算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——1.1
写在前面
整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csharp
善用 Ctrl + F 查找题目。
本节你可能会需要的两个测试数据文件:
largeW: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/11model/largeW.txt
largeT: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/11model/largeT.txt
习题 & 题解
练习(1.1.1~1.1.25)
1.1.1
解答
a.7
b.1562500.0015625
c.True
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = ( + ) / ;
double b = Math.Pow(2.0, -) * 100000000.1; //Math.Pow(double x, double y) 求x的y次方
bool c = true && false || true && true; //Console.WriteLine 向控制台窗口输出一行
Console.WriteLine($"a.{a}");
Console.WriteLine($"b.{b}");
Console.WriteLine($"c.{c}");
}
1.1.2
解答
Name Type Value
a System.Double 1.618
b System.Double 10
c System.Boolean True
d System.String 33
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//var 变量名 = 初始值 根据初始值自动判断变量类型
var a = ( + 2.236) / ;
var b = + + + 4.0;
var c = 4.1 >= ;
var d = + + ""; //Console.WriteLine 向控制台输出一行
//变量名.GetType() 返回变量类型
//Type.ToString() 将类型名转换为字符串 Console.WriteLine("\tName\tType \tValue");
Console.WriteLine($"\ta\t{a.GetType().ToString()}\t{a}");
Console.WriteLine($"\tb\t{b.GetType().ToString()}\t{b}");
Console.WriteLine($"\tc\t{c.GetType().ToString()}\t{c}");
Console.WriteLine($"\td\t{d.GetType().ToString()}\t{d}");
}
1.1.3
解答
简单的 if 判断即可
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Console.ReadLine() 从控制台读入一整行(返回int)
//string.Split(char) 根据提供的分隔符将字符串分割,返回字符串数组
//Int32.Parse(string) 将字符串转换为相应的整型数据
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int a = Int32.Parse(input.Split(' ')[]);
int b = Int32.Parse(input.Split(' ')[]);
int c = Int32.Parse(input.Split(' ')[]); //Console.WriteLine() 向控制台输出一行
if (a == b && b == c)
{
Console.WriteLine("equal");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("not equal");
}
}
1.1.4
解答
a. if 后跟 then 的语法不能在 C# 中使用。
b. if 后的判断语句需要在括号内。
c. 正确,只有一条语句时大括号可以省略。
d. c = 0 后缺少分号。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = ;
int b = ;
int c = ; //if (a > b) then c = 0;
//if 后不能跟 then //if a > b { c = 0; }
//if后必须跟括号 if (a > b) c = ;
//正确 //if (a > b) c = 0 else b = 0;
//c = 0后缺少分号 }
1.1.5
解答
比较简单,直接判断即可。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//修改这两个值进行测试
double x = 0.05;
double y = 0.01; if (x > && x < && y > && y < )
{
Console.WriteLine("true");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("false");
}
}
1.1.6
解答
输出斐波那契数列。
将书中的代码直接实现即可。
代码
//输出斐波那契数列
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int f = ;
int g = ;
for (int i = ; i <= ; i++)
{
//Console.WriteLine与StdOut.println功能相同
//实现向控制台输出一行
Console.WriteLine(f);
f = f + g;
g = f - g;
}
}
1.1.7
解答
同上题,直接实现即可。
a
3.00009
double计算存在误差,并不精确。
b
499500
1000 + 999 + 998……
c
10000
1000 * 10,外层循环的结束条件为 2i > 1000。
代码
private static void a()
{
Console.WriteLine("a");
double t = 9.0;
while (Math.Abs(t - 9.0 / t) > .)
{
t = (9.0 / t + t) / 2.0;
}
Console.Write($"{t:N5}\n");//:N5代表保留5位小数,同理可使用N1、N2……
} private static void b()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nb");
int sum = ;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < i; j++)
{
sum++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine(sum);
} private static void c()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nc");
int sum = ;
for (int i = ; i < ; i *= )
{
for (int j = ; j < ; j++)
{
sum++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine(sum);
} static void Main(string[] args)
{
//a double 计算存在误差
a(); //b 1000+999+998……
b(); //c 由于2^10 = 1024 > 1000,最终sum = 1000 * 10 = 10000
c();
}
1.1.8
解答
b
197
e
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine('b');
Console.WriteLine('b' + 'c'); //char 被隐式转为为 int 类型,取 ascii 码
Console.WriteLine((char)('a' + )); //强制转换后,ascii 码被转换为相应的字符
}
1.1.9
解答
有两种方法,要么直接调用库函数,要么用书中给出的代码转换。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = ; //1.直接转换 Convert.ToString(int, int) 第一个为要转换的数,第二个为要转换的进制
Console.WriteLine($"{Convert.ToString(N, 2)}"); //2.转换为二进制数
string s = "";
for (int n = N; n > ; n /= )
{
s = (n % ) + s;
}
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
1.1.10
解答
变量使用前需要先赋值。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] a;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
a[i] = i * i; //不允许使用未赋值的局部变量
}
}
1.1.11
解答
注意,二维数组 bool[M, N] 代表 M 行 N 列的布尔数组。
使用二重循环即可实现。
输出使用制表符 ’\t’ 作为分隔。
代码
static void PrintArray2D(bool[,] array)
{
int rows = array.GetLength();//获取行数
int columns = array.GetLength();//获取列数 //输出列号
for (int i = ; i < columns; i++)
{
Console.Write($"\t{i + 1}");
} Console.Write("\n"); for (int i = ; i < rows; i++)
{
//输出行号
Console.Write($"{i + 1}");
for (int j = ; j < columns; j++)
{
if (array[i, j])
{
Console.Write($"\t*");
}
else
{
Console.Write($"\t ");
}
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
1.1.12
解答
第一个循环初始化数组{9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0}
第二个循环用相应位置的值作为下标取值,例如:a[0] = a[a[0]] = a[9] = 0
最后结果为:0,1,2,3,4,4,3,2,1,0
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] a = new int[];
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
a[i] = - i;
}
//a[10] = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0}
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
a[i] = a[a[i]];
}
//a[0] = a[9] = 0; a[1] = a[8] = 1; a[2] = a[7] = 2;......
