spark 笔记 16: BlockManager
- /* Class for returning a fetched block and associated metrics. */
private[spark] class BlockResult(
val data: Iterator[Any],
readMethod: DataReadMethod.Value,
bytes: Long) {
val inputMetrics = new InputMetrics(readMethod)
inputMetrics.bytesRead = bytes
}
private[spark] class BlockManager(
executorId: String,
actorSystem: ActorSystem,
val master: BlockManagerMaster,
defaultSerializer: Serializer,
maxMemory: Long,
val conf: SparkConf,
securityManager: SecurityManager,
mapOutputTracker: MapOutputTracker,
shuffleManager: ShuffleManager)
extends BlockDataProvider with Logging {
- /**
* Contains all the state related to a particular shuffle. This includes a pool of unused
* ShuffleFileGroups, as well as all ShuffleFileGroups that have been created for the shuffle.
*/
private class ShuffleState(val numBuckets: Int) {
val nextFileId = new AtomicInteger(0)
val unusedFileGroups = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue[ShuffleFileGroup]()
val allFileGroups = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue[ShuffleFileGroup]()
/**
* The mapIds of all map tasks completed on this Executor for this shuffle.
* NB: This is only populated if consolidateShuffleFiles is FALSE. We don't need it otherwise.
*/
val completedMapTasks = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue[Int]()
}
- private val shuffleStates = new TimeStampedHashMap[ShuffleId, ShuffleState]
private val metadataCleaner =
new MetadataCleaner(MetadataCleanerType.SHUFFLE_BLOCK_MANAGER, this.cleanup, conf)
- /**
* Register a completed map without getting a ShuffleWriterGroup. Used by sort-based shuffle
* because it just writes a single file by itself.
*/
def addCompletedMap(shuffleId: Int, mapId: Int, numBuckets: Int): Unit = {
shuffleStates.putIfAbsent(shuffleId, new ShuffleState(numBuckets))
val shuffleState = shuffleStates(shuffleId)
shuffleState.completedMapTasks.add(mapId)
}
- /**
* Initialize the BlockManager. Register to the BlockManagerMaster, and start the
* BlockManagerWorker actor.
*/
private def initialize(): Unit = {
master.registerBlockManager(blockManagerId, maxMemory, slaveActor)
BlockManagerWorker.startBlockManagerWorker(this)
}
- /**
* A short-circuited method to get blocks directly from disk. This is used for getting
* shuffle blocks. It is safe to do so without a lock on block info since disk store
* never deletes (recent) items.
*/
def getLocalFromDisk(blockId: BlockId, serializer: Serializer): Option[Iterator[Any]] = {
diskStore.getValues(blockId, serializer).orElse {
throw new BlockException(blockId, s"Block $blockId not found on disk, though it should be")
}
}
- /** A group of writers for a ShuffleMapTask, one writer per reducer. */
private[spark] trait ShuffleWriterGroup {
val writers: Array[BlockObjectWriter]
/** @param success Indicates all writes were successful. If false, no blocks will be recorded. */
def releaseWriters(success: Boolean)
}
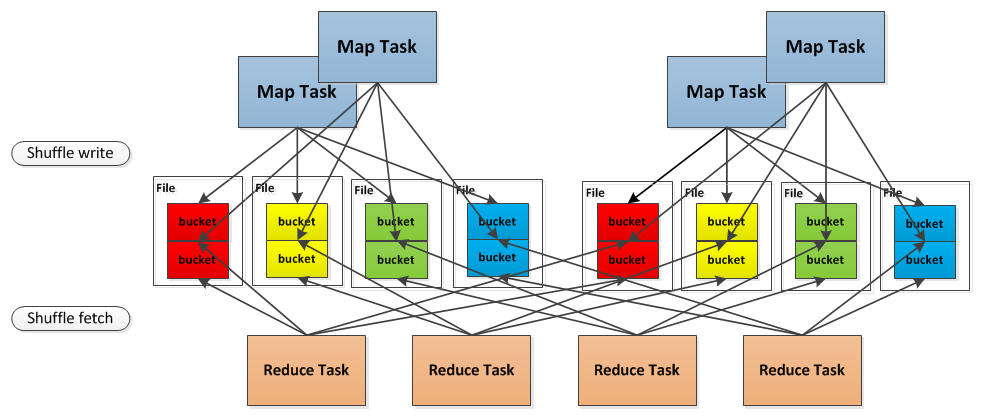
/**
* Manages assigning disk-based block writers to shuffle tasks. Each shuffle task gets one file
* per reducer (this set of files is called a ShuffleFileGroup).
