Java集合(五)--LinkedList源码解读
首先看一下LinkedList基本源码,基于jdk1.8
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
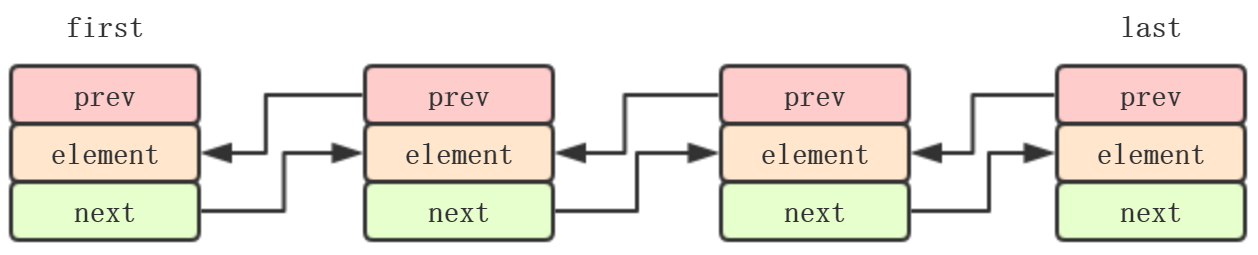
transient int size = 0; //指向第一个节点
transient Node<E> first; //指向最后一个节点
transient Node<E> last; public LinkedList() {
} public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
从LinkedList基本代码结构,可以看出来LinkedList本质上链表
链表一般分为:单向链表、单向循环链表、双向链表、双向循环链表
LinkedList就是一个双向链表,而且实现了Deque,也可以当做双端队列使用,使用方法比较丰富
PS:JDK1.6的LinkedList为双向循环链表,之后去掉header,通过双向链表实现
一、添加:
offer()、add()和linkLast():
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e); //添加到尾部
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last; //最后一个节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //生成一个新节点,前置为last,数据为e,next为null
last = newNode; //将新节点赋值为last
if (l == null) //如果l为null,意味着链表为空,所以置为首节点
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode; //否则将新节点置为l的next节点
size++;
modCount++; //修改次数modCount+1
}

addAll():
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index); //检查下标位置是否越界
Object[] a = c.toArray(); //将Collection转换为数组
int numNew = a.length; //数组的长度numNew
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ; //定义两个节点pred,succ。pred为插入集合的前一个节点,succ为插入集合的后一个节点
if (index == size) { //如果插入的位置等于size,将集合元素加到链表的尾部
succ = null; //succ赋值为null
pred = last; //pred赋值为last
} else {
succ = node(index); //succ赋值为index节点
pred = succ.prev; //succ的prev指向pred
}
for (Object o : a) { //遍历数组
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; //元素转换为E
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); //生成一个新节点,并且把prev指向pred
if (pred == null) //如果pred为null,newNode为首节点
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode; //pred的next指向newNode
pred = newNode; //把newNode赋值为pred
}
if (succ == null) { //如果插入到尾部
last = pred; pred赋值为last,pred此时为数组中最后一个元素Node
} else {
pred.next = succ; //pred的next指向succ
succ.prev = pred; //succ的prev指向pred
}
size += numNew; //重新赋值size
modCount++; //修改次数增加一次
return true;
}

图中把每一步都表现出来了,不可能看不懂吧
PS:
把Collection转换为数组的目的:toArray()保证传进来的这个集合不会被任何地方引用,也保证这个集合不会有任何机会被修改,保证了数
据的安全性
offFirst()、offLast()、addLast()和addFirst()这里就不讲了,看了上面,这里就很容易理解
二、删除:
poll()、remove()、removeFirst()和unlinkFirst():
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() { //删除first
final Node<E> f = first; //得到first节点
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item; //得到first节点的item
final Node<E> next = f.next; //first节点的next
