Spring系列13:bean的生命周期
本文内容
- bean的完整的生命周期
- 生命周期回调接口
Aware接口详解
Spring Bean的生命周期
面试热题:请描述下Spring的生命周期?
4大生命周期
从源码角度来说,简单分为4大阶段: 实例化 -> 属性赋值 -> 初始化 -> 销毁
- 实例化 Instantiation
- 属性赋值 Populate
- 初始化 Initialization
- 销毁 Destruction
实例化和属性赋值对应构造方法和 setter 方法的注入,初始化和销毁是用户能自定义扩展的两个阶段。在这四步之间穿插了各种Spring提供的容器扩展点。
看下源码实现 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean ,无关源码已经省略,会保留一定的源码的英文注释。
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 1 实例化阶段
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 2 属性赋值阶段
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 3 初始化阶段
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
return exposedObject;
}
bean销毁阶段源码可以看下 ConfigurableApplicationContext#close(),最终每个bean会调到 DisposableBeanAdapter#destroy() 方法,比较简单。
class DisposableBeanAdapter implements DisposableBean, Runnable, Serializable {
@Override
public void destroy() {
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
try {
// 1 实现DisposableBean 销毁
else {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
}
}
}
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
// 2 自定义销毁方法
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToInvoke = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);
if (methodToInvoke != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(methodToInvoke));
}
}
}
}
生命周期扩展点
Spring 之所以强大的原因是易扩展,生命周期相关的常用扩展点非常多。扩展点分2类:
作用于多个bean的增强扩展
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 作用于实例化阶段前后
- BeanPostProcessor 作用于初始化阶段前后
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 作用于销毁阶段前
