Python学习系列(四)Python 入门语法规则2
Python学习系列(四)Python 入门语法规则2
2017-4-3 09:18:04
编码和解码
- Unicode、gbk,utf8之间的关系
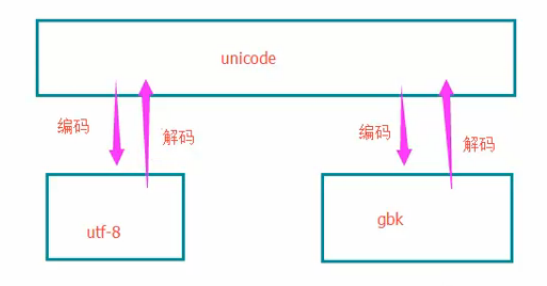
2、对于py2.7,
如果utf8>gbk,
utf8解码成Unicode,再将unicode编码成gbk
对于py3.5
如果utf8>gbk,
utf8 直接编码成gbk(中间那一步直接被优化了)
3、很多时候,这个可以直接跳过,只有当编码出下问题的时候,再考虑这个知识点
二、运算符
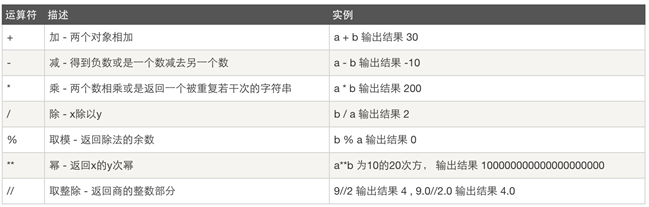
1、算数运算:
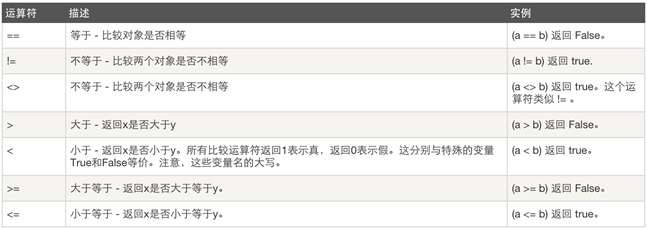
2、比较运算:
3、赋值运算:

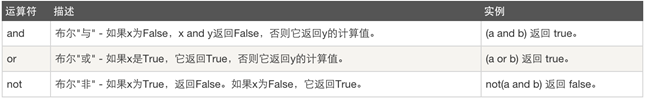
4、逻辑运算:
5、成员运算:
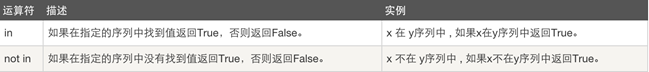
#example:1
r1="Bob is a boy"
r2= "boy" in r1
print(r2)
#example:1
classroom=["Bob","Lucy","Sb"]
r2= "Sb" in classroom
print(r2)
注意examp1和example2的区别
三、
四、基本数据类型
1、整型
a. n1=123 n2=345 print(n1+n2) print(n1.__add__(n2)) n1=123 b.获取二进制的最短位数 n=255 num=n.bit_length() print(num)
example
2、逻辑值(布尔值)
3、字符串
a.python的字符串内建函数
name='lucy'
n1=name.capitalize()
n2=name.center(20,'*')
name='lucy is a bbb lucy is a bbb'
n3=name.count('b',0,38)
n4=name.endswith('y',1,4)
name='lucy\t\t999'
n5=name.expandtabs(tabsize=34)
name='lucy is a girl'
n6=name.find('ii')
s=['lucy','is','a','girl']
n7='**'.join(s)
s=" lucy"
n8=s.lstrip()
s='lucy is a girl'
n9=s.partition('is')
n10=s.replace('cy', 'lu')
print(s)
print(n10)
b.字符串的常用功能
1)索引
s='lucy'
print(s[0])
print(s[1])
print(s[2])
print(s[3])
l=len(s) #获取长度
print(l)
2)切片
s='lucy'
l=s[0:4]
print(s[0:2])
print(l)
s='lucy'
star=0
while star<len(s):
temp = s[star]
star+=1
print(temp)
#example:2
name='abcdefghijklmeopq'
print (name)
name_new=name.upper()
print(name_new)
print(type(name)) #通过type获取 类型
example
字符串方法是从python1.6到2.0慢慢加进来的——它们也被加到了Jython中。
这些方法实现了string模块的大部分方法,如下表所示列出了目前字符串内建支持的方法,所有的方法都包含了对Unicode的支持,有一些甚至是专门用于Unicode的。
|
方法 |
描述 |
|
把字符串的第一个字符大写 |
|
|
返回一个原字符串居中,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
|
|
返回 str 在 string 里面出现的次数,如果 beg 或者 end 指定则返回指定范围内 str 出现的次数 |
|
|
以 encoding 指定的编码格式解码 string,如果出错默认报一个 ValueError 的 异 常 , 除 非 errors 指 定 的 是 'ignore' 或 者'replace' |
|
|
以 encoding 指定的编码格式编码 string,如果出错默认报一个ValueError 的异常,除非 errors 指定的是'ignore'或者'replace' |
|
|
检查字符串是否以 obj 结束,如果beg 或者 end 指定则检查指定的范围内是否以 obj 结束,如果是,返回 True,否则返回 False. |
|
|
把字符串 string 中的 tab 符号转为空格,tab 符号默认的空格数是 8。 |
|
|
检测 str 是否包含在 string 中,如果 beg 和 end 指定范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内,如果是返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1 |
|
|
跟find()方法一样,只不过如果str不在 string中会报一个异常. |
|
|
如果 string 至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或数字则返 回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母则返回 True, 否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 只包含十进制数字则返回 True 否则返回 False. |
|
|
如果 string 只包含数字则返回 True 否则返回 False. |
|
|
