PyTorch中的CUDA操作
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture)是NVIDIA推出的异构计算平台,PyTorch中有专门的模块torch.cuda来设置和运行CUDA相关操作。本地安装环境为Windows10,Python3.7.8和CUDA 11.6,安装PyTorch最新稳定版本1.12.1如下:
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu116
一.常见CPU和GPU操作命令
1.查看PyTorch版本
print(torch.__version__)
1.12.1+cu116
2.查看GPU设备是否可用
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
True
3.PyTorch默认使用设备是CPU
print("default device: {}".format(torch.Tensor([4,5,6]).device))
default device: cpu
4.查看所有可用的cpu设备的数量
print("available cpu devices: {}".format(torch.cuda.os.cpu_count()))
available cpu devices: 20
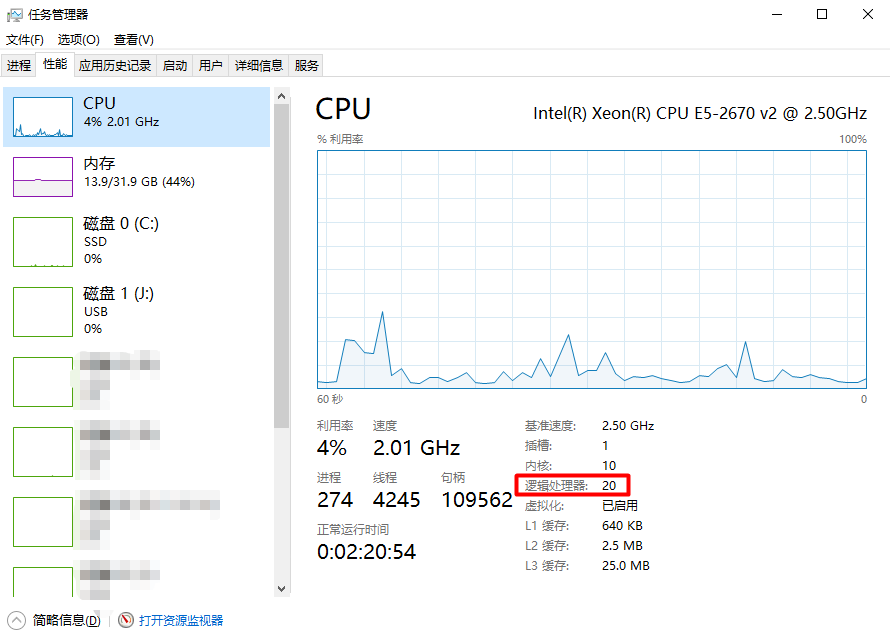
这里CPU设备数量指的是逻辑处理器的数量。
5.查看所有可用的gpu设备的数量
print("available gpu devices: {}".format(torch.cuda.device_count()))
available gpu devices: 1
6.获取gpu设备的名称
print("gpu device name: {}".format(torch.cuda.get_device_name(torch.device("cuda:0"))))
gpu device name: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti
7.通过device="cpu:0"指定cpu:0设备
device = torch.Tensor([1,2,3], device="cpu:0").device
print("device type: {}".format(device))
device type: cpu
8.通过torch.device指定cpu:0设备
cpu1 = torch.device("cpu:0")
print("cpu device: {}:{}".format(cpu1.type, cpu1.index))
cpu device: cpu:0
9.使用索引的方式,默认使用CUDA设备
gpu = torch.device(0)
print("gpu device: {}:{}".format(gpu.type, gpu.index))
gpu device: cuda:0
10.通过torch.device("cuda:0)指定cuda:0设备
gpu = torch.device("cuda:0")
print("gpu device: {}:{}".format(gpu.type, gpu.index))
gpu device: cuda:0
二.CPU和GPU设备上的Tensor
默认情况下创建Tensor是在CPU设备上的,但是可以通过copy_、to、cuda等方法将CPU设备中的Tensor转移到GPU设备上。当然也是可以直接在GPU设备上创建Tensor的。torch.tensor和torch.Tensor的区别是,torch.tensor可以通过device指定gpu设备,而torch.Tensor只能在cpu上创建,否则报错。
1.Tensor从CPU拷贝到GPU上
# 默认创建的tensor是在cpu上创建的
cpu_tensor = torch.Tensor([[1,4,7],[3,6,9],[2,5,8]])
print(cpu_tensor.device)
# 通过to方法将cpu_tensor拷贝到gpu上
gpu_tensor1 = cpu_tensor.to(torch.device("cuda:0"))
print(gpu_tensor1.device)
# 通过cuda方法将cpu_tensor拷贝到gpu上
gpu_tensor2 = cpu_tensor.cuda(torch.device("cuda:0"))
print(gpu_tensor2.device)
# 将gpu_tensor2拷贝到cpu上
gpu_tensor3 = cpu_tensor.copy_(gpu_tensor2)
print(gpu_tensor3.device)
print(gpu_tensor3)
输出结果如下:
cpu
cuda:0
cuda:0
cpu
tensor([[1., 4., 7.],
[3., 6., 9.],
[2., 5., 8.]])
