IPC——管道
概述
管道通信分为无名管道、有名管道
管道通信的本质
不管是有名管道,还是无名管道,它们的本质其实都是一样的,它们都是内核所开辟的一段缓存空间。进程间通过管道通信时,本质上就是通过共享操作这段缓存来实现,只不过操作这段缓存的方式,是以读写文件的形式来操作的。
无名管道
如何操作无名管道
以读写文件的方式操作无名管道
1)有读写用的文件描述符(API部分讲)
2)读写时会用write、read等文件IO函数。
为什么叫无名管道
既然可以通过“文件描述符”来操作管道,那么它就是一个文件(管道文件),但是无名管道文件比较特殊,它没有文件名,正是因为没有文件名,所有被称为无名管道。
看下open的原型
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
返回值是文件描述符,或者-1(此时errno被设置)
无名管道的例子说明获取文件描述符未必非得使用open函数
注意⚠️:
man手册查询pipe函数的时候,形参可能是int *pipefd。但是这种写法不太直观,所以一般写成int pipe(int pipefd[2])。那么问题来了,int[2]类型和int*类型一样吗?
这要分情况,对于函数参数,他俩没区别
其他情况是有区别的,举个数组指针的例子。
int ar[10]={0} √
int (*p)[10]=&ar √
int **p=&ar ✘
最后一句话是错的,原因就是int*和int[10]类型是不一样的。
无名管道特点
无名管道只能用于亲缘进程之间通信。
由于没有文件名,因此进程没办法使用open打开管道文件,从而得到文件描述符,所以只有一种办法,那就是父进程先调用pipe创建出管道,并得到读写管道的文件描述符。然后再fork出子进程,让子进程通过继承父进程打开的文件描述符,父子进程就能操作同一个管道,从而实现通信。
API
PIPE原型
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[]);
功能
创建一个用于亲缘进程(父子进程)之间通信的无名管道(缓存),并将管道与两个读写文件描述符关联起来。无名管道只能用于亲缘进程之间通信。
参数
缓存地址,缓存用于存放读写管道的文件描述符。从这个参数的样子可以看出,这个缓存就是一个拥有两个元素的int型数组。
1)元素[0]:里面放的是读管道的读文件描述符
2)元素[1]:里面放的是写管道的写文件描述符。
特别需要注意的是,这里的读和写文件描述符,是两个不同的文件描述符。
从这里大家也可以看出,并不是所有的文件描述符,都是通过open函数打开文件得到的。这里无名管道的读、写文件描述符,就是直接在创建管道时得到的,与open没有任何关系。而且这里也根本没办法使用open函数,因为open函数需要文件路径名,无名管道连文件名都没有,所以说根本就没办法使用open来打开文件,返回文件描述符。
返回值
成功返回0,失败则返回-1,并且errno被设置。
父子进程 借助无名管道 单向通信
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h> void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
int ret = ;
int pipefd[] = {};//用于存放管道的读写文件描述符 ret = pipe(pipefd);
if(ret == -) print_err("pipe fail"); ret = fork();
if(ret > )
{
close(pipefd[]);
while()
{
write(pipefd[], "hello", );
sleep();
}
}
else if(ret == )
{
close(pipefd[]);
while()
{
char buf[] = {};
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
read(pipefd[], buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("child, recv data:%s\n", buf);
}
} return ;
}
父子进程 借助无名管道 双向通信
双向通信使用一个管道行不行?