f.item = null; //item置为null
f.next = null; //first节点的next置为null
first = next; //将first节点的next置为首节点
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
pollLast()、removeLast()和unlinkLast():
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last; //得到last节点
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { //释放last节点
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null;
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
比较简单,看下就明白了
remove(Object)和remove(index):
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) { //如果o为null
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) { //遍历node直到找到第一个null的index
unlink(x); //删除index节点
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {//遍历node直到找到第一个o的index
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) { //如果为上个节点prev等于null,直接把下个节点指向first
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next; //prev的next赋值为下个node
x.prev = null; 当前节点的上个节点置为null
}
if (next == null) { //如果删除last节点,直接把上个节点置为last节点
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev; //next节点的prev指向prev节点
x.next = null; //当前节点的next置为null
}
x.item = null; //当前节点item置为null,size--
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}

三、修改:set(index, element):
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index); //检查index是否越界
Node<E> x = node(index); //获取index对应的节点
E oldVal = x.item; //获取节点的item
x.item = element; //重新赋值节点的item
return oldVal; //返回oldVal
}
四、获取:
get(index)和node(index):
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index); //检查下标
return node(index).item; //返回index对应node的item
}
Node<E> node(int index) { //使用二分法查找
if (index < (size >> 1)) { 如果index小于size的一半
Node<E> x = first; //获取first节点
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) //因为链表不能随机访问,所以只能从0遍历到index,最终返回index对应的node
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last; //获取last节点
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) //从size-1遍历到index,最终返回index对应的node
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
getFirst():
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
getLast():
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
contains(Object)和indexOf(Object):
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) { //如果Object为null
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { //遍历得到第一个null,返回index
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { //遍历得到第一个和object相等的node.item,返回index
