Pytorch从0开始实现YOLO V3指南 part4——置信度阈值和非极大值抑制
前一节我们实现了网络的前向传播。这一节我们对检测输出设置目标置信度阈值和进行非极大值抑制。
必要条件:
1.此系列教程的Part1到Part3。
2.Pytorch的基本知识,包括如何使用nn.Module,nn.Sequential,torch.nn.parameter类构建常规的结构
3.numpy的基础知识
此前我们已经建立了一个模型,给定一张输入图片它能产生B*10674*85维的输出向量。B是批中图片的数目,10674是每张图片预测的边界框数目,85是边界框属性数目。
但就像我们在part1中描述的那样,我们必须对输出进行目标置信度阈值化和非极大值抑制,以获得最终剩余的真正检测。为此,我们将在文件util.py中创建一个名为write_results的函数。
- def write_results(prediction, confidence, num_classes, nms_conf = 0.4):
这个函数将prediction、confidence(目标置信度阈值)、num_classes(在我们的示例中是80)和nms_conf (NMS IoU的阈值)作为输入。
目标置信度阈值:
我们的预测张量包含了关于B x 10647个边界框的信息。对于每个目标置信度低于阈值的边界框,我们将它的每个属性(行向量)的值设置为零。
- conf_mask = (prediction[:,:,4] > confidence).float().unsqueeze(2)
- prediction = prediction*conf_mask
执行极大值抑制:
我们现在拥有的是边界框的中心坐标以及高度和宽度,然而使用边界框的对角点更容易计算IOU。因此,我们将框的(center x, center y, height, width)属性转换为(左上角x,左上角y,右下角x,右下角y)。
- box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape)
- box_corner[:,:,0] = (prediction[:,:,0] - prediction[:,:,2]/2)
- box_corner[:,:,1] = (prediction[:,:,1] - prediction[:,:,3]/2)
- box_corner[:,:,2] = (prediction[:,:,0] + prediction[:,:,2]/2)
- box_corner[:,:,3] = (prediction[:,:,1] + prediction[:,:,3]/2)
- prediction[:,:,:4] = box_corner[:,:,:4]
每幅图像中真实检测框的数目可能不同。例如,一批大小为3的图像,其中图像1、2和3分别有5、2、4个真检测值。因此,每次必须对同一个图像进行置信阈值和NMS,而不能对所涉及的操作进行矢量化,必须在预测的第一个维度(包含成批图像的索引)上进行遍历操作。
- batch_size = prediction.size(0)
- write = False
- for ind in range(batch_size):
- image_pred = prediction[ind] #image Tensor
- #confidence threshholding
- #NMS
write标志位用于指示我们是否对output进行了初始化,将会使用一个向量来收集整个批中真实的预测。
循环的开始我们进行数据清理。因为每个边界框行有85个属性,其中80个是类得分。我们只关心类得分最大值的那个,所以会从每行中删除80个类得分,添加具有最大值的类的索引,以及该类的类得分。
- max_conf, max_conf_score = torch.max(image_pred[:,5:5+ num_classes], 1)
- max_conf = max_conf.float().unsqueeze(1)
- max_conf_score = max_conf_score.float().unsqueeze(1)
- seq = (image_pred[:,:5], max_conf, max_conf_score)
image_pred = torch.cat(seq, 1)
我们前面已经将目标置信度得分低于阈值的边界框行属性设置为了0,现在就筛除它们。
- non_zero_ind = (torch.nonzero(image_pred[:,4]))
- try:
- image_pred_ = image_pred[non_zero_ind.squeeze(),:].view(-1,7)
except:- continue
- #For PyTorch 0.4 compatibility
- #Since the above code with not raise exception for no detection
- #as scalars are supported in PyTorch 0.4
- if image_pred_.shape[0] == 0:
- continue
try-except块用于处理没有检测到的情况。在这种情况下,我们使用continue跳过此图像的其余循环体。
接下来,让我们在图像中检测目标。
- #Get the various classes detected in the image
