Django rest framework 限制访问频率(源码分析)
基于 http://www.cnblogs.com/ctztake/p/8419059.html
当用发出请求时 首先执行dispatch函数,当执行当第二部时:
#2.处理版本信息 处理认证信息 处理权限信息 对用户的访问频率进行限制
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
进入到initial方法:
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
#2.1处理版本信息
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
#2.2处理认证信息
self.perform_authentication(request)
#2.3处理权限信息
self.check_permissions(request)
#2.4对用户的访问频率进行限制
self.check_throttles(request)
#2.4对用户的访问频率进行限制
self.check_throttles(request)
下面 开始 限流的具体分析:
一、执行check_throttles方法
def check_throttles(self, request):
"""
Check if request should be throttled.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is throttled.
"""
#遍历throttle对象列表
for throttle in self.get_throttles():
#根据allow_request()的返回值进行下一步操作,返回True的话不执行下面代码,标识不限流,返回False的话执行下面代码,还可以抛出异常
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
#返回False的话执行
self.throttled(request, throttle.wait())
二、执行allow_request方法
首先找到BaseThrottle类,有好多类继承了该类,并且都有allow_request方法,至于执行那个类中的allow_request方法,取决于我们自定义的Throttle这个类继承谁
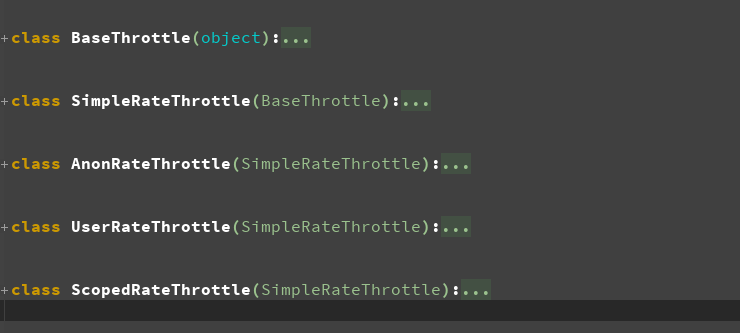
class BaseThrottle(object):
"""
Rate throttling of requests.
""" def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if the request should be allowed, `False` otherwise.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.allow_request() must be overridden')
#获取唯一标识,匿名用户用ip地址,认证用户用自己的user信息
def get_ident(self, request):
"""
Identify the machine making the request by parsing HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR
if present and number of proxies is > 0. If not use all of
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR if it is available, if not use REMOTE_ADDR.
"""
xff = request.META.get('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR')
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
num_proxies = api_settings.NUM_PROXIES if num_proxies is not None:
if num_proxies == 0 or xff is None:
return remote_addr
addrs = xff.split(',')
client_addr = addrs[-min(num_proxies, len(addrs))]
return client_addr.strip() return ''.join(xff.split()) if xff else remote_addr def wait(self):
"""
Optionally, return a recommended number of seconds to wait before
the next request.
"""
return None
三、具体分析以具有代表性的SimpleRateThrottle类分析
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
"""
A simple cache implementation, that only requires `.get_cache_key()`
to be overridden. The rate (requests / seconds) is set by a `throttle` attribute on the View
class. The attribute is a string of the form 'number_of_requests/period'. Period should be one of: ('s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day') Previous request information used for throttling is stored in the cache.
"""
cache = default_cache
timer = time.time
cache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'
scope = None
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES def __init__(self):
#判断是否有rate,实际上rate就是我们定义的scope的值
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
#没有调用get_rate()获取
self.rate = self.get_rate()
#num_requests代表具体的次数 duration代表具体的时间单位
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate) def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
"""
Should return a unique cache-key which can be used for throttling.