如果 string 中包含至少一个区分大小写的字符,并且所有这些(区分大小写的)字符都是小写,则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 中只包含数字字符,则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 中只包含空格,则返回 True,否则返回 False. |
|
|
如果 string 是标题化的(见 title())则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
如果 string 中包含至少一个区分大小写的字符,并且所有这些(区分大小写的)字符都是大写,则返回 True,否则返回 False |
|
|
以 string 作为分隔符,将 seq 中所有的元素(的字符串表示)合并为一个新的字符串 |
|
|
返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
|
|
转换 string 中所有大写字符为小写. |
|
|
截掉 string 左边的空格 |
|
|
maketrans() 方法用于创建字符映射的转换表,对于接受两个参数的最简单的调用方式,第一个参数是字符串,表示需要转换的字符,第二个参数也是字符串表示转换的目标。 |
|
|
返回字符串 str 中最大的字母。 |
|
|
返回字符串 str 中最小的字母。 |
|
|
有点像 find()和 split()的结合体,从 str 出现的第一个位置起,把 字 符 串 string 分 成 一 个 3 元 素 的 元 组 (string_pre_str,str,string_post_str),如果 string 中不包含str 则 string_pre_str == string. |
|
|
把 string 中的 str1 替换成 str2,如果 num 指定,则替换不超过 num 次. |
|
|
类似于 find()函数,不过是从右边开始查找. |
|
|
类似于 index(),不过是从右边开始. |
|
|
返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 |
|
|
string.rpartition(str) |
类似于 partition()函数,不过是从右边开始查找. |
|
删除 string 字符串末尾的空格. |
|
|
以 str 为分隔符切片 string,如果 num有指定值,则仅分隔 num 个子字符串 |
|
|
按照行('\r', '\r\n', \n')分隔,返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表,如果参数 keepends 为 False,不包含换行符,如果为 True,则保留换行符。 |
|
|
检查字符串是否是以 obj 开头,是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果beg 和 end 指定值,则在指定范围内检查. |
|
|
在 string 上执行 lstrip()和 rstrip() |
|
|
翻转 string 中的大小写 |
|
|
返回"标题化"的 string,就是说所有单词都是以大写开始,其余字母均为小写(见 istitle()) |
|
|
根据 str 给出的表(包含 256 个字符)转换 string 的字符, 要过滤掉的字符放到 del 参数中 |
|
|
转换 string 中的小写字母为大写 |
|
|
返回长度为 width 的字符串,原字符串 string 右对齐,前面填充0 |
|
|
isdecimal()方法检查字符串是否只包含十进制字符。这种方法只存在于unicode对象。 |
4、列表
创建列表
name='lucy'
age=28
name_list=["bob",'jon','lucy']
print(name_list)
print(name_list[0]) #索引
print(name_list[0:2])#切片
name_list.append('alex') #追加
name_list.append('smart')
name_list.append('smart')
n1=name_list.count('smart')#统计出现的次数
temp=[111,222,333]
name_list.extend(temp)#批量的添加数据
n2=name_list.index('jon')
print(n2)
example
python的列表内建函数
class list(object):
"""
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
"""
def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.append(object) -- append object to end #追加"""
pass
def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value#统计出现的次数"""
return 0
def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.extend(iterable) -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable #批量的添加数据"""
pass
def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
查找索引值
"""
return 0
def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index
插入数据
"""
pass
def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last).
Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
移除列表里面的最后一个值,并可以赋值给返回值
"""
pass
def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.remove(value) -- remove first occurrence of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
移除指定值
"""
pass
def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE*
顺序翻转
"""
pass
def sort(self, cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) -- stable sort *IN PLACE*;
cmp(x, y) -> -1, 0, 1
简单的排序
"""
pass
def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass
def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """
pass
def __delslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__delslice__(i, j) <==> del x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __iadd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iadd__(y) <==> x+=y """
pass
def __imul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__imul__(y) <==> x*=y """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of list.__init__
"""
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __reversed__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the list """
pass
def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass
def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """
pass
def __setslice__(self, i, j, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__setslice__(i, j, y) <==> x[i:j]=y
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.__sizeof__() -- size of L in memory, in bytes """
pass
__hash__ = None
list
python的列表内建函数
5、元祖(不能增,删,改)
lass tuple(object):
"""
tuple() -> empty tuple
tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
"""
def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value
计算元素出现的个数
"""
return 0
def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
索引位置信息
"""
return 0
def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of tuple.__init__
"""
tuple() -> empty tuple
tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__sizeof__() -- size of T in memory, in bytes """
pass
tuple
python元祖内建立函数
a.元祖和列表几乎一样
b.列表时刻可以修改的,元祖是不能修改的
c.元祖的创建
name_tuple=('lucy','bob')
#索引
print(name_tuple[0])
#len
print(name_tuple[len(name_tuple)-1])
#切片
print(name_tuple[0:1])
#for
for i in name_tuple:
print(i)
#删除 不支持
#del name_tuple[1]
print(name_tuple)
6、字典
class dict(object):
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
"""
def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 清除内容 """
""" D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """
pass
def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 浅拷贝 """
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """
pass
@staticmethod # known case
def fromkeys(S, v=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
dict.fromkeys(S[,v]) -> New dict with keys from S and values equal to v.
v defaults to None.
"""
pass
def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 根据key获取值,如果key不存在,可以指定一个默认值,d是默认值 """
""" D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None. """
pass
def has_key(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 是否有key """
""" D.has_key(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """
return False
def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有项的列表形式 """
""" D.items() -> list of D's (key, value) pairs, as 2-tuples """
return []
def iteritems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 项可迭代 """
""" D.iteritems() -> an iterator over the (key, value) items of D """
pass
def iterkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" key可迭代 """
""" D.iterkeys() -> an iterator over the keys of D """
pass
def itervalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" value可迭代 """
""" D.itervalues() -> an iterator over the values of D """
pass
def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有的key列表 """
""" D.keys() -> list of D's keys """
return []
def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 获取并在字典中移除 """
"""
D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.
If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised
"""
pass
def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 获取并在字典中移除 """
"""
D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a
2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty.
"""
pass
def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 如果key不存在,则创建,如果存在,则返回已存在的值且不修改 """
""" D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D """
pass
def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update
""" 更新
{'name':'alex', 'age': 18000}
[('name','sbsbsb'),]
"""
"""
D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F.
