浅谈平衡树splay
首先splay和treap不一样,treap通过随机数来调整树的形态。但splay不一样,再每插入或操作一次后,你都会把他旋转到根,再旋转过程中树的形态会不断改变,这样来达到均摊效果 常数据大。
来看看具体实现吧
首先定义数组,\(size\) 子树大小(包括自己),\(fa\) 节点的父亲,\(key\) 该节点的权值,\(cnt\) 该节点权值出现次数,$ch $表示儿子 0表左二子,1表右儿子
首先看几个简单函数
inline void update(int x)
{
size[x]=cnt[x]+size[ch[x][0]]+size[ch[x][1]];
}
更新子树大小
inline int get(int x){return x==ch[fa[x]][1];}
返回该节点是left儿子还是right儿子
inline void clear(int x){ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=fa[x]=size[x]=cnt[x]=key[x]=0;}
删除该节点,清空所有信息
接下来是splay的精髓所在
inline void rotate(int x,int &k)
{
static int old,oldfa,o;
old=fa[x];oldfa=fa[old];o=get(x);
if(old==k)k=x;
else ch[oldfa][get(old)]=x;
fa[x]=oldfa;
ch[old][o]=ch[x][o^1];fa[ch[x][o^1]]=old;
ch[x][o^1]=old;fa[old]=x;
update(x),update(old);
}
inline void splay(int x,int &k)
{
while(x!=k)
{
if(fa[x]!=k)rotate(get(x)^get(fa[x])?x:fa[x],k);
rotate(x,k);
}
}
rotate,splay,是splay核心操作,显然splay是依赖于rotate的,让我们看一下rotate是如何实现的吧
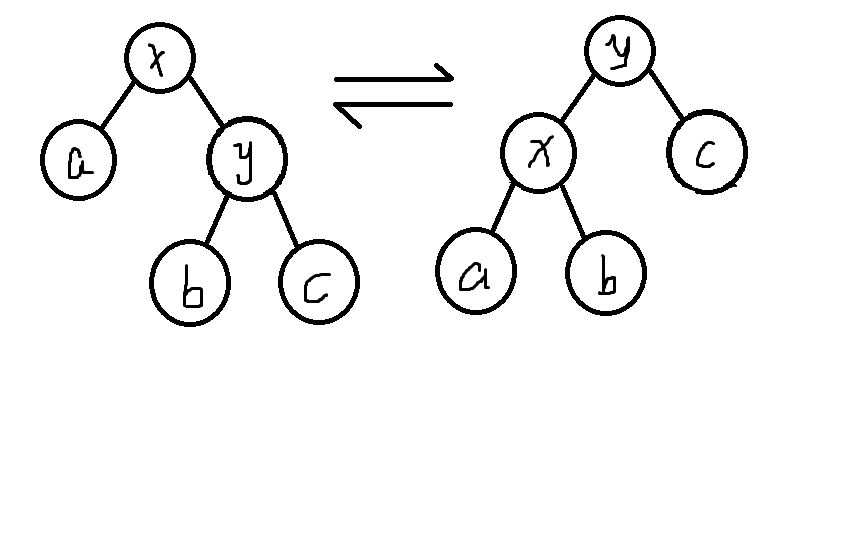
(手绘图)
我们考虑从图上左往右的过程,我们要将y旋上去,因为y本是x的右儿子,所以x放到y的左儿子,将y的原本左儿子设为x的右儿子,这是左旋,还有对称操作右旋,但我们不必要打两个函数,用 ^可以实现左右儿子的转换,用get操作实现,具体实现参考代码,打代码时最好画个图参照一下。
splay,这个操作完全依靠rotate,目的就是把你要的节点旋转到k(一般是root),k要传地址,要修改。在while循环里加了个小小的优化,但x和他的fa在同一侧时可以旋fa,以此来改变树的形态,(不怕被卡可以不写)
inline void insert(int x)
{
if(!root){root=++sz;size[sz]=cnt[sz]=1;key[sz]=x;return;}
int now=root,o;
while(1)
{
if(x==key[now])
{
++cnt[now];
splay(now,root);
update(now);
return;
}
o=x>key[now]?1:0;
if(!ch[now][o])
{
ch[now][o]=++sz;
size[sz]=cnt[sz]=1;
key[sz]=x;fa[sz]=now;
splay(sz,root);
return;
}
else now=ch[now][o];
}
}
insert,插入一个数,当没有数时就直接把这个数设为根,else 因为树满足二叉排序树的性质,所以比当前节点的key小就往左走,否则往右走,直到找到一个空节点,更新信息,由于这个点以上所有的点\(size\)都要加一,不好update,所以把这给点旋转到根,将这个点update就行了
inline int find_pos(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(1)
{
if(x==key[now]){return now;}
if(x<key[now])now=ch[now][0];
else now=ch[now][1];
}
}
找到该值在树中的节点编号
inline int pre()
{
int now=ch[root][0];
while(ch[now][1])now=ch[now][1];
return now;
}
inline int nex()
{
int now=ch[root][1];
while(ch[now][0])now=ch[now][0];
return now;
}
求前驱,后继,前驱从根的左儿子开始一直往右跑,后继从根的右儿子开始一直往左跑即可
void del(int x)
{
splay(find_pos(x),root);
if(cnt[root]>1){--cnt[root];return;}
if(!ch[root][0]&&!ch[root][1]){clear(root);root=0;return;}
if(ch[root][0]&&ch[root][1])
{
int oldroot=root;
splay(pre(),root);
fa[ch[oldroot][1]]=root;
ch[root][1]=ch[oldroot][1];
clear(oldroot);
update(root);
}
else
{
int o=ch[root][1]>0;
root=ch[root][o];
clear(fa[root]);
fa[root]=0;
}
}
