深入理解MyBatis的原理(三):配置文件(上)
前言:前文提到一个入门的demo,从这里开始,会了解深入 MyBatis 的配置,本文讲解 MyBatis 的配置文件的用法。
目录
配置 XML 文件的层次结构
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration><!--配置-->
<properties/><!--属性-->
<settions/><!--设置-->
<typeAliases/><!--类型命名,不区分大小写-->
<typeHandlers/><!--类型处理器-->
<objectFactory/><!--对象工厂-->
<plugins/><!--插件-->
<environments><!--配置环境-->
<environment>
<transactionManager/><!--事务管理器-->
<dataSource/><!--数据源-->
</environment>
</environments>
<databaseIdProvider/><!--数据库厂商标识-->
<mappers/><!--映射器-->
</configuration>
注意:MyBatis 配置 XML 文件的层次结构。这些层次是不能够颠倒顺序的,如果颠倒顺序,MyBatis 在解析 XML 文件的时候就会出现异常。
xml 为什么不能颠倒顺序
至于为什么不能颠倒顺序,是由于 MyBatis3 是使用 dtd 文件作为 xml 文件的格式校验的,而在 xml 规范中,dtd 是有严格校验顺序的。
在 idea 中,如果颠倒顺序,idea 会提示下图信息:

查看源码可以得知,在 org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-config.dtd 文件中,有明确定义该顺序:
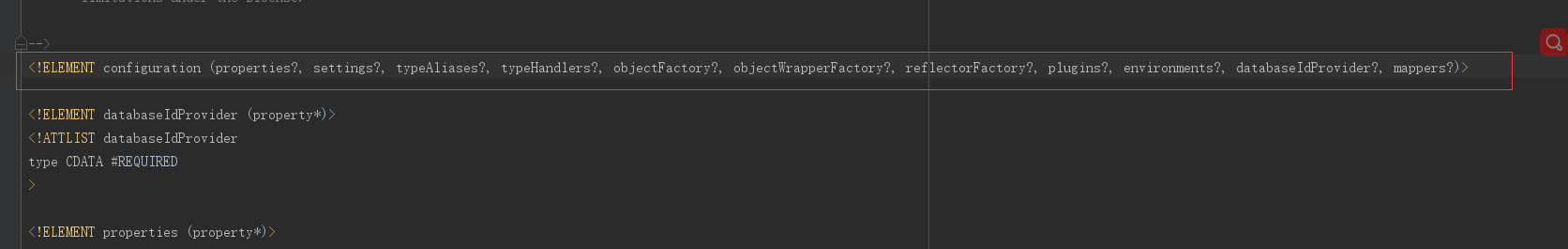
1、properties 元素
properties 是一个配置属性的元素,让我们能够在配置文件的上下文中(其他配置属性里面,比如环境配置)使用它。
我们可以有 3 种配置方式:property 子元素、properties 配置文件、程序的参数传递。
1.1、property 子元素
dtd 的规则
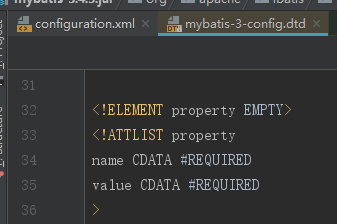
配置好后在数据库环境配置里使用
<!--属性,property 子元素-->
<properties>
<property name="driver" value="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="datasourceurl" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL"/>
<property name="username" value="testdev"/>
<property name="password" value="test1234"/>
</properties> <!--配置环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${datasourceurl}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
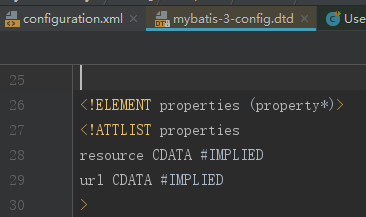
1.2 properties 配置文件
经常,我们都喜欢使用 properties 配置文件来配置属性值,方便我们在多个配置文件中重复使用,更是为了方便系统上线后的维护和修改。
dtd 的规则
建一个 db.properties 文件
driver=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
datasourceurl=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL
username=testdev
password=test1234
配置文件
<properties resource="config/system/db.properties"/>
<!--配置环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${datasourceurl}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
1.3 程序参数传递
有时,我们的数据库名和密码不对开发公布,而是由运维人员配置的,所以这是数据库名和密码可以加密配置在 db.properties 文件中,然后由程序去 decode,创建 sqlSessionFactory 时采用 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 的 public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties roperties) 方法。
程序部分代码如下
/**
* 初始化sqlSessionFactory,针对数据库的密码和用户名加密的情况
* @throws IOException
*/
public void initSqlSessionFactoryForEncodeDbInfo() throws IOException {
//读入配置文件流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("configuration.xml");
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
//读入属性文件
Reader propertiesReader = new InputStreamReader(Resources.getResourceAsStream("config/system/db.properties"));
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(propertiesReader);