Must be overridden. May return `None` if the request should not be throttled.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden') def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
#判断当前类中我们定义的scope是否有值,没有则抛出异常,告诉我们必须设置scope
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None):
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg) try:
#有的话直接返回scope对应的值
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope]
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg) def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
#rate实际就是我们自定义的scope的值 如10/m(代表10次每分钟)
#按'/'切分num代表次数,period代表时间
num, period = rate.split('/')
#多少次
num_requests = int(num)
#获取具体的时间单位
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration) def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled. On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
#如果没有rate也就是scope没有值
#如果没有则表示不限流,
if self.rate is None:
return True #get_cache_key必须自己重写,如果没有则表示不限流
#key一般是唯一标示如用户名密码 或者登陆者的ip地址
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True
#获取当前key所对应的时间列表,也就是用户每一次访问的时间都放到该列表中
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
#当前时间
self.now = self.timer() # Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
#当时间列表存在,并且当前时间已经超出了规定的时间
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
#把最开始加进去的时间删除
self.history.pop()
#如果列表中的时间数大于规定执行的次数
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
#则return False
return self.throttle_failure()
#return True
return self.throttle_success() def throttle_success(self):
"""
Inserts the current request's timestamp along with the key
into the cache.
"""
self.history.insert(0, self.now)
self.cache.set(self.key, self.history, self.duration)
return True def throttle_failure(self):
"""
Called when a request to the API has failed due to throttling.
"""
return False def wait(self):
"""
Returns the recommended next request time in seconds.
"""
if self.history:
#计算等待时间(也就是等待多久可以才可以访问下一次)
remaining_duration = self.duration - (self.now - self.history[-1])
else:
remaining_duration = self.duration #在规定的时间内还可以访问多少次
available_requests = self.num_requests - len(self.history) + 1
if available_requests <= 0:
return None return remaining_duration / float(available_requests)
四、回到第一步,执行allow_request方法
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled. On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
#如果没有rate也就是scope没有值
#如果没有则表示不限流,
if self.rate is None:
return True #get_cache_key必须自己重写,如果没有则表示不限流
#key一般是唯一标示如用户名密码 或者登陆者的ip地址
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True
#获取当前key所对应的时间列表,也就是用户每一次访问的时间都放到该列表中
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
#当前时间
self.now = self.timer() # Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
#当时间列表存在,并且当前时间已经超出了规定的时间
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
#把最开始加进去的时间删除
self.history.pop()
#如果列表中的时间数大于规定执行的次数
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
#则return False
return self.throttle_failure()
#return True
return self.throttle_success()
根据allow_request方法的返回值确定具体执行,返回False的话执行
#根据allow_request()的返回值进行下一步操作,返回True的话不执行下面代码,标识不限流,返回False的话执行下面代码,还可以抛出异常
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
#返回False的话执行