删除操作,有点麻烦,先找到x的位置
- 如果x有多个就\(cnt\)减一
- 如果一个儿子都没有就直接删掉,root设为0
- 如果 只有一个儿子就把儿子设为根,删去这个点
- 剩下两个儿子情况,找到根的前驱,把前驱旋到根,这是root只有左儿子,再把原来根的右儿子到root上,这样原来的root就脱离了树,再删掉即可。
inline int find_order_of_key(int x)
{
int res=0,now=root;
while(1)
{
if(x<key[now])now=ch[now][0];
else
{
res+=size[ch[now][0]];
if(x==key[now]){splay(now,root);return res+1;}
res+=cnt[now];
now=ch[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int find_by_order(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(1)
{
if(x<=size[ch[now][0]])now=ch[now][0];
else
{
int temp=size[ch[now][0]]+cnt[now];
if(x<=temp)return key[now];
else{x-=temp;now=ch[now][1];}
}
}
}
找x的排名,与找排名为x的数,其实大同小异,用二叉搜索树的性质即可,只是记得答案不一样罢了
inline void rever(int x)
{
swap(ch[x][0],ch[x][1]);
rev[ch[x][0]]^=1;rev[ch[x][1]]^=1;
rev[x]=0;
}
inline void rever(int l,int r)
{
l=find(l-1);r=find(r+1);
splay(l,root);splay(r,ch[l][1]);
rev[ch[r][0]]^=1;
}
找到区间左边一个和区间的右边一个点在树中位置,把左边的点旋转到根,再把右边的点旋到root的右儿子,这时这段区间一定是ch[r][0]的子树(想一想,为什么)(根据二叉搜索树的性质),把这个点打上标记即可;当遇到有翻转标记的点时,交换其左右子树,并下传标记即可,注意,翻转操作只有可能在维护无序数列时使用,在有序数列中不需要也不能翻转,不然就无法满足排序二叉树的性质。
翻转操作在找节点的编号时才执行,详见下面代码
ok,splay的基本操作就是这些了
下面是完整代码
洛谷P3369 treap模板
题目描述
您需要写一种数据结构(可参考题目标题),来维护一些数,其中需要提供以下操作:
插入x数
删除x数(若有多个相同的数,因只删除一个)
查询x数的排名(排名定义为比当前数小的数的个数+1。若有多个相同的数,因输出最小的排名)
查询排名为x的数
求x的前驱(前驱定义为小于x,且最大的数)
求x的后继(后继定义为大于x,且最小的数)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int sign;
typedef long long ll;
#define For(i,a,b) for(register sign i=(sign)a;i<=(sign)b;++i)
#define Fordown(i,a,b) for(register sign i=(sign)a;i>=(sign)b;--i)
const int N=1e5+5;
void cmax(sign &a,sign b){if(a<b)a=b;}
void cmin(sign &a,sign b){if(a>b)a=b;}
template<typename T>T read()
{
T ans=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(!isdigit(ch)&&ch!='-')ch=getchar();
if(ch=='-')f=-1,ch=getchar();
while(isdigit(ch))ans=(ans<<3)+(ans<<1)+(ch-'0'),ch=getchar();
return ans*f;
}
void file()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("splay.in","r",stdin);
freopen("splay.out","w",stdout);
#endif
}
int fa[N],size[N],key[N],cnt[N],ch[N][2],sz,root;
inline void update(int x){size[x]=cnt[x]+size[ch[x][0]]+size[ch[x][1]];}
inline int get(int x){return x==ch[fa[x]][1];}
inline void clear(int x){ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=fa[x]=size[x]=cnt[x]=key[x]=0;}
inline void rotate(int x,int &k)
{
static int old,oldfa,o;
old=fa[x];oldfa=fa[old];o=get(x);
if(old==k)k=x;
else ch[oldfa][get(old)]=x;
fa[x]=oldfa;
ch[old][o]=ch[x][o^1];fa[ch[x][o^1]]=old;
ch[x][o^1]=old;fa[old]=x;