不行,由于继承关系,父子进程都有读文件描述符,父进程发给子进程的消息,子进程不一定能收到,因为可能被父进程抢读了。
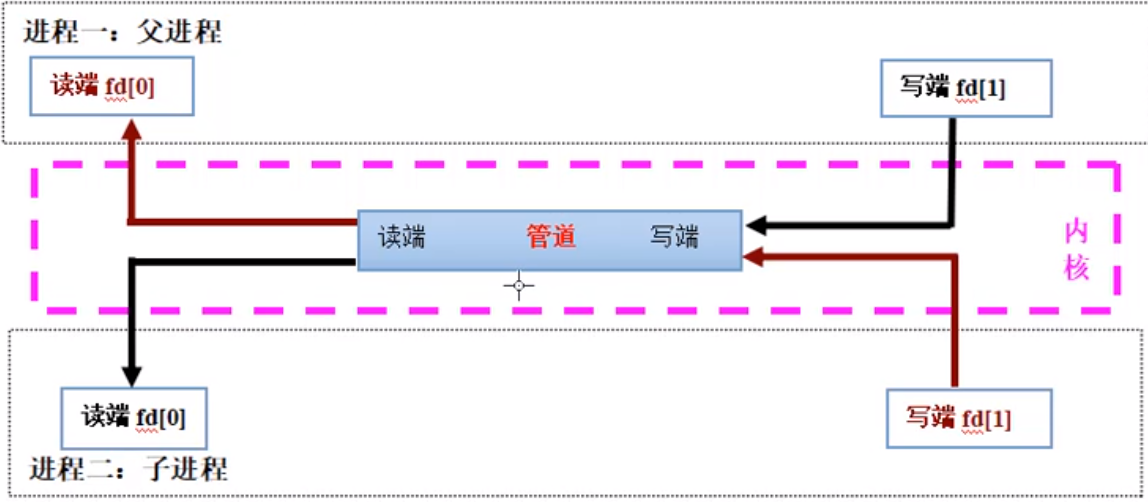
解决办法
使用2个管道,每个管道负责一个方向的通信
父进程创建2个管道,有4个文件描述符。子进程继承父进程的文件描述符,父子进程加起来有8个文件描述符。

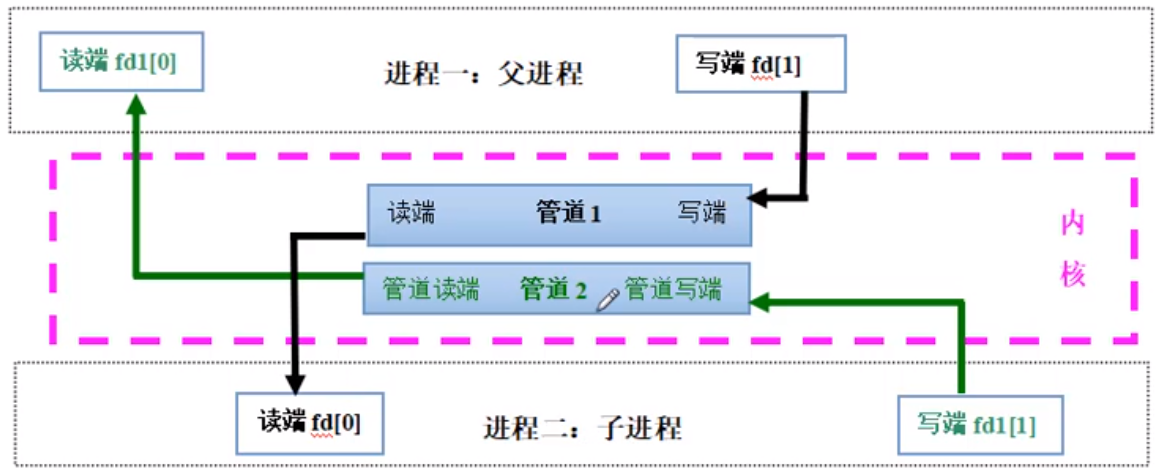
实现代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h> void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
int ret = ;
//[0]:读文件描述符
//[1]:写文件描述符
int pipefd1[] = {};//用于存放管道的读写文件描述符
int pipefd2[] = {};//用于存放管道的读写文件描述符 ret = pipe(pipefd1);
if(ret == -) print_err("pipe fail");
ret = pipe(pipefd2);
if(ret == -) print_err("pipe fail"); ret = fork();
if(ret > )
{
close(pipefd1[]);
close(pipefd2[]);
char buf[] = {};
while()
{
write(pipefd1[], "hello", );
sleep(); bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
read(pipefd2[], buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("parent, recv data:%s\n", buf);
}
}
else if(ret == )
{
close(pipefd1[]);
close(pipefd2[]);
char buf[] = {};
while()
{
sleep();
write(pipefd2[], "world", ); bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
read(pipefd1[], buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("child, recv data:%s\n", buf);
}
} return ;
}
代码里,父子进程中write都写在了read前面。write是非阻塞函数,父子进程中只需要保证至少一个write在前就不会使父子进程阻塞。 如果父子进程read都在write前,则父子进程都会因read而阻塞
有名管道
无名管道因为没有文件名,被称为了无名管道,同样的道理,有名管道之所以叫“有名管道”,是因为它有文件名。也就是说当我们调用相应的API创建好“有名管道”后,会在相应的路径下面看到一个叫某某名字的“有名管道文件”。
有名管道特点
①能够用于非亲缘进程之间的通信
因为有文件名,所以进程可以直接调用open函数打开文件,从而得到文件描述符,不需要像无名管道一样,必须在通过继承的方式才能获取到文件描述符。所以任何两个进程之间,如果想要通过“有名管道”来通信的话,不管它们是亲缘的还是非亲缘的,只要调用open函数打开同一个“有名管道”文件,然后对同一个“有名管道文件”进行读写操作,即可实现通信。
②读管道时,如果管道没有数据的话,读操作同样会阻塞(休眠)
③当进程写一个所有读端都被关闭了的管道时,进程会被内核返回SIGPIPE信号
有名管道使用步骤
①进程调用mkfifo创建有名管道
②open打开有名管道
③read/write读写管道进行通信
对于通信的两个进程来说,创建管道时,只需要一个人创建,另一个直接使用即可。为了保证管道一定被创建,最好是两个进程都包含创建管道的代码,谁先运行就谁先创建,后运行的发现管道已经创建好了,那就直接open打开使用。
API
mkfifo原型
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
功能
创建有名管道文件,创建好后便可使用open打开。
如果是创建普通文件的话,我们可以使用open的O_CREAT选项来创建,比如:open("./file", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0664);
但是对于“有名管道”这种特殊文件,这里只能使用mkfifo函数来创建。
参数
1)pathname:被创建管道文件的文件路径名。
2)mode:指定被创建时原始权限,一般为0664(110110100),必须包含读写权限。
参考:umask、setuid、setgid、sticky bit、chmod、chown 中umask
Linux——文件 中umask
返回值
成功返回0,失败则返回-1,并且errno被设置。
有名管道单项通信
单独启动2个进程通信
