HotSpot类模型之InstanceKlass
上一篇 HotSpot源码分析之类模型 介绍了类模型的基础类Klass的重要属性及方法,这一篇介绍一下InstanceKlass及InstanceKlass的子类。
1、InstanceKlass类
每个InstanceKlass对象表示一个具体的Java类(这里的Java类不包括Java数组)。InstanceKlass类及重要属性的定义如下:
class InstanceKlass: public Klass {
...
protected:
// Annotations for this class
Annotations* _annotations;
// Array classes holding elements of this class.
Klass* _array_klasses;
// Constant pool for this class.
ConstantPool* _constants;
// The InnerClasses attribute and EnclosingMethod attribute. The
// _inner_classes is an array of shorts. If the class has InnerClasses
// attribute, then the _inner_classes array begins with 4-tuples of shorts
// [inner_class_info_index, outer_class_info_index,
// inner_name_index, inner_class_access_flags] for the InnerClasses
// attribute. If the EnclosingMethod attribute exists, it occupies the
// last two shorts [class_index, method_index] of the array. If only
// the InnerClasses attribute exists, the _inner_classes array length is
// number_of_inner_classes * 4. If the class has both InnerClasses
// and EnclosingMethod attributes the _inner_classes array length is
// number_of_inner_classes * 4 + enclosing_method_attribute_size.
Array<jushort>* _inner_classes;
// Array name derived from this class which needs unreferencing
// if this class is unloaded.
Symbol* _array_name;
// Number of heapOopSize words used by non-static fields in this klass
// (including inherited fields but after header_size()).
int _nonstatic_field_size;
int _static_field_size; // number words used by static fields (oop and non-oop) in this klass
// Constant pool index to the utf8 entry of the Generic signature,
// or 0 if none.
u2 _generic_signature_index;
// Constant pool index to the utf8 entry for the name of source file
// containing this klass, 0 if not specified.
u2 _source_file_name_index;
u2 _static_oop_field_count;// number of static oop fields in this klass
u2 _java_fields_count; // The number of declared Java fields
int _nonstatic_oop_map_size;// size in words of nonstatic oop map blocks
u2 _minor_version; // minor version number of class file
u2 _major_version; // major version number of class file
Thread* _init_thread; // Pointer to current thread doing initialization (to handle recusive initialization)
int _vtable_len; // length of Java vtable (in words)
int _itable_len; // length of Java itable (in words)
OopMapCache* volatile _oop_map_cache; // OopMapCache for all methods in the klass (allocated lazily)
JNIid* _jni_ids; // First JNI identifier for static fields in this class
jmethodID* _methods_jmethod_ids; // jmethodIDs corresponding to method_idnum, or NULL if none
nmethodBucket* _dependencies; // list of dependent nmethods
nmethod* _osr_nmethods_head; // Head of list of on-stack replacement nmethods for this class
// Class states are defined as ClassState (see above).
// Place the _init_state here to utilize the unused 2-byte after
// _idnum_allocated_count.
u1 _init_state; // state of class
u1 _reference_type; // reference type
// Method array.
Array<Method*>* _methods;
// Default Method Array, concrete methods inherited from interfaces
Array<Method*>* _default_methods;
// Interface (Klass*s) this class declares locally to implement.
Array<Klass*>* _local_interfaces;
// Interface (Klass*s) this class implements transitively.
Array<Klass*>* _transitive_interfaces;
// Int array containing the vtable_indices for default_methods
// offset matches _default_methods offset
Array<int>* _default_vtable_indices;
// Instance and static variable information, starts with 6-tuples of shorts
// [access, name index, sig index, initval index, low_offset, high_offset]
// for all fields, followed by the generic signature data at the end of
// the array. Only fields with generic signature attributes have the generic
// signature data set in the array. The fields array looks like following:
//
// f1: [access, name index, sig index, initial value index, low_offset, high_offset]
// f2: [access, name index, sig index, initial value index, low_offset, high_offset]
// ...
// fn: [access, name index, sig index, initial value index, low_offset, high_offset]
// [generic signature index]
// [generic signature index]
// ...
Array<u2>* _fields;
// embedded Java vtable follows here
// embedded Java itables follows here
// embedded static fields follows here
// embedded nonstatic oop-map blocks follows here
// embedded implementor of this interface follows here
// The embedded implementor only exists if the current klass is an
// iterface. The possible values of the implementor fall into following
// three cases:
// NULL: no implementor.