update(x),update(old);
}
inline void splay(int x,int &k)
{
while(x!=k)
{
if(fa[x]!=k)rotate(get(x)^get(fa[x])?x:fa[x],k);
rotate(x,k);
}
}
inline void insert(int x)
{
//puts("");
if(!root){root=++sz;size[sz]=cnt[sz]=1;key[sz]=x;return;}
int now=root,o;
while(1)
{
if(x==key[now])
{
++cnt[now];
splay(now,root);
update(now);
return;
}
o=x>key[now]?1:0;
if(!ch[now][o])
{
ch[now][o]=++sz;
size[sz]=cnt[sz]=1;
key[sz]=x;fa[sz]=now;
splay(sz,root);
return;
}
else now=ch[now][o];
//printf("%d %d %d %d\n",now,fa[now],ch[now][0],ch[now][1]);
}
}
inline int find_pos(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(1)
{
if(x==key[now]){return now;}
if(x<key[now])now=ch[now][0];
else now=ch[now][1];
}
}
inline int pre()
{
int now=ch[root][0];
while(ch[now][1])now=ch[now][1];
return now;
}
inline int nex()
{
int now=ch[root][1];
while(ch[now][0])now=ch[now][0];
return now;
}
void del(int x)
{
splay(find_pos(x),root);
if(cnt[root]>1){--cnt[root];return;}
if(!ch[root][0]&&!ch[root][1]){clear(root);root=0;return;}
if(ch[root][0]&&ch[root][1])
{
int oldroot=root;
splay(pre(),root);
fa[ch[oldroot][1]]=root;
ch[root][1]=ch[oldroot][1];
clear(oldroot);
update(root);
}
else
{
int o=ch[root][1]>0;
root=ch[root][o];
clear(fa[root]);
fa[root]=0;
}
}
inline int find_order_of_key(int x)
{
int res=0,now=root;
while(1)
{
if(x<key[now])now=ch[now][0];
else
{
res+=size[ch[now][0]];
if(x==key[now]){splay(now,root);return res+1;}
res+=cnt[now];
now=ch[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int find_by_order(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(1)
{
if(x<=size[ch[now][0]])now=ch[now][0];
else
{
int temp=size[ch[now][0]]+cnt[now];
if(x<=temp)return key[now];
else{x-=temp;now=ch[now][1];}
}
}
}
void input()
{
int T=read<int>();
int opt,x;
while(T--)
{
opt=read<int>();x=read<int>();
if(opt==1)insert(x);
else if(opt==2)del(x);
else if(opt==3)printf("%d\n",find_order_of_key(x));
else if(opt==4)printf("%d\n",find_by_order(x));
else if(opt==5)
{
insert(x);
printf("%d\n",key[pre()]);
del(x);
}
else if(opt==6)
{
insert(x);
printf("%d\n",key[nex()]);
del(x);
}
}
}
int main()
{
file();
input();
return 0;
}
洛谷P3391 splay模板
题目描述
您需要写一种数据结构(可参考题目标题),来维护一个有序数列,其中需要提供以下操作:翻转一个区间,输出一行n个数字,表示原始序列经过m次变换后的结果
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int sign;
typedef long long ll;
#define For(i,a,b) for(register sign i=(sign)a;i<=(sign)b;++i)
#define Fordown(i,a,b) for(register sign i=(sign)a;i>=(sign)b;--i)
const int N=1e5+5;