p1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h> #define FIFONAME1 "./fifo1"
#define FIFONAME2 "./fifo2" void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int creat_open_fifo(char *fifoname, int open_mode)
{
int ret = -;
int fd = -; ret = mkfifo(fifoname, );
//如果mkfifo函数出错了,但是这个错误是EEXIST,不报这个错误(忽略错误)
if(ret == - && errno!=EEXIST) print_err("mkfifo fail"); fd = open(fifoname, open_mode);
if(fd == -) print_err("open fail"); return fd;
} void signal_fun(int signo)
{
//unlink();
remove(FIFONAME1);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
char buf[] = {};
int ret = -;
int fd1 = -;
signal(SIGINT, signal_fun);
fd1 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME1, O_WRONLY);
while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
scanf("%s", buf);
write(fd1, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
return ;
}
p2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h> #define FIFONAME1 "./fifo1"
#define FIFONAME2 "./fifo2" void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int creat_open_fifo(char *fifoname, int open_mode)
{
int ret = -;
int fd = -; ret = mkfifo(fifoname, );
//如果mkfifo函数出错了,但是这个错误是EEXIST,不报这个错误(忽略错误)
if(ret == - && errno!=EEXIST) print_err("mkfifo fail"); fd = open(fifoname, open_mode);
if(fd == -) print_err("open fail"); return fd;
} void signal_fun(int signo)
{
//unlink();
remove(FIFONAME1);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
char buf[] = {};
int ret = -;
int fd1 = -;
signal(SIGINT, signal_fun);
fd1 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME1, O_RDONLY);
while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
read(fd1,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
return ;
}
这里需要注意一点把signal注册信号处理函数放到creat_open_fifo函数之前的原因是:先让系统知道怎么处理Ctrl+C硬件中断。要不然creat_open_fifo在前的话,阻塞在mkfifo上,系统还不知道怎么处理Ctrl+C这个硬件中断信号。也就没法删除有名管道文件。这里其实OS应该是处理了,OS的处理就是默认处理方式。即干死当前进程,但是没有删除管道文件。
如果creat_open_fifo在signal之前,会出现进程被干死了,但是有名管道文件没有被删除的情况。
有名管道双向通信
使用一个有名管道是无法实现双向通信的,道理同无名管道,即存在抢读问题。
单独启动2个进程
p1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h> #define FIFONAME1 "./fifo1"
#define FIFONAME2 "./fifo2" void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int creat_open_fifo(char *fifoname, int open_mode)
{
int ret = -;
int fd = -; ret = mkfifo(fifoname, );