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1; //如果没有,返回-1
}
for循环效率:for、foreach、lambda表达式的foreach、Iterator
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("def");
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
list.add("abc");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("普通for循环花费时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String s : list) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("foreach循环花费时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime1));
long startTime3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
list.forEach(s -> {
System.out.print(s + " ");
});
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("lambda表达式foreach循环花费时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime3));
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String s = (String)iterator.next();
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("Iterator循环花费时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime2));
}
为了结果的可信度,我们得到三次输出结果:
普通for循环花费时间:105
foreach循环花费时间:43
lambda表达式foreach循环花费时间:78
Iterator循环花费时间:31 普通for循环花费时间:97
foreach循环花费时间:47
lambda表达式foreach循环花费时间:79
Iterator循环花费时间:32 普通for循环花费时间:83
foreach循环花费时间:49
lambda表达式foreach循环花费时间:77
Iterator循环花费时间:34
普通for循环和lambda表达式foreach都很慢,Iterator最快
普通for循环最慢,应该是可以想象到的,因为LinkedList不能随机访问,每次获取都要从头到尾遍历,我们遍历10000次
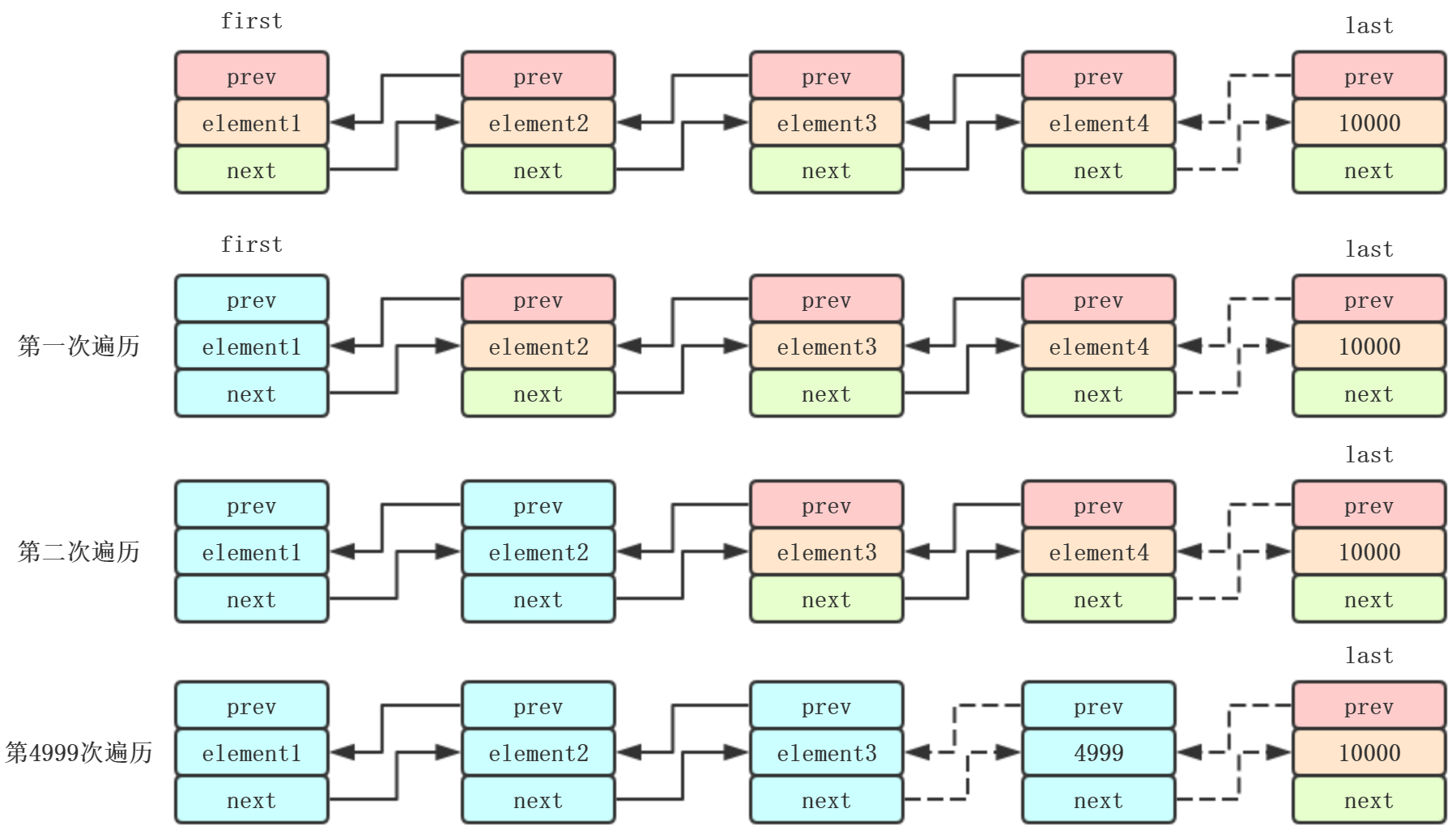
虽然使用二分法可以提高效率,靠近中间的index,效率真的很慢,例如4999,5000,5001
而Iterator通过ListItr实现:
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node<E> lastReturned; //本次返回的node
private Node<E> next; //本次返回的node的next节点
private int nextIndex; //下一个node对应的index
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next; //
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
}
每次都会记录这次返回的node,下次遍历,直接取node.next,例如第4999次遍历的时候,直接返回element4998.next,而不需要像普通for循环
一样,先得到1,再是2,然后3,最后到4999
到这里,对LinkedList的了解已经差不多零,能得到的内容:
1、LinkedList由双向链表实现,add(index,element)的效率很高,只需要直接修改node的prev和next关系,但是需要new node
2、删除的时候也很快
3、不涉及到初始容量、加载因子、扩容等概念
4、不能随机访问,查询效率较慢相对于ArrayList差很多
总结:对链表的任意修改都可以归结:改变node的前后指向关系
Java集合(五)--LinkedList源码解读的更多相关文章
- java集合之LinkedList源码解读
源自:jdk1.8.0_121 LinkedList继承自AbstractSequentialList,实现了List.Deque.Cloneable.Serializable. LinkedList ...
- 死磕 java集合之LinkedList源码分析
问题 (1)LinkedList只是一个List吗? (2)LinkedList还有其它什么特性吗? (3)LinkedList为啥经常拿出来跟ArrayList比较? (4)我为什么把LinkedL ...