作用于单个bean的增强扩展
初始化阶段
3个 Aware 接口: BeanNameAware BeanClassLoaderAware BeanFactoryAware
InitializingBean 接口
自定义的初始化方法
销毁阶段
DisposableBean 接口
自定义的销毁方法
来一张汇总图,直观明了。
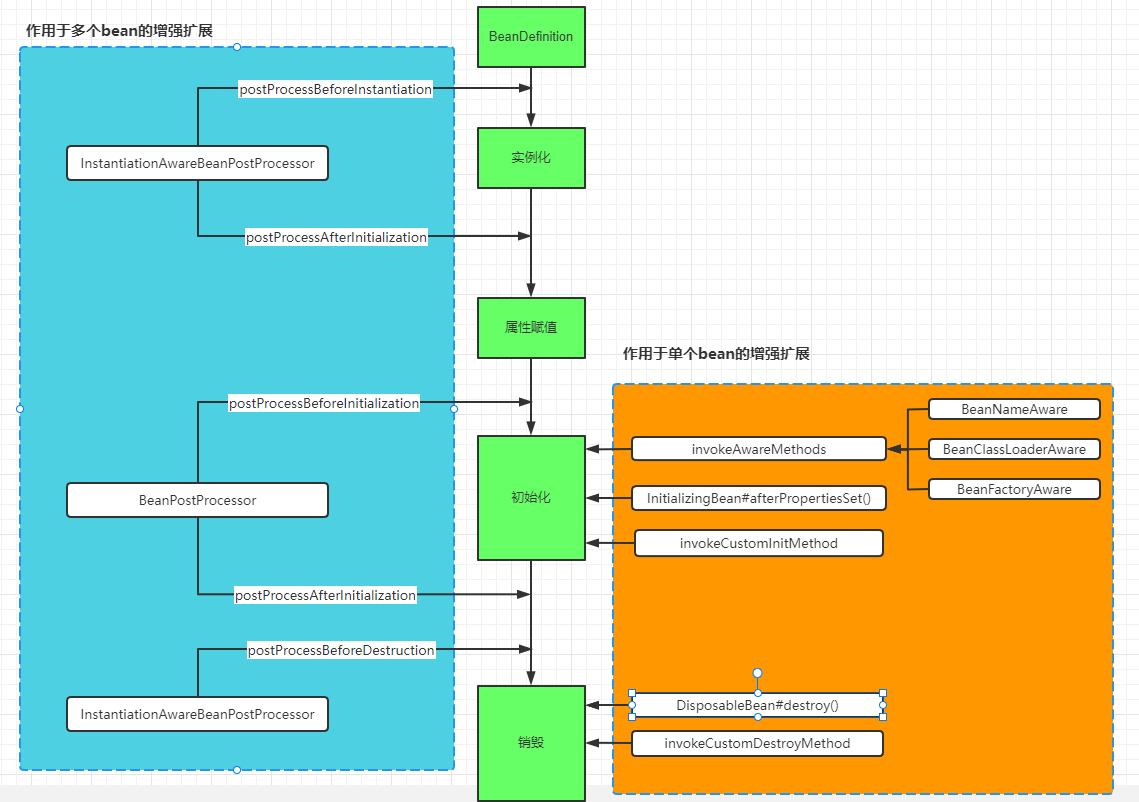
提示:
BeanNameAware BeanClassLoaderAware BeanFactoryAware是在初始化阶段调用对应的接口方法设置的;而其它Aware接口如 EnvironmentAware、EmbeddedValueResolverAware、ApplicationContextAware(ResourceLoaderAware\ApplicationEventPublisherAware\MessageSourceAware)是在初始化前通过 BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization() 来调用对应接口设置的。
后面有机会写Spring源码的时候再深入。
bean生命周期回调
挖个坟纠个错,在Spring系列2:Spring容器基本概念和使用 中我们提到:
非常建议阅读
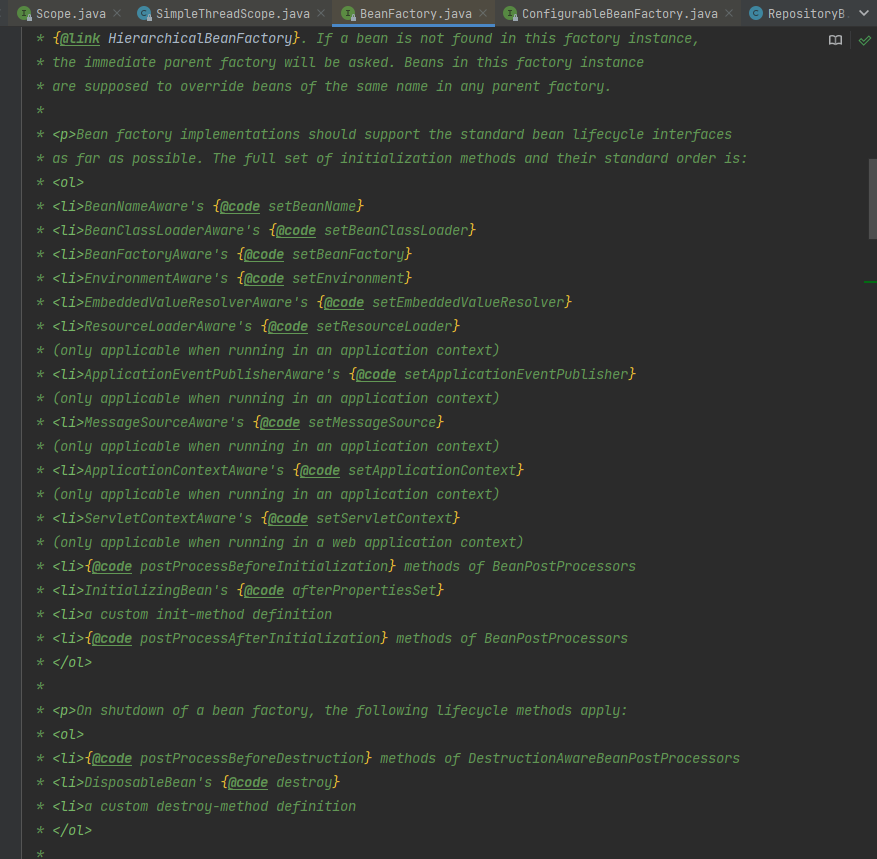
BeanFactory的源码上的注释说明,非常的详尽,常见的面试题:请描述下Spring的生命周期?注释上就有非常官方的完整说明
其实此处表述有误,准确来说如下的源码注释写的是完整的生命周期回调,局限于bean的初始化阶段和销毁阶段。完整bean的生命周期看上一小节的分析。
初始化化阶段完整的调用过程整理如下:
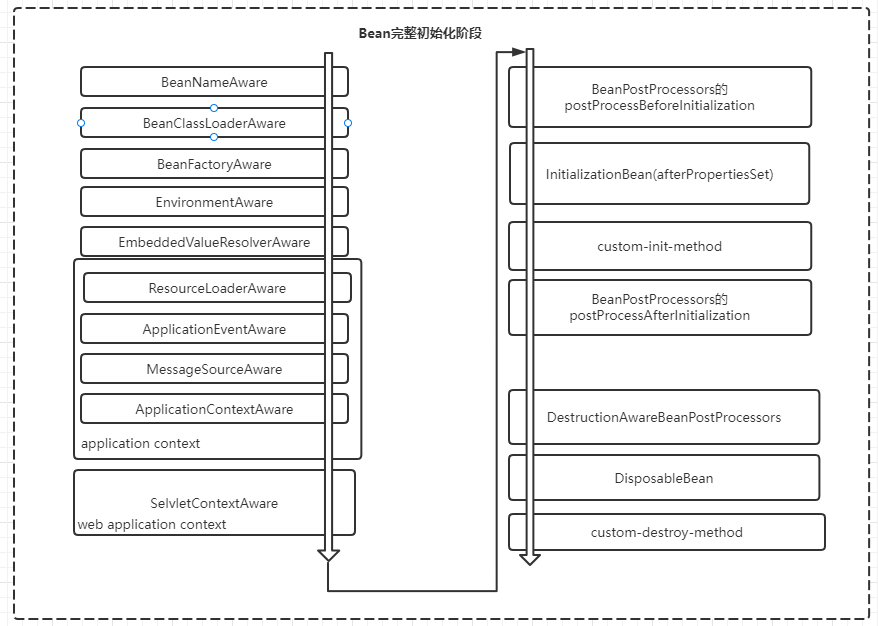
容器对 bean 生命周期的管理提供了生命周期接口,允许开发者对bean的初始化和销毁等生命周期中进行自定义的操作。
bean 初始化回调3种
Spring提供了3种方式进行bean的初始化回调:
InitializingBean 接口
org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean 接口让 bean 在容器设置了 bean 的所有必要属性后执行初始化工作。这种方式有个弊端是类中耦合了Spirng容器。
xml中
<bean/>指定init-method方法<bean class="com.crab.spring.ioc.demo11.BeanOne" id="beanOne" init-method="myInit"/>
使用@PostConstruct注解
既然提供了3种,那么不禁会有疑问:
- 同时使用3种方式,指定3个不同的方法,执行顺序是如何的?
- 同时使用3种方式,指定的是同一个方法,执行次数是多少次,3次?
直接通过案例来验证。
案例1:3种方式3个不同方法
类的定义
public class BeanOne implements InitializingBean {
// 1 实现接口的方式
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("BeanOne InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet");
}
// 通过xml init-method 配置的方式