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
}
}
1.1.13
解答
转置输出只需要在二重循环的时候将行、列输出顺序取反即可。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int M = ;
int N = ;
int[,] array = new int[M, N]; //新建一个二维数组
for (int i = ; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < N; j++)
{
array[i, j] = i + j;
}
} Console.WriteLine("Origin");
PrintArray2D(array, M, N); Console.WriteLine("Transposed");
PrintArrayTranspose2D(array, M, N);
} //转置输出
private static void PrintArrayTranspose2D(int[,] array, int rows, int columns)
{
//交换行、列输出顺序
for (int i = ; i < columns; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < rows; j++)
{
Console.Write($"\t{array[j, i]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
} //正常输出
private static void PrintArray2D(int[,] array, int rows, int columns)
{
for (int i = ; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < columns; j++)
{
Console.Write($"\t{array[i, j]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
1.1.14
解答
简单使用 log 的定义逼近即可。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = ;
Console.WriteLine($"{ lg(N)}");
} //利用循环逼近 N,得到 log2(N) 的值
static int lg(int N)
{
int baseNumber = ;
int pow = ;
int sum = ; for (pow = ; sum < N; ++pow)
{
sum *= baseNumber;
} return pow - ;
}
1.1.15
解答
利用二重循环,查找每个值在数组中出现的次数。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] a = new int[];
int M = ;
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i)
{
a[i] = i;
} int[] result = Histogram(a, M); Console.WriteLine($"a.length: {a.Length}");
Console.WriteLine($"sum of result array: {result.Sum()}");
} static int[] Histogram(int[] a, int M)
{
int[] result = new int[M]; for (int i = ; i < M; ++i)
{
//初始化
result[i] = ; //遍历数组,计算数组中值为 i 的元素个数
for (int j = ; j < a.Length; ++j)
{
if (a[j] == i) //值为 i 的元素
{
result[i]++;
}
}
} return result;
}
1.1.16
解答
填入代码测试即可。
用字符串拼接的方式展示递归。
类似于这个:

代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{exR1(6)}");
} //exR1(6) =
//exR1(3) + 6 + exR1(4) + 6
//exR1(0) + 3 + exR1(1) + 3 + 6 + exR1(4) + 6
//"" + 3 + exR1(-2) + 1 + exR1(-1) + 1 + 3 + 6 + exR1(4) + 6
//"" + 3 + "" + 1 + "" + 1 + 3 + 6 + exR1(4) + 6
//"31136" + exR1(4) + 6
//...... public static string exR1(int n)
{
if (n <= )
{
return "";
} return exR1(n - ) + n + exR1(n - ) + n;
}
1.1.17
解答
书中已经给出了解释。
递归时结束条件必须放在递归语句的前面,否则会不断展开而无法结束。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{exR2(6)}");//抛出 StackOverflow Exception
} public static string exR2(int n)
{
string s = exR2(n - ) + n + exR2(n - ) + n;//运行到 exR2 即展开,不会再运行下一句
if (n <= ) return "";
return s;
}
1.1.18
解答
其实就是一种快速乘法的实现,换成乘号之后就变成了快速乘幂。
例如对于乘法 2 * 4,可以用 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 做四次加法计算;也可以变为 (2 + 2) * 2 = (2 + 2) + (2 + 2) 的形式,用两次加法就可以完成(先计算 2 + 2 的值,再计算 4 + 4 的值)。
同理对于乘幂 28,既可以用 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 做 8 次乘法,也可以只用三次乘法就计算出来:
22 = 2 * 2
24 = 22 * 22
28 = 24 * 24
这样时间复杂度就从 O(n) 变为了 O(log n)。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine($"mystery(2, 25): {mystery(2, 25)}");
Console.WriteLine($"mystery(3, 11): {mystery(3, 11)}"); Console.WriteLine($"mysteryChanged(2, 8): {mysteryChanged(2, 8)}");
Console.WriteLine($"mysteryChanged(3, 2): {mysteryChanged(3, 2)}");
} //mystery(a, b) = a * b
//利用等式:a * b = 2a * b/2 = (2a * (b-1) / 2) + a
//示例:
//mystery(2, 25) =
//mystery(2 + 2, 12) + 2 =
//mystery(4 + 4, 6) + 2 =
//mystery(8 + 8, 3) =
//mystery(16 + 16, 1) + 16 + 2 =
//mystery(32 + 32, 0) + 32 + 16 + 2 =
//0 + 32 + 16 + 2 =
//
public static int mystery(int a, int b)
{
if (b == ) return ;
if (b % == ) return mystery(a + a, b / );
return mystery(a + a, b / ) + a;
} //mysteryChanged(a, b) = a ^ b
//同理(乘方与乘法,乘法与加法之间具有类似的性质)
//a ^ b = (a ^ 2) ^ (b / 2) = (a ^ 2) ^ ((b - 1) / 2) * a
public static int mysteryChanged(int a, int b)
{
if (b == ) return ;
if (b % == ) return mysteryChanged(a * a, b / );
return mysteryChanged(a * a, b / ) * a;
}
1.1.19
解答
普通的递归算法效率很低,原因是越到后面重复运算的数目越多。
比如:
F(2) = F(1) + F(0)
F(3) = F(2) + F(1) = F(1) + F(1) + F(0)
可以看到 F(1) 被重复计算了两次。
改进的方式是将每次运算的结果保存在数组中,之后计算过的数据直接从数组中提取。
代码
class Fibnacci
{
//long 类型不够大,换成 UINT64 类型
//用于保存计算结果的数组,UInt64? 代表可以赋值为普通 UInt64 类型的值以及 null 值
private static UInt64?[] fibnacciResults = new UInt64?[100]; static void Main(string[] args)
{
/*
* 测试环境
*
* Surface Pro3 i7
* i7 4650U + 8G
*
*/
Stopwatch timer = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int N = 0; N < 100; ++N)
{
//书本中的代码,非常慢,1小时后 N = 50
//Console.WriteLine($"{N} {F(N)}"); //利用已知结果加速
//全部计算完毕耗时 84ms
Console.WriteLine($"{N} {BetterF(N)}");
}
Console.WriteLine($"{timer.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
} //书中提供的代码
public static UInt64 F(int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
return 1; return F(N - 1) + F(N - 2);
} //更好的实现,将已经计算的结果保存,不必重复计算
public static UInt64? BetterF(int N)
{
if (N == 0)
return 0;
if (N == 1)
return 1; if (fibnacciResults[N] != null) //如果已经计算过则直接读取已知值
{
return fibnacciResults[N];
}
else
{
fibnacciResults[N] = BetterF(N - 1) + BetterF(N - 2);
return fibnacciResults[N];
}
}
}
1.1.20
解答
根据对数的性质可以得到:
ln(N!) = ln(N) + ln(N – 1) + ln(N – 2)…
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = 4;
Console.WriteLine($"{factorialLn(N)}");
} //ln(N!) =
//ln(N * (N - 1) * ... * 1) =
//ln(N) + ln((N - 1)!)