// A Klass* that's not itself: one implementor.
// Itsef: more than one implementors.
// embedded host klass follows here
// The embedded host klass only exists in an anonymous class for
// dynamic language support (JSR 292 enabled). The host class grants
// its access privileges to this class also. The host class is either
// named, or a previously loaded anonymous class. A non-anonymous class
// or an anonymous class loaded through normal classloading does not
// have this embedded field.
...
}
重要属性的介绍如下表所示。
| 字段名 | 作用 |
| _annotations | Annotations类型的指针,保存该类使用的所有注解 |
| _array_klasses |
数组元素为该类的数组Klass指针,例如ObjArrayKlass是对象数组且元素类型为Object, 那么表示Object类的InstanceKlass对象的_array_klasses就是指向ObjArrayKlass对象的指针 |
| _array_name |
以该类为数组元素的数组的名字,如果当前InstanceKlass对象表示Object类,则名称为"[Ljava/lang/Object;" |
| _constants | ConstantPool类型的指针,用来指向保存了Java类的常量池信息的ConstantPool对象 |
| _inner_classes | 用一个jushort数组保存当前类的InnerClasses属性和EnclosingMethod属性 |
| _nonstatic_field_size |
非静态字段需要占用的内存大小 ,以字为单位。在为当前类表示的Java类所创建的对象(使用oop表示)分配内存时, 会参考此属性的值分配内存,这个值在类文件解析时会计算好。 |
| _static_field_size | 静态字段需要占用的内存大小 ,以字为单位。在为当前类表示的Java类所创建的java.lang.Class对象(使用oop表示)分配内存时,
会参考此属性的值分配内存,这个值在类文件解析时会计算好。 |
| _generic_signature_index |
保存此类的签名在常量池中的索引 |
| _source_file_name_index | 保存此类的源文件名在常量池中的索引 |
| _static_oop_field_count | 此类包含的静态引用类型字段的数量 |
| _java_fields_count | 此类包含的字段总数量 |
| _nonstatic_oop_map_size | 非静态的oop map block需要占用的内存大小,以字为单位 |
| _minor_version | 类的次版本号 |
| _major_version | 类的主版本号 |
| _init_thread | 执行此类初始化的Thread指针 |
| _vtable_len | Java虚函数表(vtable)所占用的内存大小,以字为单位 |
| _itable_len | Java接口函数表(itable)所占用的内存大小,以字为单位 |
| _oop_map_cache | OopMapCache指针,该类的所有方法的OopMapCache |
| _jni_ids/_methods_jmethod_ids | JNIid指针与jmethodID指针,这2个指针对于JNI方法操作属性和方法非常重要,在介绍JNI时会详细介绍。 |
| _dependencies | nmethodBucket指针,依赖的本地方法,以根据其_next属性获取下一个nmethod |
| _osr_nmethods_head | 栈上替换的本地方法链表的头元素 |
| _init_state |
表示类的状态,为枚举类型ClassState,定义了如下常量值:
|
| _reference_type | 引用类型,可能是强引用、软引用、弱引用等 |
| _methods | 保存方法的指针数组 |
| _default_methods | 保存方法的指针数组,从接口继承的默认方法 |
| _local_interfaces | 保存接口的指针数组,直接实现的接口Klass |
| _transitive_interfaces | 保存接口的指针数组,包含_local_interfaces和间接实现的接口 |
| _default_vtable_indices | 默认方法在虚函数表中的索引 |
| _fields |
类的字段属性,每个字段的6个属性access,、name index、sig index、initial value index、low_offset、high_offset组成一个元组, access表示访问控制属性,根据name index可以获取属性名,根据initial value index可以获取初始值,根据low_offset与 high_offset可以获取该属性在内存中的偏移量。另外保存完所有属性之后还可能会保存泛型签名信息。 |
有了InstanceKlass与Klass中定义的这些属性足够用来保存Java类元信息。在后续的类解析中会看到对相关变量的属性填充操作。除了保存类元信息外,此类还有另外一个重要的功能,即支持方法分派,主要是通过Java虚函数表和Java接口函数表来完成的,不过C++并不像Java一样,保存信息时非要在类中定义出相关属性,C++只是在分配内存时为要存储的信息分配好特定的内存,然后直接通过内存偏移来操作即可。
接下来几个属性是没有对应的属性名,只能通过指针和偏移量的方式访问:
- Java vtable:Java虚函数表,大小等于_vtable_len;
- Java itables:Java接口函数表,大小等于 _itable_len;
