JUnit5编写基本测试
JUnit5的测试不是通过名称,而是通过注解来标识的。
测试类与方法
Test Class:测试类,必须包含至少一个test方法,包括:
- 最外层的class
staticmember class@Nestedclass
Test Method:测试方法,包括:
@Test@RepeatedTest@ParameterizedTest@TestFactory@TestTemplate
Lifecycle Method:生命周期方法,包括:
@BeforeAll@AfterAll@BeforeEach@AfterEach
注意:
- Test Method和Lifecycle Method不能是
abstract,也不能return。它们可以在当前测试类中声明,也可以继承自父类或接口。 - Test class、Test Method和Lifecycle Method都不能是private。
示例代码:
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.fail;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumeTrue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class StandardTests {
@BeforeAll
static void initAll() {
}
@BeforeEach
void init() {
}
@Test
void succeedingTest() {
}
@Test
void failingTest() {
fail("a failing test");
}
@Test
@Disabled("for demonstration purposes")
void skippedTest() {
// not executed
}
@Test
void abortedTest() {
assumeTrue("abc".contains("Z"));
fail("test should have been aborted");
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
}
@AfterAll
static void tearDownAll() {
}
}
自定义显示名字
Test class和test method可以使用@DisplayName自定义在测试报告中的显示名字,支持空格、特殊字符和emoji表情符号。
示例:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@DisplayName("A special test case")
class DisplayNameDemo {
@Test
@DisplayName("Custom test name containing spaces")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpaces() {
}
@Test
@DisplayName("╯°□°)╯")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpecialCharacters() {
}
@Test
@DisplayName("")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingEmoji() {
}
}
除了@DisplayName,@DisplayNameGeneration 注解能用来对显示名字做统一处理,JUnit Jupiter自带了一些生成器:
- Standard 匹配标准行为
- Simple 删除没有参数的方法后面的括号
- ReplaceUnderscores 用空格替换下划线
- IndicativeSentences 把test class和test method名字连接起来
示例代码:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayNameGeneration;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayNameGenerator;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.IndicativeSentencesGeneration;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Nested;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ValueSource;
class DisplayNameGeneratorDemo {
@Nested
@DisplayNameGeneration(DisplayNameGenerator.ReplaceUnderscores.class)
class A_year_is_not_supported {
@Test
void if_it_is_zero() {
}
@DisplayName("A negative value for year is not supported by the leap year computation.")
@ParameterizedTest(name = "For example, year {0} is not supported.")
@ValueSource(ints = { -1, -4 })
void if_it_is_negative(int year) {
}
}
@Nested
@IndicativeSentencesGeneration(separator = " -> ", generator = DisplayNameGenerator.ReplaceUnderscores.class)
class A_year_is_a_leap_year {
@Test
void if_it_is_divisible_by_4_but_not_by_100() {
}
@ParameterizedTest(name = "Year {0} is a leap year.")
@ValueSource(ints = { 2016, 2020, 2048 })
void if_it_is_one_of_the_following_years(int year) {
}
}
}
@IndicativeSentencesGeneration可以自定义separator和generator。
结果:
+-- DisplayNameGeneratorDemo [OK]
+-- A year is not supported [OK]
| +-- A negative value for year is not supported by the leap year computation. [OK]
| | +-- For example, year -1 is not supported. [OK]
| | '-- For example, year -4 is not supported. [OK]
| '-- if it is zero() [OK]
'-- A year is a leap year [OK]
+-- A year is a leap year -> if it is divisible by 4 but not by 100. [OK]
'-- A year is a leap year -> if it is one of the following years. [OK]
+-- Year 2016 is a leap year. [OK]
+-- Year 2020 is a leap year. [OK]
'-- Year 2048 is a leap year. [OK]
除了注解,也能通过配置设定全局的默认Generator,比如在 src/test/resources/junit-platform.properties文件中:
junit.jupiter.displayname.generator.default = \
org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayNameGenerator$ReplaceUnderscores
既可以指定现有Generator,也可以指定实现了DisplayNameGenerator接口的类。
自定义显示名字的优先级是:
@DisplayName@DisplayNameGenerationjunit.jupiter.displayname.generator.defaultorg.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayNameGenerator.Standard
断言(Assertions)
JUnit5的断言是包含在org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions中的静态方法,比如assertTrue、assertEquals、assertNotNull、assertAll、assertThrows、assertTimeout、assertTimeoutPreemptively等。
示例代码如下:
import static java.time.Duration.ofMillis;
import static java.time.Duration.ofMinutes;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNotNull;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTimeout;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTimeoutPreemptively;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import example.domain.Person;
import example.util.Calculator;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class AssertionsDemo {
private final Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
private final Person person = new Person("Jane", "Doe");
@Test
void standardAssertions() {
assertEquals(2, calculator.add(1, 1));
assertEquals(4, calculator.multiply(2, 2),
"The optional failure message is now the last parameter");
assertTrue('a' < 'b', () -> "Assertion messages can be lazily evaluated -- "
+ "to avoid constructing complex messages unnecessarily.");
}
@Test
void groupedAssertions() {
// In a grouped assertion all assertions are executed, and all
// failures will be reported together.
