micrometer自定义metrics
micrometer提供了基于Java的monitor facade,其与springboot应用和prometheus的集成方式如下图展示
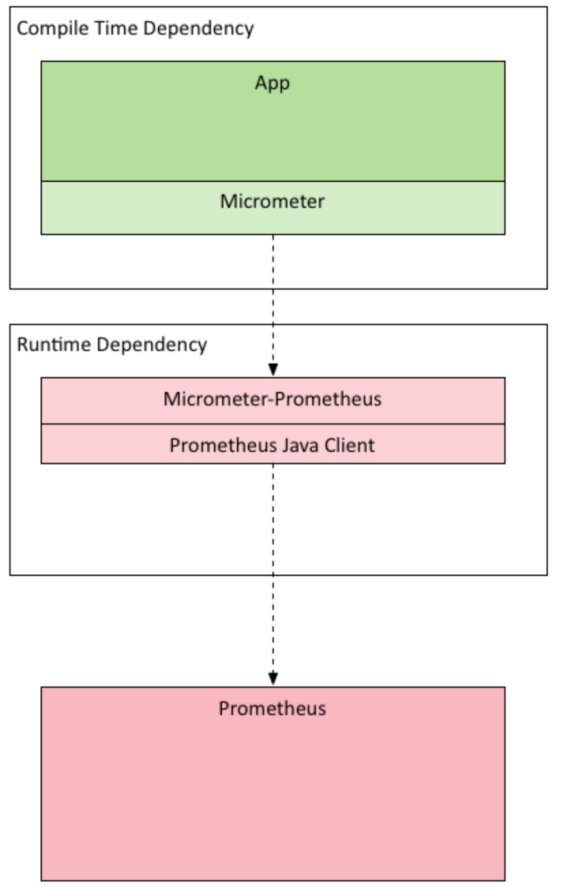
上图中展示的很清楚,应用通过micrometer采集和暴露监控端点给prometheus,prometheus通过pull模式来采集监控时序数据信息。之后作为数据源提供给grafana进行展示。
micrometer支持的度量方式及在springboot中的应用示例
Counter
Counter(计数器)简单理解就是一种只增不减的计数器。它通常用于记录服务的请求数量、完成的任务数量、错误的发生数量等等。
package com.dxz.producter.monitor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Counter;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Metrics; @Service("collectorService")
public class CollectorService { static final Counter userCounter = Metrics.counter("user.counter.total", "services", "demo"); public void processCollectResult() throws InterruptedException { while (true) {
userCounter.increment(1D);
}
}
}
Gauge
Gauge(仪表)是一个表示单个数值的度量,它可以表示任意地上下移动的数值测量。Gauge通常用于变动的测量值,如当前的内存使用情况,同时也可以测量上下移动的"计数",比如队列中的消息数量。
package com.dxz.producter.monitor; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Gauge;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.ImmutableTag;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Metrics;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Tag;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.simple.SimpleMeterRegistry; @Component("passCaseMetric")
public class PassCaseMetric { List<Tag> init() {
ArrayList<Tag> list = new ArrayList() {
};
list.add(new ImmutableTag("service", "demo"));
return list;
} AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0); Gauge passCaseGuage = Gauge.builder("pass.cases.guage", atomicInteger, AtomicInteger::get).tag("service", "demo")
.description("pass cases guage of demo").register(new SimpleMeterRegistry()); AtomicInteger passCases = Metrics.gauge("pass.cases.guage.value", init(), atomicInteger); public void handleMetrics() { while (true) {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() % 2 == 0) {
passCases.addAndGet(100);
System.out.println("ADD + " + passCaseGuage.measure() + " : " + passCases);
} else {
int val = passCases.addAndGet(-100);
if (val < 0) {
passCases.set(1);
}
System.out.println("DECR - " + passCaseGuage.measure() + " : " + passCases);
}
} } }
增加一个controller,触发他们:
package com.dxz.producter.web; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.dxz.producter.monitor.CollectorService;
import com.dxz.producter.monitor.PassCaseMetric; @RestController
@RequestMapping("/monitor")
public class MonitorController { @Autowired
CollectorService collectorService; @Autowired
PassCaseMetric passCaseMetric; @RequestMapping(value = "/counter", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String counter() throws InterruptedException {
collectorService.processCollectResult();
return "+1";
} @RequestMapping(value = "/gauge", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String gauge() throws InterruptedException {
passCaseMetric.handleMetrics();
return "+gauge";
} }
启动springboot应用,可以在http://host:port/actuator/prometheus 看到端点收集到的数据。其他的也是类似的不再一一截图展示。

这里使用了一个true的循环用来展示不断更新的效果。
同样的可以在grafana中看到监控展示信息
Timer
Timer(计时器)同时测量一个特定的代码逻辑块的调用(执行)速度和它的时间分布。简单来说,就是在调用结束的时间点记录整个调用块执行的总时间,适用于测量短时间执行的事件的耗时分布,例如消息队列消息的消费速率。
@Test
public void testTimerSample(){
Timer timer = Timer.builder("timer")
.tag("timer", "timersample")
.description("timer sample test.")