- 非静态oop-map blocks ,大小等于_nonstatic_oop_map_size。GC在垃圾回收时,遍历某个对象所引用的其它对象时,会结合此信息进行查找;
- 接口的实现类,只有当前类表示一个接口时存在。如果接口没有任何实现类则为NULL;如果只有一个实现类则为该实现类的Klass指针;如果有多个实现类,为当前类本身;
- host klass,只在匿名类中存在,为了支持JSR 292中的动态语言特性,会给匿名类生成一个host klass。
HotSpot在解析一个类时会调用InstanceKlass::allocate_instance_klass()方法分配内存,而分配多大的内存则是通过调用InstanceKlass::size()计算出来的,调用语句如下:
int size = InstanceKlass::size(vtable_len,itable_len,nonstatic_oop_map_size,isinterf,is_anonymous);
调用的size()方法的实现如下:
static int size(
int vtable_length,
int itable_length,
int nonstatic_oop_map_size,
bool is_interface,
bool is_anonymous
){
return align_object_size(header_size() + // InstanceKlass类本身占用的内存大小
align_object_offset(vtable_length) +
align_object_offset(itable_length) +
// [EMBEDDED nonstatic oop-map blocks] size in words = nonstatic_oop_map_size
// The embedded nonstatic oop-map blocks are short pairs (offset, length)
// indicating where oops are located in instances of this klass.
(
(is_interface || is_anonymous) ?
align_object_offset(nonstatic_oop_map_size) :
nonstatic_oop_map_size
) +
// [EMBEDDED implementor of the interface] only exist for interface
(
is_interface ? (int)sizeof(Klass*)/HeapWordSize : 0
) +
// [EMBEDDED host klass ] only exist for an anonymous class (JSR 292 enabled)
(
is_anonymous ? (int)sizeof(Klass*)/HeapWordSize : 0)
);
}
方法返回值就是此次创建Klass对象所需要开辟的内存大小。由此方法的计算逻辑可以看出Klass对象的内存布局情况。

图中的灰色阴影部分是可选部分。关于vtable_length和itable_length以及nonstatic_oop_map_size的值在类解析的过程中会计算好,在后续介绍类解析过程中会详细介绍。
调用的header_size()方法就是计算此类的对象所占用的内存大小,实现如下:
// Sizing (in words)
static int header_size(){
return align_object_offset(sizeof(InstanceKlass)/HeapWordSize); // 以HeapWordSize为单位,64位一个字为8字节,所以值为8
}
调用的align_object_offset()方法是进行内存对齐,这是一块非常重要的C++知识点,后面会专门进行讲解。
2、InstanceKlass类的子类
InstanceKlass共有3个直接子类,这3个子类用来表示一些特殊的类,下面简单介绍一下这3个子类:
(1)InstanceRefKlass
java/lang/ref/Reference的子类需要使用InstanceRefKlass类来表示,在创建这个类的实例时,_reference_type字段的值通常会说明当前的类表示的是哪种引用类型。取值已经在枚举类中定义,如下:
REF_NONE枚举常量的定义如下:
// ReferenceType is used to distinguish between java/lang/ref/Reference subclasses
enum ReferenceType {
REF_NONE, // Regular class
REF_OTHER, // Subclass of java/lang/ref/Reference, but not subclass of one of the classes below
REF_SOFT, // Subclass of java/lang/ref/SoftReference
REF_WEAK, // Subclass of java/lang/ref/WeakReference
REF_FINAL, // Subclass of java/lang/ref/FinalReference
REF_PHANTOM // Subclass of java/lang/ref/PhantomReference
};
可以看到,所有的Java类Reference及子类都会用C++类InstanceRefKlass的对象来表示。当无法判断到底是哪个Java子类时,会将_reference_type的值设置为REF_OTHER。
因为这些类需要垃圾回收器特殊处理 ,在后续讲解强引用、弱引用、虚引用以及幽灵引用时在详细介绍。
(2)InstanceMirrorKlass类
InstanceMirrorKlass对象用于表示特殊的java.lang.Class类,增加了一个静态属性_offset_of_static_fields,用来描述静态字段的起始偏移量。定义如下:
static int _offset_of_static_fields;