self.throttled(request, throttle.wait())
def throttled(self, request, wait):
"""
If request is throttled, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
class Throttled(APIException):
status_code = status.HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS
default_detail = _('Request was throttled.')
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = 'throttled' def __init__(self, wait=None, detail=None, code=None):
if detail is None:
detail = force_text(self.default_detail)
if wait is not None:
wait = math.ceil(wait)
detail = ' '.join((
detail,
force_text(ungettext(self.extra_detail_singular.format(wait=wait),
self.extra_detail_plural.format(wait=wait),
wait))))
self.wait = wait
super(Throttled, self).__init__(detail, code)
例子:继承BaseThrottle
url(r'^limit/', app03_views.Limitview.as_view()),
import time from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
from rest_framework import exceptions
# Create your views here. AllOW={} class MyThrottle(BaseThrottle):
'''
要求每分钟只能访问十次
'''
ip = '1.1.1.1'
def allow_request(self, request, view): ctime=time.time()
ip=self.ip
if ip not in AllOW:
AllOW[ip]=[ctime,]
else:
time_list=AllOW[ip]
while True:
if ctime-60>time_list[-1]:
time_list.pop()
else :
break
if len(AllOW[ip])>10:
return False
AllOW[ip].insert(0,ctime)
return True def wait(self):
ip=self.ip
ctime=time.time()
first_in_time=AllOW[ip][-1]
wt=60-(ctime-first_in_time)
return wt class Limitview(APIView):
throttle_classes=[MyThrottle,]
def get(self,reques):
self.dispatch()
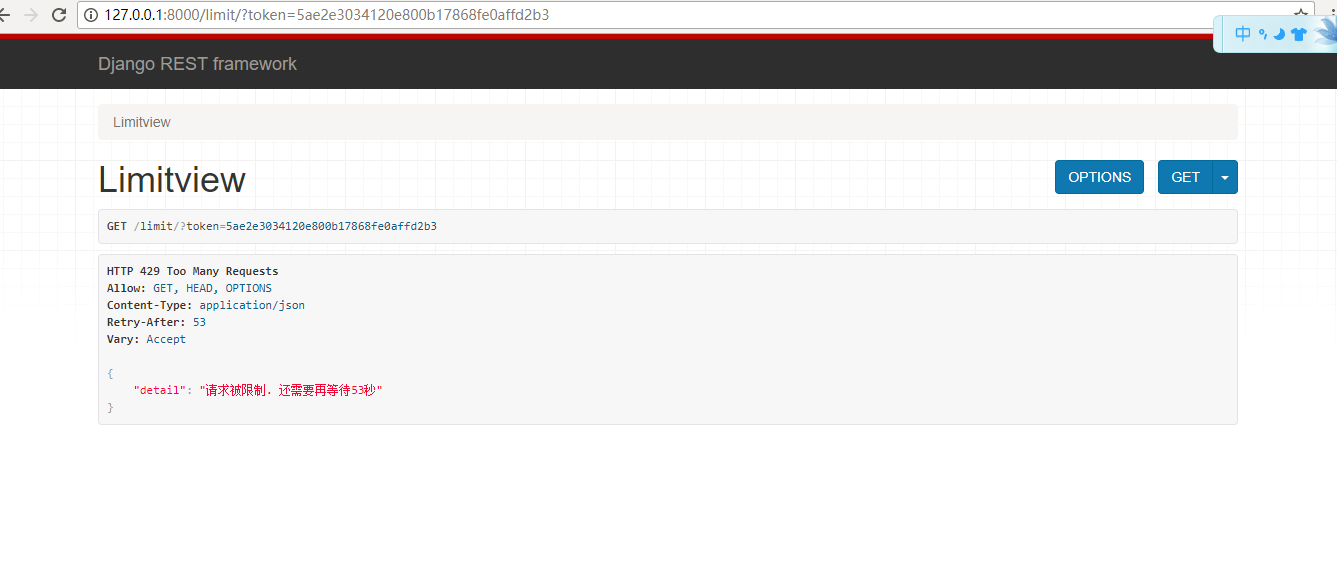
return Response('欢迎访问') def throttled(self,request,wait):
class InnerThrottled(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制.'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = '还需要再等待{wait}秒' raise InnerThrottled(wait)
Views
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": [
# "app01.utils.MyAuthentication",
"app02.utils.MyAuthentication",
],
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":[
"app02.utils.MyPermission",
"app02.utils.AdminPermission",
],
}
settings
seetings中没有配置跟Throttle有的的信息
继承SimpleRateThrottle
url(r'^limit/', app03_views.Limitview.as_view()),
urls
import time from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle
from rest_framework import exceptions
# Create your views here. AllOW={} class MyThrottle(BaseThrottle):
'''
要求每分钟只能访问十次
'''
ip = '1.1.1.1'
def allow_request(self, request, view): ctime=time.time()
ip=self.ip
if ip not in AllOW:
AllOW[ip]=[ctime,]
else:
time_list=AllOW[ip]
while True:
if ctime-60>time_list[-1]:
time_list.pop()
else :
break
if len(AllOW[ip])>10:
return False
AllOW[ip].insert(0,ctime)
return True def wait(self):
ip=self.ip
ctime=time.time()
first_in_time=AllOW[ip][-1]
wt=60-(ctime-first_in_time)
return wt class MySimpleRateThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
#必须要写因为SimpleRateThrottle中要求了必须写
'''
def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
#判断当前类中我们定义的scope是否有值,没有则抛出异常,告诉我们必须设置scope
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None):
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
'''
scope = 'tiga' #也必须必须要写
'''
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
"""
Should return a unique cache-key which can be used for throttling.
