ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined)
靠这把上了蓝
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given a string A. Find a string B, where B is a palindrome and A is a subsequence of B.
A subsequence of a string is a string that can be derived from it by deleting some (not necessarily consecutive) characters without changing the order of the remaining characters. For example, "cotst" is a subsequence of "contest".
A palindrome is a string that reads the same forward or backward.
The length of string B should be at most 104. It is guaranteed that there always exists such string.
You do not need to find the shortest answer, the only restriction is that the length of string B should not exceed 104.
First line contains a string A (1 ≤ |A| ≤ 103) consisting of lowercase Latin letters, where |A| is a length of A.
Output single line containing B consisting of only lowercase Latin letters. You do not need to find the shortest answer, the only restriction is that the length of string B should not exceed 104. If there are many possible B, print any of them.
aba
aba
ab
aabaa
In the first example, "aba" is a subsequence of "aba" which is a palindrome.
In the second example, "ab" is a subsequence of "aabaa" which is a palindrome.
输出一个字符串是输入串的子串,并且是回文串,不要求最短
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=1e5+;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
string s;
cin>>s;
cout<<s;
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
cout<<s;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Let us define two functions f and g on positive integer numbers.
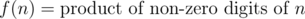

You need to process Q queries. In each query, you will be given three integers l, r and k. You need to print the number of integers xbetween l and r inclusive, such that g(x) = k.
The first line of the input contains an integer Q (1 ≤ Q ≤ 2 × 105) representing the number of queries.
Q lines follow, each of which contains 3 integers l, r and k (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ 106, 1 ≤ k ≤ 9).
For each query, print a single line containing the answer for that query.
4
22 73 9
45 64 6
47 55 7
2 62 4
1
4
0
8
4
82 94 6
56 67 4
28 59 9
39 74 4
3
1
1
5
In the first example:
- g(33) = 9 as g(33) = g(3 × 3) = g(9) = 9
- g(47) = g(48) = g(60) = g(61) = 6
- There are no such integers between 47 and 55.
- g(4) = g(14) = g(22) = g(27) = g(39) = g(40) = g(41) = g(58) = 4
他本来是递归函数,我们需要先预处理就可以了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=1e6+;
int a[N][];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
for(int i=;i<=1e6;i++)
{
int t=i;
while(t>=)
{
int s=;
while(t)
{
if(t%)s*=t%;
t/=;
}
t=s;
}
for(int j=;j<;j++)
a[i][j]=a[i-][j]+(t==j);
}
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int l,r,k;
cin>>l>>r>>k;
cout<<a[r][k]-a[l-][k]<<"\n";
} return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
For a permutation P[1... N] of integers from 1 to N, function f is defined as follows:
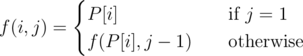
Let g(i) be the minimum positive integer j such that f(i, j) = i. We can show such j always exists.
For given N, A, B, find a permutation P of integers from 1 to N such that for 1 ≤ i ≤ N, g(i) equals either A or B.
The only line contains three integers N, A, B (1 ≤ N ≤ 106, 1 ≤ A, B ≤ N).
If no such permutation exists, output -1. Otherwise, output a permutation of integers from 1 to N.
9 2 5
6 5 8 3 4 1 9 2 7
3 2 1
1 2 3
In the first example, g(1) = g(6) = g(7) = g(9) = 2 and g(2) = g(3) = g(4) = g(5) = g(8) = 5
In the second example, g(1) = g(2) = g(3) = 1
递归版的轮换,一组等于a,一组等于b即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,a,b,f=,fa,fb;
cin>>n>>a>>b;
if(b>a)swap(a,b);
for(int i=; i<=n&&f; i+=a)
if((n-i)%b==)
fa=i/a,fb=(n-i)/b,f=;
if(f)
cout<<-;
else
{
int i=;
for(; i<=fa*a; i+=a)
{
cout<<i+a-<<" ";
for(int j=i; j<i+a-; j++)
cout<<j<<" ";
}
for(; i<=n; i+=b)
{
cout<<i+b-<<" ";
for(int j=i; j<i+b-; j++)
cout<<j<<" ";
}
}
return ;
}
2 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given a node of the tree with index 1 and with weight 0. Let cnt be the number of nodes in the tree at any instant (initially, cnt is set to 1). Support Q queries of following two types:
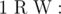 Add a new node (index cnt + 1) with weight W and add edge between node R and this node.
Add a new node (index cnt + 1) with weight W and add edge between node R and this node.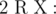 Output the maximum length of sequence of nodes which
Output the maximum length of sequence of nodes which
- starts with R.
- Every node in the sequence is an ancestor of its predecessor.
- Sum of weight of nodes in sequence does not exceed X.
- For some nodes i, j that are consecutive in the sequence if i is an ancestor of j then w[i] ≥ w[j] and there should not exist a node k on simple path from i to j such that w[k] ≥ w[j]
The tree is rooted at node 1 at any instant.
Note that the queries are given in a modified way.
First line containing the number of queries Q (1 ≤ Q ≤ 400000).
Let last be the answer for previous query of type 2 (initially last equals 0).
Each of the next Q lines contains a query of following form:
- 1 p q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ 1018): This is query of first type where
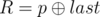 and
and 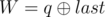 . It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cnt and 0 ≤ W ≤ 109.