只所以增加这个属性,是由于java.lang.Class类比较特殊。正常情况下,HotSpot使用Klass来表示Java类,用oop来表示Java对象,而Java对象中可能定义静态或非静态字段,非静态字段值存储在oop中,而静态字段值存储在表示当前Java类的java.lang.Class对象中。java.lang.Class类用InstanceMirrorKlass对象来表示,java.lang.Class对象用oop来表示,那么Class对象的非静态字段值存储在oop中,而Class类自身也定义了静态字段,那么这些值同样存储在了Class对象中,也就是表示Class对象的oop中,这样静态与非静态字段存储在了一个oop上,通过_offset_of_static_fields属性偏移来定位静态字段的存储位置。
该属性是通过init_offset_of_static_fields方法初始化的,其初始化的过程如下:
static void init_offset_of_static_fields() {
// Cache the offset of the static fields in the Class instance
assert(_offset_of_static_fields == 0, "once");
// java.lang.Class类使用InstanceMirrorKlass对象来表示,而java.lang.Class对象通过Oop对象来表示,那么imk->size_helper()获取的就是
// Oop对象的大小,左移3位将字转换为字节。紧要着Oop对象后存储静态字段的值
InstanceMirrorKlass* imk = InstanceMirrorKlass::cast(SystemDictionary::Class_klass());
_offset_of_static_fields = imk->size_helper() << LogHeapWordSize; // LogHeapWordSize=3
}
int size_helper() const {
return layout_helper_to_size_helper(layout_helper());
}
static int layout_helper_to_size_helper(jint lh) {
assert(lh > (jint)_lh_neutral_value, "must be instance");
return lh >> LogHeapWordSize;
}
int layout_helper() const{ return _layout_helper; }
调用java.lang.Class类(通过InstanceMirrorKlass对象来表示)的size_helper()方法来获取java.lang.Class对象(通过Oop对象来表示)的大小,这个大小是java.lang.Class类中本身声明的一些属性需要占用的大小,紧随其后的就是静态存储的区域。
打开命令-XX:+PrintFieldLayout后的打印结果如下:
非静态的布局如下:
java.lang.Class: field layout
@ 12 --- instance fields start ---
@ 12 "cachedConstructor" Ljava.lang.reflect.Constructor;
@ 16 "newInstanceCallerCache" Ljava.lang.Class;
@ 20 "name" Ljava.lang.String;
@ 24 "reflectionData" Ljava.lang.ref.SoftReference;
@ 28 "genericInfo" Lsun.reflect.generics.repository.ClassRepository;
@ 32 "enumConstants" [Ljava.lang.Object;
@ 36 "enumConstantDirectory" Ljava.util.Map;
@ 40 "annotationData" Ljava.lang.Class$AnnotationData;
@ 44 "annotationType" Lsun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationType;
@ 48 "classValueMap" Ljava.lang.ClassValue$ClassValueMap;
@ 52 "protection_domain" Ljava.lang.Object;
@ 56 "init_lock" Ljava.lang.Object;
@ 60 "signers_name" Ljava.lang.Object;
@ 64 "klass" J
@ 72 "array_klass" J
@ 80 "classRedefinedCount" I
@ 84 "oop_size" I
@ 88 "static_oop_field_count" I
@ 92 --- instance fields end ---
@ 96 --- instance ends ---
这就是java.lang.Class非静态字段的布局,在类解析过程中已经计算好了各个字段的偏移量。在完成非静态字段布局后,紧接着会布局静态字段,此时的_offset_of_static_fields字段的值为96。
我们需要分清相关类的表示方法,如下图所示。
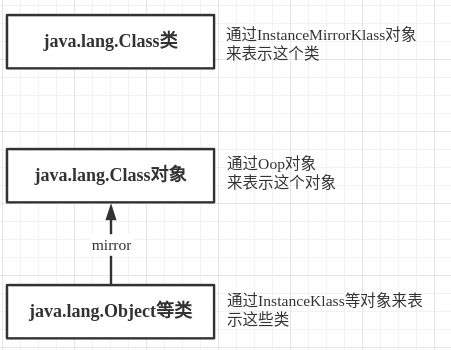
java.lang.Class对象是通过对应的Oop对象来保存类的静态属性,因此他们的实例大小不同,需要特殊的方式来计算他们的大小以及属性遍历。
Klass的属性_java_mirror就指向保存该类静态字段的Oop对象,可通过该属性访问类的静态字段。 Oop是HotSpot的对象表示模型,在后面会详细介绍。
(3)InstanceClassLoaderKlass类
没有添加新的字段,增加了新的oop遍历方法,主要用于类加载器依赖遍历使用。
3、创建类的实例
创建InstanceKlass实例会调用InstanceKlass::allocate_instance_klass()方法。在创建时,会涉及到C++对new运算符的重载,通过重载new运算符来分配对象的内存空间,然后再调用类的构造函数初始化相应的属性。方法的实现如下:
InstanceKlass* InstanceKlass::allocate_instance_klass(
ClassLoaderData* loader_data,
int vtable_len,