bool cmax(sign &a,sign b){return (a<b)?a=b,1:0;}
bool cmin(sign &a,sign b){return (a>b)?a=b,1:0;}
template<typename T>T read()
{
T ans=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(!isdigit(ch)&&ch!='-')ch=getchar();
if(ch=='-')f=-1,ch=getchar();
while(isdigit(ch))ans=(ans<<3)+(ans<<1)+(ch-'0'),ch=getchar();
return ans*f;
}
void file()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("splay.in","r",stdin);
freopen("splay.out","w",stdout);
#endif
}
int ch[N][2],fa[N],size[N],rev[N],root,sz;
inline int get(int x){return x==ch[fa[x]][1];}
inline void update(int x){size[x]=1+size[ch[x][0]]+size[ch[x][1]];}
inline void rotate(int x,int &k)
{
int old=fa[x],oldfa=fa[old],o=get(x);
if(k==old)k=x;
else ch[oldfa][ch[oldfa][1]==old]=x;
fa[x]=oldfa;fa[old]=x;fa[ch[x][o^1]]=old;
ch[old][o]=ch[x][o^1];ch[x][o^1]=old;
update(x),update(old);
}
inline void splay(int x,int &k)
{
while(x!=k)
{
if(fa[x]!=k)rotate(get(x)^get(fa[x])?x:fa[x],k);
//printf("%d %d\n",x,k);
rotate(x,k);
}
}
#define mid ((l+r)>>1)
inline void build(int l,int r,int pre)
{
if(l>r)return;
ch[pre][mid>=pre]=mid;
fa[mid]=pre;size[mid]=1;
if(l==r)return;
build(l,mid-1,mid);build(mid+1,r,mid);
update(mid);
}
#undef mid
int n,m;
void input(){n=read<int>();m=read<int>();}
inline void rever(int x)
{
swap(ch[x][0],ch[x][1]);
rev[ch[x][0]]^=1;rev[ch[x][1]]^=1;
rev[x]=0;
}
int find(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(1)
{
if(rev[now])rever(now);
if(size[ch[now][0]]>=x)now=ch[now][0];
else
{
if(size[ch[now][0]]==x-1)return now;
x=x-size[ch[now][0]]-1;
now=ch[now][1];
}
}
}
void work()
{
int l,r;
root=(n+3)>>1;
build(1,n+2,root);
fa[root]=0;
while(m--)
{
l=read<int>();r=read<int>();
l=find(l);r=find(r+2);
splay(l,root);splay(r,ch[l][1]);
rev[ch[r][0]]^=1;
}
}
void out(int x)
{
if(rev[x])rever(x);
if(ch[x][0])out(ch[x][0]);
if(x>1&&x<n+2)printf("%d ",x-1);
if(ch[x][1])out(ch[x][1]);
}
int main()
{
file();
input();
work();
out(root);
return 0;
}
另外推荐一篇写得好的博客
浅谈平衡树splay的更多相关文章
- 浅谈算法——splay
BST(二叉查找树)是个有意思的东西,种类巨TM多,然后我们今天不讲其他的,我们今天就讲splay 首先,如果你不知道Splay是啥,你也得知道BST是啥 如上图就是一棵优美的BST,它对于每个点保证 ...
- 浅谈splay(点的操作)
浅谈splay(点的操作) 一.基本概念 splay本质:二叉查找树 特点:结点x的左子树权值都小于x的权值,右子树权值都大于x的权值 维护信息: 整棵树:root 当前根节点 sz书上所有结点编号 ...
- 浅谈JAVA集合框架
浅谈JAVA集合框架 Java提供了数种持有对象的方式,包括语言内置的Array,还有就是utilities中提供的容器类(container classes),又称群集类(collection cl ...
- 浅谈SQL Server数据内部表现形式
在上篇文章 浅谈SQL Server内部运行机制 中,与大家分享了SQL Server内部运行机制,通过上次的分享,相信大家已经能解决如下几个问题: 1.SQL Server 体系结构由哪几部分组成? ...