//解密
properties.setProperty("username", decode(properties.get("username")));
properties.setProperty("password", decode(properties.get("password")));
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, properties);
}
1.4 优先级
方法参数传递的属性优先级最高,次之是 resource/url 属性中的配置,最后是 property 中的属性。
但是在实际中最好使用 properties 文件的配置方式。
2、设置(settings)
settings 比较复杂,也很重要,它会改变 MyBatis 运行时的行文。不配置 settings,MyBatis也可以正常工作。
大部分情况下,我们都可以不去配置 settings,或者只需修改几个配置即可。
| 设置参数 | 描述 | 有效值 | 默认值 |
| cacheEnabled | 该配置影响的所有映射器中配置的缓存的全局开关 | true | false | true |
| lazyLoadingEnabled | 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置fetchType属性来覆盖该项的开关状态 | true | false | false |
| aggressiveLazyLoading | 当启用时,对任意延迟属性的调用会使带有延迟加载属性的对象完整加载;反之,每种属性将会按需加载。 | true | false | true |
| multipleResultSetsEnabled | 是否允许单一语句返回多结果集(需要兼容驱动)。 | true | false | true |
| useColumnLabel | 使用列标签代替列名。不同的驱动在这方面会有不同的表现, 具体可参考相关驱动文档或通过测试这两种不同的模式来观察所用驱动的结果。 | true | false | true |
| useGeneratedKeys | 允许 JDBC 支持自动生成主键,需要驱动兼容。 如果设置为 true 则这个设置强制使用自动生成主键,尽管一些驱动不能兼容但仍可正常工作(比如 Derby)。 | true | false | False |
| autoMappingBehavior | 指定 MyBatis 应如何自动映射列到字段或属性。 NONE 表示取消自动映射;PARTIAL 只会自动映射没有定义嵌套结果集映射的结果集。 FULL 会自动映射任意复杂的结果集(无论是否嵌套)。 | NONE, PARTIAL, FULL | PARTIAL |
| defaultExecutorType | 配置默认的执行器。SIMPLE 就是普通的执行器;REUSE 执行器会重用预处理语句(prepared statements); BATCH 执行器将重用语句并执行批量更新。 | SIMPLE REUSE BATCH | SIMPLE |
| defaultStatementTimeout | 设置超时时间,它决定驱动等待数据库响应的秒数。 | Any positive integer | Not Set (null) |
| defaultFetchSize | Sets the driver a hint as to control fetching size for return results. This parameter value can be override by a query setting. | Any positive integer | Not Set (null) |
| safeRowBoundsEnabled | 允许在嵌套语句中使用分页(RowBounds)。 | true | false | False |
| mapUnderscoreToCamelCase | 是否开启自动驼峰命名规则(camel case)映射,即从经典数据库列名 A_COLUMN 到经典 Java 属性名 aColumn 的类似映射。 | true | false | False |
| localCacheScope | MyBatis 利用本地缓存机制(Local Cache)防止循环引用(circular references)和加速重复嵌套查询。 默认值为 SESSION,这种情况下会缓存一个会话中执行的所有查询。 若设置值为 STATEMENT,本地会话仅用在语句执行上,对相同 SqlSession 的不同调用将不会共享数据。 | SESSION | STATEMENT | SESSION |
| jdbcTypeForNull | 当没有为参数提供特定的 JDBC 类型时,为空值指定 JDBC 类型。 某些驱动需要指定列的 JDBC 类型,多数情况直接用一般类型即可,比如 NULL、VARCHAR 或 OTHER。 | JdbcType enumeration. Most common are: NULL, VARCHAR and OTHER | OTHER |
| lazyLoadTriggerMethods | 指定哪个对象的方法触发一次延迟加载。 | A method name list separated by commas | equals,clone,hashCode,toString |
| defaultScriptingLanguage | 指定动态 SQL 生成的默认语言。 | A type alias or fully qualified class name. | org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.XMLDynamicLanguageDriver |
| callSettersOnNulls | 指定当结果集中值为 null 的时候是否调用映射对象的 setter(map 对象时为 put)方法,这对于有 Map.keySet() 依赖或 null 值初始化的时候是有用的。注意基本类型(int、boolean等)是不能设置成 null 的。 | true | false | false |