.register(new SimpleMeterRegistry()); for(int i=0; i<2; i++) {
timer.record(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
}catch (InterruptedException e){ } });
} System.out.println(timer.count());
System.out.println(timer.measure());
System.out.println(timer.totalTime(TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(timer.mean(TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(timer.max(TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
响应数据
2
[Measurement{statistic='COUNT', value=2.0}, Measurement{statistic='TOTAL_TIME', value=4.005095763}, Measurement{statistic='MAX', value=2.004500494}]
4.005095763
2.0025478815
2.004500494
Summary
Summary(摘要)用于跟踪事件的分布。它类似于一个计时器,但更一般的情况是,它的大小并不一定是一段时间的测量值。在micrometer中,对应的类是DistributionSummary,它的用法有点像Timer,但是记录的值是需要直接指定,而不是通过测量一个任务的执行时间。
@Test
public void testSummary(){ DistributionSummary summary = DistributionSummary.builder("summary")
.tag("summary", "summarySample")
.description("summary sample test")
.register(new SimpleMeterRegistry()); summary.record(2D);
summary.record(3D);
summary.record(4D); System.out.println(summary.count());
System.out.println(summary.measure());
System.out.println(summary.max());
System.out.println(summary.mean());
System.out.println(summary.totalAmount());
}
响应数据:
3
[Measurement{statistic='COUNT', value=3.0}, Measurement{statistic='TOTAL', value=9.0}, Measurement{statistic='MAX', value=4.0}]
4.0
3.0
9.0
序
本文主要研究下如何使用自定义micrometer的metrics
实例
DemoMetrics
public class DemoMetrics implements MeterBinder {
AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public void bindTo(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
Gauge.builder("demo.count", count, c -> c.incrementAndGet())
.tags("host", "localhost")
.description("demo of custom meter binder")
.register(meterRegistry);
}
}这里实现了MeterBinder接口的bindTo方法,将要采集的指标注册到MeterRegistry
注册
- 原始方式
new DemoMetrics().bindTo(registry);- springboot autoconfigure
@Bean
public DemoMetrics demoMetrics(){
return new DemoMetrics();
}在springboot只要标注下bean,注入到spring容器后,springboot会自动注册到registry。springboot已经帮你初始化了包括UptimeMetrics等一系列metrics。详见源码解析部分。
验证
curl -i http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/demo.count返回实例
{
"name": "demo.count",
"measurements": [
{
"statistic": "VALUE",
"value": 6
}
],
"availableTags": [
{
"tag": "host",
"values": [
"localhost"
]
}
]
}源码解析
MetricsAutoConfiguration
spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure-2.0.0.RELEASE-sources.jar!/org/springframework/boot/actuate/autoconfigure/metrics/MetricsAutoConfiguration.java
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(Timed.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MetricsProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureBefore(CompositeMeterRegistryAutoConfiguration.class)
public class MetricsAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public Clock micrometerClock() {
return Clock.SYSTEM;
}
@Bean
public static MeterRegistryPostProcessor meterRegistryPostProcessor(
ApplicationContext context) {
return new MeterRegistryPostProcessor(context);
}
@Bean
@Order(0)
public PropertiesMeterFilter propertiesMeterFilter(MetricsProperties properties) {
return new PropertiesMeterFilter(properties);
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "management.metrics.binders.jvm.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
static class JvmMeterBindersConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public JvmGcMetrics jvmGcMetrics() {
return new JvmGcMetrics();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public JvmMemoryMetrics jvmMemoryMetrics() {
return new JvmMemoryMetrics();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public JvmThreadMetrics jvmThreadMetrics() {
return new JvmThreadMetrics();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ClassLoaderMetrics classLoaderMetrics() {
return new ClassLoaderMetrics();
}
}
@Configuration
static class MeterBindersConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = { "ch.qos.logback.classic.LoggerContext",
"org.slf4j.LoggerFactory" })
@Conditional(LogbackLoggingCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(LogbackMetrics.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "management.metrics.binders.logback.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public LogbackMetrics logbackMetrics() {
return new LogbackMetrics();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "management.metrics.binders.uptime.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public UptimeMetrics uptimeMetrics() {