public static double factorialLn(int N)
{
if (N == 1)
{
return 0;
} return Math.Log(N) + factorialLn(N - 1);
}
1.1.21
解答
实现上没什么难度,打印表格的部分可以参考之前打印二位布尔数组的方法。
注意整型数据之间相除得到的仍然是整型,小数部分会直接舍去,例如 2 / 3 = 0。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int columns = ;
int rows = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); //行号 string[] names = new string[rows]; //姓名
int[,] array = new int[rows, columns]; //输入的两个整数
double[] results = new double[rows]; //计算结果 for (int i = ; i < rows; ++i)
{
string temp = Console.ReadLine();
names[i] = temp.Split(' ')[];
for (int j = ; j < columns; ++j)
{
array[i, j] = int.Parse(temp.Split(' ')[j + ]);
}
results[i] = (double)array[i, ] / array[i, ];
} PrintArray2D(names, array, results);
} static void PrintArray2D(string[] names, int[,] array, double[] results)
{
int rows = array.GetLength();//获取行数
int columns = array.GetLength();//获取列数 for (int i = ; i < rows; i++)
{
Console.Write($"\t{names[i]}");
for (int j = ; j < columns - ; j++)
{
Console.Write($"\t{array[i, j]}");
}
Console.Write($"\t{array[i, columns - 1]}");
Console.Write($"\t{results[i]:N3}"); //变量名:N3 保留三位小数
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
1.1.22
解答
按照书中的提示增加一个保存深度的参数。
代码
class BinarySearch
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] array = new int[] { , , , , , , , , , }; rank(, array);
} //重载方法,用于启动二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
return rank(key, a, , a.Length - , );
} //二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi, int number)
{ for (int i = ; i < number; ++i)
{
Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine($"{number}: {lo} {hi}"); if (lo > hi)
{
return -;
} int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ; if (key < a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - , number + );
}
else if (key > a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, mid + , hi, number + );
}
else
{
return mid;
}
}
}
1.1.23
解答
在主函数里做一下判断就可以了,加号则输出所有找不到的值,减号则相反。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//从largeW.txt中读取数据
string[] whiteList = File.ReadAllLines("largeW.txt");
int[] WhiteList = new int[whiteList.Length]; for (int i = ; i < whiteList.Length; ++i)
{
WhiteList[i] = int.Parse(whiteList[i]);
} Array.Sort<int>(WhiteList); Console.WriteLine("Type the numbers you want to query: ");
//输入样例:5 824524 478510 387221
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int[] Query = new int[input.Split(' ').Length];
for (int i = ; i < Query.Length; ++i)
{
Query[i] = int.Parse(input.Split(' ')[i]);
} Console.WriteLine("Type '+' to get the numbers that not in the whitelist," +
"'-' to get the numbers that in the whitelist.");
char operation = Console.ReadLine()[]; foreach (int n in Query)
{
if (rank(n, WhiteList) == -)
{
if (operation == '+')
{
Console.WriteLine(n);
}
}
else if (operation == '-')
{
Console.WriteLine(n);
}
}
} //重载方法,用于启动二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
return rank(key, a, , a.Length - );
} //二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi)
{ if (lo > hi)
{
return -;
} int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ; if (key < a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - );
}
else if (key > a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, mid + , hi);
}
else
{
return mid;
}
}
1.1.24
解答
在书本中 GCD 的基础上,在函数开始时增加一条输出语句即可。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
GCD(, );
Console.WriteLine();
GCD(, );
} public static int GCD(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{a} {b}");
if (b == )
{
return a;
} return GCD(b, a % b);
}
1.1.25
解答
证明见代码。
也可以访问维基百科:辗转相除法
代码
namespace _1._1._25
{
/*
* 1.1.25
*
* 用数学归纳法证明欧几里得算法能够计算出任意一对非负整数 p 和 q 的最大公约数
*
*/
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 证明:
*
* 已知: a, b 皆为正整数,且 a > b。g 是 a、b 的最大公约数
* 设 r0 = a % b, rk = rk-2 % rk-1
* 那么有 gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, r0) = gcd(r0, r1)... = gcd(rn-1, rn)
* 且 rn = 0 (此时算法终止)
*
* 由于 rn-2 = qn * rn - 1 + rn = qn * rn-1 (qn = [rn-2 / rn-1] []代表向下取整)
* 可得 rn-2 能被 rn-1 整除
* 则
* rn-3 = qn-1 * rn-2 + rn-1
* = qn-1 * (qn * rn-1) + rn-1 (代入 rn-2 = qn * rn-1)
* = qn-1 * qn * rn-1 + rn-1
* = (qn-1 * qn + 1) * rn-1
* 可得 rn-3 也能被 rn-1 整除
* 以此类推,rn-1 可以整除 a 和 b,即 rn-1 是 a 和 b 的公约数
* 则 rn-1 <= g
*
* 因为 g 是 a、b 的最大公约数,由性质可得:
* a = mg, b = ng (m、n 是自然数)
*
* r0
* = a % b
* = a - q0 * b (q0 = [a / b] []代表向下取整)
* = mg - q0 * ng (代入 34 行的结论)
* = (m - q0 * n)g
*
* 可得 r0 能被 g 整除
* 同理 r1, r2, r3, ..., rn-1 都可以被 g 整除
* 因此 g <= rn-1
*
* 综合 31 行和 44 行的结论可得 rn-1 = g
*
* 证明完毕
*/
} static int gcd(int p, int q)
{
if (q == )
{
return p;
} int r = p % q; return gcd(q, r);
}
}
}
提高题(1.1.26~1.1.34)
1.1.26
解答
见代码部分。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = ;
int b = ;
int c = ;
int t = ; if (a > b) { t = a; a = b; b = t; } //如果 a > b,那么 a, b 交换,保证b >= a
if (a > c) { t = a; a = c; c = t; } //如果 b >= a > c,那么 a, c 交换,保证 c >= a
if (b > c) { t = b; b = c; c = t; } //如果 b > c >= a,那么 b, c 交换,保证 c >= b
Console.WriteLine($"{a} {b} {c}"); //最终结果为 c >= b >= a,保证升序排列
}
1.1.27
解答
与之前的斐波那契数列类似,都是重复计算的问题。
7751次。
代码
class Program
{
static int BinomialCalled = ; //计算递归调用次数
static double?[,] BinomialCache; //保存计算结果的数组 static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinomialCache = new double?[, ];
Console.WriteLine(Binomial(, , 0.25));
Console.WriteLine(BinomialCalled);
} public static double? Binomial(int N, int k, double p)
{
BinomialCalled++;