| logPrefix | 指定 MyBatis 增加到日志名称的前缀。 | Any String | Not set |
| logImpl | 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找。 | SLF4J | LOG4J | LOG4J2 | JDK_LOGGING | COMMONS_LOGGING | STDOUT_LOGGING | NO_LOGGING | Not set |
| proxyFactory | 指定 Mybatis 创建具有延迟加载能力的对象所用到的代理工具。 | CGLIB | JAVASSIST | JAVASSIST (MyBatis 3.3 or above) |
3、别名(typeAliases)
别名是一个指代的名称。可以在 MyBatis 的上下文中使用。
在 MyBatis 中别名是不分大小写的。
一个 typeAliases 的实例是在解析配置文件时(源码在 XMLConfigBuilder 中)生成的,然后长期保存在 Configuration 对象中,当我们使用它时,再把它拿出来,这样就没有必要运行时再次生成它的实例了。
别名分为系统定义别名和自定义别名。
3.1 为什么 MyBatis 中别名是部分大小写的
因为源码 org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeAliasRegistry 如下:
public void registerAlias(String alias, Class<?> value) {
if(alias == null) {
throw new TypeException("The parameter alias cannot be null");
} else {
String key = alias.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if(this.TYPE_ALIASES.containsKey(key) && this.TYPE_ALIASES.get(key) != null && !((Class)this.TYPE_ALIASES.get(key)).equals(value)) {
throw new TypeException("The alias '" + alias + "' is already mapped to the value '" + ((Class)this.TYPE_ALIASES.get(key)).getName() + "'.");
} else {
this.TYPE_ALIASES.put(key, value);
}
}
}
3.2 系统定义别名
MyBatis 自己有定义一些常用的别名,我们可以直接使用它们,不用自己定义,也不要再使用时重复定义把它们给覆盖了。
支持数组类型的只要加“[]”即可。比如 Integer 数组,则别名为 int[]。
| 别名 | Java类型 | 是否支持数组 |
| _byte | byte | y |
| _long | long | y |
| _short | short | y |
| _int | int | y |
| _integer | int | y |
| _double | double | y |
| _float | float | y |
| _boolean | boolean | y |
| string | String | y |
| byte | Byte | y |
| long | Long | y |
| short | Short | y |
| int | Integer | y |
| integer | Integer | y |
| double | Double | y |
| float | Float | y |
| boolean | Boolean | y |
| date | Date | y |
| decimal | BigDecimal | y |
| bigdecimal | BigDecimal | y |
| object | Object | y |
| map | Map | n |
| hashmap | HashMap | n |
| list | List | n |
| arraylist | ArrayList | n |
| collection | Collection | n |
| iterator | Iterator | n |
| ResultSet | ResultSet |
n |
源码 org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeAliasRegistry 中可以看出其自定义注册的信息,源码如下:
public TypeAliasRegistry() {
this.registerAlias("string", String.class);
this.registerAlias("byte", Byte.class);
this.registerAlias("long", Long.class);
this.registerAlias("short", Short.class);
this.registerAlias("int", Integer.class);
this.registerAlias("integer", Integer.class);
this.registerAlias("double", Double.class);
this.registerAlias("float", Float.class);
this.registerAlias("boolean", Boolean.class);
this.registerAlias("byte[]", Byte[].class);
this.registerAlias("long[]", Long[].class);
this.registerAlias("short[]", Short[].class);
this.registerAlias("int[]", Integer[].class);
this.registerAlias("integer[]", Integer[].class);