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("BeanOne init-method myInit");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("BeanOne PostConstruct postConstruct");
}
}
通过xml配置文件的方式定义bean信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描指定包下的bean并自动DI-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean class="com.crab.spring.ioc.demo11.BeanOne" id="beanOne" init-method="myInit"/>
</beans>
运行测试
@org.junit.Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("开始初始化容器");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("demo11/spring.xml");
System.out.println("容器使用中----");
BeanOne beanOne = context.getBean(BeanOne.class);
System.out.println(beanOne);
System.out.println("开始销毁容器");
context.close();
System.out.println("结束销毁容器");
}
测试结果
开始初始化容器
BeanOne PostConstruct postConstruct
BeanOne InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet
BeanOne init-method myInit
容器使用中----
com.crab.spring.ioc.demo11.BeanOne@f0f2775
开始销毁容器
结束销毁容器
结论:@PostConstruct > InitializingBean > xml init-method
案例2:3种方式指定同一个方法
类定义如下
public class BeanTwo implements InitializingBean {
// 1 实现接口的方式
// 2 通过xml init-method 配置的方式
// 3 注解方式
@PostConstruct
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("BeanTwo InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet");
}
}
xml配置文件和测试程序和上面的类似,不重复。
运行结果如下
开始初始化容器
BeanTwo InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet
容器使用中----
com.crab.spring.ioc.demo11.BeanTwo@3f200884
开始销毁容器
结束销毁容器
结论:3种方式指定同一方法,只会回调一次,不会重复调用
思考下: 一个类中配置2个@PostConstruct注解的初始化方法 init1()和 init2() ,回调初始化哪一个?
