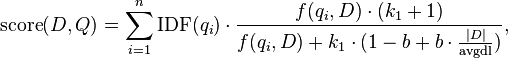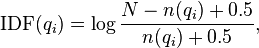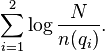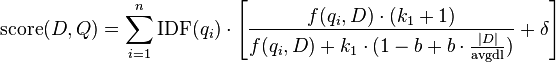Solr相似度算法二:Okapi BM25
In information retrieval, Okapi BM25 (BM stands for Best Matching) is a ranking function used by search engines to rank matching documents according to their relevance to a given search query. It is based on the probabilistic retrieval framework developed in the 1970s and 1980s byStephen E. Robertson, Karen Spärck Jones, and others.
The name of the actual ranking function is BM25. To set the right context, however, it usually referred to as "Okapi BM25", since the Okapi information retrieval system, implemented at London's City University in the 1980s and 1990s, was the first system to implement this function.
BM25, and its newer variants, e.g. BM25F (a version of BM25 that can take document structure and anchor text into account), represent state-of-the-art TF-IDF-like retrieval functions used in document retrieval, such as web search.
The ranking function[edit]
BM25 is a bag-of-words retrieval function that ranks a set of documents based on the query terms appearing in each document, regardless of the inter-relationship between the query terms within a document (e.g., their relative proximity). It is not a single function, but actually a whole family of scoring functions, with slightly different components and parameters. One of the most prominent instantiations of the function is as follows.
Given a query 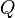 , containing keywords
, containing keywords 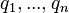 , the BM25 score of a document
, the BM25 score of a document  is:
is:
where  is
is  's term frequency in the document
's term frequency in the document  ,
,  is the length of the document
is the length of the document  in words, and
in words, and 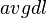 is the average document length in the text collection from which documents are drawn.
is the average document length in the text collection from which documents are drawn. 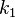 and
and  are free parameters, usually chosen, in absence of an advanced optimization, as
are free parameters, usually chosen, in absence of an advanced optimization, as 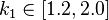 and
and 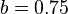 .[1]
.[1] 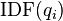 is the IDF (inverse document frequency) weight of the query term
is the IDF (inverse document frequency) weight of the query term  . It is usually computed as:
. It is usually computed as:
where 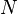 is the total number of documents in the collection, and
is the total number of documents in the collection, and 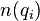 is the number of documents containing
is the number of documents containing  .
.
There are several interpretations for IDF and slight variations on its formula. In the original BM25 derivation, the IDF component is derived from the Binary Independence Model.
Please note that the above formula for IDF shows potentially major drawbacks when using it for terms appearing in more than half of the corpus documents. These terms' IDF is negative, so for any two almost-identical documents, one which contains the term and one which does not contain it, the latter will possibly get a larger score. This means that terms appearing in more than half of the corpus will provide negative contributions to the final document score. This is often an undesirable behavior, so many real-world applications would deal with this IDF formula in a different way:
- Each summand can be given a floor of 0, to trim out common terms;
- The IDF function can be given a floor of a constant
 , to avoid common terms being ignored at all;
, to avoid common terms being ignored at all; - The IDF function can be replaced with a similarly shaped one which is non-negative, or strictly positive to avoid terms being ignored at all.
IDF information theoretic interpretation[edit]
Here is an interpretation from information theory. Suppose a query term  appears in
appears in 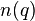 documents. Then a randomly picked document
documents. Then a randomly picked document  will contain the term with probability
will contain the term with probability 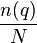 (where
(where 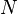 is again the cardinality of the set of documents in the collection). Therefore, the informationcontent of the message "
is again the cardinality of the set of documents in the collection). Therefore, the informationcontent of the message " contains
contains  " is:
" is:
Now suppose we have two query terms  and
and 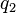 . If the two terms occur in documents entirely independently of each other, then the probability of seeing both
. If the two terms occur in documents entirely independently of each other, then the probability of seeing both  and
and 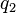 in a randomly picked document
in a randomly picked document  is:
is:
and the information content of such an event is:
With a small variation, this is exactly what is expressed by the IDF component of BM25.
Modifications[edit]
- At the extreme values of the coefficient
 BM25 turns into ranking functions known as BM11 (for
BM25 turns into ranking functions known as BM11 (for  ) and BM15 (for
) and BM15 (for  ).[2]
).[2] - BM25F[3] is a modification of BM25 in which the document is considered to be composed from several fields (such as headlines, main text, anchor text) with possibly different degrees of importance.