. It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cnt and 0 ≤ W ≤ 109. - 2 p q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ 1018): This is query of second type where
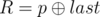 and
and 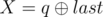 . It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cntand 0 ≤ X ≤ 1015.
. It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cntand 0 ≤ X ≤ 1015.
 denotes bitwise XOR of a and b.
denotes bitwise XOR of a and b.
It is guaranteed that at least one query of type 2 exists.
Output the answer to each query of second type in separate line.
6
1 1 1
2 2 0
2 2 1
1 3 0
2 2 0
2 2 2
0
1
1
2
6
1 1 0
2 2 0
2 0 3
1 0 2
2 1 3
2 1 6
2
2
3
2
7
1 1 2
1 2 3
2 3 3
1 0 0
1 5 1
2 5 0
2 4 0
1
1
2
7
1 1 3
1 2 3
2 3 4
1 2 0
1 5 3
2 5 5
2 7 22
1
2
3
In the first example,
last = 0
- Query 1: 1 1 1, Node 2 with weight 1 is added to node 1.
- Query 2: 2 2 0, No sequence of nodes starting at 2 has weight less than or equal to 0. last = 0
- Query 3: 2 2 1, Answer is 1 as sequence will be {2}. last = 1
- Query 4: 1 2 1, Node 3 with weight 1 is added to node 2.
- Query 5: 2 3 1, Answer is 1 as sequence will be {3}. Node 2 cannot be added as sum of weights cannot be greater than 1. last = 1
- Query 6: 2 3 3, Answer is 2 as sequence will be {3, 2}. last = 2
对于一棵树,你有2种操作
ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 932 A.Palindromic Supersequence (ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined))
占坑,明天写,想把D补出来一起写.2/20/2018 11:17:00 PM ----------------------------------------------------------我是分 ...
- ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined) A
2018-02-19 A. Palindromic Supersequence time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 mega ...
- Codeforces 932 C.Permutation Cycle-数学 (ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined))
C. Permutation Cycle time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- Codeforces 932 B.Recursive Queries-前缀和 (ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined))
B. Recursive Queries time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- 【ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined) D】Tree
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 让你在树上找一个序列. 这个序列中a[1]=R 然后a[2],a[3]..a[d]它们满足a[2]是a[1]的祖先,a[3]是a[2]的祖先... 且w[a[ ...
- 【ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined) C】 Permutation Cycle
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] p[i] = p[p[i]]一直进行下去 在1..n的排列下肯定会回到原位置的. 即最后会形成若干个环. g[i]显然等于那个环的大 ...
- 【ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined) B】Recursive Queries
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 写个记忆化搜索. 接近O(n)的复杂度吧 [代码] #include <bits/stdc++.h> using nam ...
- 【ICM Technex 2018 and Codeforces Round #463 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined) A】 Palindromic Supersequence
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 字符串倒着加到原串右边就好 [代码] #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace ...
- ICM Technex 2017 and Codeforces Round #400 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, combined) A map B贪心 C思路前缀
A. A Serial Killer time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
随机推荐
- 干货|java缓存技术详解
一.缓存是什么? 请点击此处输入图片描述 Cache ①高速缓冲存储器,其中复制了频繁使用的数据以利于快速访问. ②位于速度相差较大的两种硬件/软件之间,用于协调两者数据传输速度差异的结构 二.缓存有 ...
- 2017微软骇客马拉松精彩大回Fun:不一样的Hacker,一Young的Cool
丹棱君有话说:一年一度激动人心的骇客马拉松大会结束了!这场内部创意大比拼硕果累累,丹棱君准备好了 6 组 Cool 骇客的别 Young 作品——沉浸式销售工具如何能守得“云”开见月明?“骇客马拉松超 ...
- 【虚拟机-部署】通过 Powershell 来调整 ARM 模式下虚拟机的尺寸
需求描述 在部署完 ARM 模式的虚拟机以后,可以通过 PowerShell 命令来调整虚拟机的尺寸,以下是通过 PowerShell 命令来调整 ARM 模式的虚拟机尺寸. Note 本文只限于 A ...
- jsp跳转标签<jsp:forward>
forward.jsp <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" p ...
- HDU Rabbit and Grass 兔子和草 (Nim博弈)
思路:简单Nim博弈,只需要将所给的数字全部进行异或,结果为0,则先手必败.否则必胜. #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main( ...
- 人脸识别 python调用face++ 功能测试
使用python调用face++的API,调用detect功能,识别人脸 首先进入face++官网注册,获得API Key和API Secret.使用官网提供的免费python api调用功能,提供了 ...
- sql server 定时备份 脚本
) DECLARE @date DATETIME SELECT @date = GETDATE() SELECT @filename = 'G:\backup\NewPlulishSQL-' + CA ...
- 51nod——1548 欧姆诺姆和糖果
一开始以为是贪心,然后发现没法贪.暴力枚举肯定T,于是用约束关系优化: 假设wr >= wb, 第一种情况:wr >= sqrt (c), 则此时最多吃c / wr个r,且c / wr & ...
- BZOJ-1833(数位DP)
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; ll a,b; int k[20]; ll dp[2 ...
- 初学者之 Git 和 Github
git和github是两个完全不同的概念. git 是一个版本管理工具,是可以在你电脑不联网的情况下,只在本地使用的一个版本管理工具,其作用就是可以让你更好的管理你的程序,比如你原来提交过的内容, ...