- img_classes = unique(image_pred_[:,-1]) # -1 index holds the class index
因为对于同一个类别可能存在多个正确检测,我们使用一个叫unique的函数来获得给定图片中所有出现的类。
- def unique(tensor):
- tensor_np = tensor.cpu().numpy()
- unique_np = np.unique(tensor_np)
- unique_tensor = torch.from_numpy(unique_np)
- tensor_res = tensor.new(unique_tensor.shape)
- tensor_res.copy_(unique_tensor)
- return tensor_res
之后我们对于每个类进行NMS
- for cls in img_classes:
- #perform NMS
一进入这个循环,首先要做的事情就是提取对于某一特定类别的检测(用变量cls表示)
- #get the detections with one particular class
- cls_mask = image_pred_*(image_pred_[:,-1] == cls).float().unsqueeze(1)
- class_mask_ind = torch.nonzero(cls_mask[:,-2]).squeeze()
- image_pred_class = image_pred_[class_mask_ind].view(-1,7)
- #sort the detections such that the entry with the maximum objectness
- #confidence is at the top
- conf_sort_index = torch.sort(image_pred_class[:,4], descending = True )[1]
- image_pred_class = image_pred_class[conf_sort_index]
- idx = image_pred_class.size(0) #Number of detections
然后我们进行NMS
- for i in range(idx):
- #Get the IOUs of all boxes that come after the one we are looking at
- #in the loop
- try:
- ious = bbox_iou(image_pred_class[i].unsqueeze(0), image_pred_class[i+1:])
- except ValueError:
- break
- except IndexError:
- break
- #Zero out all the detections that have IoU > treshhold
- iou_mask = (ious < nms_conf).float().unsqueeze(1)
- image_pred_class[i+1:] *= iou_mask
- #Remove the non-zero entries
- non_zero_ind = torch.nonzero(image_pred_class[:,4]).squeeze()
- image_pred_class = image_pred_class[non_zero_ind].view(-1,7)
这里我们使用到了一个函数bbox_iou。第一个输入参数是循环体变量i索引处的边界框,第二个输入参数是多行边界框的一个tensor。函数bbox_iou的输出是一个tensor它包含了第一个输入的边界框与第二个输入的所有边界框的IOU。如下:
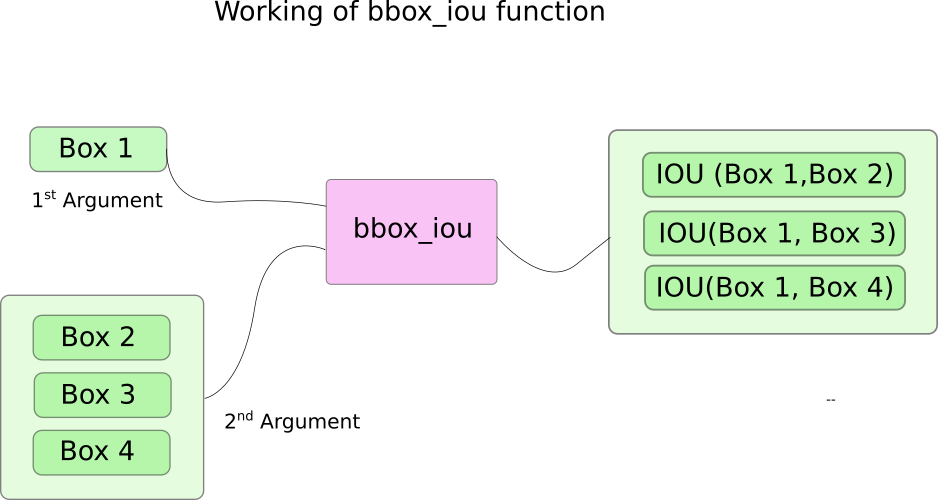
之前我们已经将目标置信度高的边界框放在前面,如果后面的边界框IoU值与前面的相比超过了阈值,那后者就会被删去。
循环体里面下面这行计算IoU。
- ious = bbox_iou(image_pred_class[i].unsqueeze(0), image_pred_class[i+1:])
每轮迭代,如果有任何索引大于i的边界框与第i个边界框的IoU大于阈值nms_thresh,那这个边界框就会被删除。
- #Zero out all the detections that have IoU > treshhold
- iou_mask = (ious < nms_conf).float().unsqueeze(1)
- image_pred_class[i+1:] *= iou_mask
- #Remove the non-zero entries
- non_zero_ind = torch.nonzero(image_pred_class[:,4]).squeeze()
- image_pred_class = image_pred_class[non_zero_ind]
还要注意的是,我们将计算IoU的代码行放在try-catch块中。这是因为此循环按照id进行迭代(image_pred_class中的行数)。但因为我们循环过程中可能会从image_pred_class中删除一些边界框。这样一来,迭代可能会出现索引越界触发IndexError或者image_pred_class[i+1:]返回一个空张量触发ValueError。此时我们可以确定NMS已经无法删除多余的边界框了,从而跳出循环。
计算IoU:
- def bbox_iou(box1, box2):