- BM25+[4] is an extension of BM25. BM25+ was developed to address one deficiency of the standard BM25 in which the component of term frequency normalization by document length is not properly lower-bounded; as a result of this deficiency, long documents which do match the query term can often be scored unfairly by BM25 as having a similar relevancy to shorter documents that do not contain the query term at all. The scoring formula of BM25+ only has one additional free parameter
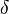 (a default value is
(a default value is 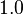 in absence of a training data) as compared with BM25:
in absence of a training data) as compared with BM25:
Solr相似度算法二:Okapi BM25的更多相关文章
- Solr相似度算法二:BM25Similarity
BM25算法的全称是 Okapi BM25,是一种二元独立模型的扩展,也可以用来做搜索的相关度排序. Sphinx的默认相关性算法就是用的BM25.Lucene4.0之后也可以选择使用BM25算法(默 ...
- Solr相似度算法三:DRFSimilarity框架介绍
地址:http://terrier.org/docs/v3.5/dfr_description.html The Divergence from Randomness (DFR) paradigm i ...
- elasticsearch算法之词项相似度算法(二)
六.莱文斯坦编辑距离 前边的几种距离计算方法都是针对相同长度的词项,莱文斯坦编辑距离可以计算两个长度不同的单词之间的距离:莱文斯坦编辑距离是通过添加.删除.或者将一个字符替换为另外一个字符所需的最小编 ...
- Solr相似度算法四:IBSimilarity
Information based:它与Diveragence from randomness模型非常相似.与DFR相似度模型类似,据说该模型也适用于自然语言类的文本.
- Solr相似度算法三:DRFSimilarity
该Similarity 实现了 divergence from randomness (偏离随机性)框架,这是一种基于同名概率模型的相似度模型. 该 similarity有以下配置选项: basic ...
- Okapi BM25算法
引言 Okapi BM25,一般简称 BM25 算法,在 20 世纪 70 年代到 80 年代,由英国一批信息检索领域的计算机科学家发明.这里的 BM 是"最佳匹配"(Best M ...
- ES BM25 TF-IDF相似度算法设置——
Pluggable Similarity Algorithms Before we move on from relevance and scoring, we will finish this ch ...
- TensorFlow 入门之手写识别(MNIST) softmax算法 二
TensorFlow 入门之手写识别(MNIST) softmax算法 二 MNIST Fly softmax回归 softmax回归算法 TensorFlow实现softmax softmax回归算 ...
- elasticsearch算法之词项相似度算法(一)
一.词项相似度 elasticsearch支持拼写纠错,其建议词的获取就需要进行词项相似度的计算:今天我们来通过不同的距离算法来学习一下词项相似度算法: 二.数据准备 计算词项相似度,就需要首先将词项 ...
随机推荐
- alibaba fastjson的使用总结和心得
最初接触alibaba fastjson是由于其性能上的优势,对比原来采用codehause.jackson的解析,在hadoop平台上的手动转换对象有着将近1/3的性能提升,但随着开发应用越来越 ...
- [Z] Windbg以及vs debug使用
Windbg 一篇中国人写的质量非常高的Windbg文章:篇中国人写的质量非常高的Windbg文章: http://www.yiiyee.cn/Blog/windbg/ code project上的W ...
- 概率分布之间的距离度量以及python实现
1. 欧氏距离(Euclidean Distance) 欧氏距离是最易于理解的一种距离计算方法,源自欧氏空间中两点间的距离公式.(1)二维平面上两点a(x1,y1)与b(x2,y2)间的欧 ...
- Servlet类源码说明
servlet是学习java web不可不懂的一个类,网上各种教程都参杂太多,每次理解都感觉像把别人吐出来的食物再放在嘴里咀嚼,小编一怒之下,直接打开源码,原汁原味的芬芳扑面而来: /** * Def ...
- Java路程
Java学习这一部分其实也算是今天的重点,这一部分用来回答很多群里的朋友所问过的问题,那就是你是如何学习Java的,能不能给点建议?今天我是打算来点干货,因此咱们就不说一些学习方法和技巧了,直接来谈每 ...
- win7局域网内共享文件夹及安全设置
右键想要共享的文件夹,选择属性. 在文件夹属性对话框中选择共享标签,如图: 点击共享按钮,弹出文件共享对话框. 添加 Everyone ,并根据实际需要修改权限.权限可以是读取 或 读取/写入. 到此 ...
- ERROR 程序出错,错误原因:'bytes' object has no attribute 'read'
使用json解析数据时,通常遇到这里就会出现问题'bytes' object has no attribute 'read',这是由于使用的json内置函数不同,一个是load另一个是loads. i ...
- Spring的Cache注解
Spring的Cache注解如下所示: @CacheConfig:主要用于配置该类中会用到的一些共用的缓存配置.在这里@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "users&quo ...
- vargant
http://blog.csdn.net/openn/article/details/54927375
- Java NIO API详解(转)
原文连接: http://www.blogjava.net/19851985lili/articles/93524.html 感谢原作者 NIO API 主要集中在 java.nio 和它的 subp ...