【LINUX/UNIX网络编程】之简单多线程服务器(多人群聊系统)
RT,Linux下使用c实现的多线程服务器。这个真是简单的不能再简单的了,有写的不好的地方,还希望大神轻拍。(>﹏<)
本学期Linux、unix网络编程的第四个作业。
先上实验要求:
【实验目的】
1、熟练掌握线程的创建与终止方法;
2、熟练掌握线程间通信同步方法;
3、应用套接字函数完成多线程服务器,实现服务器与客户端的信息交互。
【实验内容】
通过一个服务器实现最多5个客户之间的信息群发。
服务器显示客户的登录与退出;
客户连接后首先发送客户名称,之后发送群聊信息;
客户输入bye代表退出,在线客户能显示其他客户的登录于退出。
实现提示:
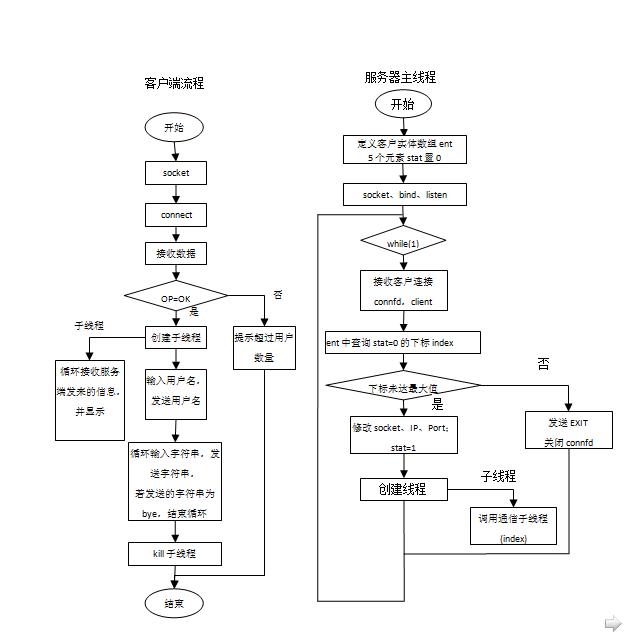
1、服务器端:
主线程:
定义一个全局客户信息表ent,每个元素对应一个客户,存储:socket描述符、客户名、客户IP、客户端口、状态(初值为0)。
主线程循环接收客户连接请求,在ent中查询状态为0的元素,
如果不存在状态为0的元素(即连接数超过最大连接数),向客户发送EXIT标志;
否则,修改客户信息表中该元素的socket描述符、客户IP、客户端口号,状态为1(表示socket可用);
同时创建一个通信线程并将客户索引号index传递给通信线程。
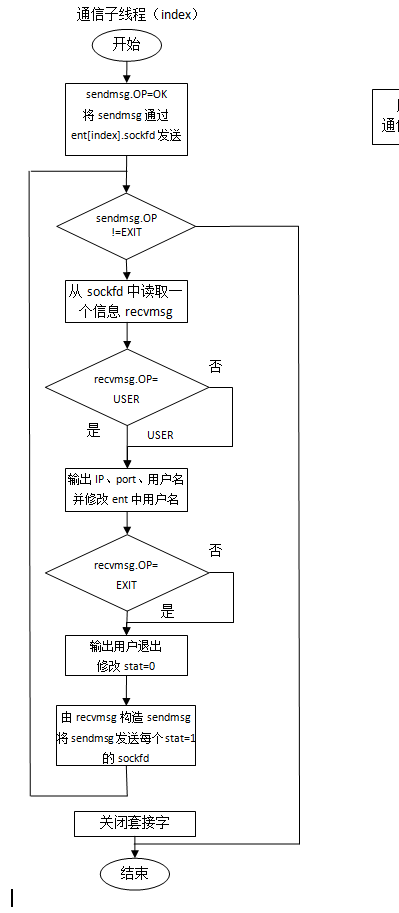
通信线程:
首先向客户端发送OK标志
循环接收客户发来信息,若信息长度为0,表示客户端已关闭,向所有在线客户发送该用户退出;
若信息为用户名,修改全局客户信息表ent中index客户的用户名name,并显示该用户登录;
若信息为退出,修改全局客户信息表ent中index客户状态为0,并显示该用户退出,终止线程;
同时查询全局客户信息表ent,向状态为1的客户发送接收的信息。
2、客户端:
根据用户从终端输入的服务器IP地址及端口号连接到相应的服务器;
连接成功后,接收服务端发来的信息,若为EXIT,则达到最大用户量,退出;
若为OK,可以通讯,首先先发送客户名称;
主进程循环从终端输入信息,并将信息发送给服务器;
当发送给服务器为bye后,程序退出。
同时创建一个线程负责接收服务器发来的信息,并显示,当接收的长度小于等于0时终止线程;
有了上一次多进程服务器的编写经验以后,写起多线程就简单多了。
照例还是绘制一下流程图,以方便我们理清思路。
好啦,现在可以开始撸代码了。
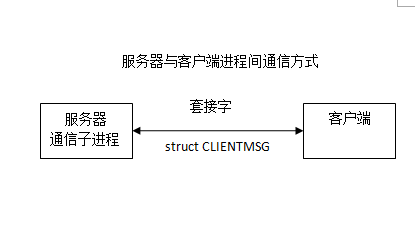
先实现一下用于通信的结构体clientmsg.h:(和多进程服务器是一样的)
//CLIENTMSG between server and client
#ifndef _clientmsg
#define _clientmsg //USER MSG EXIT for OP of CLIENTMSG
#define EXIT -1
#define USER 1
#define MSG 2
#define OK 3 #ifndef CMSGLEN
#define CMSGLEN 100
#endif struct CLIENTMSG{
int OP;
char username[];
char buf[CMSGLEN];
}; #endif
客户端程序看起来比较简单,咱们把它实现了,client.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "clientmsg.h" struct ARG{
int sockfd;
struct CLIENTMSG clientMsg;
}; void *func(void *arg);
void process_cli(int sockfd,struct CLIENTMSG clientMsg);
int main(){
int sockfd;
char ip[];
int port;
pthread_t tid;
struct sockaddr_in server;
struct CLIENTMSG clientMsgSend;
struct ARG *arg;
/*---------------------socket---------------------*/
if((sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,))== -){
perror("socket error\n");
exit();
} /*---------------------connect--------------------*/
printf("Please input the ip:\n");
scanf("%s",ip);
printf("Please input the port:\n");