*
* As an optimization to reduce the number of physical shuffle files produced, multiple shuffle
* blocks are aggregated into the same file. There is one "combined shuffle file" per reducer
* per concurrently executing shuffle task. As soon as a task finishes writing to its shuffle
* files, it releases them for another task.
* Regarding the implementation of this feature, shuffle files are identified by a 3-tuple:
* - shuffleId: The unique id given to the entire shuffle stage.
* - bucketId: The id of the output partition (i.e., reducer id)
* - fileId: The unique id identifying a group of "combined shuffle files." Only one task at a
* time owns a particular fileId, and this id is returned to a pool when the task finishes.
* Each shuffle file is then mapped to a FileSegment, which is a 3-tuple (file, offset, length)
* that specifies where in a given file the actual block data is located.
*
* Shuffle file metadata is stored in a space-efficient manner. Rather than simply mapping
* ShuffleBlockIds directly to FileSegments, each ShuffleFileGroup maintains a list of offsets for
* each block stored in each file. In order to find the location of a shuffle block, we search the
* files within a ShuffleFileGroups associated with the block's reducer.
*/
// TODO: Factor this into a separate class for each ShuffleManager implementation
private[spark]
class ShuffleBlockManager(blockManager: BlockManager,
shuffleManager: ShuffleManager) extends Logging {
- private[spark]
object ShuffleBlockManager {
/**
* A group of shuffle files, one per reducer.
* A particular mapper will be assigned a single ShuffleFileGroup to write its output to.
*/
private class ShuffleFileGroup(val shuffleId: Int, val fileId: Int, val files: Array[File]) {
private var numBlocks: Int = 0
/**
* Stores the absolute index of each mapId in the files of this group. For instance,
* if mapId 5 is the first block in each file, mapIdToIndex(5) = 0.
*/
private val mapIdToIndex = new PrimitiveKeyOpenHashMap[Int, Int]()
/**
* Stores consecutive offsets and lengths of blocks into each reducer file, ordered by
* position in the file.
* Note: mapIdToIndex(mapId) returns the index of the mapper into the vector for every
* reducer.
*/
private val blockOffsetsByReducer = Array.fill[PrimitiveVector[Long]](files.length) {
new PrimitiveVector[Long]()
}
private val blockLengthsByReducer = Array.fill[PrimitiveVector[Long]](files.length) {
new PrimitiveVector[Long]()
}
def apply(bucketId: Int) = files(bucketId)
def recordMapOutput(mapId: Int, offsets: Array[Long], lengths: Array[Long]) {
assert(offsets.length == lengths.length)
mapIdToIndex(mapId) = numBlocks
numBlocks += 1
for (i <- 0 until offsets.length) {
blockOffsetsByReducer(i) += offsets(i)
blockLengthsByReducer(i) += lengths(i)
}
}
/** Returns the FileSegment associated with the given map task, or None if no entry exists. */
def getFileSegmentFor(mapId: Int, reducerId: Int): Option[FileSegment] = {
val file = files(reducerId)
val blockOffsets = blockOffsetsByReducer(reducerId)
val blockLengths = blockLengthsByReducer(reducerId)
val index = mapIdToIndex.getOrElse(mapId, -1)
if (index >= 0) {
val offset = blockOffsets(index)
val length = blockLengths(index)
Some(new FileSegment(file, offset, length))
} else {
None
}
}
}
}
spark 笔记 16: BlockManager的更多相关文章
- Ext.Net学习笔记16:Ext.Net GridPanel 折叠/展开行
Ext.Net学习笔记16:Ext.Net GridPanel 折叠/展开行 Ext.Net GridPanel的行支持折叠/展开功能,这个功能个人觉得还说很有用处的,尤其是数据中包含图片等内容的时候 ...
- 安装Hadoop及Spark(Ubuntu 16.04)
安装Hadoop及Spark(Ubuntu 16.04) 安装JDK 下载jdk(以jdk-8u91-linux-x64.tar.gz为例) 新建文件夹 sudo mkdir /usr/lib/jvm ...
