6、Kubernetes Pod控制器应用进阶
定义pod时,在spec字段中常用的定义字段有哪些?
master ~]# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: containers <[]Object> DESCRIPTION:
List of containers belonging to the pod. Containers cannot currently be
added or removed. There must be at least one container in a Pod. Cannot be
updated. A single application container that you want to run within a pod. FIELDS:
args <[]string>
Arguments to the entrypoint. The docker image's CMD is used if this is not
provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the
container's environment. If a variable cannot be resolved, the reference in
the input string will be unchanged. The $(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped
with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME). Escaped references will never be
expanded, regardless of whether the variable exists or not. Cannot be
updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-command-argument-container/#running-a-command-in-a-shell
command <[]string>
Entrypoint array. Not executed within a shell. The docker image's
ENTRYPOINT is used if this is not provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME)
are expanded using the container's environment. If a variable cannot be
resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. The
$(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME).
Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless of whether the
variable exists or not. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-command-argument-container/#running-a-command-in-a-shell env <[]Object>
List of environment variables to set in the container. Cannot be updated. envFrom <[]Object>
List of sources to populate environment variables in the container. The
keys defined within a source must be a C_IDENTIFIER. All invalid keys will
be reported as an event when the container is starting. When a key exists
in multiple sources, the value associated with the last source will take
precedence. Values defined by an Env with a duplicate key will take
precedence. Cannot be updated. image <string>
Docker image name. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images This field is
optional to allow higher level config management to default or override
container images in workload controllers like Deployments and StatefulSets. imagePullPolicy <string>
Image pull policy. One of Always, Never, IfNotPresent. Defaults to Always
if :latest tag is specified, or IfNotPresent otherwise. Cannot be updated.
More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#updating-images lifecycle <Object>
Actions that the management system should take in response to container
lifecycle events. Cannot be updated. livenessProbe <Object>
Periodic probe of container liveness. Container will be restarted if the
probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes name <string> -required-
Name of the container specified as a DNS_LABEL. Each container in a pod
must have a unique name (DNS_LABEL). Cannot be updated. ports <[]Object>
List of ports to expose from the container. Exposing a port here gives the
system additional information about the network connections a container
uses, but is primarily informational. Not specifying a port here DOES NOT
prevent that port from being exposed. Any port which is listening on the
default "0.0.0.0" address inside a container will be accessible from the
network. Cannot be updated. readinessProbe <Object>
Periodic probe of container service readiness. Container will be removed
from service endpoints if the probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes resources <Object>
Compute Resources required by this container. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-compute-resources-container/ securityContext <Object>
Security options the pod should run with. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/security-context/ More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/ stdin <boolean>
Whether this container should allocate a buffer for stdin in the container
runtime. If this is not set, reads from stdin in the container will always
result in EOF. Default is false. stdinOnce <boolean>
Whether the container runtime should close the stdin channel after it has
been opened by a single attach. When stdin is true the stdin stream will
remain open across multiple attach sessions. If stdinOnce is set to true,
stdin is opened on container start, is empty until the first client
attaches to stdin, and then remains open and accepts data until the client
disconnects, at which time stdin is closed and remains closed until the
container is restarted. If this flag is false, a container processes that
reads from stdin will never receive an EOF. Default is false terminationMessagePath <string>
Optional: Path at which the file to which the container's termination
message will be written is mounted into the container's filesystem. Message
written is intended to be brief final status, such as an assertion failure
message. Will be truncated by the node if greater than bytes. The
total message length across all containers will be limited to 12kb.
Defaults to /dev/termination-log. Cannot be updated. terminationMessagePolicy <string>
Indicate how the termination message should be populated. File will use the
contents of terminationMessagePath to populate the container status message
on both success and failure. FallbackToLogsOnError will use the last chunk
of container log output if the termination message file is empty and the
container exited with an error. The log output is limited to bytes or
lines, whichever is smaller. Defaults to File. Cannot be updated. tty <boolean>
Whether this container should allocate a TTY for itself, also requires
'stdin' to be true. Default is false. volumeDevices <[]Object>
volumeDevices is the list of block devices to be used by the container.