this.registerAlias("double[]", Double[].class);
this.registerAlias("float[]", Float[].class);
this.registerAlias("boolean[]", Boolean[].class);
this.registerAlias("_byte", Byte.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_long", Long.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_short", Short.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_int", Integer.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_integer", Integer.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_double", Double.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_float", Float.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_boolean", Boolean.TYPE);
this.registerAlias("_byte[]", byte[].class);
this.registerAlias("_long[]", long[].class);
this.registerAlias("_short[]", short[].class);
this.registerAlias("_int[]", int[].class);
this.registerAlias("_integer[]", int[].class);
this.registerAlias("_double[]", double[].class);
this.registerAlias("_float[]", float[].class);
this.registerAlias("_boolean[]", boolean[].class);
this.registerAlias("date", Date.class);
this.registerAlias("decimal", BigDecimal.class);
this.registerAlias("bigdecimal", BigDecimal.class);
this.registerAlias("biginteger", BigInteger.class);
this.registerAlias("object", Object.class);
this.registerAlias("date[]", Date[].class);
this.registerAlias("decimal[]", BigDecimal[].class);
this.registerAlias("bigdecimal[]", BigDecimal[].class);
this.registerAlias("biginteger[]", BigInteger[].class);
this.registerAlias("object[]", Object[].class);
this.registerAlias("map", Map.class);
this.registerAlias("hashmap", HashMap.class);
this.registerAlias("list", List.class);
this.registerAlias("arraylist", ArrayList.class);
this.registerAlias("collection", Collection.class);
this.registerAlias("iterator", Iterator.class);
this.registerAlias("ResultSet", ResultSet.class);
}
3.3 自定义别名
(1)在配置文件中写法如下
<!--定义别名-->
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.yule.user.entity.User" alias="user"/>
</typeAliases>
(2)或者当实体类较多的时候,使用自动扫描的形式自定义别名
<!--定义别名-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.yule.user.entity"/>
</typeAliases>
同时也可以在实体类上使用注解 @Alias
@Alias("user")
public class User {
//do somethings
}
注意:如果配置了包扫描的路径,那么没有在实体上加注解 @Alias 的类也在装载在 MyBatis 的上下文中,只是 MyBatis 将类名的第一个字母变为小写,作为 MyBatis 上下文中的别名,所以要特别注意避免重名的情况,建议使用部分包名+类名的限定。
深入理解MyBatis的原理(三):配置文件(上)的更多相关文章
- 深入理解MyBatis的原理:整个体系
前言:工作中虽然用到了 MyBatis,可完全不知道为什么,再不学习就晚了,这里将记录我的学习笔记,整个 MyBatis 的体系. 一.简介 1.传统的JDBC JDBC 是一种典型的桥接模式. 使用 ...
- 深入理解MyBatis的原理(三):配置文件用法(续)
前言:前文讲解了 MyBatis 的配置文件一部分用法,本文将继续讲解 MyBatis 的配置文件的用法. 目录 1.typeHandler 类型处理器 2.ObjectFactory 3.插件 4. ...
- 深入理解MyBatis的原理(四):映射器的用法
前言:继续深入学习 mybatis 的用法及原理,还是先会用再学习原理. 映射器的主要元素有:select.insert.update.delete.parameterMap(即将被删除,不建议使用) ...