if (N == && k == )
return 1.0;
if (N < || k < )
return 0.0;
if (BinomialCache[N, k] != null)
{
return BinomialCache[N, k];
}
else
{
BinomialCache[N, k] = (1.0 - p) * Binomial(N - , k, p) + p * Binomial(N - , k - , p);
return BinomialCache[N, k];
}
}
}
1.1.28
解答
实现方法有很多,这里是使用一个 HashSet 做中转,删除所有的重复元素。
也可以使用 Linq 里的 Distinct() 方法,
也可以排序后直接遍历一遍,遇到相同的就删除,遇到不同的就保存起来用于之后的比较。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//从largeW.txt中读取数据
//用 HashSet 的不可重复性去除重复
HashSet<string> h = new HashSet<string>(File.ReadAllLines("largeW.txt"));
string[] whiteList = new string[h.Count];
h.CopyTo(whiteList);
int[] WhiteList = new int[whiteList.Length]; for (int i = ; i < whiteList.Length; ++i)
{
WhiteList[i] = int.Parse(whiteList[i]);
} Array.Sort<int>(WhiteList); Console.WriteLine("Type the numbers you want to query: ");
//输入样例:5 824524 478510 387221
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int[] Query = new int[input.Split(' ').Length];
for (int i = ; i < Query.Length; ++i)
{
Query[i] = int.Parse(input.Split(' ')[i]);
} Console.WriteLine("Irrelevant:");
foreach (int n in Query)
{
if (rank(n, WhiteList) == -)
{
Console.WriteLine(n);
}
}
} //重载方法,用于启动二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
return rank(key, a, , a.Length - );
} //二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi)
{ if (lo > hi)
{
return -;
} int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ; if (key < a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - );
}
else if (key > a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, mid + , hi);
}
else
{
return mid;
}
}
1.1.29
解答
查找小于指定值的元素数量可以多次使用二分查找实现。
例如:
序号:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
元素:1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3
二分查找返回 4
再次在 0~3 之间查找
二分查找返回 1
再次在 0~1 之间查找
二分查找返回 -1,没有指定值了
因此小于该值的元素数量就是 1 – 0 = 1 个
用同样的方法可以找到大于指定值的元素个数,从总数中减去这两个数值就是等于指定值的元素数量。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] WhiteList = new int[] { , , , , , , , , , , , }; Array.Sort<int>(WhiteList); Console.WriteLine("Type the numbers you want to query: ");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
int[] Query = new int[input.Split(' ').Length];
for (int i = ; i < Query.Length; ++i)
{
Query[i] = int.Parse(input.Split(' ')[i]);
} Console.WriteLine("Result:");
foreach (int n in Query)
{
int less = rank(n, WhiteList);
int equal = count(n, WhiteList);
Console.WriteLine($"Less: {less} Equal: {equal}");
}
} //返回数组中相等元素的个数
public static int count(int key, int[] a)
{
int lowerBound = rank(key, a);
int upperBound = lowerBound; if (lowerBound == -)
return ; int result = ;
while (true)
{
result = rank(key, a, upperBound + , a.Length - );
if (result == -)
break;
if (result > upperBound)
{
upperBound = result;
}
} return upperBound - lowerBound + ;
} //返回数组中小于该数的数字个数
public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
int mid = rank(key, a, , a.Length - );
if (mid == -)
return ;
int result = mid;
while (true)
{
result = rank(key, a, , mid - ); if (result == -)
break;
if (result < mid)
mid = result;
}
return mid;
} //二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi)
{ if (lo > hi)
{
return -;
} int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ; if (key < a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - );
}
else if (key > a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, mid + , hi);
}
else
{
return mid;
}
}
}
1.1.30
解答
互质可以用之前的 GCD 最大公因数算法判断,如果最大公因数是 1 则两数互质。
代码
//互质 = 最大公约数为 1 = gcd(i, j) == 1
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); bool[,] a = new bool[N, N]; for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = ; j < N; ++j)
{
a[i, j] = (gcd(i, j) == );
}
} PrintArray2D(a, N, N);
} static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == )
return a; return gcd(b, a % b);
} private static void PrintArray2D(bool[,] array, int rows, int columns)
{
for (int i = ; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = ; j < columns; j++)
{
Console.Write($"\t{array[i, j]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
}
1.1.31
解答
概率的实现方法:
例如概率是 60 %,就在 [0, 100) 之间随机一个值,小于等于 60 则执行操作,反之不执行。
需要更精确的情况可以增大随机的范围,例如 [0, 1000)。
绘图结果:
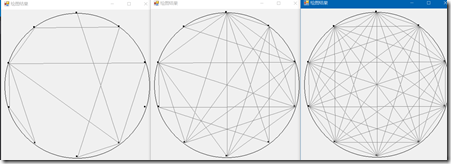
N = 10,p = 0.2, 0.5, 1
完整项目可以到 Github 上下载。
代码(绘图部分)
/// <summary>
/// 主绘图函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="N">点的总数目</param>
/// <param name="p">每对点之间连接的概率</param>
public static void StartDrawing(int N, double p)
{
int pointSize = ;//每个点绘制的大小
int precious = ;//概率判断的精度 //新建一个绘图窗口
Form2 DrawPad = new Form2();
//显示绘图窗口
DrawPad.Show(); //新建画布
Graphics graphics = DrawPad.CreateGraphics(); //建立绘图区域(矩形)
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(, , , ); //画圆
graphics.DrawEllipse(Pens.Black, rect); //计算旋转角度
double rotateDgree = 360.0 / N; //计算点的坐标
Point Center = new Point(rect.Top + rect.Height / , rect.Top + rect.Height / );
Point[] points = new Point[N];
points[].X = rect.Left + rect.Width / ;
points[].Y = rect.Top; for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
points[i] = Rotate(Center, points[i - ], rotateDgree);
} //绘制点
foreach (Point point in points)
{
graphics.FillEllipse(Brushes.Black, point.X - pointSize, point.Y - pointSize, pointSize, pointSize);
} //按照概率绘制直线
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = i + ; j < N; ++j)
{
//举例:输入概率为 0.6,精度为 1000
//在 0~1000 范围内等概率取值,如果小于等于 600 则视为事件发生
if (random.Next(, precious) <= p * precious)
{