If E present and has a .keys() method, does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k]
If E present and lacks .keys() method, does: for (k, v) in E: D[k] = v
In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k]
"""
pass
def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有的值 """
""" D.values() -> list of D's values """
return []
def viewitems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有项,只是将内容保存至view对象中 """
""" D.viewitems() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items """
pass
def viewkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.viewkeys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys """
pass
def viewvalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.viewvalues() -> an object providing a view on D's values """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __contains__(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__contains__(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """
return False
def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """
pass
__hash__ = None
dict
python字典内建函数
a.字典的每一个元素,都是一个键值对
'''
user_info={
1:"lucy",
2:73,
3:'M'
}
#索引
print(user_info[2])
user_info={
'name':"lucy",
"age":73,
"gender":'M'
}
#索引
print(user_info['name'])
#不能进行
#循环,默认值输出key
for i in user_info:
print(i)
print(user_info.keys())#获取所有的键
print(user_info.values())#获取所有的值
print(user_info.items())#获取所有的键值对
for i in user_info.values():
print(i)
for i,j in user_info.items():
print(i)
print(j)
#get,注意get和索引之间的差别
val=user_info.get('age')#根据key获取值,如果key不存在,可以指定一个默认值,d是默认值
print(val)
val=user_info.get('age11',123)
print(val)
#update更新
test={
'name':'yaun',
"age":24,
'adress':'hb',
'tel':18272163806
}
user_info.update(test)
print(user_info)
#删除
del user_info['name']
print(user_info)
#note:查看对象的类,或对象所具备的的功能
方法一:
temp="lucy"
t=type(tenp)
print(t)
#str,ctr+鼠标左,找到str类,内部所有的方法
方法二:
temp="lucy"
b = dir(temp)
方法三:
help(str)
五、内容补充
内容补充:
一、运算符
二、基本的数据类型
1、int
n1 = 456 # 根据int类,创建了一个对象
n2 = 456 # 根据int类,创建了一个对象
特有的功能表现在:
int类
功能1
功能2
功能3
_int_ #(初始化)
2、str
str()
str类 _init_ #(初始化)
a、创建方式
#无参数,创建空字符串
#一个参数,创建普通字符串
#两个参数,int(字节),编码===》。
n='LUCY'
n1='lucy'
n2=str('lucy')
n3=str()
b、特有功能
n.strip() #两端去除空格
n.startswith()#以。。。开头
n.find()#找到子序列
n.replace(old, new)#将字符串中的某子序列替换成指定值
n.upper()#变大写
n.isalpha()#是,,,吗
c、公共功能
索引:只能取一个元素
切片:可以取多个元素
len: name='湖北' len(name)=2
for:
编码:3.5循环的时候,循环的每一个元素是“字符”
d、bytes和str的转换
name="湖北"
#将字符串转换成字节
b1=bytes(name,encoding='utf-8')
print(b1)
b2=bytes(name,encoding='gbk')
print(b2)
#将字节转换成字符串
n1=str(b1,encoding='utf-8')
print(n1)
n2=str(b2,encoding='gbk')
print(n2)
#=======
n=str()
#创建字符串
#转换成字符串,字节,编码
m=bytes()