主要说明下这个copy_()方法,实现如下:
def copy_(self, src, non_blocking=False):
......
return _te.Tensor(*(), **{})
就是从src中拷贝元素到self的tensor中,然后返回self。以gpu_tensor3 = cpu_tensor.copy_(gpu_tensor2)为例,就是把gpu中的gpu_tensor2拷贝到cpu中的cpu_tensor中。
2.直接在GPU上创建Tensor
gpu_tensor1 = torch.tensor([[2,5,8],[1,4,7],[3,6,9]], device=torch.device("cuda:0"))
print(gpu_tensor1.device)
# 在gpu设备上创建随机数tensor
print(torch.rand((3,4), device=torch.device("cuda:0")))
# 在gpu设备上创建0值tensor
print(torch.zeros((2,5), device=torch.device("cuda:0")))
输出结果,如下:
cuda:0
tensor([[0.7061, 0.2161, 0.8219, 0.3354],
[0.1697, 0.1730, 0.1400, 0.2825],
[0.1771, 0.0473, 0.8411, 0.2318]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]], device='cuda:0')
3.CUDA Streams
Steam是CUDA命令线性执行的抽象形式,分配给设备的CUDA命令按照入队序列的顺序执行。每个设备都有一个默认的Steam,也可以通过torch.cuda.Stream()创建新的Stream。如果不同Stream中的命令交互执行,那么就不能保证命令绝对按顺序执行。下面的这个例子不同的Stream就可能会产生错误。
cuda = torch.device("cuda")
# 创建默认的stream,A就是使用的默认stream
s = torch.cuda.Stream()
A = torch.randn((1,10), device=cuda)
for i in range(100):
# 在新的stream上对默认的stream上创建的tensor进行求和
with torch.cuda.stream(s):
# 存在的问题是:torch.sum()可能会在torch.randn()之前执行
B = torch.sum(A)
print(B)
这个例子存在的问题是torch.sum()可能会在torch.randn()之前就执行。为了保证Stream中的命令绝对按顺序执行,接下来使用Synchronize同步方法解决上面例子的问题:
cuda = torch.device("cuda")
s = torch.cuda.Stream()
A = torch.randn((1,10), device=cuda)
default_stream = torch.cuda.current_stream()
print("Default Stream: {}".format(default_stream))
# 等待创建A的stream执行完毕
torch.cuda.Stream.synchronize(default_stream)
for i in range(100):
# 在新的stream上对默认的stream上创建的tensor进行求和
with torch.cuda.stream(s):
print("current stream: {}".format(torch.cuda.current_stream()))
B = torch.sum(A)
print(B)
解决问题的思路就是通过torch.cuda.Stream.synchronize(default_stream)等待创建A的stream执行完毕,然后再执行新的Stream中的指令。
除此之外,使用memory_cached方法获取缓存内存的大小,使用max_memory_cached方法获取最大缓存内存的大小,使用max_memory_allocated方法获取最大分配内存的大小。可以使用empty_cache方法释放无用的缓存内存。
三.固定缓冲区
缓存就是当计算机内存不足的时候,就会把内存中的数据存储到硬盘上。固定缓冲区就是说常驻内存,不能把这部分数据缓存到硬盘上。可以直接使用pin_memory方法或在Tensor上直接调用pin_memory方法将Tensor复制到固定缓冲区。为什么要做固定缓冲区呢?目的只有一个,就是把CPU上的固定缓冲区拷贝到GPU上时速度快。Tensor上的is_pinned方法可以查看该Tensor是否加载到固定缓冲区中。
from torch.utils.data._utils.pin_memory import pin_memory
x = torch.Tensor([[1,2,4], [5, 7, 9], [3, 7, 10]])