int itable_len,
int static_field_size,
int nonstatic_oop_map_size,
ReferenceType rt,
AccessFlags access_flags,
Symbol* name,
Klass* super_klass,
bool is_anonymous,
TRAPS
){
bool isinterf = access_flags.is_interface();
int size = InstanceKlass::size(
vtable_len,
itable_len,
nonstatic_oop_map_size,
isinterf,
is_anonymous
); // Allocation
InstanceKlass* ik;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if (rt == REF_NONE) {
if (name == vmSymbols::java_lang_Class()) { // 通过InstanceMirrorKlass对象表示java.lang.Class类
ik = new (loader_data, size, THREAD) InstanceMirrorKlass(
vtable_len,
itable_len,
static_field_size,
nonstatic_oop_map_size,
rt,
access_flags,
is_anonymous);
} else if (
name == vmSymbols::java_lang_ClassLoader() ||
(
SystemDictionary::ClassLoader_klass_loaded() &&
super_klass != NULL && // ClassLoader_klass为java_lang_ClassLoader
super_klass->is_subtype_of(SystemDictionary::ClassLoader_klass())
)
){ // 通过InstanceClassLoaderKlass对象表示java.lang.ClassLoader或相关子类
ik = new (loader_data, size, THREAD) InstanceClassLoaderKlass(
vtable_len,
itable_len,
static_field_size,
nonstatic_oop_map_size,
rt,
access_flags,
is_anonymous);
} else { // 通过InstanceKlass对象表示普通类
// normal class
ik = new (loader_data, size, THREAD) InstanceKlass(
vtable_len, itable_len,
static_field_size,
nonstatic_oop_map_size,
rt,
access_flags,
is_anonymous);
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
else { // 通过InstanceRefKlass对象表示引用
// reference klass
ik = new (loader_data, size, THREAD) InstanceRefKlass(
vtable_len, itable_len,
static_field_size,
nonstatic_oop_map_size,
rt,
access_flags,
is_anonymous);
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 添加所有类型到我们内部类加载器列表中,包括在根加载器中的类
// Add all classes to our internal class loader list here,
// including classes in the bootstrap (NULL) class loader.
// loader_data的类型为ClassLoaderData*,通过ClassLoaderData中的_klasses保持通过InstanceKlass._next_link属性保持的列表
loader_data->add_class(ik);
Atomic::inc(&_total_instanceKlass_count);
return ik;
}
方法的实现比较简单,当rt等于REF_NONE时,也就是为非Reference类型时,会根据类名创建对应C++类的对象。Class类创建InstanceMirrorKlass、ClassLoader类或ClassLoader的子类创建InstanceClassLoaderKlass类、普通类通过InstanceKlass来表示。当rt不为REF_NONE时,会创建InstanceRefKlass对象。
调用的size()函数在之前介绍InstanceKlass类时已经介绍过,这里不再介绍。得到size后会调用new重载运算符函数来开辟内存空间,如下:
void* Klass::operator new(size_t size, ClassLoaderData* loader_data, size_t word_size, TRAPS) throw() {
void* x = Metaspace::allocate( // 在元数据区分配内存空间
loader_data,
word_size,
false, /*read_only*/
MetaspaceObj::ClassType,
CHECK_NULL
);
return x;
}
可以看到,对于jdk1.8版本来说,Klass对象在元数据区分配内存。由于C++没有像Java一样的垃圾回收机制,所以Metaspace的内存需要自动管理和释放,这一块知识将在后面详细介绍。
其它参考文章:
1、在Ubuntu 16.04上编译OpenJDK8的源代码(配视频)
搭建过程中如果有问题可直接评论留言或加作者微信mazhimazh。
作者持续维护的个人博客 classloading.com。
B站上有HotSpot源码分析相关视频 https://space.bilibili.com/27533329
关注公众号,有HotSpot源码剖析系列文章!