#创建字节
#转换成字节,字符串,要变成什么编码字节的类型字节
3、list
元素的‘集合’,列表
list()
list类 _init_ #(初始化)
----------
str—>创建字符串,或者将其他的准换成字符串
----------
list—>创建列表,将其他元素转换成列表
a、创建和转换
1、创建
list=[11,22,33,44,55]
list=list()
list=list([11,22,33,44,55])
2、转换(字符串,元祖、字典都可以转换成列表)
s1='湖北'
l1=list(s1) #for循环,将循环的每一个元素,当做了列表的元素
#print(l1) ['湖', '北'] t2=('lucy','bob','earth')
l2=list(t2)
#print(l2) ['lucy', 'bob', 'earth'] dic={'k1':'lucy','k2':'earth'}
l3=list(dic.keys())
l4=list(dic.items())
print(l3)
b、列表特有的功能
li=list()
new_list=list.append(object)#追加字符串(改变自身)
new_list=list.clear()#清除
new_list=list.extend(iterable)#批量增加,用另外一个可以迭代的 对象扩展到自己的内部
new_list=list.reverse()#翻转,自己内部元素翻转
new_list=list.insert(index, object)#向指定的位置插入一个元素
c、公共功能:
索引:
切片:
4、元组(tuple)
a、创建和转换
t=(11,22,33)
t=tuple(t)
t=tuple([])#字符串,列表,字典都可以
b、特有的方法
count
index
c、嵌套(元素不可修改)
t= (11,22,33)
t= (11,22,['lucy',{'k1':'v1'}])
t[2][1][k1]
e、元祖的特性,(元祖的元素)不可修改,
儿子不能变,孙子可以(可能)变,,,,
#'k2':'123'
t=(11,22,["lucy",{'k1':'v1'}])
#t2=t[2].append('&*&*&') #None
#t[2].append('&*&*&') #(11, 22, ['lucy', {'k1': 'v1'}, '&*&*&'])
t2=t[2][1].update({'k2':''})
t2=t[2][1]['k3']='' #(11, 22, ['lucy', {'k1': 'v1', 'k2': '123', 'k3': '987'}])
整理:
一般字符串,执行一个功能,生成一个新内容,原来内容不变
list,tuple,dict,执行一个功能,自身发生变化
5、字典
a、创建和转换
a={'k1':''} #{'k1': '467'}
a=dict(k1=4324,k2='yuan') #{'k2': 'yuan', 'k1': 4324}
li=['lucy','bob','earth']
new_dict=dict(enumerate(li)) #自动为列表添加key
#{0: 'lucy', 1: 'bob', 2: 'earth'}
b、字典的内部功能
六、新加元素
1、for循环
2、enumrate
'''enumrate 为可迭代的对象添加序号,
自动生成1列,从0开始,自增1,默认值可以更改
'''
list=['电脑','手机','家具','课本']
for key,item in enumerate(list,1):
print(key,item)
temp=int(input('请选择一个'))-1
print(list[temp])
3、range和xrange
python2.7 range,用获取指定范围内的数 range(0,10000)
xrange,只有在循环的时候才会使用,循环一次,+一次,
python3.0 只有range,等同于xrange
'''
#
print(range(1,10))
for i in range(20,1,-3):
print(i)
六、exercise
1、
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。
即: {'k1': 大于66的所有值, 'k2': 小于66的所有值}
2、
查找列表中元素,移除每个元素的空格,并查找以 a或A开头并且以 c 结尾的所有元素。
li = ["alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain"]
tu = ("alec", " aric", "Alex", "Tony", "rain")
dic = {'k1': "alex", 'k2': ' aric', "k3": "Alex", "k4": "Tony"}
3、输出商品列表,用户输入序号,显示用户选中的商品
商品 li = ["手机", "电脑", '鼠标垫', '游艇']
4、购物车
功能要求:
- 要求用户输入总资产,例如:2000
- 显示商品列表,让用户根据序号选择商品,加入购物车
- 购买,如果商品总额大于总资产,提示账户余额不足,否则,购买成功。
- 附加:可充值、某商品移除购物车
5、用户交互,显示省市县三级联动的选择
Python学习系列(四)Python 入门语法规则2的更多相关文章
- Python学习系列之一: python相关环境的搭建
前言 学习python和使用已经一年多了,这段时间抽空整理了一下以前的笔记,方便日后查阅. Python介绍 Python 是一个高层次的结合了解释性.编译性.互动性和面向对象的脚本语言. Pytho ...
- Python学习笔记(四)Python函数的参数
Python的函数除了正常使用的必选参数外,还可以使用默认参数.可变参数和关键字参数. 默认参数 基本使用 默认参数就是可以给特定的参数设置一个默认值,调用函数时,有默认值得参数可以不进行赋值,如: ...