bean的销毁回调
类似初始化回调,Spring提供了3种方式进行bean的销毁回调:
- 实现 DisposableBean接口
- xml中配置destroy-method
- 使用@PreDestroy
类似执行顺序和次数结论:
- 3种方式指定3个不同方法,回调顺序:@PreDestroy > DisposableBean > xml中配置destroy-method
- 3种方式指定同一个方法,只回调1次
综合案例
定义类
public class BeanThree implements DisposableBean {
// 方式1 实现DisposableBean
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("BeanThree DisposableBean destroy");
}
// 方式2 xml中配置destroy-method
public void destroy2(){
System.out.println("BeanThree destroy-method destroy3");
}
// 方式3 使用 @PreDestroy 注解
@PreDestroy
public void destroy3(){
System.out.println("BeanThree @PreDestroy destroy3");
}
}
xml中配置销毁回调
<!--扫描指定包下的bean并自动DI-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean class="com.crab.spring.ioc.demo11.BeanThree" destroy-method="destroy2"/>
测试程序和结果
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() {
System.out.println("开始初始化容器");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("demo11/spring3.xml");
System.out.println("容器使用中----");
BeanThree beanOne = context.getBean(BeanThree.class);
System.out.println(beanOne);
System.out.println("开始销毁容器");
context.close();
System.out.println("结束销毁容器");
}
// 结果对照结论看
开始初始化容器
容器使用中----
com.crab.spring.ioc.demo11.BeanThree@f0f2775
开始销毁容器
BeanThree @PreDestroy destroy3
BeanThree DisposableBean destroy
BeanThree destroy-method destroy3
结束销毁容器
思考下:xml配置中如何配置全局默认的初始化和销毁回调方法,而不用每个bean都配置?default-init-method default-destroy-method
Aware接口详解
原理解析
Aware 是一个标记超接口,Spring 提供了广泛的 Aware 回调接口实现,让 bean 向容器获取它们需要特定的基础设施依赖项。
public interface Aware {}
来看一下``ApplicationContextAware 接口
public interface ApplicationContextAware {
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
当 ApplicationContext 创建一个实现 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware 接口的对象实例时,会为该实例提供对该 ApplicationContext 的引用。直接上案例。
定义一个类实现 ApplicationContextAware
public class BeanFour implements ApplicationContextAware {
// 用于获取初始该类对象的容器对象ApplicationContext
private ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.context = applicationContext;
}
public ApplicationContext getContext() {
return context;
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class AppConfig {
}
测试程序和结果
@org.junit.Test
public void test_aware() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
BeanFour bean = context.getBean(BeanFour.class);
System.out.println(bean.getContext() == context);
context.close();
}
// 结果
true
从结果看,BeanFour实例已获取到创建它的容器对象。
使用 Aware 接口主要目的是获取容器中相关的基础对象,也就是依赖注入,但这样做的弊端是将应用程序类和Spring强耦合在一起了。换个角度,依赖注入通过 @Autowired 也可以实现,耦合更低。
@Component
public class BeanFour2 {
// 用于获取初始该类对象的容器对象ApplicationContext
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext context;
public ApplicationContext getContext() {
return context;
}
}
Aware 接口汇总
Spring 提供了广泛的 Aware 回调接口,让 bean 向容器指示它们需要特定的基础设施依赖项,如下表。作为一般规则,名称表示依赖类型。
| 接口名 |
|---|
ApplicationContextAware |
ApplicationEventPublisherAware |
BeanClassLoaderAware |
BeanFactoryAware |
BeanNameAware |
LoadTimeWeaverAware |
MessageSourceAware |
NotificationPublisherAware |
ResourceLoaderAware |
总结
本文介绍各种bean的完整的生命周期、生命周期回调接口和Aware接口。
知识分享,转载请注明出处。学无先后,达者为先!
Spring系列13:bean的生命周期的更多相关文章
- (转)Spring管理的Bean的生命周期
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52834011 bean的初始化时机 前面讲解了Spring容器管理的bean的作用域.接着我们 ...
- Spring 容器中 Bean 的生命周期
Spring 容器中 Bean 的生命周期 1. init-method 和 destory-method 方法 Spring 初始化 bean 或销毁 bean 时,有时需要作一些处理工作,因此 s ...
- (spring-第1回【IoC基础篇】)Spring容器中Bean的生命周期
日出日落,春去秋来,花随流水,北雁南飞,世间万物皆有生死轮回.从调用XML中的Bean配置信息,到应用到具体实例中,再到销毁,Bean也有属于它的生命周期. 人类大脑对图像的认知能力永远高于文字,因此 ...
- Spring 学习笔记---Bean的生命周期
生命周期图解 由于Bean的生命周期经历的阶段比较多,我们将通过一个图形化的方式进行描述.下图描述了BeanFactory中Bean生命周期的完整过程: Bean 的生命周期从Spring容器着手实例 ...
