PAT A1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)——最小路径,溯源,二标尺,DFS
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists from all over the world. One may rent a bike at any station and return it to any other stations in the city.
The Public Bike Management Center (PBMC) keeps monitoring the real-time capacity of all the stations. A station is said to be in perfect condition if it is exactly half-full. If a station is full or empty, PBMC will collect or send bikes to adjust the condition of that station to perfect. And more, all the stations on the way will be adjusted as well.
When a problem station is reported, PBMC will always choose the shortest path to reach that station. If there are more than one shortest path, the one that requires the least number of bikes sent from PBMC will be chosen.
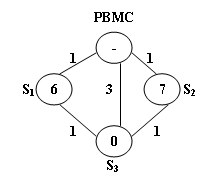
The above figure illustrates an example. The stations are represented by vertices and the roads correspond to the edges. The number on an edge is the time taken to reach one end station from another. The number written inside a vertex S is the current number of bikes stored at S. Given that the maximum capacity of each station is 10. To solve the problem at S3, we have 2 different shortest paths:
PBMC -> S1 -> S3. In this case, 4 bikes must be sent from PBMC, because we can collect 1 bike from S1 and then take 5 bikes to S3, so that both stations will be in perfect conditions.
PBMC -> S2 -> S3. This path requires the same time as path 1, but only 3 bikes sent from PBMC and hence is the one that will be chosen.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 numbers: Cmax (≤100), always an even number, is the maximum capacity of each station; N (≤500), the total number of stations; Sp, the index of the problem station (the stations are numbered from 1 to N, and PBMC is represented by the vertex 0); and M, the number of roads. The second line contains N non-negative numbers Ci (i=1,⋯,N) where each Ci is the current number of bikes at Si respectively. Then M lines follow, each contains 3 numbers: Si, Sj, and Tij which describe the time Tij taken to move betwen stations Si and Sj. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print your results in one line. First output the number of bikes that PBMC must send. Then after one space, output the path in the format: 0−>S1−>⋯−>Sp. Finally after another space, output the number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC after the condition of Sp is adjusted to perfect.
Note that if such a path is not unique, output the one that requires minimum number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC. The judge's data guarantee that such a path is unique.
Sample Input:
10 3 3 5
6 7 0
0 1 1
0 2 1
0 3 3
1 3 1
2 3 1
Sample Output:
3 0->2->3 0
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = , inf = ;
int cmax, n, sp, m;
int g[maxn][maxn], c[maxn] = { };
vector<int> pre[maxn];
int d[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void dijkstra(int s) {
fill(vis, vis + maxn, false);
fill(d, d + maxn, inf);
d[s] = ;
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
int u = -, min = inf;
for (int j = ; j < n; j++) {
if (vis[j] == false && d[j] < min) {
min = d[j];
u = j;
}
}
if (u == -) return;
vis[u] = true;
for (int v = ; v <= n; v++) {
if (vis[v] == false && g[u][v]!=inf) {
if (d[v] > d[u] + g[u][v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + g[u][v];
pre[v].clear();
pre[v].push_back(u);
}
else if (d[v] == d[u] + g[u][v]) {
pre[v].push_back(u);
}
}
}
}
}
vector<int> shortpath, temppath;
int min_c = inf, min_t = inf;
void dfs(int v) {
if (v == ) {
temppath.push_back(v);
int s;
int carry = , take = ;
for (int i = temppath.size() - ; i >= ;i--) {
s = temppath[i];
if (cmax / < c[s]) {
take += c[s] - (cmax / );
}
else {
carry = carry + max(, cmax / - c[s] - take);
take = max(, take - (cmax / - c[s]));
}
}
if (carry < min_c || (carry==min_c && take<min_t)) {
min_c = carry;
shortpath = temppath;
min_t = take;
}
temppath.pop_back();
return;
}
temppath.push_back(v);
for (int i = ; i < pre[v].size(); i++) {
dfs(pre[v][i]);
}
temppath.pop_back();
}
int main() {
cin >> cmax >> n >> sp >> m;
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &c[i]);
}
fill(g[], g[] + maxn * maxn, inf);
for (int i = ; i < m; i++) {
int c1, c2, w;
scanf("%d %d %d", &c1, &c2, &w);
g[c1][c2] = w;
g[c2][c1] = w;
}
dijkstra();
dfs(sp);
printf("%d ", min_c);
for (int i = shortpath.size() - ; i > ; i--) {
printf("%d->", shortpath[i]);
}
printf("%d %d\n",shortpath[], min_t); system("pause");
return ;
}
注意点:还是一道逻辑看似简单的题,考察一个多尺度最短路径。知道用dijkstra+dfs的方法最方便,就是死不相信想只用dijkstra做出来,发现真的不行,当带的车一样多时,最后带回来的车要最少,这个光用dijkstra是算不出来的,因为中间要尽可能多的带车出来,但最后要最少,如果中间带少的车出来,最后需要带的车又会太多。还是老老实实用dijkstra+dfs最方便。一定要把这个模板记住熟练了!