- EJS学习(四)之语法规则下
模版函数 在 EJS 之外,提供了一些额外的模版函数来简化我们的一些工作 GIT:https://github.com/willerce/tmt-ejs-helper css()方法 快速的引用 CS ...
- Python学习系列(四)(列表及其函数)
Python学习系列(四)(列表及其函数) Python学习系列(一)(基础入门) Python学习系列(二)(基础知识) Python学习系列(三)(字符串) 一.基本概念 1,列表是什么? ...
- python学习第四讲,python基础语法之判断语句,循环语句
目录 python学习第四讲,python基础语法之判断语句,选择语句,循环语句 一丶判断语句 if 1.if 语法 2. if else 语法 3. if 进阶 if elif else 二丶运算符 ...
- Python学习系列(二)(基础知识)
Python基础语法 Python学习系列(一)(基础入门) 对于任何一门语言的学习,学语法是最枯燥无味的,但又不得不学,基础概念较繁琐,本文将不多涉及概念解释,用例子进行相关解析,适当与C语言对比, ...
- Python学习系列:目录
Python学习系列(二)Python 编译原理简介 Python学习系列(三)Python 入门语法规则1 Python学习系列(四)Python 入门语法规则2
- Python学习系列(五)(文件操作及其字典)
Python学习系列(五)(文件操作及其字典) Python学习系列(四)(列表及其函数) 一.文件操作 1,读文件 在以'r'读模式打开文件以后可以调用read函数一次性将文件内容全部读出 ...
- python入门灵魂5问--python学习路线,python教程,python学哪些,python怎么学,python学到什么程度
一.python入门简介 对于刚接触python编程或者想学习python自动化的人来说,基本都会有以下python入门灵魂5问--python学习路线,python教程,python学哪些,pyth ...
随机推荐
- Web自动化测试 二 ----- HTML
HTML 一.结构 html> 与 </html> 之间的文本描述网页 <body> 与 </body> 之间的文本是可见的页面内容 <h1> 与 ...
- mysql中TINYINT的取值范围
在MySQL的数据类型中,Tinyint的取值范围是:带符号的范围是-128到127.无符号的范围是0到255(见官方<MySQL 5.1参考手册>http://dev.mysql.com ...
- C++ 洛谷 P2921 [USACO08DEC]在农场万圣节Trick or Treat on the Farm 题解
P2921 [USACO08DEC]在农场万圣节Trick or Treat on the Farm 分析: 这棵树上有且仅有一个环 两种情况: 1.讨论一个点在环上,如果在则答案与它指向点相同, 2 ...
- 并发编程-concurrent指南-计数器CountDownLatch
java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch 是一个并发构造,它允许一个或多个线程等待一系列指定操作的完成. CountDownLatch 以一个给定的数量初始化.count ...
- 并发编程-concurrent指南-阻塞双端队列BlockingDeque
java.util.concurrent 包里的 BlockingDeque 接口表示一个线程安放入和提取实例的双端队列. BlockingDeque 类是一个双端队列,在不能够插入元素时,它将阻塞住 ...
- 阿里巴巴 -- MySQL DBA 面试题
1.MySQL的复制原理以及流程 (1).先问基本原理流程,3个线程以及之间的关联: (2).再问一致性延时性,数据恢复: (3).再问各种工作遇到的复制bug的解决方法. 2.MySQL中myisa ...
- centos 5.2 php升级
# gedit /etc/yum.repos.d/utterramblings.repo [utterramblings] name=Jason's Utter Ramblings Repo base ...
- shell_chmod与目录权限
此篇文档将讲解关于linux中文件权限常用命令chmod.为了达到一个比较好的效果,我会在需要的地方实际上机验证测试,并截图给朋友们看.我的linux机器装的是(opensuse-11.3),并且以文 ...
- 一个简单的EJB例子
转载自 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_678530f60100hvwy.html 声明:这个Converter的例子应该是J2EE 1.4 Tutorial上面的.不过 ...
- ZIP:GZIP
GZIPInputStream: GZIPInputStream(InputStream in) :使用默认缓冲区大小创建新的输入流. GZIPInputStream(InputStream in, ...