This is a beta feature. volumeMounts <[]Object>
Pod volumes to mount into the container's filesystem. Cannot be updated. workingDir <string>
Container's working directory. If not specified, the container runtime's
default will be used, which might be configured in the container image.
Cannot be updated.
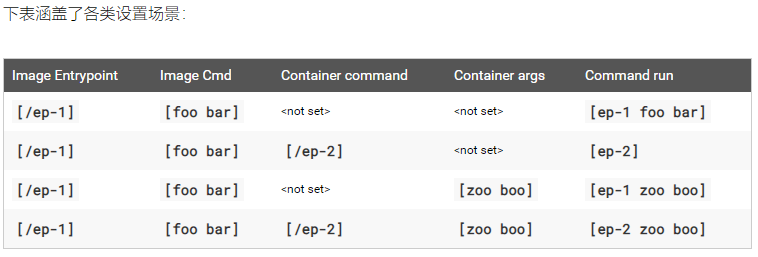
修改镜像中的默认应用:为容器设置启动时要执行的命令及其入参
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-command-argument-container/

Docker 与 Kubernetes中对应的字段名称

标签
一个资源可以拥有多个标签,同一个标签可以被添加至多个资源对象;
标签可以在资源创建时指定,
标签:
key=value
key:字母、数字、_、-、.
value:可以为空,只能字母或数字开头及结尾,中间可使用字母、数字、_、-、.
查看标签
master manifests]# kubectl create -f pod-demo.yaml
pod/pod-demo created
master ~]# kubectl get pods --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
client / Error 12d run=client
client1 / Completed 11d run=client1
client2 / Error 2d7h run=client2
client3 / Error 2d6h run=client3
myapp-5bc569c47d-5cdpw / Running 2d3h pod-template-hash=5bc569c47d,run=myapp
myapp-5bc569c47d-c4gr2 / Running 2d3h pod-template-hash=5bc569c47d,run=myapp
myapp-5bc569c47d-njr5w / Running 2d3h pod-template-hash=5bc569c47d,run=myapp
nginx-deploy-55d8d67cf-hlj9v / Running 12d pod-template-hash=55d8d67cf,run=nginx-deploy
pod-demo / ImagePullBackOff 8m23s app=myapp,tier=frontend
# kubectl get pods -L app //-L选项用于显示指定资源对象类别下的所有资源的对应的标签的值
# kubectl get pods -l app //做标签过滤
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod-demo / ImagePullBackOff 12m
# kubectl get pods -l app --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
pod-demo / ImagePullBackOff 13m app=myapp,tier=frontend
如何打标签
# kubectl label --help //打标签的用法
Usage:
kubectl label [--overwrite] (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME) KEY_1=VAL_1 ... KEY_N=VAL_N [--resource-version=version]
# kubectl label pods pod-demo release=canary //打标签
pod/pod-demo labeled
# kubectl get pods -l app --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
pod-demo / Running 165m app=myapp,release=canary,tier=frontend
# kubectl label pods pod-demo release=stable //强行打标会报错
error: 'release' already has a value (canary), and --overwrite is false
# kubectl label pods pod-demo release=stable --overwrite //此处需要将替换的标签进行覆盖
pod/pod-demo labeled
# kubectl get pods -l app --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
pod-demo / Running 167m app=myapp,release=stable,tier=frontend
标签选择器:
等值关系:=,==,!=
集合关系:
KEY in(VALUE1,VALUE2,...)
KEY notin(VALUE1,VALUE2,...)