assertAll("person",
() -> assertEquals("Jane", person.getFirstName()),
() -> assertEquals("Doe", person.getLastName())
);
}
@Test
void dependentAssertions() {
// Within a code block, if an assertion fails the
// subsequent code in the same block will be skipped.
assertAll("properties",
() -> {
String firstName = person.getFirstName();
assertNotNull(firstName);
// Executed only if the previous assertion is valid.
assertAll("first name",
() -> assertTrue(firstName.startsWith("J")),
() -> assertTrue(firstName.endsWith("e"))
);
},
() -> {
// Grouped assertion, so processed independently
// of results of first name assertions.
String lastName = person.getLastName();
assertNotNull(lastName);
// Executed only if the previous assertion is valid.
assertAll("last name",
() -> assertTrue(lastName.startsWith("D")),
() -> assertTrue(lastName.endsWith("e"))
);
}
);
}
@Test
void exceptionTesting() {
Exception exception = assertThrows(ArithmeticException.class, () ->
calculator.divide(1, 0));
assertEquals("/ by zero", exception.getMessage());
}
@Test
void timeoutNotExceeded() {
// The following assertion succeeds.
assertTimeout(ofMinutes(2), () -> {
// Perform task that takes less than 2 minutes.
});
}
@Test
void timeoutNotExceededWithResult() {
// The following assertion succeeds, and returns the supplied object.
String actualResult = assertTimeout(ofMinutes(2), () -> {
return "a result";
});
assertEquals("a result", actualResult);
}
@Test
void timeoutNotExceededWithMethod() {
// The following assertion invokes a method reference and returns an object.
String actualGreeting = assertTimeout(ofMinutes(2), AssertionsDemo::greeting);
assertEquals("Hello, World!", actualGreeting);
}
@Test
void timeoutExceeded() {
// The following assertion fails with an error message similar to:
// execution exceeded timeout of 10 ms by 91 ms
assertTimeout(ofMillis(10), () -> {
// Simulate task that takes more than 10 ms.
Thread.sleep(100);
});
}
@Test
void timeoutExceededWithPreemptiveTermination() {
// The following assertion fails with an error message similar to:
// execution timed out after 10 ms
assertTimeoutPreemptively(ofMillis(10), () -> {
// Simulate task that takes more than 10 ms.
