Ubuntu18.04安装 NVIDIA驱动
Ubuntu18.04安装 NVIDIA驱动
参考自博客:https://blog.csdn.net/jsjason1/article/details/88086904
我确定这篇文章是否很有必要,我最开始的时候,按照这篇文章所述,重新安装了NVIDIA驱动,但是后来以为 CUDA与TensorFlow的版本问题,选择了软件更新管理器中附加驱动里的专有驱动(nvidia-driver-390),然后后续安装成功没再进行测试,但可以肯定,因为本文章是带领着安装最新的官方NVIDIA驱动,所以,支持的CUDA版本也较高,我当时看到信息中支持的CUDA版本是10.0,但我需要的是9.0
下面开始讲述安装官方最新NVIDIA显卡驱动的步骤
为了减少重启次数,并不丢失本文章,建议你,先把本文章链接保存一下,然后到BIOS里的security选项中禁用secure boot,然后你就可以跳过第2步。
1.删除原有NVIDIA驱动
sudo apt-get remove --purge nvidia*
2.在BIOS的security选项中禁用secure boot
3.禁用nouveau
sudo gedit /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
在最后一行添加
blacklist nouneau
执行
sudo update-initramfs -u
重启
lsmod | grep nouveau # 没输出代表禁用生效,要在重启之后执行
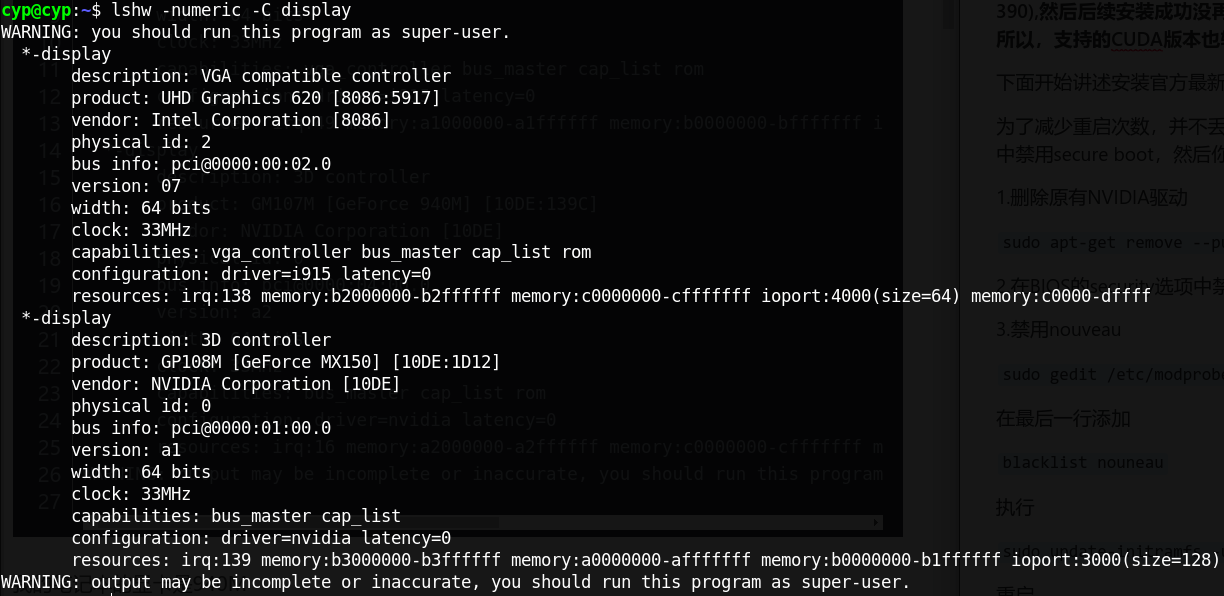
4.查询自己的显卡型号
lshw -numeric -C display
以下是我的显卡信息,我的时Geforce MX150
5.从'>NVIDIA显卡驱动下载对应的显卡驱动
6.安装
sudo chmod a+x NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-418.43.run
sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-418.43.run --no-opengl-files --no-x-check --no-nouveau-check
- –no-opengl-files 只安装驱动文件,不安装OpenGL文件。这个参数最重要
- –no-x-check 安装驱动时不检查X服务
- –no-nouveau-check 安装驱动时不检查nouveau
如果遇到./nvidia-installer: unrecognized option:
执行sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-418.43.run -A #查询高级选项,输出太多,放在文章最后(附录),就是介绍一些后面可以加的指令,因为本文讲的随时间推移有些命令可能也会不再合适
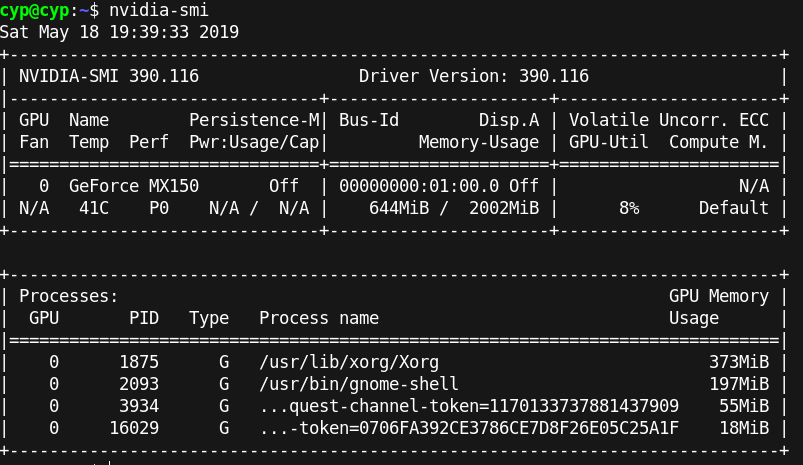
7.检验是否安装成功,命令nvidia-smi
附录:
-v, --version
Print the nvidia-installer version and exit.
-h, --help
Print usage information for the common commandline options and exit.
-A, --advanced-options
Print usage information for the common commandline options as well as the
advanced options, and then exit.
-a, --accept-license
This option is obsolete and ignored by nvidia-installer. It is provided
for compatibility with older versions of nvidia-installer, which required