- 【Java集合】ArrayDeque源码解读
简介 双端队列是一种特殊的队列,它的两端都可以进出元素,故而得名双端队列. ArrayDeque是一种以循环数组方式实现的双端队列,它是非线程安全的. 它既可以作为队列也可以作为栈. 继承体系 Arr ...
- Java集合:LinkedList源码解析
Java集合---LinkedList源码解析 一.源码解析1. LinkedList类定义2.LinkedList数据结构原理3.私有属性4.构造方法5.元素添加add()及原理6.删除数据re ...
- Java集合之LinkedList源码分析
概述 LinkedLIst和ArrayLIst一样, 都实现了List接口, 但其内部的数据结构不同, LinkedList是基于链表实现的(从名字也能看出来), 随机访问效率要比ArrayList差 ...
- Java集合之LinkedList源码解析
LinkedList简介 LinkedList基于双向链表,即FIFO(先进先出)和FILO(先进后出)都是支持的,这样它可以作为堆栈,队列使用 继承AbstractSequentialList,该类 ...
- Java 集合之LinkedList源码分析
1.介绍 链表是数据结构中一种很重要的数据结构,一个链表含有一个或者多个节点,每个节点处理保存自己的信息之外还需要保存上一个节点以及下一个节点的指针信息.通过链表的表头就可以访问整个链表的信息.Jav ...
- java集合之ArrayList源码解读
源自:jdk1.8.0_121 ArrayList继承自AbstractList,实现了List.RandomAccess.Cloneable.Serializable. ArrayList内部是通过 ...
- Java集合干货——LinkedList源码分析
前言 在上篇文章中我们对ArrayList对了详细的分析,今天我们来说一说LinkedList.他们之间有什么区别呢?最大的区别就是底层数据结构的实现不一样,ArrayList是数组实现的(具体看上一 ...
随机推荐
- opencord视频截图
参考:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Teu9jK6GF6s
- 洛谷 - P1403 - 约数研究 - 数论
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1403 可以直接用线性筛约数个数求出来,但实际上n以内i的倍数的个数为n/i的下整,要求的其实是 $$\sum\limi ...
- 洛谷 - P1739 - 表达式括号匹配 - 模拟 - 栈
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1739 虽然应该是用栈的……但是直接模拟就可以了. #include<bits/stdc++.h> usin ...
- poj1661【DP,左右两端dp】
/* [过滤这一段~~~] 一开始想的[错误的,为自己的总结的写的,读者略过]: 每个状态的点肯定是高度,那么我DP每一层,这样的话就有一层循环,其实这无关复杂度,不会很多时间 错误的是想法是从最高层 ...
- 使用PDO操作数据库的好处
PDO一是PHP数据对象(PHP Data Object)的缩写. 并不能使用PDO扩展本身执行任何数据库操作,必须使用一个database-specific PDO driver(针对特定数据库的P ...
- IT兄弟连 JavaWeb教程 HTTP协议
超文本传输协议(HTTP,Hypertext Transfer Protocol)是互联网上应用最为广泛的一种网络协议.所有的Web文件都必须遵守这个标准.设计HTTP最初的目的是为了提供一种发布和接 ...
- hdu1856 More is better 基础并查集
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdlib> ...
- Centos6.8 搭建 Mysql 主从复制
实例环境: MySQL-Master:Centos-6.8:192.168.153.130 MySQL-Slave:Centos-6.8:192.168.153.131 1.两台服务器安装mysql ...
- spring mvc No mapping found for HTTP request with URI [/web/test.do] in DispatcherServlet with name 'spring'
原因: spring-servlet.xml 中 <context:component-scan base-package="com.test.controller" /&g ...
- linux虚拟机时间不准的问题
如果时区不准, 使用tzselect命令(timezone选择),选择北京时间.然后把输出的命令写入/etc/profile.d/time.sh里. 然后用crontab写定时任务,每天执行一次. 3 ...