- 浅谈SQL Server---1
浅谈SQL Server优化要点 https://www.cnblogs.com/wangjiming/p/10123887.html 1.SQL Server 体系结构由哪几部分组成? 2.SQL ...
- cdq分治浅谈
$cdq$分治浅谈 1.分治思想 分治实际上是一种思想,这种思想就是将一个大问题划分成为一些小问题,并且这些小问题与这个大问题在某中意义上是等价的. 2.普通分治与$cdq$分治的区别 普通分治与$c ...
- Lct浅谈
Lct浅谈 1.对lct的认识 首先要知道$lct$是什么.$lct$的全称为$link-cut-tree$.通过全称可以看出,这个数据结构是维护树上的问题,并且是可以支持连边断边操作.$lct$ ...
- HTTP协议漫谈 C#实现图(Graph) C#实现二叉查找树 浅谈进程同步和互斥的概念 C#实现平衡多路查找树(B树)
HTTP协议漫谈 简介 园子里已经有不少介绍HTTP的的好文章.对HTTP的一些细节介绍的比较好,所以本篇文章不会对HTTP的细节进行深究,而是从够高和更结构化的角度将HTTP协议的元素进行分类讲 ...
- 浅谈BST(二叉查找树)
目录 BST的性质 BST的建立 BST的检索 BST的插入 BST求前驱/后继 BST的节点删除 复杂度 平衡树 BST的性质 树上每个节点上有个值,这个值叫关键码 每个节点的关键码大于其任意左侧子 ...
随机推荐
- Django Rest Framework源码剖析(八)-----视图与路由
一.简介 django rest framework 给我们带来了很多组件,除了认证.权限.序列化...其中一个重要组件就是视图,一般视图是和路由配合使用,这种方式给我们提供了更灵活的使用方法,对于使 ...
- # 20155319 Exp3 免杀原理与实践
20155319 Exp3 免杀原理与实践 基础问题 (1)杀软是如何检测出恶意代码的? 基于特征码的检测 启发式的恶意软件检测 基于行为的恶意软件检测 (2)免杀是做什么? 免杀,从字面进行理解,避 ...
- linux下通过软连接实现访问项目路径外面的资源
在javaweb项目开发中,图片上传是个比较常见的场景.一般都是在项目路径下建个文件夹,然后上传到该文件夹下:这样这个图片就可以和静态资源一样被直接访问.这样的好处就是访问这图片特别方 ...
- 【LG3768】简单的数学题
[LG3768]简单的数学题 题面 求 \[ (\sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^nij\text{gcd}(i,j))\text{mod}p \] 其中\(n\leq 10^{10},5 ...
- Codeforces 954C Matrix Walk (思维)
题目链接:Matrix Walk 题意:设有一个N×M的矩阵,矩阵每个格子都有从1-n×m的一个特定的数,具体数的排列如图所示.假设一个人每次只能在这个矩阵上的四个方向移动一格(上下左右),给出一条移 ...
- 2、Docker镜像和镜像管理
一.镜像介绍 1.定义 一个只读层被称为镜像,一个镜像是永久不会变的. 由于 Docker 使用一个统一文件系统,Docker 进程认为整个文件系统是以读写方式挂载的. 但是所有的变更都发生顶层的可写 ...
- 数位DP模板详解
// pos = 当前处理的位置(一般从高位到低位) // pre = 上一个位的数字(更高的那一位) // status = 要达到的状态,如果为1则可以认为找到了答案,到时候用来返回, // 给计 ...
- JQ_下雪特效
这是一个jQuery下雪特效.特效的代码如下: <style>body{background:black;color:white}</style><script>/ ...
- 容器flappybird游戏——图文操作指引贴
第一步:打开华为云容器引擎产品首页,点击免费体验馆 第二步:进入免费体验馆,点击体验按钮,获得3天免费集群 第三步:创建免费集群完成后,进入产品console页,如图所示: 第四步:如 ...
- 如何使用URLOS进行docker应用开发
使用Docker技术可以帮助企业快速水平扩展服务,从而到达弹性部署业务的能力.在云服务概念兴起之后,Docker的使用场景和范围进一步发展,如今在微服务架构越来越流行的情况下,微服务+Docker的完 ...