KEY 存在此键
!KEY 不存在此键
等值关系示例:
# kubectl get pods -l release=stable --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
pod-demo / Running 172m app=myapp,release=stable,tier=frontend
集合关系示例:
# kubectl get pods -l "release in (stable,beta,alpha)" --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
pod-demo / Running 3h5m app=myapp,release=stable,tier=frontend
# kubectl get pods -l "release notin (stable,beta,alpha)" --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
client / Error 12d run=client
client1 / Completed 12d run=client1
client2 / Error 2d10h run=client2
client3 / Error 2d9h run=client3
myapp-5bc569c47d-5cdpw / Running 2d6h pod-template-hash=5bc569c47d,run=myapp
myapp-5bc569c47d-c4gr2 / Running 2d6h pod-template-hash=5bc569c47d,run=myapp
myapp-5bc569c47d-njr5w / Running 2d6h pod-template-hash=5bc569c47d,run=myapp
nginx-deploy-55d8d67cf-hlj9v / Running 12d pod-template-hash=55d8d67cf,run=nginx-deploy
许多资源支持内嵌字段定义其使用标签选择器
matchLabels:直接给定键值
matchExpressions:基于给定的表达式来定义使用的标签选择器,{key:"KEY",operator:"OPERATOR",values:[VAL1,VAL2,...]},表示意思是:将KEY和VAL1、VAL2通过操作符OPERATOR进行比较;
操作符:
In,Notin:其values字段必须为非空列表;
Exists,NotExists:其values字段必须为空列表。
不但可以为pod打标签,各种对象都可以打标签
# kubectl get nodes --show-labels
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION LABELS
master Ready master 15d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=master,kubernetes.io/os=linux,node-role.kubernetes.io/master=
node01 Ready <none> 13d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=node01,kubernetes.io/os=linux
node02 Ready <none> 15d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=node02,kubernetes.io/os=linux
node03 Ready <none> 13d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=node03,kubernetes.io/os=linux
# kubectl label nodes node01 disktype=ssd //为node01节点打标签
node/node01 labeled
# kubectl get nodes --show-labels
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION LABELS
master Ready master 15d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=master,kubernetes.io/os=linux,node-role.kubernetes.io/master=
node01 Ready <none> 13d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,disktype=ssd,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=node01,kubernetes.io/os=linux
node02 Ready <none> 15d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=node02,kubernetes.io/os=linux
node03 Ready <none> 13d v1.14.2 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=node03,kubernetes.io/os=linux
节点带有标签的好处在于在添加资源时,可以让资源对带有某标签的节点具有倾向性
# kubectl explain pods.spec
nodeSelector <map[string]string>映射值 //节点选择器,可以限定pod运行在哪个节点上
NodeSelector is a selector which must be true for the pod to fit on a node.
Selector which must match a node's labels for the pod to be scheduled on
that node. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
nodeName <string> //节点名称
NodeName is a request to schedule this pod onto a specific node. If it is
non-empty, the scheduler simply schedules this pod onto that node, assuming
that it fits resource requirements.
示例:
pod-demo运行在node02上,如果想让pod-demo运行在node01上,可以在yaml文件中添加标签选择器
# kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
...........
pod-demo 2/2 Running 3 3h57m 10.244.2.10 node02 <none> <none>
master manifests]# vim pod-demo.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-demo
namespace: default
labels:
app: myapp
tier: frontend
spec:
10 containers:
- name: myapp
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v1
- name: busybox
image: busybox:latest
command:
- "/bin/sh"
- "-c"
- "sleep 3600"
19 nodeSelector: //此处要和上面的container对齐,因为这里不是容器的属性,而是pod的属性
disktype: ssd
# kubectl create -f pod-demo.yaml //重新创建pod
# kubectl describe pods pod-demo
Name: pod-demo
Namespace: default
Priority:
PriorityClassName: <none>
Node: node01/192.168.184.142
........