- """
- Returns the IoU of two bounding boxes
- """
- #Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
- b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[:,0], box1[:,1], box1[:,2], box1[:,3]
- b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[:,0], box2[:,1], box2[:,2], box2[:,3]
- #get the corrdinates of the intersection rectangle
- inter_rect_x1 = torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)
- inter_rect_y1 = torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)
- inter_rect_x2 = torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2)
- inter_rect_y2 = torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2)
- #Intersection area
- inter_area = torch.clamp(inter_rect_x2 - inter_rect_x1 + 1, min=0) * torch.clamp(inter_rect_y2 - inter_rect_y1 + 1, min=0)
- #Union Area
- b1_area = (b1_x2 - b1_x1 + 1)*(b1_y2 - b1_y1 + 1)
- b2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1 + 1)*(b2_y2 - b2_y1 + 1)
- iou = inter_area / (b1_area + b2_area - inter_area)
- return iou
写入预测:
write_results函数输出一个形状为 Dx8 的tensor。这里D是所有图像的真实检测,每个都用一行表示。每个检测有8个属性,即检测所属批次图像的索引、4个角坐标、目标置信度得分、最大置信类得分、该类的索引。
和此前一样,我们等到有一个检测时才初始化输出向量并将后续的检测拼接进来。使用写标志来表示tensor是否已经初始化。在遍历类的循环结束时,我们将检测结果添加到输出tensor中。
- batch_ind = image_pred_class.new(image_pred_class.size(0), 1).fill_(ind)
- #Repeat the batch_id for as many detections of the class cls in the image
- seq = batch_ind, image_pred_class
- if not write:
- output = torch.cat(seq,1)
- write = True
else:- out = torch.cat(seq,1)
- output = torch.cat((output,out))
在函数的末尾,我们检查输出是否已经初始化。如果没有,就意味着这批图像中没有一个检测到。在这种情况下,我们返回0。
- try:
- return output
- except:
- return 0
这就是这一部分所要讲解的内容了。现在我们终于有了一个预测,它以tensor的形式列出了每一个边界框。所以只剩下一件事就是创建一个输入管道来从磁盘读取图像,计算预测,在图像上绘制边界框,然后显示/写入这些图像。这是我们下一部分要做的。
Further Reading
Pytorch从0开始实现YOLO V3指南 part4——置信度阈值和非极大值抑制的更多相关文章
- Pytorch从0开始实现YOLO V3指南 part1——理解YOLO的工作
本教程翻译自https://blog.paperspace.com/how-to-implement-a-yolo-object-detector-in-pytorch/ 视频展示:https://w ...
- Pytorch从0开始实现YOLO V3指南 part3——实现网络前向传播
本节翻译自:https://blog.paperspace.com/how-to-implement-a-yolo-v3-object-detector-from-scratch-in-pytorch ...
- Pytorch从0开始实现YOLO V3指南 part5——设计输入和输出的流程
本节翻译自:https://blog.paperspace.com/how-to-implement-a-yolo-v3-object-detector-from-scratch-in-pytorch ...
- Pytorch从0开始实现YOLO V3指南 part2——搭建网络结构层
本节翻译自:https://blog.paperspace.com/how-to-implement-a-yolo-v3-object-detector-from-scratch-in-pytorch ...