//如果mkfifo函数出错了,但是这个错误是EEXIST,不报这个错误(忽略错误)
if(ret == - && errno!=EEXIST) print_err("mkfifo fail"); fd = open(fifoname, open_mode);
if(fd == -) print_err("open fail"); return fd;
} void signal_fun(int signo)
{
//unlink();
remove(FIFONAME1);
remove(FIFONAME2);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
char buf[] = {};
int ret = -;
int fd1 = -;
int fd2 = -; fd1 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME1, O_WRONLY);
fd2 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME2, O_RDONLY); while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
scanf("%s", buf);
write(fd1, buf, sizeof(buf)); read(fd2, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
return ;
}
p2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h> #define FIFONAME1 "./fifo1"
#define FIFONAME2 "./fifo2" void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int creat_open_fifo(char *fifoname, int open_mode)
{
int ret = -;
int fd = -; ret = mkfifo(fifoname, );
//如果mkfifo函数出错了,但是这个错误是EEXIST,不报这个错误(忽略错误)
if(ret == - && errno!=EEXIST) print_err("mkfifo fail"); fd = open(fifoname, open_mode);
if(fd == -) print_err("open fail"); return fd;
} void signal_fun(int signo)
{
//unlink();
remove(FIFONAME1);
remove(FIFONAME2);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
char buf[] = {};
int ret = -;
int fd1 = -;
int fd2 = -; fd1 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME1, O_RDONLY);
fd2 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME2, O_WRONLY); while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
scanf("%s", buf);
read(fd1, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("recv:%s\n", buf);
write(fd2, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
return ;
}
这2个代码体验及其糟糕,p2;里面read在write之前,read会阻塞p2。这也是没办法避免的,read和write放一块就会出问题。解决之道
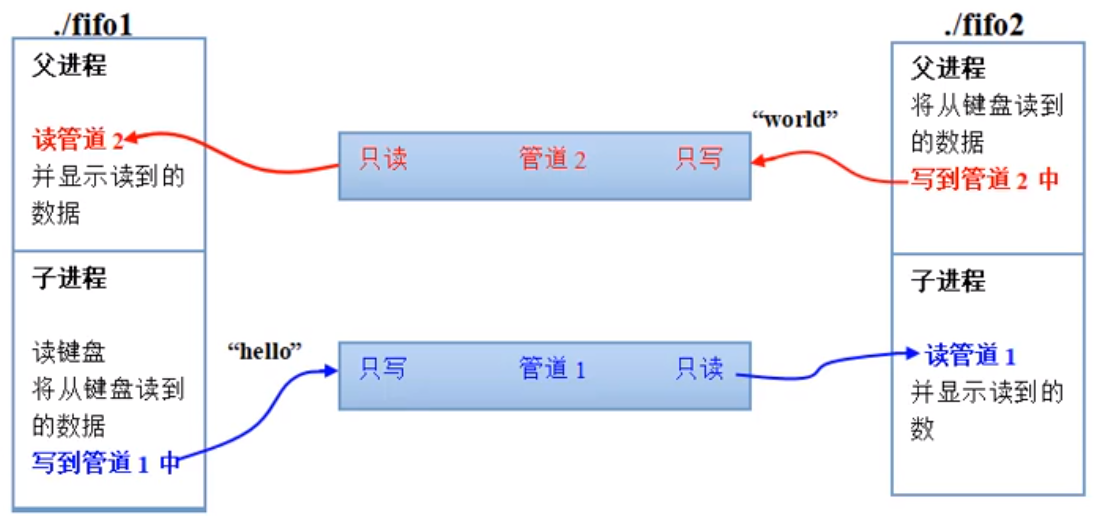
代码
p1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h> #define FIFONAME1 "./fifo1"
#define FIFONAME2 "./fifo2" void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int creat_open_fifo(char *fifoname, int open_mode)
{
int ret = -;
int fd = -; ret = mkfifo(fifoname, );
//如果mkfifo函数出错了,但是这个错误是EEXIST,不报这个错误(忽略错误)
if(ret == - && errno!=EEXIST) print_err("mkfifo fail"); fd = open(fifoname, open_mode);
