Executors Future Callable 使用场景实例
https://www.jb51.net/article/132606.htm:
我们都知道实现多线程有2种方式,一种是继承Thread,一种是实现Runnable,但这2种方式都有一个缺陷,在任务完成后无法获取返回结果。要想获得返回结果,就得使用Callable,Callable任务可以有返回值,但是没法直接从Callable任务里获取返回值;想要获取Callabel任务的返回值,需要用到Future。所以Callable任务和Future模式,通常结合起来使用。
试想一个场景:需要一个帖子列表接口,除了需要返回帖子列表之外,还需要返回每条帖子的点赞列表和评论列表。一页10条帖子来计算,这个接口需要访问21次数据库,访问一次数据库按100ms计算,21次,累计时间为2.1s。这个响应时间,怕是无法令人满意的。怎么办呢?异步化改造接口。
查出帖子列表后,迭代帖子列表,在循环里起10个线程,并发去获取每条帖子的点赞列表,同时另起10个线程,并发去获取每条帖子的评论列表。这样改造之后,接口的响应时间大大缩短,在200ms。这个时候就要用Callabel结合Future来实现。
private List<PostResponse> createPostResponseList(Page<PostResponse> page,final String userId){
if(page.getCount()==0||page==null||page.getList()==null){
return null;
}
//获取帖子列表
List<PostResponse> circleResponseList = page.getList();
int size=circleResponseList.size();
ExecutorService commentPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(size);
ExecutorService supportPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(size);
try {
List<Future> commentFutureList = new ArrayList<Future>(size);
if (circleResponseList != null && circleResponseList.size() > 0) {
for (PostResponse postResponse : circleResponseList) {
final String circleId=postResponse.getId();
final String postUserId=postResponse.getUserId();
//查评论列表
Callable<List<CircleReviews>> callableComment = new Callable<List<CircleReviews>>() {
@Override
public List<CircleReviews> call() throws Exception {
return circleReviewsBiz.getPostComments(circleId);
}
};
Future f = commentPool.submit(callableComment);
commentFutureList.add(f);
//查点赞列表
Callable<List<CircleZan>> callableSupport = new Callable<List<CircleZan>>() {
@Override
public List<CircleZan> call() throws Exception {
return circleZanBiz.findList(circleId);
}
};
Future supportFuture = supportPool.submit(callableSupport);
commentFutureList.add(supportFuture);
}
}
// 获取所有并发任务的执行结果
int i = 0;
PostResponse temp = null;
for (Future f : commentFutureList) {
temp = circleResponseList.get(i);
temp.setCommentList((List<CircleReviews>) f.get();
temp.setSupportList((List<CircleZan>) f.get();
circleResponseList.set(i, temp);
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭线程池
commentPool.shutdown();
supportPool.shutdown();
}
return circleResponseList;
}
★ 下面给出一个Executor执行Callable任务的示例代码(https://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17465497?utm_source=blogxgwz0):
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CallableDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
List<Future<String>> resultList = new ArrayList<Future<String>>(); //创建10个任务并执行
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
//使用ExecutorService执行Callable类型的任务,并将结果保存在future变量中
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(new TaskWithResult(i));
//将任务执行结果存储到List中
resultList.add(future);
} //遍历任务的结果
for (Future<String> fs : resultList){
try{
while(!fs.isDone);//Future返回如果没有完成,则一直循环等待,直到Future返回完成
System.out.println(fs.get()); //打印各个线程(任务)执行的结果
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(ExecutionException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//启动一次顺序关闭,执行以前提交的任务,但不接受新任务
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
} class TaskWithResult implements Callable<String>{
private int id; public TaskWithResult(int id){
this.id = id;
} /**
* 任务的具体过程,一旦任务传给ExecutorService的submit方法,
* 则该方法自动在一个线程上执行
*/
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("call()方法被自动调用!!! " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
//该返回结果将被Future的get方法得到
return "call()方法被自动调用,任务返回的结果是:" + id + " " + Thread.currentThread().getName();
}
}
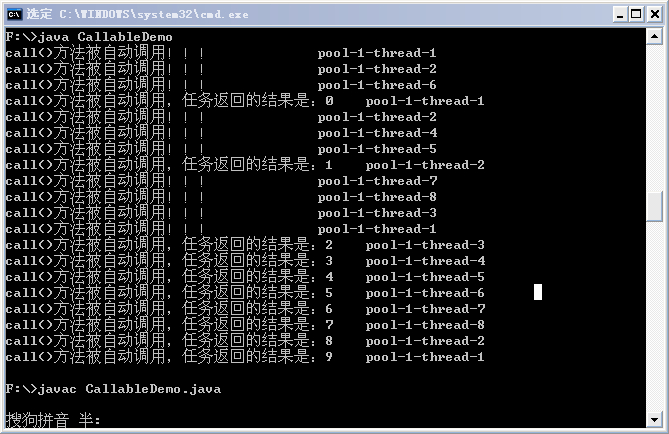
某次执行结果如下:
从结果中可以同样可以看出,submit也是首先选择空闲线程来执行任务,如果没有,才会创建新的线程来执行任务。另外,需要注意:如果Future的返回尚未完成,则get()方法会阻塞等待,直到Future完成返回,可以通过调用isDone()方法判断Future是否完成了返回。
Executors Future Callable 使用场景实例的更多相关文章
- Java多线程之Executor、ExecutorService、Executors、Callable、Future与FutureTask
1. 引子 初学Java多线程,常使用Thread与Runnable创建.启动线程.如下例: Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override pub ...