graphics.DrawLine(Pens.Gray, points[i], points[j]);
}
}
} //释放资源
graphics.Dispose();
} /// <summary>
/// 计算一个点绕某点旋转之后的坐标值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="origin">旋转的圆心</param>
/// <param name="point">需要旋转的点</param>
/// <param name="dgree">旋转的角度(逆时针)</param>
/// <returns>返回旋转后的坐标</returns>
public static Point Rotate(Point origin, Point point, double dgree)
{
Point rotated = new Point();
double dgreePi = dgree / * Math.PI; rotated.X = (int)((point.X - origin.X) * Math.Cos(dgreePi) -
(point.Y - origin.Y) * Math.Sin(dgreePi) + origin.X);
rotated.Y = (int)((point.X - origin.X) * Math.Sin(dgreePi) +
(point.Y - origin.Y) * Math.Cos(dgreePi) + origin.Y); return rotated;
}
1.1.32
解答
绘图结果:

完整的项目代码可以去 Github 上下载。
代码(绘图部分)
public static void StartDrawing(double[] array, int N, double l, double r)
{
//创建并显示绘图窗口
Form2 DrawPad = new Form2();
DrawPad.Show(); //新建画布
Graphics graphics = DrawPad.CreateGraphics(); //翻转默认坐标系
graphics.TranslateTransform(, DrawPad.Height);
graphics.ScaleTransform(, -); //对原始数组排序
Array.Sort(array); //计算各区域的值
int[] counts = new int[N];
int index = ;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = index; j < array.Length; ++j)
{
if (array[j] <= (r - l) * (i + ) / N)
{
counts[i]++;
index++;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
} //获取最大值
double max = counts.Max();
//计算间距
double unit = DrawPad.Width / (3.0 * N + );
//计算直方图的矩形
Rectangle[] rects = new Rectangle[N];
rects[].X = (int)unit;
rects[].Y = ;
rects[].Width = (int)( * unit);
rects[].Height = (int)((counts[] / max) * DrawPad.Height);
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
rects[i].X = (int)(rects[i - ].X + * unit);
rects[i].Y = ;
rects[i].Width = (int)( * unit);
rects[i].Height = (int)((counts[i] / (max + )) * DrawPad.Height);
} //绘图
graphics.FillRectangles(Brushes.Black, rects); //释放资源
graphics.Dispose();
}
1.1.33
解答
这里矩阵使用交错数组实现(方便取行向量),不是普通的二维数组。
矩阵和矩阵、矩阵和向量、向量和矩阵都使用行向量点乘列向量的方式计算。
代码
public class Matrix
{
/// <summary>
/// 计算两个向量的点积
/// </summary>
/// <param name="x">需要点乘的向量</param>
/// <param name="y">需要点乘的另一个向量</param>
/// <returns>返回点乘的结果</returns>
/// <exception cref="FormatException"></exception>
public static double Dot(double[] x, double[] y)
{
//确保两向量等长
if (x.Length != y.Length)
{
throw new FormatException("the length of two vectors must be equal");
} //点乘
double result = ;
for (int i = ; i < x.Length; ++i)
{
result += x[i] * y[i];
} return result;
} /// <summary>
/// 计算两个矩阵相乘的结果,返回一个矩阵
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">用交错数组表示的 m * p 矩阵</param>
/// <param name="b">用交错数组表示的 p * n 矩阵</param>
/// <returns>返回 m * n 的矩阵</returns>
/// <exception cref="FormatException"></exception>
/// <example>
/// a = {(1,2,3),(4,5,6)}
/// b = {(1,4),(2,5),(3,6)}
/// Mult(a, b) = {(14,32),(32,77)}
/// </example>
public static double[][] Mult(double[][] a, double[][] b)
{
if (a[].Length != b.GetLength())
{
throw new FormatException("a's column number must be equal to b's row number");
} int m = a.GetLength();
int n = b[].Length;
int p = a[].Length; double[][] result = new double[m][]; for (int i = ; i < m; ++i)
{
double[] resultrow = new double[n];
for (int j = ; j < n; ++j)
{
//result[i][j] = 行向量 a[i] 与列向量 b[j] 的点积
double[] row = a[i];
double[] col = new double[p];
//取得列向量
for (int k = ; k < p; ++k)
{
col[k] = b[k][j];
}
//点积
resultrow[j] = Dot(row, col);
}
result[i] = resultrow;
}
return result;
} /// <summary>
/// 将一个矩阵转置
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">待转置的矩阵</param>
/// <returns>返回转置后的数组</returns>
public static double[][] Transpose(double[][] a)
{
double[][] trans = new double[a[].Length][];
for (int i = ; i < a[].Length; ++i)
{
double[] row = new double[a.GetLength()];
for (int j = ; j < a.GetLength(); ++j)
{
row[j] = a[j][i];
}
trans[i] = row;
}
return trans;
} /// <summary>
/// 计算矩阵与向量的乘积
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">左乘的矩阵</param>
/// <param name="x">列向量</param>
/// <returns>返回一个向量</returns>
/// <exception cref="FormatException"></exception>
public static double[] Mult(double[][] a, double[] x)
{
if (a[].Length != x.Length)
{
throw new FormatException("a's column number must be equal to x's length");
} double[] result = new double[a.GetLength()]; for (int i = ; i < a.GetLength(); ++i)
{
result[i] = Dot(a[i], x);
} return result;
} /// <summary>
/// 计算向量与矩阵的乘积
/// </summary>
/// <param name="x">行向量</param>
/// <param name="a">矩阵</param>
/// <returns>返回一个向量</returns>
/// <exception cref="FormatException"></exception>
public static double[] Mult(double[] x, double[][] a)
{
if (a.GetLength() != x.Length)
{
throw new FormatException("a's column number must be equal to x's length");
} double[] result = new double[a[].Length]; for (int i = ; i < a[].Length; ++i)
{
double[] colVector = new double[a.GetLength()];
for (int j = ; j < colVector.Length; ++j)
{
colVector[j] = a[j][i];
}
result[i] = Dot(x, colVector);
} return result;
} /// <summary>
/// 在控制台上输出矩阵
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要输出的矩阵</param>
public static void PrintMatrix(double[][] a)
{
for (int i = ; i < a.GetLength(); ++i)
{
for (int j = ; j < a[i].Length; ++j)
{
Console.Write($"\t{a[i][j]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
} /// <summary>
/// 在控制台上输出一行向量
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要输出的向量</param>
public static void PrintVector(double[] a)
{
for (int i = ; i < a.Length; ++i)
{