if(fd == -) print_err("open fail"); return fd;
} void signal_fun(int signo)
{
//unlink();
remove(FIFONAME1);
remove(FIFONAME2);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
char buf[] = {};
int ret = -;
int fd1 = -;
int fd2 = -; fd1 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME1, O_WRONLY);
fd2 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME2, O_RDONLY); ret = fork();
if(ret > )
{
signal(SIGINT, signal_fun);
while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
scanf("%s", buf);
write(fd1, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
}
else if(ret == )
{
while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
read(fd2, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
} return ;
}
p2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h> #define FIFONAME1 "./fifo1"
#define FIFONAME2 "./fifo2" void print_err(char *estr)
{
perror(estr);
exit(-);
} int creat_open_fifo(char *fifoname, int open_mode)
{
int ret = -;
int fd = -; ret = mkfifo(fifoname, );
//如果mkfifo函数出错了,但是这个错误是EEXIST,不报这个错误(忽略错误)
if(ret == - && errno!=EEXIST) print_err("mkfifo fail"); fd = open(fifoname, open_mode);
if(fd == -) print_err("open fail"); return fd;
} void signal_fun(int signo)
{
//unlink();
remove(FIFONAME1);
remove(FIFONAME2);
exit(-);
} int main(void)
{
char buf[] = {};
int ret = -;
int fd1 = -;
int fd2 = -; fd1 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME1, O_RDONLY);
fd2 = creat_open_fifo(FIFONAME2, O_WRONLY); ret = fork();
if(ret > )
{
signal(SIGINT, signal_fun);
while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
read(fd1, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("recv:%s\n", buf);
}
}
else if(ret == )
{
while()
{
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
scanf("%s", buf);
write(fd2, buf, sizeof(buf)); }
} return ;
}
注意:父子进程的buf是不一样的,这得益于子进程继承父进程。
处理Ctrl+C硬件中断,只有父进程做了扫尾工作(即删除管道文件),然后父进程正常终止(调用exit(-1))。子进程采用默认处理方式,即被OS直接干死。
网状通信
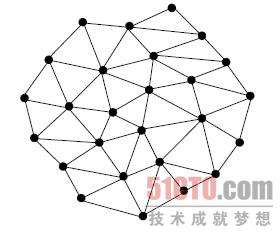
每一个节点想象成一个进程
不管是无名管道、还是有名管道,实现网状通信都很困难
IPC——管道的更多相关文章
- 进程间通信IPC -- 管道, 队列
进程间通信--IPC(Inter-Process Communication) 管道 from multiprocessing import Pipecon1,con2 = Pipe()管道是不安全的 ...
- 进程-IPC 管道 (一)
详见:https://github.com/ZhangzheBJUT/linux/blob/master/IPC(%E4%B8%80).md 一 IPC 概述 进程间通信就是在不同进程之间传播或交换信 ...