scanf("%d",&port);
bzero(&server,sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(port);
inet_aton(ip,&server.sin_addr);
if(connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)&server,sizeof(server))== -){
perror("connect() error\n");
exit();
}
recv(sockfd,&clientMsgSend,sizeof(clientMsgSend),);
if(clientMsgSend.OP == OK){
//创建一个线程
arg = (struct ARG *)malloc(sizeof(struct ARG));
arg->sockfd = sockfd;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,func,(void *)arg);
//主线程
printf("Please input the username:\n");
scanf("%s",clientMsgSend.username);
clientMsgSend.OP = USER;
send(sockfd,&clientMsgSend,sizeof(clientMsgSend),);
while(){
clientMsgSend.OP = MSG;
scanf("%s",clientMsgSend.buf);
if(strcmp("bye",clientMsgSend.buf) == ){
clientMsgSend.OP = EXIT;
send(sockfd,&clientMsgSend,sizeof(clientMsgSend),);
break;
}
send(sockfd,&clientMsgSend,sizeof(clientMsgSend),);
}
pthread_cancel(tid);
}
else{
printf("以达到最大连接数!\n");
}
/*------------------------close--------------------------*/
close(sockfd); return ;
} void *func(void *arg){
struct ARG *info;
info = (struct ARG *)arg;
process_cli(info->sockfd,info->clientMsg);
free(arg);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void process_cli(int sockfd,struct CLIENTMSG clientMsg){
int len;
while(){
bzero(&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg));
len =recv(sockfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),);
if(len > ){
if(clientMsg.OP ==USER){
printf("the user %s is login.\n",clientMsg.username );
}
else if(clientMsg.OP == EXIT){
printf("the user %s is logout.\n",clientMsg.username);
}
else if(clientMsg.OP == MSG){
printf("%s: %s\n",clientMsg.username,clientMsg.buf );
}
}
}
}
然后是服务器端的实现,server.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "clientmsg.h" struct Entity{
int sockfd;
char username[];
char buf[CMSGLEN];
struct sockaddr_in client;
int stat;
}; void *func(void *arg);
void communicate_process(int index);
struct Entity ent[]; int main(){ struct sockaddr_in server;
struct sockaddr_in client;
int listenfd,connetfd;
char ip[];
int port;