Console.Write($"\t{a[i]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
1.1.34
解答
第二个以及最后三个需要,其他都可以设计成过滤器的模式。
这里的 largeW.txt 只需要保留前 100 个数字就可以了,太多的话最后两个测试会刷屏。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] AllNumbers = File.ReadAllLines("largeW.txt");
int N = AllNumbers.Length;
int[] input = new int[N]; for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
input[i] = int.Parse(AllNumbers[i]);
} MinAndMax(input);
Console.WriteLine(); MidNumber(input);
Console.WriteLine(); NumberK(, input);
Console.WriteLine(); SquareSum(input);
Console.WriteLine(); AboveAverage(input);
Console.WriteLine(); Ascending(input);
Console.WriteLine(); Shuffle(input);
Console.WriteLine();
} /// <summary>
/// 获取最大值和最小值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
static void MinAndMax(int[] input)
{
//只用到了两个变量
int min = input[];
int max = input[]; //只对输入值正向遍历一遍,不需要保存
for (int i = ; i < input.Length; ++i)
{
if (input[i] > max)
{
max = input[i];
} if (input[i] < min)
{
min = input[i];
}
} Console.WriteLine("Min and Max:");
Console.WriteLine($"Min: {min}\nMax: {max}");
} /// <summary>
/// 获取中位数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
/// <returns>中位数</returns>
static int MidNumber(int[] input)
{
//需要对输入值进行去重 & 排序,故需要保存
List<int> DistinctNumbers = new List<int>(input.Distinct());
DistinctNumbers.Sort();
Console.WriteLine("MidNumber:");
Console.WriteLine(DistinctNumbers[DistinctNumbers.Count / ]); return DistinctNumbers[DistinctNumbers.Count / ];
} /// <summary>
/// 获取第 k 小的数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="k">需要获取的排名</param>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
/// <returns>第 k 小的数</returns>
static int NumberK (int k, int[] input)
{
int[] temp = new int[]; //只正向遍历一遍,不需要保存
for (int i = ; i < input.Length; ++i)
{
if (i < )
{
temp[i] = input[i];
}
else
{
temp[] = input[i];
Array.Sort(temp);
}
} Console.WriteLine("NumberK");
Console.WriteLine($"No.k: {temp[k - 1]}"); return temp[k - ];
} /// <summary>
/// 计算输入流中所有数的平方和
/// </summary>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
/// <returns>所有数的平方和</returns>
static long SquareSum(int[] input)
{
long sum = ;
//只正向遍历一遍,不需要保存
for (int i = ; i < input.Length; ++i)
{
sum += input[i] * input[i];
} Console.WriteLine("Sum Of Square:");
Console.WriteLine(sum); return sum;
} /// <summary>
/// 计算所有输入数据的平均值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
/// <returns>所有输入数据的平均值</returns>
static double Average(int[] input)
{
long sum = ; //只遍历一遍,且不保存整个数组
for (int i = ; i < input.Length; ++i)
{
sum += input[i];
} double ave = sum / (double)input.Length; Console.WriteLine("Average:");
Console.WriteLine(ave); return ave;
} /// <summary>
/// 计算大于平均值的元素数量
/// </summary>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
/// <returns>大于平均值的元素数量</returns>
static double AboveAverage(int[] input)
{
double ave = Average(input);
Console.WriteLine();
double count = ; for (int i = ; i < input.Length; ++i)
{
if (input[i] > ave)
{
count++;
}
} Console.WriteLine("AboveAverage:");
Console.WriteLine($"{(count / input.Length) * 100}%"); return count;
} /// <summary>
/// 升序打印数组
/// </summary>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
static void Ascending(int[] input)
{
Array.Sort(input); Console.WriteLine("Ascending:");
for (int i = ; i < input.Length; ++i)
{
Console.Write($" {input[i]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
} /// <summary>
/// 随机打印数组
/// </summary>
/// <param name="input">输入流</param>
static void Shuffle(int[] input)
{
Random random = new Random();
List<int> All = new List<int>(input);
int N = input.Length;
int temp = ; Console.WriteLine("Shuffle:");
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
temp = random.Next(, All.Count - );
Console.Write($" {All[temp]}");
All.RemoveAt(temp);
}
}
实验题(1.1.35~1.1.39)
1.1.35
解答
这里用 Random 类模拟掷骰子并计算概率,最后和程序得出的比较。
代码
//程序运行大概需要十几秒时间(也可能更长,看运气)
//我的数据:
//24098 44448 37776 44401 32541
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//书中给出的程序
int SIDES = ;
double[] dist = new double[ * SIDES + ];
for (int i = ; i <= SIDES; i++)
for (int j = ; j <= SIDES; j++)
dist[i + j] += 1.0; for (int k = ; k <= * SIDES; k++)
dist[k] /= 36.0; //不断进行模拟,直至误差小于 0.001
int N = ;
bool isAccepted = false;
double[] disttemp = null;
double error = 0.001;
while (isAccepted == false)
{
disttemp = PlayDice(N);
isAccepted = true;
for (int i = ; i < disttemp.Length; ++i)
{
if (Math.Abs(disttemp[i] - dist[i]) >= error)
isAccepted = false;
}
N++;
} Console.WriteLine($"N:{N}\n");
for (int i = ; i < dist.Length; ++i)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{i}:\n Standerd:{dist[i]}\nSimulated:{disttemp[i]}\nOffset:{Math.Abs(disttemp[i] - dist[i])}");
}
} //利用随机数模拟掷骰子
static double[] PlayDice(int N)
{
Random random = new Random(); int SIDES = ;
double[] dist = new double[ * SIDES + ]; //掷 N 次
int sumtemp = ;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
sumtemp = random.Next(, ) + random.Next(, );
dist[sumtemp]++;
} //计算概率
for (int i = ; i < dist.Length; ++i)
{
dist[i] /= N;
} return dist;
}
1.1.36
解答
N 取到 1000 左右数据就比较明显了。
N = 1000, M = 10
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int M = ;//数组大小
int N = ;//打乱次数
int[] a = new int[]; int[,] result = new int[M, M]; for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
//初始化
for (int j = ; j < a.Length; ++j)
{
a[j] = j;
} //打乱
Shuffle(a, i); //记录
for (int j = ; j < M; ++j)
{
result[a[j], j]++;
}
} PrintMatrix(result);
