Unity实现A*寻路算法学习2.0
二叉树存储路径节点
1.0中虽然实现了寻路的算法,但是使用List<>来保存节点性能并不够强
寻路算法学习1.0在这里:https://www.cnblogs.com/AlphaIcarus/p/16185843.html
更好的方法是使用堆(或者叫树)来代替列表存储节点
注意:这里使用数组来实现堆,而非使用链表实现堆
这里使用二叉树的方式来存储节点之间的关系
如果在树的末尾添加了一个较小的值,
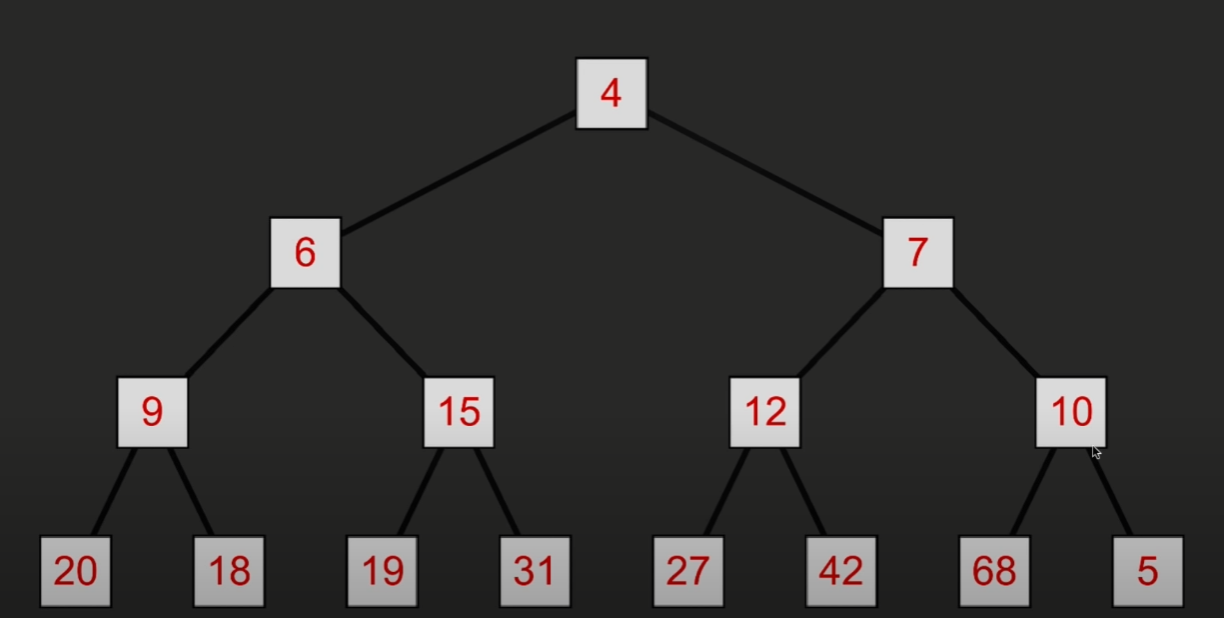
那么需要和父节点比较大小,如果更小,则交换位置

然后再与父节点比较大小,如果小于父节点,则再次交换位置
如果大于父节点,则停止交换
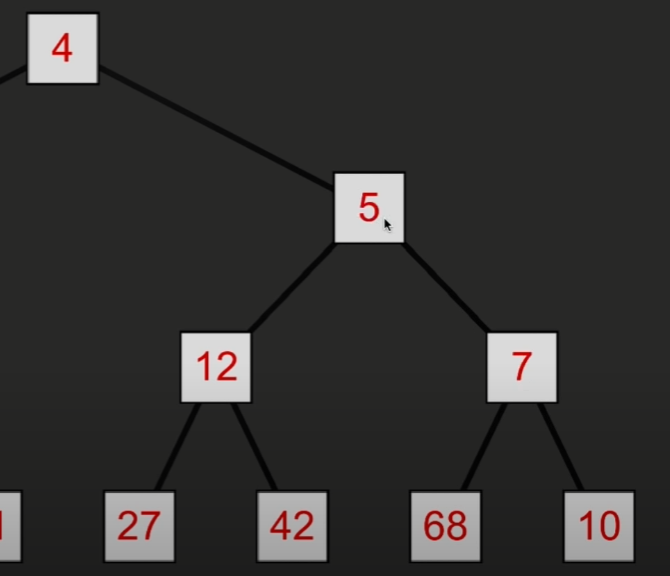
那如果较小的元素被移除了又怎么排序呢?(之前说过因为Clsot值比较后有时需要重新设置父节点)
首先把树末尾的节点数据添加到树顶
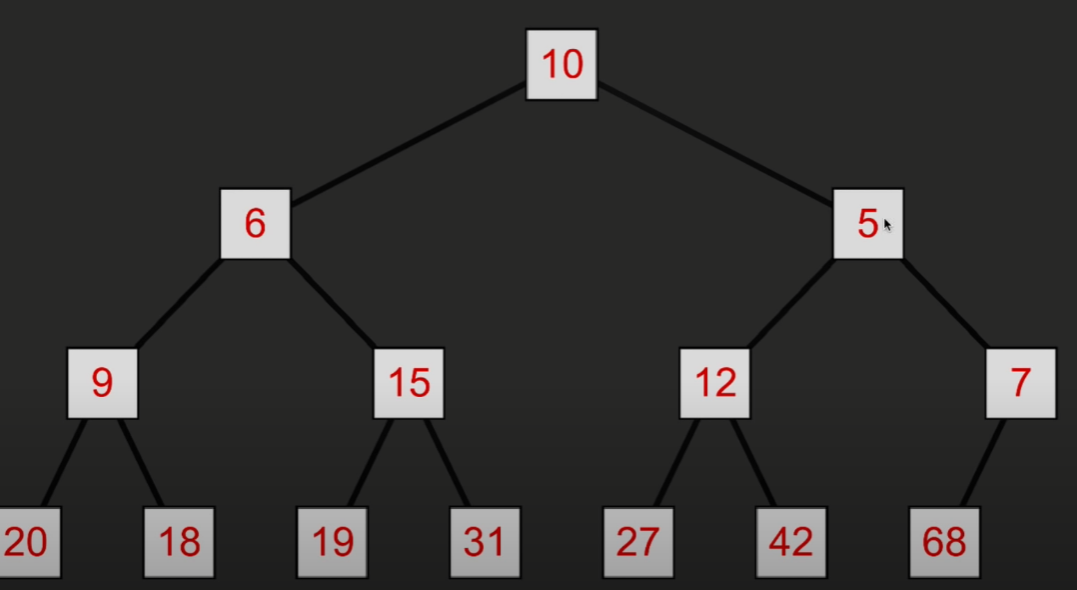
然后与两个子节点比较大小,和更小的那一个交换位置
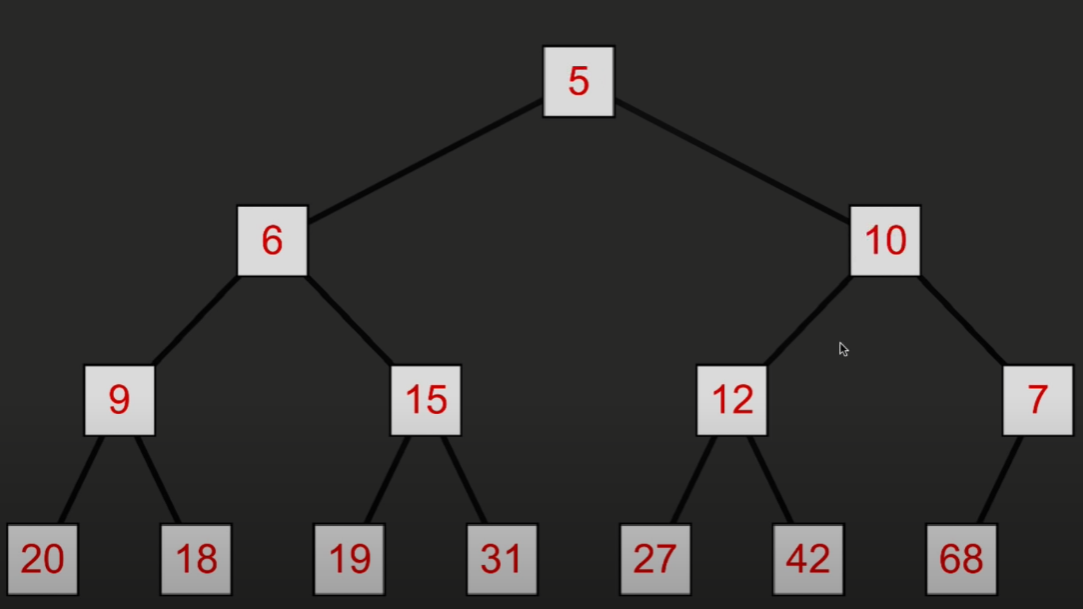
然后再与两个子节点比较大小,直到两个子节点都更大
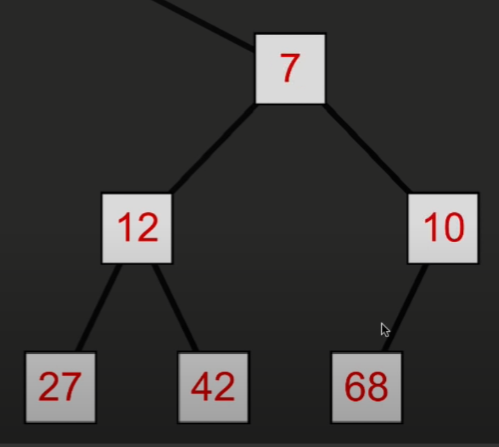
那么如何获取相关的节点呢?这里的数字表示第几个节点而不是存储的具体数据
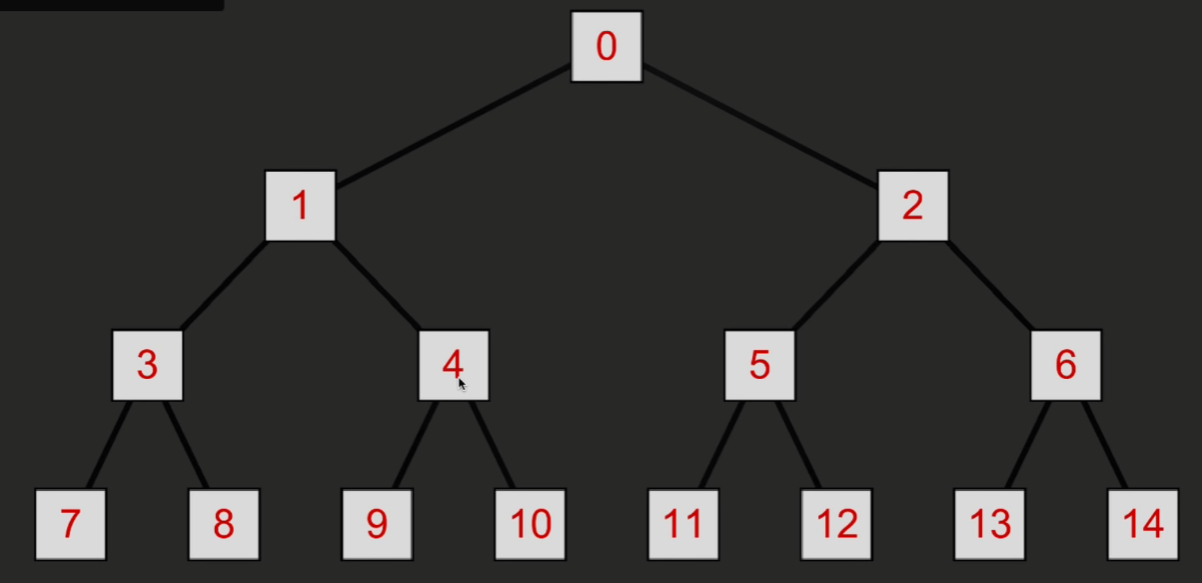
可以发现以下关系
如果获取某个节点 n (第 n 个节点)
那么该节点的父节点为 ( n - 1) / 2
左子节点为 2n + 1
右子节点为 2n + 2
在Unity中应用
新建脚本Heap,这是一个数据类型,用来代替List类型,由数组构成
public class Heap<T> where T : IHeapItem<T> //继承了该接口之后,需要实现数据类型T比较大小的方法{T[] items; //泛型数组,可以为任何类型的数据int currentItemCount; //当前总共有多少元素public int Count //属性,访问返回元素个数{get { return currentItemCount; }}public Heap(int maxHeapSize) //构造器{items = new T[maxHeapSize];}public void Add(T item) //添加新元素的方法{item.HeapIndex = currentItemCount;items[currentItemCount] = item; //末尾添加新元素SortUp(item); //排序currentItemCount++; //元素总数+1}public T RemoveFirt() //获取堆顶部元素并移除{T