int addrlen;
struct CLIENTMSG clientMsg;
pthread_t tid;
int *arg;
/*---------------------socket-------------------*/
if((listenfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,))== -){
perror("socket() error\n");
exit();
} /*----------------------IO-----------------------*/
printf("Please input the ip:\n");
scanf("%s",ip);
printf("Please input the port:\n");
scanf("%d",&port); /*---------------------bind----------------------*/
bzero(&server,sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(port);
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip);
if(bind(listenfd,(struct sockaddr *)&server,sizeof(server))== -){
perror("bind() error\n");
exit();
} /*----------------------listen-------------------*/
if (listen(listenfd,)== -){
perror("listen() error\n");
exit();
}
int i;
for(i=;i<;i++){
ent[i].stat = ;
}
while(){
addrlen = sizeof(client);
if((connetfd = accept(listenfd,(struct sockaddr *)&client,&addrlen))== -){
perror("accept() error\n");
exit();
}
int index = ;
for(i=;i<;i++){
if(ent[i].stat == ){
index = i;
break;
}
}
if(index <= ){
printf("connetfd:%d\n",connetfd );
ent[index].client = client;
ent[index].sockfd = connetfd;
ent[index].stat = ;
arg = malloc(sizeof(int));
*arg = index;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,func,(void *)arg); }
else{
bzero(&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg));
clientMsg.OP = EXIT;
send(connetfd,&clientMsg,sizeof(clientMsg),);
close(connetfd);
} } /*----------------------close-------------------*/ close(listenfd); return ;
} /*----------------------------函数实现区----------------------------*/
void *func(void *arg){
int *info ;
info = (int *)arg;
communicate_process( *info);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void communicate_process(int index){
struct CLIENTMSG sendMsg;
struct CLIENTMSG recvMsg;
printf("sockfd:%d\n",ent[index].sockfd );
sendMsg.OP = OK;
send(ent[index].sockfd,&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg),); while(){
bzero(&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg));
bzero(&recvMsg,sizeof(recvMsg));