} /// <summary>
/// 打乱数组
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要打乱的数组</param>
/// <param name="seed">用于生成随机数的种子值</param>
static void Shuffle(int[] a, int seed)
{
int N = a.Length;
Random random = new Random(seed);
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
int r = i + random.Next(N - i);//等于StdRandom.uniform(N-i)
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 在控制台上输出矩阵
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要输出的矩阵</param>
public static void PrintMatrix(int[,] a)
{
for (int i = ; i < a.GetLength(); ++i)
{
for (int j = ; j < a.GetLength(); ++j)
{
Console.Write($"\t{a[i,j]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
1.1.37
解答
使用 0~N-1 的随机数会导致每次交换的数字可能相同。
例如:
原数组: 1 2 3 4。
第一次: 2 1 3 4 random = 1,第 0 个和第 1 个交换。
第二次: 1 2 3 4 random = 0,第 1 个和第 0 个交换。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int M = ;//数组大小
int N = ;//打乱次数
int[] a = new int[]; int[,] result = new int[M, M]; for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
//初始化
for (int j = ; j < a.Length; ++j)
{
a[j] = j;
} //打乱
Shuffle(a, i); //记录
for (int j = ; j < M; ++j)
{
result[a[j], j]++;
}
} PrintMatrix(result);
} /// <summary>
/// 打乱数组(不够好的版本)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要打乱的数组</param>
/// <param name="seed">用于生成随机数的种子值</param>
static void Shuffle(int[] a, int seed)
{
int N = a.Length;
Random random = new Random(seed);
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
//int r = i + random.Next(N - i);
int r = random.Next(N); //返回的是 0 ~ N-1 之间的随机整数
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 在控制台上输出矩阵
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要输出的矩阵</param>
public static void PrintMatrix(int[,] a)
{
for (int i = ; i < a.GetLength(); ++i)
{
for (int j = ; j < a.GetLength(); ++j)
{
Console.Write($"\t{a[i, j]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
1.1.38
解答
为了使差距比较明显,故意取了比较靠后的数字。
代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] largeWString = File.ReadAllLines("largeW.txt");
int[] largeW = new int[largeWString.Length];
for (int i = ; i < largeW.Length; ++i)
{
largeW[i] = int.Parse(largeWString[i]);
}
Stopwatch timer = Stopwatch.StartNew();
BruteForceSearch(, largeW);
Console.WriteLine($"BruteForceSearch: {timer.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms"); timer.Restart();
rank(, largeW);
Console.WriteLine($"BinarySearch: {timer.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms"); string[] largeTString = File.ReadAllLines("largeT.txt");
int[] largeT = new int[largeTString.Length];
for (int i = ; i < largeW.Length; ++i)
{
largeT[i] = int.Parse(largeTString[i]);
} timer.Restart();
BruteForceSearch(, largeT);
Console.WriteLine($"BruteForceSearch: {timer.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms"); timer.Restart();
rank(, largeT);
Console.WriteLine($"BinarySearch: {timer.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
} //暴力查找
public static int BruteForceSearch(int key, int[] a)
{
for (int i = ; i < a.Length; ++i)
{
if (a[i] == key)
return i;
} return -;
} //重载方法,用于启动二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
return rank(key, a, , a.Length - , );
} //二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi, int number)
{
if (lo > hi)
{
return -;
} int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ; if (key < a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - , number + );
}
else if (key > a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, mid + , hi, number + );
}
else
{
return mid;
}
}
1.1.39
解答
按照要求编程就好,视机器不同需要的时间也不同。
代码
//需要 6 秒左右的运算时间
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Random r = new Random();
int baseNum = ;
int powNum = ;
int T = ;
int M = ; double[,] Matrix = new double[M,]; for (int i = ; i < M; ++i)
{
int N = (int)Math.Pow(baseNum, powNum + i);
double sum = ;
for (int j = ; j < T; ++j)
{
sum += Test(N, r.Next());
}
Matrix[i, ] = N;
Matrix[i, ] = sum / T;
} PrintMatrix(Matrix);
} /// <summary>
/// 执行一次“实验”
/// </summary>
/// <param name="N">数组的大小</param>
/// <param name="seed">随机种子</param>
/// <returns>返回相同数字的数目</returns>
static int Test(int N, int seed)
{
Random random = new Random(seed);
int[] a = new int[N];
int[] b = new int[N];
int count = ; for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
a[i] = random.Next(, );
b[i] = random.Next(, );
} for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
if (rank(a[i], b) != -)
count++;
} return count;
} //重载方法,用于启动二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
return rank(key, a, , a.Length - , );
} //二分查找
public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi, int number)
{
if (lo > hi)
{
return -;
} int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / ; if (key < a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - , number + );
}
else if (key > a[mid])
{
return rank(key, a, mid + , hi, number + );
}
else
{
return mid;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 在控制台上输出矩阵
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">需要输出的矩阵</param>
public static void PrintMatrix(double[,] a)
{
for (int i = ; i < a.GetLength(); ++i)
{
for (int j = ; j < a.GetLength(); ++j)
{
Console.Write($"\t{a[i, j]}");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——1.1的更多相关文章
- 算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1
算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1 写在前面 整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csh ...