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 2m1s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/pod-demo to node01
annotations:资源也可以使用注解,也是键值类型的
与label不同的地方在于,annotations不能用于挑选资源对象,仅用于为对象提供"元数据"
查看资源注解:
# kubectl describe pod-demo
# kubectl describe pods pod-demo
Name: pod-demo
Namespace: default
Priority:
Node: knode3/10.129.7.224
Start Time: Wed, May :: +
Labels: app=myapp
tier=frontend
Annotations: <none> //此时是空的
Status: Running# kubectl delete -f pod-damo.yaml //先删除pod,然后再yaml文件中添加
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-demo
namespace: default
labels:
app: myapp
tier: frontend
annotations: //此处添加资源注解
zhou/created-by: "cluster admin" //zhou表示组织即由哪个组织添加,created-by是键,cluster admin是值;
spec:# kubectl create -f pod-damo.yaml
# kubectl describe pods pod-demo
Annotations: zhou/created-by: cluster admin //会有此行注解
pod的生命周期:官方参考
pod状态的unknown状态
pod所处的状态信息,是api server跟运行这个pod的节点上kubelet通信,进而获取的pod状态信息。
如果pod所处的node上的kubelet故障,那么api server就无法获取pod的信息,此时pod的节点就是unknown;
创建pod过程详解:
当用户创建pod时,这个请求就会提交给api server,api server会先把创建请求的目标状态保存到etcd中,api server接下来会请求scheduler进行调度(scheduler需要负责挑选一个合理的节点运行pod);如果调度成功,会把调度结果存到etcd中;一旦存到etcd中并完成更新,那么这个请求所调度到的节点,比如这个请求被调度到node2节点,那么node2上的kubelet通过api server中的状态变化得知有一个新任务,此时kubelet会拿到此前用户提交的pod创建清单,kubelet会根据清单在node2上创建并启动pod,无论创建成功或者失败,pod都会有一个当前结果status,这个当前结果状态就会被发送给api server,然后由api server存到etcd中。
pod生命周期的重要行为:
初始化容器:
容器探测:
liveness
readiness
restartpolicy:pod的重启策略
Always,Onfailure,Never,Default to Always
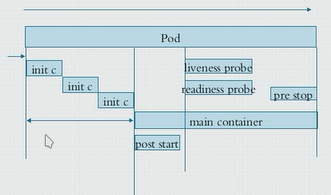
探针类型三种:
ExecAction、TcpSocketAction、HTTPAction
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers
lifecycle <Object>
Actions that the management system should take in response to container
lifecycle events. Cannot be updated. livenessProbe <Object>
Periodic probe of container liveness. Container will be restarted if the
probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes readinessProbe <Object>
Periodic probe of container service readiness. Container will be removed
from service endpoints if the probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.livenessProbe
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: livenessProbe <Object> DESCRIPTION:
Periodic probe of container liveness. Container will be restarted if the
probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes Probe describes a health check to be performed against a container to
determine whether it is alive or ready to receive traffic. FIELDS:
exec <Object>
One and only one of the following should be specified. Exec specifies the
action to take. failureThreshold <integer>
Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after
having succeeded. Defaults to . Minimum value is . httpGet <Object>
HTTPGet specifies the http request to perform. initialDelaySeconds <integer>
Number of seconds after the container has started before liveness probes
are initiated. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes periodSeconds <integer>
How often (in seconds) to perform the probe. Default to seconds. Minimum
value is . successThreshold <integer>
Minimum consecutive successes for the probe to be considered successful
after having failed. Defaults to . Must be for liveness and startup.
Minimum value is . tcpSocket <Object>
TCPSocket specifies an action involving a TCP port. TCP hooks not yet
supported
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.livenessProbe.exec //exec探测测试,直接执行自定义的命令进行探测
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: exec <Object> DESCRIPTION:
One and only one of the following should be specified. Exec specifies the
action to take. ExecAction describes a "run in container" action. FIELDS:
command <[]string>
Command is the command line to execute inside the container, the working
directory for the command is root ('/') in the container's filesystem. The
command is simply exec'd, it is not run inside a shell, so traditional
shell instructions ('|', etc) won't work. To use a shell, you need to
explicitly call out to that shell. Exit status of is treated as
live/healthy and non-zero is unhealthy.