# 通过pin_memory()方法将x复制到固定缓冲区
y = pin_memory(x)
# 在tensor上直接调用pin_memory()方法将tensor复制到固定缓冲区
z = x.pin_memory()
# id()方法返回tensor的内存地址,pin_memory()返回tensor对象的拷贝,因此内存地址是不同的
print("id: {}".format(id(x)))
print("id: {}".format(id(y)))
print("id: {}".format(id(z)))
# 当tensor放入固定缓冲区后,就可以异步将数据复制到gpu设备上了
a = z.cuda(non_blocking=True)
print(a)
print("is_pinned: {}/{}".format(x.is_pinned(), z.is_pinned()))
输出结果如下所示:
id: 1605289350472
id: 1605969660408
id: 1605969660248
tensor([[ 1., 2., 4.],
[ 5., 7., 9.],
[ 3., 7., 10.]], device='cuda:0')
is_pinned: False/True
说明:通过id()查看对象的内存地址。
四.自动设备感知
1.适配CPU和GPU设备
自动设备感知本质上就是有GPU时就使用GPU,没有GPU时就使用CPU,即一套代码适配CPU和GPU设备。GPU是否存在是通过torch.cuda.is_available()判断的。常见的写法如下:
device = torch.device("cpu")
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
a = torch.tensor([1,2,3], device=device)
print(a)
输出结果如下所示:
tensor([1, 2, 3], device='cuda:0')
2.模型迁移到GPU设备
在Module对象上调用to()方法可以把模型也迁移到GPU设备上,如下所示:
class LinearRegression(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LinearRegression, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
regression = LinearRegression().to(device=device)
for param in regression.parameters():
print(param)
从上述输出参数中可以看到param都是device='cuda:0'上的tensor,所以可以说模型通过to()迁移到GPU设备上了。
参考文献:
[1]PyTorch官网:https://pytorch.org/
[2]PyTorch中文官方教程1.7:https://pytorch.apachecn.org/#/docs/1.7/README
[3]PyTorch GitHub:https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch
[4]TORCH.CUDA:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/cuda.html
[5]CUDA SEMANTICS:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#cuda-semantics
[6]PyTorch深度学习实战
PyTorch中的CUDA操作的更多相关文章
- pytorch中使用cuda扩展
以下面这个例子作为教程,实现功能是element-wise add: (pytorch中想调用cuda模块,还是用另外使用C编写接口脚本) 第一步:cuda编程的源文件和头文件 // mathutil ...
- pytorch中Math operation操作:torch.ger()
torch.ger(vec1, vec2, out=None) → Tensor Outer product of vec1 and vec2. If vec1 is a vector of size ...
- 详解Pytorch中的网络构造,模型save和load,.pth权重文件解析
转载:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/53927068 https://blog.csdn.net/wangdongwei0/article/details/88956527 ...
- PyTorch中的C++扩展
今天要聊聊用 PyTorch 进行 C++ 扩展. 在正式开始前,我们需要了解 PyTorch 如何自定义module.这其中,最常见的就是在 python 中继承torch.nn.Module,用 ...