return new UptimeMetrics();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "management.metrics.binders.processor.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ProcessorMetrics processorMetrics() {
return new ProcessorMetrics();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "management.metrics.binders.files.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public FileDescriptorMetrics fileDescriptorMetrics() {
return new FileDescriptorMetrics();
}
}
static class LogbackLoggingCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
ILoggerFactory loggerFactory = LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory();
ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage
.forCondition("LogbackLoggingCondition");
if (loggerFactory instanceof LoggerContext) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(
message.because("ILoggerFactory is a Logback LoggerContext"));
}
return ConditionOutcome
.noMatch(message.because("ILoggerFactory is an instance of "
+ loggerFactory.getClass().getCanonicalName()));
}
}
}可以看到这里注册了好多metrics,比如UptimeMetrics,JvmGcMetrics,ProcessorMetrics,FileDescriptorMetrics等
这里重点看使用@Bean标注了MeterRegistryPostProcessor
MeterRegistryPostProcessor
spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure-2.0.0.RELEASE-sources.jar!/org/springframework/boot/actuate/autoconfigure/metrics/MeterRegistryPostProcessor.java
class MeterRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final ApplicationContext context;
private volatile MeterRegistryConfigurer configurer;
MeterRegistryPostProcessor(ApplicationContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof MeterRegistry) {
getConfigurer().configure((MeterRegistry) bean);
}
return bean;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private MeterRegistryConfigurer getConfigurer() {
if (this.configurer == null) {
this.configurer = new MeterRegistryConfigurer(beansOfType(MeterBinder.class),
beansOfType(MeterFilter.class),
(Collection<MeterRegistryCustomizer<?>>) (Object) beansOfType(
MeterRegistryCustomizer.class),
this.context.getBean(MetricsProperties.class).isUseGlobalRegistry());
}
return this.configurer;
}
private <T> Collection<T> beansOfType(Class<T> type) {
return this.context.getBeansOfType(type).values();
}
}可以看到这里new了一个MeterRegistryConfigurer,重点注意这里使用beansOfType(MeterBinder.class)方法的返回值给其构造器
MeterRegistryConfigurer
spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure-2.0.0.RELEASE-sources.jar!/org/springframework/boot/actuate/autoconfigure/metrics/MeterRegistryConfigurer.java
class MeterRegistryConfigurer {
private final Collection<MeterRegistryCustomizer<?>> customizers;
private final Collection<MeterFilter> filters;
private final Collection<MeterBinder> binders;
private final boolean addToGlobalRegistry;
MeterRegistryConfigurer(Collection<MeterBinder> binders,
Collection<MeterFilter> filters,
Collection<MeterRegistryCustomizer<?>> customizers,
boolean addToGlobalRegistry) {
this.binders = (binders != null ? binders : Collections.emptyList());
this.filters = (filters != null ? filters : Collections.emptyList());
this.customizers = (customizers != null ? customizers : Collections.emptyList());
this.addToGlobalRegistry = addToGlobalRegistry;
}
void configure(MeterRegistry registry) {
if (registry instanceof CompositeMeterRegistry) {
return;
}
// Customizers must be applied before binders, as they may add custom
// tags or alter timer or summary configuration.
customize(registry);
addFilters(registry);
addBinders(registry);
if (this.addToGlobalRegistry && registry != Metrics.globalRegistry) {
Metrics.addRegistry(registry);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void customize(MeterRegistry registry) {
LambdaSafe.callbacks(MeterRegistryCustomizer.class, this.customizers, registry)
.withLogger(MeterRegistryConfigurer.class)
.invoke((customizer) -> customizer.customize(registry));
}
private void addFilters(MeterRegistry registry) {
this.filters.forEach(registry.config()::meterFilter);
}
private void addBinders(MeterRegistry registry) {
this.binders.forEach((binder) -> binder.bindTo(registry));
}
}可以看到configure方法里头调用了addBinders,也就是把托管给spring容器的MeterBinder实例bindTo到meterRegistry
小结
springboot2引入的micrometer,自定义metrics只需要实现MeterBinder接口,然后托管给spring即可,springboot的autoconfigure帮你自动注册到meterRegistry。
micrometer自定义metrics的更多相关文章
- 自定义Metrics:让Prometheus监控你的应用程序
前言 Prometheus社区提供了大量的官方以及第三方Exporters,可以满足Prometheus的采纳者快速实现对关键业务,以及基础设施的监控需求. 如上所示,一个简单的应用以及环境架构.一般 ...