Must be overridden. May return `None` if the request should not be throttled.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden')
'''
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request) class Limitview(APIView):
throttle_classes=[MySimpleRateThrottle,]
def get(self,reques):
return Response('欢迎访问') def throttled(self,request,wait):
class InnerThrottled(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制.'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = '还需要再等待{wait}秒' raise InnerThrottled(wait)
Views
from django.db import models # Create your models here.
class Userinfo(models.Model):
name=models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name='用户名')
pwd=models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name='密码')
token=models.CharField(max_length=64,null=True) def __str__(self):
return self.name
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": [
# "app01.utils.MyAuthentication",
"app02.utils.MyAuthentication",
],
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":[
"app02.utils.MyPermission",
"app02.utils.AdminPermission",
],
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES":{
'tiga':'10/m',
}
}
settings
认证,权限,限流综合联系
url(r'^index/', app04_views.IndexView.as_view()),
url(r'^user/', app04_views.UserView.as_view()),
url(r'^manage/', app04_views.ManageView.as_view()),
urls
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle
from rest_framework import exceptions from app01 import models # Create your views here.
class MyAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token=request.query_params.get('token')
user=models.Userinfo.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if user:
return (user.name,user)
return None class UserPermission(BasePermission):
message='登录用户才可以访问'
def has_permission(self, request, view):
if request.user:
return True
return False
class AdminPermission(BasePermission):
message='管理员才能访问'
def has_permission(self, request, view):
if request.user =='ctz':
return True
return False class AnnoThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'anno'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
#如果是匿名用户则执行
if not request.user:
return self.get_ident(request)
#如果不是匿名用户则让他执行
return None class UserThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'user' def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
#当前用户登陆了,并且当前用户不是管理员
if request.user and request.user!='ctz':
return self.get_ident(request)
#如果是匿名用户和管理员 则让他继续执行
return None class AdminThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'admin' def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
#如果是管理员
if request.user=='ctz':
return self.get_ident(request)
#不是管理员
return None class IndexView(APIView):
'''
要求,所有用户都能访问,匿名用户5/m,普通用户10/m,管理员不限
'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = []
throttle_classes = [AnnoThrottle,UserThrottle,AdminThrottle]
def get(self,request):
return Response('首页') def throttled(self, request, wait):
class UserInnerThrottled(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制.'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = '还需要再等待{wait}秒'
raise UserInnerThrottled(wait) class UserView(APIView):
'''
要求:登录用户能访问,普通用户10/m,管理员20/m
'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [UserPermission,]
throttle_classes = [UserThrottle,AdminThrottle]
def get(self,request):
return Response('用户界面') def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
""" if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated('无权访问')
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message) def throttled(self, request, wait):
class UserInnerThrottled(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制.'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = '还需要再等待{wait}秒'
raise UserInnerThrottled(wait) class ManageView(APIView):
'''
要求:只有管理园能访问,5/m
'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [AdminPermission,]
throttle_classes = [AdminThrottle]
def get(self,request):
return Response('管理员界面') def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
""" if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated('无权访问')
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message) def throttled(self, request, wait):
class UserInnerThrottled(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制.'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = '还需要再等待{wait}秒'
raise UserInnerThrottled(wait)
Views
from django.db import models # Create your models here.
class Userinfo(models.Model):
name=models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name='用户名')
pwd=models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name='密码')
token=models.CharField(max_length=64,null=True) def __str__(self):
return self.name
models
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": [
# "app01.utils.MyAuthentication",
"app02.utils.MyAuthentication",
],
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":[
"app02.utils.MyPermission",
"app02.utils.AdminPermission",
],
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES":{
'tiga':'10/m',
'anno':'5/m',
'user':'10/m',
'admin':'20/m',
}
}
settings
Django rest framework 限制访问频率(源码分析)的更多相关文章
- Django rest framework 的认证流程(源码分析)
一.基本流程举例: urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^users/', views.HostView.as_view() ...
- Django(63)drf权限源码分析与自定义权限
前言 上一篇我们分析了认证的源码,一个请求认证通过以后,第二步就是查看权限了,drf默认是允许所有用户访问 权限源码分析 源码入口:APIView.py文件下的initial方法下的check_per ...