int len =recv(ent[index].sockfd,&recvMsg,sizeof(recvMsg),);
if(len > ){
if(recvMsg.OP == USER){
printf("user %s login from ip:%s,port:%d\n",recvMsg.username,inet_ntoa(ent[index].client.sin_addr),ntohs(ent[index].client.sin_port) );
bcopy(recvMsg.username,ent[index].username,strlen(recvMsg.username));
sendMsg.OP = USER;
}
else if(recvMsg.OP == EXIT){
printf("user %s is logout\n",recvMsg.username );
sendMsg.OP = EXIT;
ent[index].stat = ;
int i;
for(i=;i<;i++){
if(ent[i].stat == ){ send(ent[i].sockfd,&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg),);
}
}
break;
}
else if(recvMsg.OP == MSG){
sendMsg.OP = MSG;
}
bcopy(recvMsg.username,sendMsg.username,strlen(recvMsg.username));
bcopy(recvMsg.buf,sendMsg.buf,strlen(recvMsg.buf));
int i;
for(i=;i<;i++){
if(ent[i].stat == ){
printf("stat 1...\n");
send(ent[i].sockfd,&sendMsg,sizeof(sendMsg),);
}
}
}
else{
continue;
}
}
}
最后是makefile文件:
main:server.o client.o
gcc server.o -oserver -lpthread
gcc client.o -oclient -lpthread
server.o:server.c clientmsg.h
gcc -c server.c
client.o:client.c clientmsg.h
gcc -c client.c
如果程序中引入了#include <pthread.h>,要记得在编译的时候 加上 -lpthread。
下面上一下演示过程:(测试环境,Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 + centos系Linux,ubuntu下可能会有些问题。)
首先先把服务端启动开来,为了方便测试,这里直接使用的是127.0.0.1的localhost。

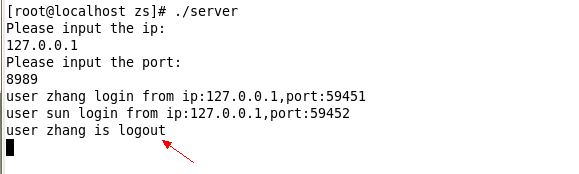
然后启动两个客户端用来测试,在用户登录的时候客户端会有消息提醒。服务端会有日志打印输出客户端的名字和登录ip、端口。
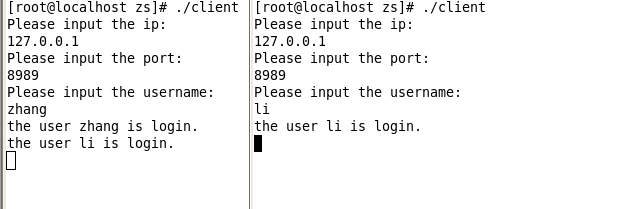
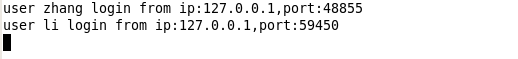
客户可以发送消息了,如图发送与接收均正常。这里为了简单演示只是启动了2个。
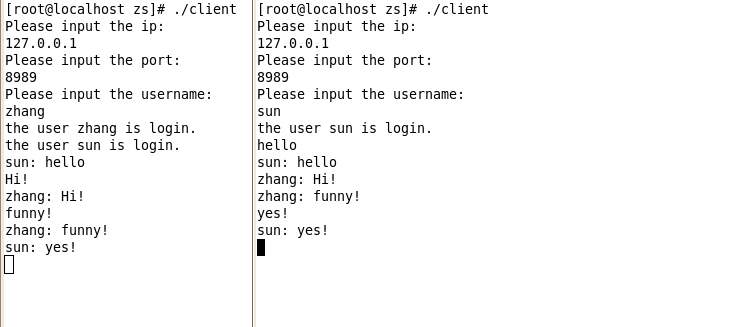
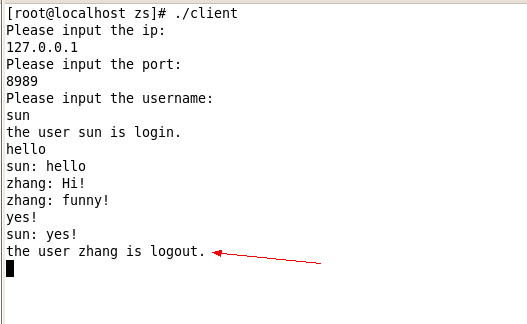
输入bye以后即可退出聊天并下线。当有客户下线的时候,在线的客户端会收到下线提醒,客户端会有日志打印输出。
【LINUX/UNIX网络编程】之简单多线程服务器(多人群聊系统)的更多相关文章
- 【LINUX/UNIX网络编程】之使用消息队列,信号量和命名管道实现的多进程服务器(多人群聊系统)
RT,使用消息队列,信号量和命名管道实现的多人群聊系统. 本学期Linux.unix网络编程的第三个作业. 先上实验要求: 实验三 多进程服务器 [实验目的] 1.熟练掌握进程的创建与终止方法: 2 ...
- 【Linux/unix网络编程】之使用socket进行TCP编程
实验一 TCP数据发送与接收 [实验目的] 1.熟练掌握套接字函数的使用方法. 2.应用套接字函数完成基本TCP通讯,实现服务器与客户端的信息交互. [实验学时] 4学时 [实验内容] 实现一个服务器 ...
- 《UNIX网络编程》TCP客户端服务器例子
最近在看<UNIX网络编程>(简称unp)和<Linux程序设计>,对于unp中第一个获取服务器时间的例子,实践起来总是有点头痛的,因为作者将声明全部包含在了unp.h里,导致 ...