firstItem = items[0]; //取得顶部元素currentItemCount--; //元素总数-1items[0] = items[currentItemCount]; //将最后一个元素移到顶部items[0].HeapIndex = 0; //将该元素的索引设为0,即第一个元素SortDown(items[0]); //下沉元素return firstItem; //返回取得的顶部元素}public void UpdateItem(T item){SortUp(item);}public bool Contains(T item) //判断是否包含元素{return Equals(items[item.HeapIndex], item);}void SortDown(T item) //下沉元素{while (true) //一直循环,直到值小于左右子树或到最后位置{int childIndexLeft = item.HeapIndex * 2 + 1; //左子树的索引int childIndexRight = item.HeapIndex * 2 + 2; //右子树的索引int swapIndex = 0;if (childIndexLeft < currentItemCount) //{swapIndex = childIndexLeft;if (childIndexRight < currentItemCount){if (items[childIndexLeft].CompareTo(items[childIndexRight]) < 0){swapIndex = childIndexRight;}}if (item.CompareTo(items[swapIndex]) < 0){Swap(item, items[swapIndex]);}else{return;}}else{return;}}}private void SortUp(T item) //上浮元素{int parentIndex = (item.HeapIndex - 1) / 2; //父节点的位置while (true) //循环直至数据比父节点大{T parentItem = items[parentIndex];if (item.CompareTo(parentItem) > 0) //如果新的数据比父节点更小(f值更小){Swap(item, parentItem); //交换位置}else{break;}parentIndex = (item.HeapIndex - 1) / 2; //下次循环前再次验证父节点索引}}private void Swap(T itemA, T itemB) //交换数组中两个元素的位置{items[itemA.HeapIndex] = itemB;items[itemB.HeapIndex] = itemA;int