ...
随机推荐
- 【大数据】Hadoop的高可用HA
第1章 HA高可用 1.1 HA概述 1)所谓HA(high available),即高可用(7*24小时不中断服务). 2)实现高可用最关键的策略是消除单点故障(single point of fa ...
- 【刷题】BZOJ 4636 蒟蒻的数列
Description 蒟蒻DCrusher不仅喜欢玩扑克,还喜欢研究数列 题目描述 DCrusher有一个数列,初始值均为0,他进行N次操作,每次将数列[a,b)这个区间中所有比k小的数改为k,他想 ...
- Go 示例测试实现原理剖析
简介 示例测试相对于单元测试和性能测试来说,其实现机制比较简单.它没有复杂的数据结构,也不需要额外的流程控制,其核心工作原理在于收集测试过程中的打印日志,然后与期望字符串做比较,最后得出是否一致的报告 ...
- hdu2138 Miller_Rabin
Description Give you a lot of positive integers, just to find out how many prime numbers there are ...
- BZOJ 2426: [HAOI2010]工厂选址
2426: [HAOI2010]工厂选址 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 364 Solved: 248[Submit][Status ...
- java之初学线程
线程 学习线程相关的笔记,前面写过关于很多线程的使用,有兴趣的可以去了解下 线程 概念理解 并发 : 指两个或多个事件在同一个时间段内发生(交替执行). 并行 : 指两个或多个事件在同一时刻发生(同时 ...
- Java之集合Collection
集合 初次学习集合过程中的学习笔记,学习顶层,使用底层.包括常用的API Collection接口 概述 集合 : 集合是Java中提供的一种容器,可以用来存储多个数据. 与数组的区别: 数组的长度是 ...
- bzoj2755【SCOI2012】喵星人的入侵
输入格式 第一行为三个整数n,m,K,分别表示地图的长和宽,以及最多能放置的炮塔数量. 接下来的n行,每行包含m个字符,‘#’表示地图上原有的障碍,‘.’表示该处为空地,数据保证在原地图上存在S到T的 ...
- SIFT算法学习
几个关于SIFT算法的blog,写的很好,链接学习一下 小北的家谈谈SIFT.PCA-SIFT.SURF及我的一点思考http://blog.csdn.net/ijuliet/article/deta ...
- 服务器(Linux) 安装python3
1.python3和python2可以共存,不用删自带的python2 服务器Linux下默认系统自带python2.6的版本,这个版本被系统很多程序所依赖,所以不建议删除.如果使用最新的Python ...