- 【Unix 网络编程】TCP 客户/服务器简单 Socket 程序
建立一个 TCP 连接时会发生下述情形: 1. 服务器必须准备好接受外来的连接.这通常通过调用 socket.bind 和 listen 这三个函数来完成,我们称之为被动打开. 2. 客户通过调用 c ...
- UNIX网络编程——TCP回射服务器/客户端程序
下面通过最简单的客户端/服务器程序的实例来学习socket API. serv.c 程序的功能是从客户端读取字符然后直接回射回去: #include<stdio.h> #include&l ...
- UNIX网络编程——UDP回射服务器程序(初级版本)以及漏洞分析
该函数提供的是一个迭代服务器,而不是像TCP服务器那样可以提供一个并发服务器.其中没有对fork的调用,因此单个服务器进程就得处理所有客户.一般来说,大多数TCP服务器是并发的,而大多数UDP服务器是 ...
- 【LINUX/UNIX网络编程】之使用SOCKET进行UDP编程
先看任务需求: 实验二 UDP数据发送与接收 [实验目的] 1.熟练掌握套接字函数的使用方法. 2.应用套接字函数完成基本UDP通讯,实现服务器与客户端的文件传送 [实验学时] 4学时 [实验内容] ...
- 《UNIX网络编程》UDP客户端服务器:消息回显
udp写的程序相比tcp简单一些,在socket()与bind()之后,不需要connect(),accept()等步骤,直接简化为了sendto()与recvfrom(). 编译运行同前面的tcp. ...
- 《UNIX网络编程》TCP客户端服务器:并发、消息回显
经过小小改动,把前面基础的例子做出一点修改. 并发服务器,服务器每accept一个请求就fork()一个新的子进程. 编译运行方法同前一篇. /*client_tcp.c*/ #include < ...
随机推荐
- Mysql之复制服务
Replication[复制]使得数据可以从一个Master服务器上复制到一个或多个Slave上,默认是异步复制,不需要与Master建立永久连接:基于配置,可以作用于所有库,指定的库或库中的某些表. ...
- 使用vsphere client 克隆虚拟机
免费的VMWare ESXi5.0非常强大,于是在vSphere5.0平台中ESXi取代了ESX.,使用ESXi经常会遇到这样的问题,我需要建立多个虚拟机,都是windows2003操作系统,难道必须 ...
- 昨晚把家里的ie升级到11
其实网上有些东西是实用的,不过之前的一次锁屏唤醒机器死机我就强制关机了,昨天把大部分驱动升级.
- CLR via C#(11)-无参属性、有参数属性(索引器)
一. 无参属性 1. 定义属性 无参属性就是我们最常见的属性方式,在赋值时可以加入一定的逻辑判断.属性的定义其实不复杂,先看个直观的例子: 说明: 属性要定义名称和类型,且类型不能是void. 属性是 ...
- 常用的数据统计Sql 总结(转)
转:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangweizhong/p/5577842.html 最近刚在搞一个BI的项目,里面需要大量的sql 数据统计相关运用,加深了我又对SQL的理解与 ...
- 【转载】python super的用法
转载地址: http://blog.csdn.net/cxm19830125/article/details/20610533 super的用法是调用继承类的初始化方法,如下面的代码: class A ...
- 取得表中数据的insert语句
Build Insert Statements for the Existing Data in Tables 下面这个脚本实现了取得一个非空表中的所有insert语句 This script bui ...
- Oracle【IT实验室】数据库备份与恢复之五:Flashback
Flashback在开发环境(有时生产环境的特殊情况下)是很有用的一个工具. 5.1 9i Flashback 简介 5.1.1 原理 当数据 update 或 delete ...
- html5 svg
html5 svg <html > <body> <p>canvas 用js 绘画,是整幅画布,适合游戏 svg可放大,支持dom 操作,js事件 线性渐变.高斯模 ...
- apt-get常见错误——Unmet dependencies
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4980828b0100zicn.html 安装错误:“E: Unmet dependencies.”原因:非正常停止apt-get ...