PAT A1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)——最小路径,溯源,二标尺,DFS的更多相关文章
- PAT 甲级 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(dijstra+dfs,dfs记录路径,做了两天)
1018 Public Bike Management (30 分) There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists fro ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) 思路分析 + 满分代码
题目 There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) PAT甲级真题 dijkstra + dfs
前言: 本题是我在浏览了柳神的代码后,记下的一次半转载式笔记,不经感叹柳神的强大orz,这里给出柳神的题解地址:https://blog.csdn.net/liuchuo/article/detail ...
- 【PAT甲级】1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(SPFA,DFS)
题意: 输入四个正整数C,N,S,M(c<=100,n<=500),分别表示每个自行车站的最大容量,车站个数,此次行动的终点站以及接下来的M行输入即通路.接下来输入一行N个正整数表示每个自 ...
- [PAT] A1018 Public Bike Management
[思路] 题目生词 figure n. 数字 v. 认为,认定:计算:是……重要部分 The stations are represented by vertices and the roads co ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) (迪杰斯特拉+dfs)
思路就是dijkstra找出最短路,dfs比较每一个最短路. dijkstra可以找出每个点的前一个点, 所以dfs搜索比较的时候怎么处理携带和带走的数量就是关键,考虑到这个携带和带走和路径顺序有关, ...
- PAT 1018 Public Bike Management[难]
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/4b20ed271e864f06ab77a984e71c090f来源:牛客网PAT 1018 Public ...
- PAT 1018 Public Bike Management(Dijkstra 最短路)
1018. Public Bike Management (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yu ...
随机推荐
- MVC中返回json数据的两种方式
MVC里面如果直接将数据返回到前端页面,我们常用的方式就是用return view(): 那么我不想直接用razor语法,毕竟razor这玩意儿实在是太难记了,还不如写ajax对接来得舒服不是 那么我 ...
- 每个JavaScript工程师都应懂的33个概念
摘要: 基础很重要啊! 原文:33 concepts every JavaScript developer should know 译文:每个 JavaScript 工程师都应懂的33个概念 作者:s ...
- python自动化开发-6-面向对象编程
面向对象编程 面向对象的特性 封装:把客观事物封装成抽象的类,并且类可以把自己的数据和方法只让可信的类或者对象操作,对不可信的进行信息隐藏. 继承:面向对象编程 (OOP) 语言的一个主要功能就是“ ...
- Flutter 布局(十)- ListBody、ListView、CustomMultiChildLayout详解
本文主要介绍Flutter布局中的ListBody.ListView.CustomMultiChildLayout控件,详细介绍了其布局行为以及使用场景,并对源码进行了分析. 1. ListBody ...
- C# 异步编程3 TPL Task 异步程序开发
.Net在Framework4.0中增加了任务并行库,对开发人员来说利用多核多线程CPU环境变得更加简单,TPL正符合我们本系列的技术需求.因TPL涉及内容较多,且本系列文章为异步程序开发,所以本文并 ...
- python 报错RuntimeError: dictionary changed size during iteration
a = {':0} for b in list(a.keys()): if a[b] == 0: del a[b] print(a) 报错是因为在字典迭代期间改变字典大小 我们可以通过取出字典的键值, ...
- Kubernetes的搭建与配置(一):集群环境搭建
1.环境介绍及准备: 1.1 物理机操作系统 物理机操作系统采用Centos7.3 64位,细节如下. [root@localhost ~]# uname -a Linux localhost.loc ...
- 19LaTeX学习系列之---LaTeX的总结
目录 目录 前言 (一)本系列的章节目录 (二)快速温习LaTeX 1.介绍 2.源文件结构 3.文档的结构 4.字体的设置 5.图片的插入 6.表格的插入 7.数学公式的插入 8.交叉引用与浮动体 ...
- January 12th, 2018 Week 02nd Friday
Nothing behind me, everything ahead of me, as is ever so on the road. 我的身后空空荡荡,整个世界都在前方,这就是在路上. That ...
- Beta冲刺(4/5)(麻瓜制造者)
今日已完成 邓弘立:完成了商品管理(下架)和搜索功能 符天愉:完成了后台管理员界面的登录和其他视图的载入 江郑:昨天来决定跨域执行请求,后台参考一些意见以后,操作起来没有那么容易实现,和队友交流以后本 ...