- SQL反模式学习笔记16 使用随机数排序
目标:随机排序,使用高效的SQL语句查询获取随机数据样本. 反模式:使用RAND()随机函数 SELECT * FROM Employees AS e ORDER BY RAND() Limit 1 ...
- golang学习笔记16 beego orm 数据库操作
golang学习笔记16 beego orm 数据库操作 beego ORM 是一个强大的 Go 语言 ORM 框架.她的灵感主要来自 Django ORM 和 SQLAlchemy. 目前该框架仍处 ...
- spark的存储系统--BlockManager源码分析
spark的存储系统--BlockManager源码分析 根据之前的一系列分析,我们对spark作业从创建到调度分发,到执行,最后结果回传driver的过程有了一个大概的了解.但是在分析源码的过程中也 ...
- spark笔记 环境配置
spark笔记 spark简介 saprk 有六个核心组件: SparkCore.SparkSQL.SparkStreaming.StructedStreaming.MLlib,Graphx Spar ...
- spark 笔记 15: ShuffleManager,shuffle map两端的stage/task的桥梁
无论是Hadoop还是spark,shuffle操作都是决定其性能的重要因素.在不能减少shuffle的情况下,使用一个好的shuffle管理器也是优化性能的重要手段. ShuffleManager的 ...
- spark 笔记 12: Executor,task最后的归宿
spark的Executor是执行task的容器.和java的executor概念类似. ===================start executor runs task============ ...
- Spark笔记:复杂RDD的API的理解(下)
本篇接着谈谈那些稍微复杂的API. 1) flatMapValues:针对Pair RDD中的每个值应用一个返回迭代器的函数,然后对返回的每个元素都生成一个对应原键的键值对记录 这个方法我最开始接 ...
随机推荐
- 110、通过案例学习Secret (Swarm17)
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/CloudMan6/p/8098761.html 在下面的例子中,我们会部署一个 WordPress 应用,WordPress 是流行的开源博客 ...
- ubuntu18.04系统安装及php7.2,apache2,mysql8,git,svn,composer,vs code 到安装 php 扩展配置php.ini 实现 laravel5.8 运行
简介:记录自己从系统安装到环境配置完毕运行laravel的记录 • 下载ubuntu18.04桌面版 ○ ubuntu18.04中国官网 https://cn.ubuntu.com ...
- 【项目构建工具】 Gradle笔记1
一.Gradle简介 Gradle是一个基于Apache Ant和Apache Maven概念的项目自动化构建开源工具.它使用一种基于Groovy的特定领域语言(DSL)来声明项目设置,抛弃了基于XM ...
- 前端开发 | 尝试用Markdown写一下近几个月的总结
近期总结 回顾 半年前 半年前,接触了前端一年多(工作半年)的我了解的东西只有下面这些.因为在公司里的工作就是切静态页,捣鼓CMS. HTML (比较简洁的编写HTML) CSS/CSS3 (PC兼容 ...
- centos6和centos7的区别和常用的简单配置优化
- 本节主要介绍centos6和centos7的区别和常用的简单配置优化:- 第一部分: - 1.对比文件系统 - 2.对比防火墙,内核版本,默认数据库 - 3.对比时间同步,修改时区,修改语言 - ...
- cmd窗口颜色设置
color 02 第一个数字是背景颜色,第二个是文字颜色.
- (转) Linux安装启动FTP服务
Linux安装启动FTP服务 Linux服务器默认是没有开启FTP服务的.也没有FTP服务器,为了文件的传输需要用到FTP服务器,以典型的vsftpd为例.vsftpd作为FTP服务器,在Linux系 ...
- ArcMap常用操作
1.矢量数据融合 数据管理->制图综合->融合 Data Management Tools -> Generalization -> Dissolve
- 在哪里查看java的jar包版本?
jar包根目录里的META-INF目录下的MANIFEST.MF文件里一般有会记录版本信息,可以到这个文件里查看 .
- LightOJ-1027-A Dangerous Maze(概率)
链接: https://vjudge.net/problem/LightOJ-1027#author=634579757 题意: You are in a maze; seeing n doors i ...