- JVM源码分析-类加载场景实例分析
A类调用B类的静态方法,除了加载B类,但是B类的一个未被调用的方法间接使用到的C类却也被加载了,这个有意思的场景来自一个提问:方法中使用的类型为何在未调用时尝试加载?. 场景如下: public cl ...
- Linux 下 svn 场景实例及常用命令详解
一.SVN使用场景实例 问题: 在使用svn做为版本控制系统的软件开发中,经常会有这样的需求:在工作复本目录树的不同目录中增加了很多文件,但未纳入版本控制系统,这时如果使用svn add命令一个一个的 ...
- Java并发编程 - Executor,Executors,ExecutorService, CompletionServie,Future,Callable
一.Exectuor框架简介 Java从1.5版本开始,为简化多线程并发编程,引入全新的并发编程包:java.util.concurrent及其并发编程框架(Executor框架). Executor ...
- Java 多线程并发 Future+callable 实例
需求:一个业务实现 查询, 因为 要查询十几次, 所以每个平均0.6秒, 之前只有主线程一步步查 ,结果用了10秒,效率十分低下 , 于是改用线程池并发: 以下是代码设计: 1.线程池工具类: pac ...
- java 多线程 Future callable
面向对象5大设计原则 1.单一职责原则 一个类只包含它相关的方法,增删改查.一个方法只包含单一的功能,增加.一个类最多包含10个方法,一个方法最多50行,一个类最多500行.重复的代码进行封装,Do ...
- 并发编程-Future+callable+FutureTask 闭锁机制
项目中经常有些任务需要异步(提交到线程池中)去执行,而主线程往往需要知道异步执行产生的结果,这时我们要怎么做呢?用runnable是无法实现的,我们需要用callable实现. FutureTask ...
- 多线程常用代码 Future Callable Runable
public class ThreadPoolTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { E ...
- Future Callable 线程池 例1
package com.niewj.concurrent; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.Exec ...
随机推荐
- win7创建 VirtualBox COM 对象失败。 应用程序现在将终止。 Callee RC: E_NOINTERFACE (0x80004002)
win7创建 VirtualBox COM 对象失败. 应用程序现在将终止. Callee RC: E_NOINTERFACE (0x80004002) 启动VirtualBox提示这个错误, ...
- jsp动作之 getProperty
getProperty就是用来获取(读取)实例化的内容的. 说明了就是(Techerobj实例为样,用name=张三,age=21等属性) <%=Techerobj.getName()%> ...
- 记一次无法正常本地登陆Linux服务器(确定密码正确)
首先,ssh可以正常登陆使用.但是,本地可以确定密码是正确的情况还是不能登陆. 然后查看/var/log/secure文件如下提示: 然后,尝试去看了下/etc/pam.d/login 下面(有问题的 ...
- 源代码方式调试Mycat
如果是第一次刚接触MyCat建议下载源码在本地通过eclipse等工具进行配置和运行,便于深入了解和调试程序运行逻辑. 1)源代码方式调试与配置 由于MyCat源代码目前主要托管在github上,大家 ...
- quick pow
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #define LL long long LL qpow(LL a,LL b,LL m) { LL r=1; ...
- 基础最短路(模板 bellman_ford)
Description 在每年的校赛里,所有进入决赛的同学都会获得一件很漂亮的t-shirt.但是每当我们的工作人员把上百件的衣服从商店运回到赛场的时候,却是非常累的!所以现在他们想要寻找最短的从商店 ...
- 手动安装Silverlight 4 Tools for Visual Studio 2010
手动安装吧,将Silverlight 4 Tools for Visual Studio 2010.exe改成rar文件,解压缩,按照下面的步骤安装: 1.silverlight_developer. ...
- web前端切图处理
技巧: 一. 如何在 Retina 屏幕的设备使用更高分辨率的图片 以 MacBook Pro 为例,它的标准分辨率高达 2560 x 1600,但是如果真的以这个分辨率显示网页,网页的有效区域就小的 ...
- Oracle连接知识
Oracle基本连接知识 登录sys用户或 sysdba用户权限的账号 Sqlplus 建用户 Create user test identified by 12345678 ...
- learning docker steps(2) ----- docker contailner 初次体验
参考:https://docs.docker-cn.com/get-started/part2/ Dockerfile的内容如下所示: # 将官方 Python 运行时用作父镜像 FROM pytho ...