- django Rest Framework----APIView 执行流程 APIView 源码分析
在django—CBV源码分析中,我们是分析的from django.views import View下的执行流程,这篇博客我们介绍django Rest Framework下的APIView的源码 ...
- Django框架(十七)-- CBV源码分析、restful规范、restframework框架
一.CBV源码分析 1.url层的使用CBV from app01 import views url(r'book/',views.Book.as_view) 2.as_view方法 as_view是 ...
- Django(44)drf序列化源码分析(1)
序列化与反序列化 一般后端数据返回给前端的数据格式都是json格式,简单易懂,但是我们使用的语言本身并不是json格式,像我们使用的Python如果直接返回给前端,前端用的javascript语言 ...
- Django之admin的使用及源码分析
一.admin组件使用 Django本身提供了基于 web 的管理工具.其管理工具是django.contrib的一部分,可在settings.py中的 INSTALLED_APPS 看到: INST ...
- Django day24 cbv和APIView的源码分析 和 resful的规范
一:cbv的源码分析 1.CBV和FBV的区别: - Class Base View CBV(基于类的视图) - Function Base View FBV(基于函数的视图) 2.as_vi ...
- Django REST framework 总结(附源码剖析)
Django 的 CBV&FBV Django FBV, function base view 视图里使用函数处理请求 url url(r‘^users/‘, views.users), v ...
- Django Rest Framework用户访问频率限制
一. REST framework的请求生命周期 基于rest-framework的请求处理,与常规的url配置不同,通常一个django的url请求对应一个视图函数,在使用rest-framewor ...
随机推荐
- mysql 重置 root 密码
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables & UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD('mima') W ...
- [洛谷P4688][Ynoi2016]掉进兔子洞
题目大意:给定一个$n(n\leqslant10^5)$序列,$m(m\leqslant10^5)$个询问,每个询问给出$l_1,r_1,l_2,r_2,l_3,r_3$.令$s$为该三个区间的交集的 ...
- [洛谷P1452]Beauty Contest
题目大意:给你$n$个点,求出其中最远点的距离 题解:求出凸包,最远点一定都在凸包上,可以对每条边求出最远的点(可以双指针),然后求出和这条边的端点的距离,更新答案 卡点:最开始对每个点求出最远点,但 ...
- [洛谷P3250][HNOI2016]网络
题目大意:给定一棵树.有三种操作: $0\;u\;v\;t:$在$u$到$v$的链上进行重要度为$t$的数据传输. $1\;x:$结束第$x$个数据传输. $2\;x:$询问不经过点$x$的数据传输中 ...
- 2018牛客多校第六场 G.Pikachu
题意: 给出一棵n个点的树,每条边有边权.对这个树加边变成一个完全图.新加的边的权值为边上两点在树上的距离.求完全图上任意两点的最大流之和. 题解: 一共有C(n,2)个点对.假设当前求s到t之间的最 ...
- 在Windows*上编译Tensorflow教程
背景介绍 最简单的 Tensorflow 的安装方法是在 pip 一键式安装官方预编译好的包 pip install tensorflow 通常这种预编译的包的编译参数选择是为了最大兼容性而不是为了最 ...
- LG. 1003 铺地毯
LG. 1003 铺地毯 题意分析 给出平面中地毯的左上角坐标和长宽,然后给出一点(x,y).求此点最上面是哪个地毯的编号,若没被覆盖则输出-1. 将所有地毯的信息存在一个结构体中,由于后埔地毯在上面 ...
- Spring中@Resource与@Autowired、@Qualifier的用法与区别(转)
1.@Autowired与@Resource都可以用来装配bean. 都可以写在字段上,或写在setter方法上. 2.@Autowired默认按类型装配(这个注解是属业spring的),默认情况下必 ...
- 洛谷P4198 楼房重建 (分块)
洛谷P4198 楼房重建 题目描述 小A的楼房外有一大片施工工地,工地上有N栋待建的楼房.每天,这片工地上的房子拆了又建.建了又拆.他经常无聊地看着窗外发呆,数自己能够看到多少栋房子. 为了简化问题, ...
- DOM动态操纵控件案例
点击登陆显示登陆框 <!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head ...