HotSpot类模型之InstanceKlass的更多相关文章
- HotSpot类模型之ArrayKlass
上一篇分析了 HotSpot类模型之InstanceKlass ,这次主要分析表示java数组类型的C++类. 1.ArrayKlass类 ArrayKlass继承自Klass,是所有数组类的抽象基类 ...
- HotSpot的类模型(2)
在前一篇文章 HotSpot的二分模型中已经讲过,HotSpot采用了OOP-Klass模型描述Java的类和对象.Klass模型采用Klass类及相关子类来表示具体的Java类,可以理解这些类为Ja ...
- HotSpot的类模型(3)
上一篇 HotSpot的类模型(2) 介绍了类模型的基础类Klass的重要属性及方法,这一篇介绍一下InstanceKlass及InstanceKlass的子类. 2.InstanceKlass类 每 ...
- HotSpot的类模型(4)
我们继续接着上一篇 HotSpot的类模型(3)分析,这次主要分析表示java数组的C++类. 4.ArrayKlass类 ArrayKlass继承自Klass,是所有数组类的抽象基类,类及重要属性的 ...
- .NET使用DAO.NET实体类模型操作数据库
一.新建项目 打开vs2017,新建一个项目,命名为orm1 二.新建数据库 打开 SqlServer数据库,新建数据库 orm1,并新建表 student . 三.新建 ADO.NET 实体数据模型 ...
- laravel5.8笔记五:基类控制器和基类模型
建立基类的目的就是为了方便继承.比如:Admin模块访问,是否登陆.检测登陆可以写到基类里面 控制器基类 原始基类:app\Http\Controllers\Controller.php,我们下面要做 ...
- Paddle Graph Learning (PGL)图学习之图游走类模型[系列四]
Paddle Graph Learning (PGL)图学习之图游走类模型[系列四] 更多详情参考:Paddle Graph Learning 图学习之图游走类模型[系列四] https://aist ...
- HotSpot二分模型(1)
HotSpot采用了OOP-Klass模型来描述Java类和对象.OOP(Ordinary Object Pointer)指的是普通对象指针,而Klass用来描述对象的具体类型. 那么为何要设计这样一 ...
- DL4NLP——词表示模型(一)表示学习;syntagmatic与paradigmatic两类模型;基于矩阵的LSA和GloVe
本文简述了以下内容: 什么是词表示,什么是表示学习,什么是分布式表示 one-hot representation与distributed representation(分布式表示) 基于distri ...
随机推荐
- abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统——出库管理之三(五十一)
abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统目录 abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统--ABP总体介绍(一) abp(net core)+ ...
- Nginx常见错误解决办法
报错: nginx: [error] CreateFile() "C:\mytools\nginx-1.8.1/logs/nginx.pid" failed (2: The sys ...
- 为啥 Response.Write 后,View就不渲染了?
一:背景 1. 讲故事 前几天群里有一位朋友聊到,为什么我在 Action 中执行一句 Response.Write 之后,后续的 View 就不呈现了,如果脑子中没有画面,那就上测试代码: publ ...
- RocketMQ 4.7.1 环境搭建、集群、MQ整合SpringBoot
导读 之前学过ActiveMQ但是并发量不是很大点我直达,所以又学阿里开源的RocketMQ,据说队列可以堆积亿级别.下面是网上找的消息队列对比图,仅供参考 部署 官网 点我直达 前置条件 推荐使用6 ...
- Parquet 源码解析
date: 2020-07-20 16:15:00 updated: 2020-07-27 13:40:00 Parquet 源码解析 Parquet文件是以二进制方式存储的,所以是不可以直接读取的, ...
- SpringBoot + Swagger Demo
Swagger是什么? Swagger 是一个规范且完整的框架,用于生成.描述.调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务. Swagger 的目标是对 REST API 定义一个标准且和语 ...
- jquery里面的一些方法使用
prop("属性名"); //获取属性名 prop("属性名","属性值"); //设置属性名 change(fucntion(){ ...
- Django项目-个人网站之事项模块
Django项目之个人网站 关注公众号"轻松学编程"了解更多. Github地址:https://github.com/liangdongchang/MyWeb.git 感兴趣的可 ...
- 841. Keys and Rooms —— weekly contest 86
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/keys-and-rooms/description/ 简单DFS time:9ms 1 class Solution { 2 p ...
- PAT Saving James Bond - Easy Version
Saving James Bond - Easy Version This time let us consider the situation in the movie "Live and ...