new CountDownLatch(1).await();
});
}
private static String greeting() {
return "Hello, World!";
}
}
假设(Assumptions)
JUnit5的断言是包含在org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions中的静态方法,比如assumeTrue、assumingThat等。
示例代码:
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumeTrue;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumingThat;
import example.util.Calculator;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class AssumptionsDemo {
private final Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
@Test
void testOnlyOnCiServer() {
assumeTrue("CI".equals(System.getenv("ENV")));
// remainder of test
}
@Test
void testOnlyOnDeveloperWorkstation() {
assumeTrue("DEV".equals(System.getenv("ENV")),
() -> "Aborting test: not on developer workstation");
// remainder of test
}
@Test
void testInAllEnvironments() {
assumingThat("CI".equals(System.getenv("ENV")),
() -> {
// perform these assertions only on the CI server
assertEquals(2, calculator.divide(4, 2));
});
// perform these assertions in all environments
assertEquals(42, calculator.multiply(6, 7));
}
}
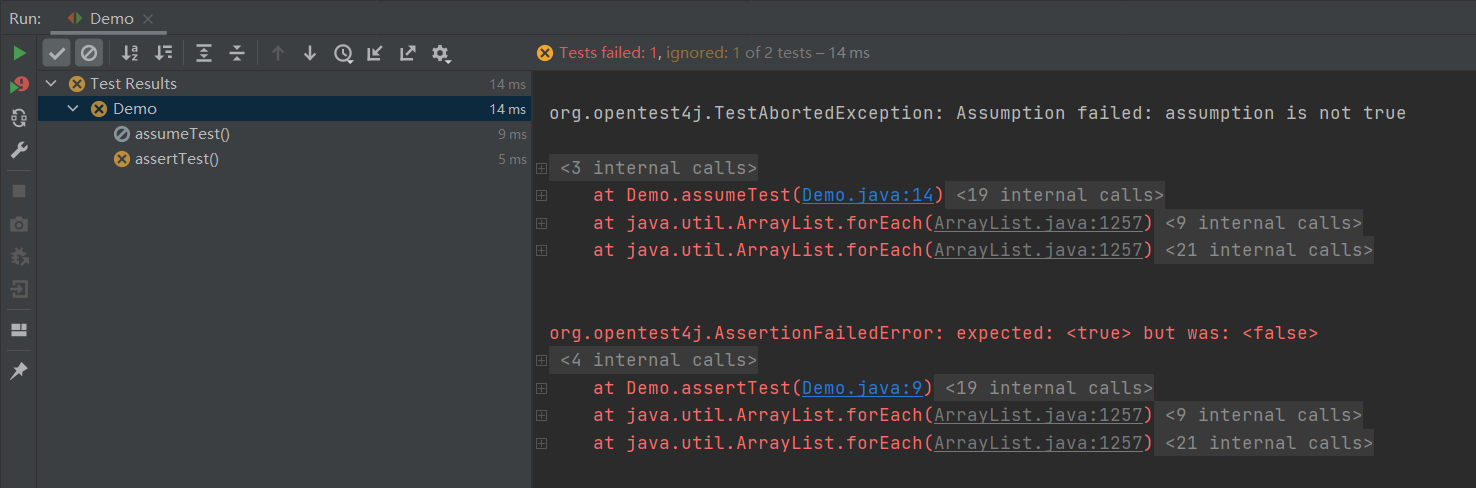
Assertions与Assumptions区别
Assertions如果失败,test会被标记为failed。Assumptions如果失败,test会被标记为ignored,测试不会执行。
示例:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumeTrue;
public class Demo {
@Test
void assertTest() {
assertTrue(false);
}
@Test
void assumeTest() {
assumeTrue(false);
}
}
结果:
禁用测试
@Disabled能用来禁用test class或test method,建议在括号内填写上禁用理由。
示例:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@Disabled("Disabled until bug #99 has been fixed")
class DisabledClassDemo {
@Test
void testWillBeSkipped() {
}
}
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class DisabledTestsDemo {
@Disabled("Disabled until bug #42 has been resolved")
@Test
void testWillBeSkipped() {
}
@Test
void testWillBeExecuted() {
}
}
小结
本文首先介绍了如何使用测试类与方法,来编写一个JUnit5的基本测试,然后介绍了如何自定义测试报告中的显示名字。使用断言(Assertions)可以把test标记为failed,使用假设(Assumptions)可以把test标记为ignored。最后介绍了如何禁用测试。除了基本测试,JUnit5还能编写带条件的测试。
参考资料:
https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#writing-tests
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44628483/assume-vs-assert-in-junit-tests
JUnit5编写基本测试的更多相关文章
- 新书《编写可测试的JavaScript代码 》出版,感谢支持
本书介绍 JavaScript专业开发人员必须具备的一个技能是能够编写可测试的代码.不管是创建新应用程序,还是重写遗留代码,本书都将向你展示如何为客户端和服务器编写和维护可测试的JavaScript代 ...