- [DeeplearningAI笔记]卷积神经网络3.6-3.9交并比/非极大值抑制/Anchor boxes/YOLO算法
4.3目标检测 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 3.6交并比intersection over union 交并比函数(loU)可以用来评价对象检测算法,可以被用来进一步改善对 ...
- pytorch实现yolov3(4) 非极大值抑制nms
在上一篇里我们实现了forward函数.得到了prediction.此时预测出了特别多的box以及各种class probability,现在我们要从中过滤出我们最终的预测box. 理解了yolov3 ...
- YOLO v3
yolo为you only look once. 是一个全卷积神经网络(FCN),它有75层卷积层,包含跳跃式传递和降采样,没有池化层,当stide=2时用做降采样. yolo的输出是一个特征映射(f ...
- 深度学习笔记(十三)YOLO V3 (Tensorflow)
[代码剖析] 推荐阅读! SSD 学习笔记 之前看了一遍 YOLO V3 的论文,写的挺有意思的,尴尬的是,我这鱼的记忆,看完就忘了 于是只能借助于代码,再看一遍细节了. 源码目录总览 tens ...
- 一文看懂YOLO v3
论文地址:https://pjreddie.com/media/files/papers/YOLOv3.pdf论文:YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement YOLO系列的 ...
随机推荐
- 【笔记】排查CPU占用过高
本文是该教程视频的笔记 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15T4y1y7eH 1. 问题演示 将演示项目打包放到服务器运行 执行 curl http://localh ...
- Halo 开源项目学习(三):注册与登录
基本介绍 首次启动 Halo 项目时需要安装博客并注册用户信息,当博客安装完成后用户就可以根据注册的信息登录到管理员界面,下面我们分析一下整个过程中代码是如何执行的. 博客安装 项目启动成功后,我们可 ...
- CentOS8更换yum源后出现同步仓库缓存失败的问题
1.错误情况更新yum时报错: 按照网上教程,更换阿里源.清华源都还是无法使用.可参考: centos8更换国内源(阿里源)_大山的博客-CSDN博客_centos8更换阿里源icon-default ...
- umi框架应用服务端SSR,实现数据预渲染
当我们的应用使用服务端渲染的方式时,可能需要把初始化加载的数据例如推荐等不需要用户输入的内容直接渲染获取,也有利于SEO. 上一篇已经实现服务端渲染,本次实现服务端获取数据后在做渲染. 利用getIn ...
- 详解Fiddler Classic过滤、重放、转发HTTP请求
更多干货文章,更多最新文章,欢迎到作者主博客 菜鸟厚非 一.简介 今天介绍一下 Fiddler Classic 对 HTPP 的过滤.重放.转发操作,这在开发中,尤其在微服务中调试中是经常用到的功能, ...
- JZ008和大于等于target的最短数组
title: 长度最小的子数组 题目描述 题目链接:长度最小的子数组.剑指offer008 解题思路 简单滑动窗口题目,需要知道: 窗口左指针移动条件:窗口内总和 ≥ target 即可以不断移动窗口 ...
- Nacos源码系列—服务端那些事儿
点赞再看,养成习惯,微信搜索[牧小农]关注我获取更多资讯,风里雨里,小农等你,很高兴能够成为你的朋友. 项目源码地址:公众号回复 nacos,即可免费获取源码 前言 在上节课中,我们讲解了客户端注册服 ...
- NS2的LEACH仿真出来的nam文件拓扑的节点为什么x=0,且y=0
查看.tr文件和.nam发文件下所有的节点的x,y值都是(0,0),nam图像更没有运行出来 于是我将if { $opt(sc) == "" } {puts "*** N ...
- 最新版2022年任我行管家婆工贸版ERP M7 V22.0进销存财务生产管理软件网络版——云上的集团化制造管理系统
在互联网+制造业的时代背景下,制造业在利用互联网技术进行转型升级的同时,也面临着供应链体系和生产模式的重塑,主要呈现出以下特点: 多元化发展 对外,传统企业正在通过"互联网+"逐步 ...
- 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation - LeetCode
Question 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation Solution 2 1 + 3 * 是((2+1)*3)的后缀(postfix)或逆波兰(reverse ...