- IoC基础篇(一)--- Spring容器中Bean的生命周期
日出日落,春去秋来,花随流水,北雁南飞,世间万物皆有生死轮回.从调用XML中的Bean配置信息,到应用到具体实例中,再到销毁,Bean也有属于它的生命周期. 人类大脑对图像的认知能力永远高于文字,因此 ...
- Spring容器中bean的生命周期以及关注spring bean对象的后置处理器:BeanPostProcessor(一个接口)
Spring IOC 容器对 Bean 的生命周期进行管理的过程: 1.通过构造器或工厂方法创建 Bean 实例 2.为 Bean 的属性设置值和对其他 Bean 的引用 3.将 Bean 实例传递给 ...
- Spring实战(二)Spring容器和bean的生命周期
引入问题: 在XML配置文件中配置bean后,这些文件又是如何被加载的?它们被加载到哪里去了? Spring容器——框架核心 1.什么是Spring容器?它的功能是什么? 在基于Spring的应用中, ...
- Spring基础14——Bean的生命周期
1.IOC容器中的Bean的生命周期方法 SpringIOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,Spring允许在Bean生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务.SpringIOC容器对Bean的生命周期进行管理 ...
- spring(二):bean的生命周期
bean的生命周期指的是bean的创建——>初始化——>销毁的过程,该过程是由spring容器进行管理的 我们可以自定义bean初始化和销毁的方法:容器在bean进行到当前生命周期时,调用 ...
- spring框架中Bean的生命周期
一.Bean 的完整生命周期 在传统的Java应用中,bean的生命周期很简单,使用Java关键字 new 进行Bean 的实例化,然后该Bean 就能够使用了.一旦bean不再被使用,则由Java自 ...
随机推荐
- CS5265替代CH7211|Capstone CS5265芯片|替代CH7211芯片
龙迅Chrontel的CH7211是一款Type-C转HDMI2.0半导体设备,可通过USB Type-C连接器将DisplayPort信号转换为HDMI/DVI.这款创新的基于USB Type-C的 ...
- 【jvm】04-我偷偷改了你编译后的class文件
[jvm]04-我偷偷改了你编译后的class文件 欢迎关注b站账号/公众号[六边形战士夏宁],一个要把各项指标拉满的男人.该文章已在github目录收录. 屏幕前的大帅比和大漂亮如果有帮助到你的话请 ...
- 【jvm】09-full gc分析思路
[jvm]09-full gc分析思路 欢迎关注b站账号/公众号[六边形战士夏宁],一个要把各项指标拉满的男人.该文章已在github目录收录. 屏幕前的大帅比和大漂亮如果有帮助到你的话请顺手点个赞. ...
- Android程序设计基础作业目录 (作业笔记)
Android程序设计基础 • [目录] 第1章 Android程序入门 >>> 1.2.4 安装并配置 Android Studio 开发工具和 Genymotion 模拟器. 1 ...
- Eclipse导包
导包快捷键:"Ctrl+Shift+M",但是一般不用,一般利用整理包的快捷键. 整理包的快捷键:"Ctrl+Shift+O",与导包的区别在于,有用的留着,没 ...
- MYSQL实现上一条下一条功能
select id from(select *, (@i:=@i+1) as rownum from pre_bet_zhibo,(select @i:=0) as itwhere link_cone ...
- 解压安装Cacti在apache中的补充
如果你不是安装 Cacti 到 Apache 默认的网络目录文件夹位置,那么在 /etc/httpd/conf.d 中新增配置文件 cacti.conf,并且按如下内容编辑.设置 /your/cact ...
- Nginx 基础入门
目录 Nginx 基础入门 1.Nginx简介 1.1.相关名词解释 2.Nginx优势 3.Nginx部署 4.Nginx配置文件 5.Nginx模块 6.Nginx配置文件 6.1.Locatio ...
- jQuery里的mouseover与mouseenter事件类型区别
JQ里面有mouseover和mouseenter 2个事件类型干着差不多的活,用不好经常出现些小问题. 今天我解释一下原理: 事件类型翻译: mouseover 鼠标移上 mouseenter 鼠 ...
- Matlab R2019b安装中的问题
1.licens文件以及dll文件的放置 MATLAB的安装镜像文件放置在D:\MATLAB,我们MATLAB安装在D:\MATLAB2019B,在激活过程中,我们需要破解文件夹中的license_s ...