- 深入理解MyBatis的原理(一): 独立的入门demo
前言:不结合spring,只有 mybatis+maven.数据库使用 oracle.不尝试永远不知道会发生什么事,其中遇到两个小问题,也记录下来了.转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblo ...
- 《深入理解mybatis原理》 Mybatis初始化机制具体解释
对于不论什么框架而言.在使用前都要进行一系列的初始化,MyBatis也不例外. 本章将通过下面几点具体介绍MyBatis的初始化过程. 1.MyBatis的初始化做了什么 2. MyBatis基于XM ...
- 《深入理解mybatis原理》 MyBatis的架构设计以及实例分析
作者博客:http://blog.csdn.net/u010349169/article/category/2309433 MyBatis是目前非常流行的ORM框架,它的功能很强大,然而其实现却比较简 ...
- 深入理解Mybatis技术与原理
目录 第1章 Mybatis简介 1.1 传统的JDBC编程 1.2 ORM模型 1.4 MyBatis 1.5 什么时候用MyBatis 第2章 MyBatis入门 2.2 MyBatis构成 2. ...
- 深入理解mybatis原理, Mybatis初始化SqlSessionFactory机制详解(转)
文章转自http://blog.csdn.net/l454822901/article/details/51829785 对于任何框架而言,在使用前都要进行一系列的初始化,MyBatis也不例外.本章 ...
- 《深入理解mybatis原理2》 Mybatis初始化机制详解
<深入理解mybatis原理> Mybatis初始化机制详解 对于任何框架而言,在使用前都要进行一系列的初始化,MyBatis也不例外.本章将通过以下几点详细介绍MyBatis的初始化过程 ...
随机推荐
- react.js 点击事件传递参数的方法
<button onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this, props0, props1, ...}></button> handleClick( ...
- fullpage.js与animate.css搭配使用
jquery的fullpage.js插件的使用 https://alvarotrigo.com/fullPage/#3rdPage 官网 https://github.com/alvarotrig ...
- Redis数据类型之SDS简单动态字符串
一,简单的动态字符串 1,Redis自己构建了一种名为简单动态字符串的抽象类型,并将SDS用作Redis的默认字符串表示, 2,在redis的数据库里面,包含字符串值的键值对在底层都是由SDS实现的 ...
- 解决ssh/scp报错:Someone could be eavesdropping on you right now (man-in-the-middle attack)!
主要现象:ssh/scp 失败,host key verification failed. # scp /home/iso/********.iso root@192.168.1.***:/home/ ...
- 机器学习实战(一)k-近邻算法
转载请注明源出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/7593656.html 1.原理 本章介绍机器学习实战的第一个算法——k近邻算法(k Nearest Neighb ...
- Java之IO(十四)IO包中其它类
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lighten/p/7267553.html 1.前言 此章介绍IO包中剩余未介绍的几个流和工具类,包括LineNumberReader. ...
- ActiveMQ学习--002--Topic消息例子程序
一.非持久的Topic消息示例 注意 此种方式消费者只能接收到 消费者启动之后,发送者发送的消息. 发送者 package com.lhy.mq.helloworld; import java.uti ...
- Mapreduce部署与第三方依赖包管理
Mapreduce部署是总会涉及到第三方包依赖问题,这些第三方包配置的方式不同,会对mapreduce的部署便捷性有一些影响,有时候还会导致脚本出错.本文介绍几种常用的配置方式: 1. HADOOP_ ...
- Exceptionless搭配log4net记录日志
接上篇: Exceptionless 本地部署 在部署完成后可以使用log4net搭配Exceptionless来记录日志. 过程很简单,使用Nuget安装Exceptionless.Log4net, ...
- WordPress主题制作导航的N种方法
在WordPress主 题制作中,导航菜单的制作算是一个重点,已经写好导航菜单的HTML代码,放在WordPress主题中如何动态调用呢?本文将给你介绍几种编写PHP代 码动态实现导航的方法,本文也将 ...