# vim livenes.exec.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: livene-exec-pod
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-exec-container
image: busybox:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","touch /tmp/healthy; sleep 30; rm -rf /tmp/healthy; sleep 3600"]
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test","-e","/tmp/healthy"]
initialDelaySeconds:
periodSeconds:
# kubectl create -f livenes.exec.yaml
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.livenessProbe.tcpSocket
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.livenessProbe.httpGet 使用pod必须要做readinessProbe和livenessProbe的原因: 比如一个pod运行的是一个web站点,从pod启动到web站点就绪可能需要5秒钟甚至更多;
在这几秒钟的时间里,可能pod已经启动起来,但是web站点服务还没有准备好,这是web服务是不能被访问到的;
所以就绪性探测和service调度有着重要的关联性;
service为动态的、有生命周期的pod资源提供了一个固定访问入口端点,因此客户端访问时直接访问service;
service使用标签选择器关联至各pod资源,那么如果创建了一个pod资源,且这个pod资源正好符合标签选择器的选择条件,
那么service就会立即把这个新创建的pod作为后端调度的对象,当用户请求进service时,那么新的请求就有可能被调度至刚才新创建的pod,
但是这个新pod是在刚刚被创建成功时关联进service的,但是pod的web服务很可能还没有就绪,因此请求得到的结果就是失败的;
但是我们期望的是service把请求调度到每一个关联的pod上来时,pod内的服务一定时就绪的,因此如果pod在创建时没有就绪性探测,
那么可能来自service的请求就会失败,所以在pod创建中,readinessProbe是很有必要的;
livenessprobe是探测pod存活,readinessprobe是探测就绪;
示例:
# vim readiness-httpget.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: readiness-httpget-pod
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: readiness-httpget-container
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: http
containerPort:
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
port: http
path: /index.html
initialDelaySeconds:
periodSeconds:
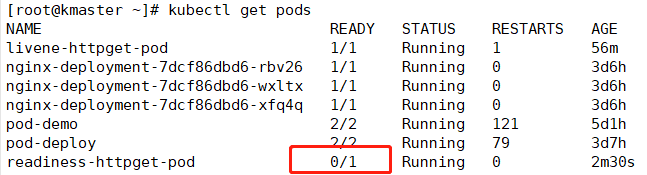
# kubectl create -f readiness-httpget.yaml
# kubectl get pods //此时查看,readiness-httpget-pod是就绪的,但是如果网页文件不存在,那么就不会就绪了
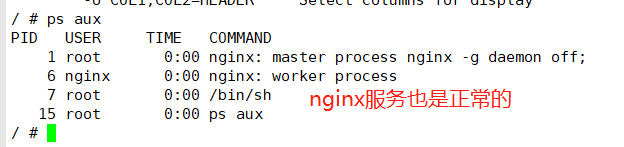
# kubectl exec -it readiness-httpget-pod -- /bin/sh
# rm -f /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html //此时就绪的pod就是0个,此时pod运行,但是网页文件不存在
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.lifecycle //生命周期的启动后钩子和终止前钩子
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: lifecycle <Object> DESCRIPTION:
Actions that the management system should take in response to container
lifecycle events. Cannot be updated. Lifecycle describes actions that the management system should take in
response to container lifecycle events. For the PostStart and PreStop
lifecycle handlers, management of the container blocks until the action is
complete, unless the container process fails, in which case the handler is
aborted. FIELDS:
postStart <Object> //启动后
PostStart is called immediately after a container is created. If the
handler fails, the container is terminated and restarted according to its
restart policy. Other management of the container blocks until the hook
completes. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/container-lifecycle-hooks/#container-hooks
preStop <Object> //终止前
PreStop is called immediately before a container is terminated due to an
API request or management event such as liveness/startup probe failure,
preemption, resource contention, etc. The handler is not called if the
container crashes or exits. The reason for termination is passed to the
handler. The Pod's termination grace period countdown begins before the
PreStop hooked is executed. Regardless of the outcome of the handler, the
container will eventually terminate within the Pod's termination grace
period. Other management of the container blocks until the hook completes
or until the termination grace period is reached. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/container-lifecycle-hooks/#container-hooks
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.lifecycle.postStart
# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.lifecycle.preStop
定义postStop,即在pod启动后立即执行一个钩子
比如镜像中自带了一个httpd运行web服务,但是没有默认的目录和页面存在,因此做一个在pod启动后立即执行钩子;
比如创建一个目录并创建一个网页,然后在启动http,看两个是否能够关联起来
# cat poststart.yaml
apiVerion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: poststart-pod
namepace: default
spec:
containers:
- name: busy-httpd
image: busybox: latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: [/bin/sh","-c","mkdir -p/data/web/html"] /此command是定义pod启动后执行的初始化任务
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","sleep 3600"] //此command是定义容器中的command,当容器启动后,先执行此command,然后执行args命令,然后执行lifecycle的postStart,然而/bin/httpd依赖于上面command的执行结果
#args: ["-f","mkdir -p /data/web/html","-h /data/web/html"] //使用args传递参数,-f是运行在前台,-h是指定表示家目录
kubectl create -f poststart.yaml
6、Kubernetes Pod控制器应用进阶的更多相关文章
- 6and7.Pod控制器应用进阶
Pod控制器应用进阶:imagepullpolicy: 镜像获取策略 Always,Never,IfNoPresent 暴露端口: portslabels 标签可以后期添加修改. ========== ...