- 算法第四版 在Eclipse中调用Algs4库
首先下载Eclipse,我选择的是Eclipse IDE for Java Developers64位版本,下载下来之后解压缩到喜欢的位置然后双击Eclipse.exe启动 然后开始新建项目,File ...
- 算法第四版jar包下载地址
算法第四版jar包下载地址:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/code/
- 算法第四版-文字版-下载地址-Robert Sedgewick
下载地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/moshenglv/10777447 算法第四版,文字版,可复制,方便copy代码 目录: 第1章 基 础 ...... ...
- 二项分布。计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数(算法第四版1.1.27)
算法第四版35页问题1.1.27,估计用一下代码计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数: public static double binomial(int n,int ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之优先队列--Priority Queues
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.4优先队列(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:API 与初级实现 2:堆得定义 3:堆排序 4:事件驱动的仿真 优先队列最重要的操作就是删 ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之快速排序 QuickSort
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.3快速排序(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:快速排序 2:
- C程序设计(第四版)课后习题完整版 谭浩强编著
//复习过程中,纯手打,持续更新,觉得好就点个赞吧. 第一章:程序设计和C语言 习题 1.什么是程序?什么是程序设计? 答:程序就是一组计算机能识别和执行的指令.程序设计是指从确定任务到得到结果,写出 ...
- 算法第四版 coursera公开课 普林斯顿算法 ⅠⅡ部分 Robert Sedgewick主讲《Algorithms》
这是我在网上找到的资源,下载之后上传到我的百度网盘了. 包含两部分:1:算法视频的种子 2:字幕 下载之后,请用迅雷播放器打开,因为迅雷可以直接在线搜索字幕. 如果以下链接失效,请在下边留言,我再更新 ...
- 相似度分析,循环读入文件(加入了HanLP,算法第四版的库)
相似度分析的,其中的分词可以采用HanLP即可: http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1421978002609.htm /****************** ...
随机推荐
- MQTT 嵌入式端通讯协议解析(转)
MQTT,目前物联网的最主要的协议,基本所有收费的云平台都是基于MQTT协议,比如机智云,和所有的开放云平台比如中国移动的oneNet.百度的云平台也都支持MQTT的接入.虽然MQTT很火,但是目前对 ...
- 18、MySQL
++主键(primary key) 能够唯一标识表中某一行的属性或属性组++.==一个表只能有一个主键==,但可以有多个候选索引.==主键可以保证记录的唯一==和==主键域非空==,数据库管理系统对于 ...
- java的Io流学习
Java中io流的学习(一)File:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41061437/article/details/81672859 Java中io流的学习(二)FileInpu ...
- MySQL数据库导出
因为业务需要,把MySQL查询的数据导出成csv文件,操作在Navicat中完成. 首选用SELECT语句查询数据,然后Navicat的导出,然后选csv,选路径,再加上首栏就可以了
- HTML、CSS知识点,面试开发都会需要--No.1 HTML
No.1 HTML 1.网页结构 网页结构一般都包含文档声明DOCTYPE,并且在head中的meta应该包含编码格式.关键字.网页描述信息.简单格式如下: <!DOCTYPE html&g ...
- [No000018A]改善C#程序的建议11-20
建议11:区别对待 == 和Equals CLR中将“相等性”分为两类:1.值相等性:两个变量包含的数值相等.2.引用相等性:两个变量引用的是内存中的同一个对象. 但并不是所有的类型的比较都是按照其本 ...
- Qt带返回值的信号发射方式(使用QMetaObject::invokeMethod)
一般来说,我们发出信号使用emit这个关键字来操作,但是会发现,emit并不算一个调用,所以它没有返回值.那么如果我们发出这个信号想获取一个返回值怎么办呢? 两个办法:1.通过出参形式返回,引用或者指 ...
- libvirt虚拟库
转载自:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-libvirt/index.html Libvirt 虚拟化库剖析 讲到向外扩展计算(比如云计算 ...
- Jedis简介
实际开发中,我们需要用Redis的连接工具连接Redis然后操作Redis, 对于主流语言,Redis都提供了对应的客户端: https://redis.io/clients https://redi ...
- C#基础加强(1)之索引器
索引器 介绍 索引器,初学者可能听起来有些陌生,但其实我们经常会用到它,例如: // 字符串的索引器 string str = "hello world"; ]; // 获取到字符 ...