itemAIndex = itemA.HeapIndex;itemA.HeapIndex = itemB.HeapIndex;itemB.HeapIndex = itemAIndex;}}public interface IHeapItem<T> : IComparable<T> //接口,Heap必须实现该接口,IHeapItem继承可比较接口{int HeapIndex { get; set; }}
接下来是Node
public class Node : IHeapItem<Node> //继承接口,需要实现能够比较Node大小的方法{......private int heapIndex; //声明节点的索引......public int HeapIndex //属性{get { return heapIndex; }set { heapIndex = value; }}public int CompareTo(Node needToCompare) //实现的比较大小的方法{//通过比较 F 值的大小,来判断节点的大小int compare = FCost.CompareTo(needToCompare.FCost);if (compare == 0){compare = hCost.CompareTo(needToCompare.hCost);}return -compare;}}
接下来是PathFinding
public class PathFinding : MonoBehaviour{......private void Update(){if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space)){//分别注释方法,运行后比较两个方法寻找相同路径所需的时间//FindPath(seeker.position, target.position); //之前使用List的方法FindPathHeap(seeker.position, target.position); //新的使用Heap的方法}}......private void FindPathHeap(Vector3 startPos, Vector3 targetPos){Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); //计时器sw.Start();Node startNode = grid.NodeFromWorldPos(startPos); //输入空间坐标,计算出处于哪个节点位置Node targwtNode = grid.NodeFromWorldPos(targetPos);//这里将List替换为了Heap,初始化HeapHeap<Node> openSet = new Heap<Node>(grid.MaxSize); //用于存储需要评估的节点HashSet<Node> closedSet = new HashSet<Node>(); //用于存储已经评估的节点openSet.Add(startNode);while (openSet.Count > 0) //如果还有待评估的节点{Node currentNode = openSet.RemoveFirt(); //获取其中一个待评估的节点closedSet.Add(currentNode); //将该节点加入已评估的节点,之后不再参与评估if (currentNode == targwtNode) //如果该节点为目标终点,就计算出实际路径并结束循环{sw.Stop();print("Path found: " + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds + "ms");RetracePath(startNode, targwtNode);return;}//如果该节点不是目标点,遍历该点周围的所有节点foreach (Node neighbor in grid.GetNeighbors(currentNode)){//如果周围某节点不能行走 或 周围某节点已经评估,为上一个节点,则跳过// 说明某节点已经设置父节点if (!neighbor.walkable || closedSet.Contains(neighbor)){continue;}//计算前起始点前往某节点的 gCost 值,起始点的 gCost 值就是0//经过循环这里会计算周围所有节点的g值int newMovementCostToNeighbor = currentNode.gCost + GetDinstance(currentNode, neighbor);//如果新路线 gCost 值更小(更近), 或 某节点没有评估过(为全新的节点)if (newMovementCostToNeighbor < neighbor.gCost || !openSet.Contains(neighbor)){neighbor.gCost = newMovementCostToNeighbor; //计算某节点gCostneighbor.hCost = GetDinstance(neighbor, targwtNode); //计算某节点hCostneighbor.parent = currentNode; //将中间节点设为某节点的父节点//如果存在某节点gCost更小的节点,会重新将中间节点设为某节点父节点if (!openSet.Contains(neighbor)) //如果某节点没有评估过{openSet.Add(neighbor); //将某节点加入待评估列表,在下一次循环进行评估,}}}}}......}
接下来是MyGrid