- Kubernetes 学习6 Pod控制器应用进阶
一.资源配置清单 1.自主式Pod资源 2.资源的清单格式,大多数清单格式都遵循如下条件: a.一级字段:apiVersion(group/version),kind,metadata(name,na ...
- 05-kubernetes Pod控制器应用进阶
目录 Pod 资源 标签 给资源打标签 标签选择器 Pod 生命周期 实际操作 livenessProbe 实战 livenessProbe exec 测试 livenessProbe httpGet ...
- (六)Kubernetes Pod控制器-ReplicaSet和Deployment和DaemonSet
Pod控制器相关知识 控制器的必要性 自主式Pod对象由调度器调度到目标工作节点后即由相应节点上的kubelet负责监控其容器的存活状态,容器主进程崩溃后,kubelet能够自动重启相应的容器.但对出 ...
- 五,pod控制器应用进阶
目录 Pod 资源 标签 给资源打标签 标签选择器 Pod 生命周期 pod状态探测 livenessProbe 状态探测 livenessProbe exec 测试 livenessProbe ht ...
- Kubernetes 学习7 Pod控制器应用进阶2
一.容器探测器 1.所谓的容器探测无非就是我们在里面设置了一些探针,或者称之为传感器来获取相应的数据作为判定其存活与否或就绪与否的标准,目前k8s所支持的存活性和就绪性探测方式都是一样的. 2.k8s ...
- 3.Pod控制器应用进阶
一.Pod的生命周期 init container -- Post start -- running -- pre stop -- main container 创建Pod经历的过程:->a ...
- kubernetes系列07—Pod控制器详解
本文收录在容器技术学习系列文章总目录 1.Pod控制器 1.1 介绍 Pod控制器是用于实现管理pod的中间层,确保pod资源符合预期的状态,pod的资源出现故障时,会尝试 进行重启,当根据重启策略无 ...
- kubernetes 的pod控制器
转载于网络 pod是kubernetes的最小单元,自主式创建的pod删除就没有了,但是通过资源控制器创建的pod如果删除还会重建.pod控制器就是用于实现代替我们去管理pod的中间层,并帮我们确 ...
随机推荐
- Java语言基础(14)
1 访问控制修饰符(二) 1)public:公共的,可以用来修饰类,属性,构造方法以及方法,被public修饰的类,属性,构造方法以及方法,可以任意的进行访问. 2)private:私有的,可以用来修 ...
- Flutter入门(三)-底部导航+路由
* StatefulWidget 如果想改变页面中的数据就要用到StatefulWidget,之前自定义组件继承的StatelessWidget是不能动态修改页面数据的 //自定义有状态组件 clas ...
- Android蓝牙操作
1.添加蓝牙权限 <uses-permission android:name = "android.permission.BLUETOOTH"/> <!--启用应 ...
- 【SQL Server】使用SQL比较版本号
最近遇到这么一个场景,需要用SQL从表里取出版本号小于'10.2'的所有数据.目前表中以存在的数据中,版本号有两种格式,一个是'X.Y',另一个是'X'.对于SQL Server来说,其没有strin ...
- 适合没有ui的项目的样式
官网: https://www.tailwindcss.cn/
- keras中常用的初始化器
keras中常用的初始化器有恒值初始化器.正态分布初始化器.均匀分布初始化器 恒值初始化器: keras.initializers.Zeros() keras.initializers.Ones() ...
- vue子路由设置、全局组件、局部组件的原生写法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 使用wait/notify实现生产消费模型
public class A { private Deque<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); private int max = 10; ...
- LOJ #2734 Luogu P3615 [JOI2016春季合宿]Toilets (结论、贪心)
题目链接 (loj) https://loj.ac/problem/2734 (luogu) https://www.luogu.org/problem/P3615 题解 嗯,考场上肝了\(3h\)然 ...
- JavaWeb_(Struts2框架)Servlet与Struts区别
JavaWeb_(SSH)使用Servlet实现用户的登陆 传送门 JavaWeb_(SSH)使用Struts框架实现用户的登陆 传送门 MySQL数据库中存在Gary用户,密码为123:第一次登陆时 ...