- 编写可测试的JavaScript代码
<编写可测试的JavaScript代码>基本信息作者: [美] Mark Ethan Trostler 托斯勒 著 译者: 徐涛出版社:人民邮电出版社ISBN:9787115373373上 ...
- 使用FsCheck编写Property-based测试
使用FsCheck编写Property-based的测试 在编写基于Property-based的单元测试一文中,我们介绍了什么是Property-based测试.同时我们也总结了Property-b ...
- 编写Avocado测试
编写Avocado测试 现在我们开始使用python编写Avocado测试,测试继承于avocado.Test. 基本例子 创建一个时间测试,sleeptest,测试非常简单,只是sleep一会: i ...
- springboot快速入门02--Controller编写和测试
02springboot快速入门--Controller编写和测试 1.新建一个HelloController import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplic ...
- Shell脚本的编写及测试
Shell脚本的编写及测试 1.1问题 本例要求两个简单的Shell脚本程序,任务目标如下: 编写一 ...
- 098 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 03 综合案例(学生信息管理) 02 案例分析及实现 02 编写并测试Subject类
098 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 03 综合案例(学生信息管理) 02 案例分析及实现 02 编写并测试Subject类 本文知识点:编写并测试Subject类 说明: ...
- 099 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 03 综合案例(学生信息管理) 02 案例分析及实现 03 编写并测试Student类
099 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 03 综合案例(学生信息管理) 02 案例分析及实现 03 编写并测试Student类 本文知识点:编写并测试Subject类 说明: ...
- JUnit5的条件测试、嵌套测试、重复测试
条件测试 JUnit5支持条件注解,根据布尔值判断是否执行测试. 自定义条件 @EnabledIf和@DisabledIf注解用来设置自定义条件,示例: @Test @EnabledIf(" ...
随机推荐
- KVM性能优化
一.KVM为什么要调优 性能的损耗是关键.KVM采用全虚拟化技术,全虚拟化要由一个软件来模拟硬件,故有一定的损耗,特别是I/O,因此需要优化.KVM性能优化主要在CPU.内存.I/O这几方面.当然对于 ...
- LTP--linux稳定性测试 linux性能测试 ltp压力测试 ltp-pan
LTP--linux稳定性测试 linux性能测试 ltp压力测试 zhangzj1030关注14人评论33710人阅读2011-12-09 12:07:45 说明:在写这篇文章之前,本人也不曾了 ...
- 8.12-14 df 、mkswap、swapon、swapoff、sync
8.12 df:报告文件系统磁盘空间的使用情况 -a 显示所有文件系统 -h 以容易理解的格式显示磁盘的使用情况端 -i 显示文件系统的inode信息迷 -t 显示指定类型 ...
- svg 飞线,源码
<html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" ...
- jQuery的链式编程风格
jQuery的链式编程风格 首先本人通过一个案例来展示jQuery的链式编程风格.先写一个页面,展示一个列表,代码如下: <body> <div> <ul class=& ...
- 微服务架构(Microservices) ——Martin Flower
不知不觉到达了Sring Boot的学习中了,在学习之前,了解微服务架构是很有必要的,对于自己提升今后面试的软实力有很大帮助,在此写下. 让我们接下来看下Martin Flower 如何解释微服务架构 ...
- Task类学习教程—组合任务ContinueWith
Task类学习教程-组合任务.ContinueWith 一.简介 通过任务,可以指定在任务完成之后,应开始运行之后另一个特定任务.ContinueWith是Task根据其自身状况,决定后续应该作何操作 ...
- Python脚本语言写法
Python脚本语言写法 脚本语言的开始行,是指文件中的代码用什么可执行程序去运行它,就这么简单. #!/usr/bin/python是告诉操作系统执行这个脚本的时候,调用/usr/bin下的pyth ...
- 编译原理-翻译程序(Translator)
分为编译程序(compiler)和解释程序(interpreter) 编译程序:把源程序(高级语言编写)转换成目标程序(汇编语言或机器语言编写). 解释程序:对源程序边翻译边执行. 编译型语言 优点: ...
- jmeter--JSON Extractor 用法
JMeter处理大部分请求返回的结果,都是json.对于请求返回的结果,处理以后作为其他请求的参数,有一个方便使用的插件:JSON Extractor JSON Extractor中文叫做json提取 ...