public class MyGrid : MonoBehaviour{public bool onlyPlayPathGizmos; //是否只绘制路径,便于观察......void Start(){nodeDiameter = nodeRadius * 2;gridSizeX = Mathf.RoundToInt(gridWorldSize.x / nodeDiameter); //计算出x轴方向有多少个节点gridSizeY = Mathf.RoundToInt(gridWorldSize.y / nodeDiameter); //计算出z轴方向有多少个节点CreateGrid();}public int MaxSize //属性,返回地图路径点的数量{get { return gridSizeX * gridSizeY; }}......private void OnDrawGizmos(){Gizmos.DrawWireCube(transform.position, new Vector3(gridWorldSize.x, 1, gridWorldSize.y));if (grid != null){Node playerNode = NodeFromWorldPos(player.position);if (onlyPlayPathGizmos){//只绘制路径if (path != null){foreach (Node node in path){Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;Gizmos.DrawCube(node.worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - 0.1f));}}}else //绘制地图所有点和路径{foreach (Node node in grid){......}}}}}
接下来为了体现两个方法的耗时差距
修改一下地图的大小和节点的大小
运行结果:
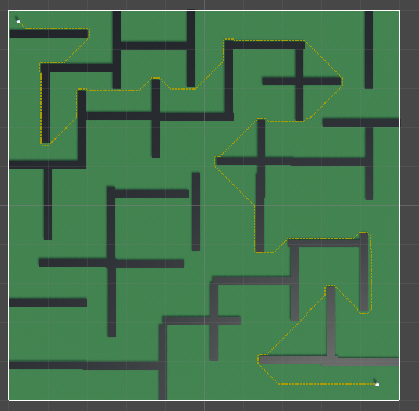
使用Heap的耗时
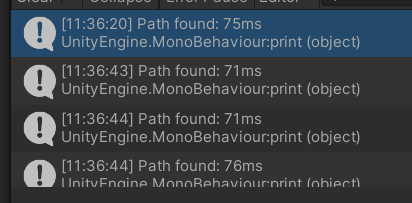
使用List的耗时
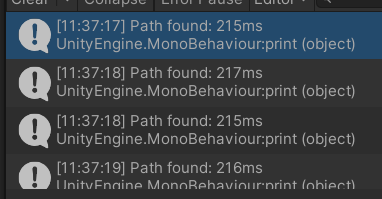
可以看见速度大概提高了三倍
Unity实现A*寻路算法学习2.0的更多相关文章
- Unity实现A*寻路算法学习1.0
一.A*寻路算法的原理 如果现在地图上存在两点A.B,这里设A为起点,B为目标点(终点) 这里为每一个地图节点定义了三个值 gCost:距离起点的Cost(距离) hCost:距离目标点的Cost(距 ...
- A* 寻路算法学习
代码小记 #include <iostream> #include <list> struct POINT { int X; int Y; }; // G: 起点到当前点的成本 ...