- IPC$管道的利用与远程控制
实验目的 通过实验了解IPC$攻击的原理与方法. 实验原理 IPC$攻击的相关原理 IPC$(Internet Process Connection)是共享"命名管道"的资源,它是为了让进程间通信而开 ...
- Linux 进程间通信(一)(经典IPC:管道、FIFO)
管道 管道是Unix系统IPC的最古老方式,有两种局限性: (1) 历史上它们是半双工的(即数据只能在一个方向上流动),虽然现在某些系统提供了全双工管道,但是为了可移植性,不要抱有绝对的全双工假设 ...
- IPC$命令详解
一 摘要二 什么是ipc$三 什么是空会话四 空会话可以做什么五 ipc$所使用的端口六 ipc管道在hack攻击中的意义七 ipc$连接失败的常见原因八 复制文件失败的原因九 关于at命令和xp对i ...
- 空连接ipc$入侵
使用命令 net use url=file://\\IP\ipc$\\IP\ipc$ "" /user:"" 就可以简单地和目标建立一个空连接(需要目标开放ip ...
- unix进程间通信方式(IPC)
unix进程间通信方式(IPC) 管道(Pipe):管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,允许一个进程和另一个与它有共同祖先的进程之间进行通信. 命名管道(named pipe):命名管道克服了管道没有 ...
- nodejs复习02
process 这个模块是单线程的,无法完全利用多核CPU 基本信息 //程序目录 process.cwd(); //应用程序当前目录 process.chdir('/home'); //改变应用程序 ...
- 【NodeJS线程】Boss和他的职员们
>>>[说明]还是一如既往的,这篇文章是从我的个人博客里挪过来的.原文参见:http://www.jscon.co/coding/frontend/nodejs_fork_child ...
随机推荐
- react中,用key值来解决一些奇葩问题
编辑用户信息,角色信息无法加载到值 改进之后:思路:由于值是设置在state里面的,界面编辑时,会重服务器拉去数据,值也设置在state里面了,但是CheckboxGroup依然不会去渲染选中的值, ...
- Vector3.Angle问题
Angle角度 public static float Angle(Vector3 from, Vector3 to); 返回的角度总是两个向量之间的较小的角(实测返回不大于 180 度, 并不是 u ...
- Turbine聚合https微服务
- abp(net core)+easyui+efcore
abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统——展现层实现增删改查之控制器(六) abp(net core)+easyui+efcore实现仓储管理系统目录 abp(ne ...
- springboot集成webSocket能启动,但是打包不了war
1.pom.xml少packing元素 https://www.cnblogs.com/zeussbook/p/10790339.html 2.SpringBoot项目中增加了WebSocket功能无 ...
- 深入理解linux内核-进程和程序
进程描述符task_struct task_struct { //进程基本信息 pid 进程id号 tgid 线程组id号,与线程组领头线程pid号相同 getpid()返回该值 tasks in ...
- lamp和xampp和lampp的区别
lamp:我们最常说的lamp,是一种系统环境,由Linux+Apache+Mysql+PHP构成,常用来运行web服务器.要在系统上完成这个环境的安装,可以很复杂的一步一步编译和设置,也可以用已经集 ...
- 【牛客网】Longest Common Subsequence
[牛客网]Longest Common Subsequence 发现只有d数组最格路 于是我们把前三个数组中相同的数记成一个三维坐标,同一个数坐标不会超过8个 从前往后枚举d,每次最多只会更新不超过8 ...
- Java语言资源国际化步骤
语言资源国际化步骤: 1. 定义资源文件(如:language),需要使用命令native2ascii命令进行转码:(native2ascii是jdk中的转码工具,在jdk的bin目录下) 2 ...
- 剑指offer52:正则表达式匹配
1 题目描述 请实现一个函数用来匹配包括'.'和'*'的正则表达式.模式中的字符‘.’表示任意一个字符,而'*'表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次). 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个 ...