- PyTorch中的MIT ADE20K数据集的语义分割
PyTorch中的MIT ADE20K数据集的语义分割 代码地址:https://github.com/CSAILVision/semantic-segmentation-pytorch Semant ...
- PyTorch官方中文文档:PyTorch中文文档
PyTorch中文文档 PyTorch是使用GPU和CPU优化的深度学习张量库. 说明 自动求导机制 CUDA语义 扩展PyTorch 多进程最佳实践 序列化语义 Package参考 torch to ...
- PyTorch中ReLU的inplace
0 - inplace 在pytorch中,nn.ReLU(inplace=True)和nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True)中存在inplace字段.该参数的inplace=True的 ...
- pytorch中tensorboardX的用法
在代码中改好存储Log的路径 命令行中输入 tensorboard --logdir /home/huihua/NewDisk1/PycharmProjects/pytorch-deeplab-xce ...
- Pytorch中RoI pooling layer的几种实现
Faster-RCNN论文中在RoI-Head网络中,将128个RoI区域对应的feature map进行截取,而后利用RoI pooling层输出7*7大小的feature map.在pytorch ...
随机推荐
- 一个 curl 配置引发的惨案
问题 这两天想装新版本的 node,发现 nvm 一直报下面这个错误.我反复 Google 了,但是并没有找到一条我能用的. 痛苦 我起初一直怀疑是我用的 zsh-nvm 抽疯,所以今天有空就把它还有 ...
- 前端3JS1
内容概要 溢出属性 定位属性 z-index JavaScript简介 变量与注释 数据类型 内容详情 溢出属性 # 文本内容超出了标签的最大范围 overflow: hidden; 接隐藏文本内容 ...
- iOS全埋点解决方案-采集奔溃
前言 采集应用程序奔溃信息,主要分为以下两种场景: NSException 异常 Unix 信号异常 一.NSException 异常 NSException 异常是 Objectiv ...
- 基于.NetCore开发博客项目 StarBlog - (12) Razor页面动态编译
系列文章 基于.NetCore开发博客项目 StarBlog - (1) 为什么需要自己写一个博客? 基于.NetCore开发博客项目 StarBlog - (2) 环境准备和创建项目 基于.NetC ...
- JS:条件语句2
1.for循环:循环代码块一定的次数 例: for(var i = 0;i<5;i++){ console.log(i); } // 0 1 2 3 4 遍历对象: var arr=[" ...
- vi与vim使用
简介 Vi是一个命令行界面下的文本编辑工具(最早1976年由Bill Joy开发,原名ex),vi 支持就大多数操作系统(最早在BSD上发布)并且功能已经十分强大. 1991年Bram Moolena ...
- 所有人都说Python 简单易学,为何我觉得难?
来谈谈心 记得刚学Python的时候,几乎所有人都说Python 简单易学,而对于编程零基础,只掌握Word和Excel的人来说,感觉真的好难. 学习之前网上的教材看了,Python的书也看了,包括& ...
- gitlab和jenkins做持续集成构建教程
背景介绍 上一个轮回,我花了三篇文章的时间着重向大家介绍了在条件有限的情况下,如果优雅地进行前端发版和迭代.庆七一,热烈庆祝香港回归,人民生活水平越来越好,昨天上午我自掏腰包买了台服务器,决定由冷兵器 ...
- Cf #782 (Div. 2)
A. Red Versus Blue 题意 共有 n 个连续字符 ,其中有 a 个 R ,b 个 B (a+b=n),问怎么排列使 R 的最大连续个数最小,输出一种可能排列 思路 b 个B可以把a个 ...
- 全国30m精度二级分类土地利用数据
数据下载链接:数据下载链接 引言 全国土地利用数据产品是以Landsat TM/ETM/OLI遥感影像为主要数据源,经过影像融合.几何校正.图像增强与拼接等处理后,通过人机交互目视解译的方法,将全国 ...