- A星寻路算法入门(Unity实现)
最近简单学习了一下A星寻路算法,来记录一下.还是个萌新,如果写的不好,请谅解.Unity版本:2018.3.2f1 A星寻路算法是什么 游戏开发中往往有这样的需求,让玩家控制的角色自动寻路到目标地点, ...
- 基于Unity的A星寻路算法(绝对简单完整版本)
前言 在上一篇文章,介绍了网格地图的实现方式,基于该文章,我们来实现一个A星寻路的算法,最终实现的效果为: 项目源码已上传Github:AStarNavigate 在阅读本篇文章,如果你对于里面提到的 ...
- cocos2d-x学习日志(13) --A星寻路算法demo
你是否在做一款游戏的时候想创造一些怪兽或者游戏主角,让它们移动到特定的位置,避开墙壁和障碍物呢?如果是的话,请看这篇教程,我们会展示如何使用A星寻路算法来实现它! A星算法简介: A*搜寻算法俗称A星 ...
- js实现A*寻路算法
这两天在做百度前端技术学院的题目,其中有涉及到寻路相关的,于是就找来相关博客进行阅读. 看了Create Chen写的理解A*寻路算法具体过程之后,我很快就理解A*算法的原理.不得不说作者写的很好,通 ...
- A*寻路算法的探寻与改良(二)
A*寻路算法的探寻与改良(二) by:田宇轩 第二部分:这部分内容主要是使用C语言编程实现A*, ...
- A*寻路算法lua实现
前言:并在相当长的时间没有写blog该,我觉得有点"颓废"该,最近认识到各种同行,也刚刚大学毕业,我认为他们是优秀的.认识到与自己的间隙,有点自愧不如.我没有写blog当然,部分原 ...
- 如何在Cocos2D游戏中实现A*寻路算法(六)
大熊猫猪·侯佩原创或翻译作品.欢迎转载,转载请注明出处. 如果觉得写的不好请告诉我,如果觉得不错请多多支持点赞.谢谢! hopy ;) 免责申明:本博客提供的所有翻译文章原稿均来自互联网,仅供学习交流 ...
随机推荐
- synchronized和 synchronized 了解偏向锁、轻量级锁、重量级锁的概念以及升级机制、以及和ReentrantLock的区别。
并发 synchronized 了解偏向锁.轻量级锁.重量级锁的概念以及升级机制.以及和ReentrantLock的区别. https://www.cnblogs.com/deltadeb ...
- redis 为什么是单线程的?
一.Redis为什么是单线程的? 因为Redis是基于内存的操作,CPU不是Redis的瓶颈,Redis的瓶颈最有可能是机器内存的大小或者网络带宽.既然单线程容易实现,而且CPU不会成为瓶颈,那就顺理 ...
- 转载:23种常用设计模式的UML类图
转载至:https://www.cnblogs.com/zytrue/p/8484806.html 23种常用设计模式的UML类图 本文UML类图参考<Head First 设计模式>(源 ...
- remote debug 的详细配置
一.remote debug 的简单介绍 何为远程debug,项目写完后就需要进入到测试环节,将代码打包发布到测试环境(服务器)上.这时候测试人员测试出一个缺陷(bug).由于代码已经发布到测试环境, ...
- 学习Puppet(三)
一.相关概念: 1. puppet基于C/S架构,使用ruby编写,在类UNIX平台上集中配置管理系统,它可以管理配置文件.用户.cron任务.软件包.系统服务. 2. puppet把系统实体称为 ...
- centos云服务器配置redis外网可访问
找到这行,注释 bind 127.0.0.1 #bind 127.0.0.1 找到这行,修改 protected-mode yes protected-mode no 重启服务 ./redis-ser ...
- python 保存图片被截断
运行如下代码发现横坐标属性值被截断 plt.savefig('D:\\project\\python\\zhifangtu\\a.png') plt.show() plt.savefig('D:\\p ...
- mysql学习 | LeetCode数据库简单查询练习
力扣:https://leetcode-cn.com/ 力扣网数据库练习:https://leetcode-cn.com/problemset/database/ 文章目录 175. 组合两个表 题解 ...
- 二十二、导入DXF文件
x
- Canvas 与 SVG
什么是SVG? 引用w3c的一段话就是: SVG 指可伸缩矢量图形 (Scalable Vector Graphics) SVG 用来定义用于网络的基于矢量的图形 SVG 使用 XML 格式定义图形 ...