- Spring Boot 2.x 自定义metrics 并导出到influxdb
Step 1.添加依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactI ...
- Spring cloud微服务安全实战-7-6自定义metrics监控指标(1)
自己写代码来定义一个metrics,然后让prmetheus收走,在grafana里面定义一个panel并展示出来. prometheus的四种metrics指标.虽然所有的metrics都是数字,但 ...
- Spring cloud微服务安全实战-7-7自定义metrics监控指标(2)
Gauge用来显示单词一个数的 勾选,这里编程仪表盘 设置仪表盘的最大值.最小值 保存 直接保存 保存成功的提示 返回 这就是我们做的一个简单的仪表盘 这个不适合我们的counter,因为没有最大值 ...
- Springboot2 Metrics之actuator集成influxdb, Grafana提供监控和报警
到目前为止,各种日志收集,统计监控开源组件数不胜数,即便如此还是会有很多人只是tail -f查看一下日志文件.随着容器化技术的成熟,日志和metrics度量统计已经不能仅仅靠tail -f来查看了,你 ...
- 如何用prometheus监控k8s集群中业务pod的metrics
一般,我们从网上看到的帖子和资料, 都是用prometheus监控k8s的各项资源, 如api server, namespace, pod, node等. 那如果是自己的业务pod上的自定义metr ...
- Apache Flink 进阶(八):详解 Metrics 原理与实战
本文由 Apache Flink Contributor 刘彪分享,本文对两大问题进行了详细的介绍,即什么是 Metrics.如何使用 Metrics,并对 Metrics 监控实战进行解释说明. 什 ...
- hystrix文档翻译之metrics
metrics和监控 动机 HystrixCommands和HystrixObservableCommands执行过程中会产生相关运行情况的metrics.这些metrics对于监控系统表现有很大的 ...
- 朱晔和你聊Spring系列S1E7:简单好用的Spring Boot Actuator
阅读PDF版本 本文会来看一下Spring Boot Actuator提供给我们的监控端点Endpoint.健康检查Health和打点指标Metrics等所谓的Production-ready(生产环 ...
随机推荐
- linux 基础命令,未完待续
1, cd 进入系统根目录 cd / 进入当前用户的主目录 cd ~ 进入当前目录的上一级目录 cd .. 跳转到指定目录,从根目录开始 cd /apps/ 2, pwd 查看当前工作目录的完整路径 ...
- python网络爬虫&&爬取网易云音乐
#爬取网易云音乐 url="https://music.163.com/discover/toplist" #歌单连接地址 url2 = 'http://music.163.com ...
- python之模块定义、导入、优化详解
一.模块 1.模块的定义 模块是一组包含了一组功能的python文件,比如test.py,模块名为test,可以通过import test进行调用.模块可以分为以下四个通用类别 1 使用python编 ...
- IIS SSL证书 指定的登录会话不存在,可能已被终止 HRESULT:0x80070520
指定的登录会话不存在,可能已被终止 HRESULT:0x80070520 IIS导入证书时,选择”允许导出此证书” 服务器证书名称,在mmc控制台中个人证书中命名
- [Leetcode 105]*前序后序遍历形成树
public TreeNode find(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int j, int start, int end) { if (j > preorder. ...
- centos7源码安装Python3的前提条件
centos7源码安装Python3的前提条件: # yum -y install openssl-devel bzip2-devel expat-devel gdbm-devel readline- ...
- SpringMvc开发报找不到springmvc配置文件
param-name标签属性值必须为contextConfigLocation
- Redis常用命令与高级应用
附: 127.0.0.1:6379> set xiaofei 小飞 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get xiaofei "\xe5\xb0\x8f\xe9\xa3\x9 ...
- 在HTML中用循环语句
<%for(){% > <tr> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <%}%> 注意 ...
- 5.使用std的迭代器访问并修改图像
void Test_ColorReduceByIterator() { Mat g_srcImage=imread("D:\\OpenCV Projects\\OpenCV_Test_Ima ...