this option for explicit license acceptance. Use of the NVIDIA driver
implies acceptance of the NVIDIA Software License Agreement, contained in
the file 'LICENSE' (in the top level directory of the driver package).
-i, --driver-info
Print information about the currently installed NVIDIA driver version.
--uninstall
Uninstall the currently installed NVIDIA driver.
--skip-module-unload
When uninstalling the driver, skip unloading of the NVIDIA kernel module.
This option is ignored when the driver is being installed.
--sanity
Perform basic sanity tests on an existing NVIDIA driver installation.
-e, --expert
Enable 'expert' installation mode; more detailed questions will be asked,
and more verbose output will be printed; intended for expert users. The
questions may be suppressed with the '--no-questions' commandline
option.
-q, --no-questions
Do not ask any questions; the default (normally 'yes') is assumed for all
yes/no questions, and the default string is assumed in any situation
where the user is prompted for string input.
-s, --silent
Run silently; no questions are asked and no output is printed, except for
error messages to stderr. This option implies '--ui=none
--no-questions'.
--x-prefix=X-PREFIX
The prefix under which the X components of the NVIDIA driver will be
installed; the default is '/usr/X11R6' unless nvidia-installer detects
that X.Org >= 7.0 is installed, in which case the default is '/usr'.
Only under rare circumstances should this option be used.
--xfree86-prefix=XFREE86-PREFIX
This is a deprecated synonym for --x-prefix.
--x-module-path=X-MODULE-PATH
The path under which the NVIDIA X server modules will be installed. If
this option is not specified, nvidia-installer uses the following search
order and selects the first valid directory it finds: 1) `X
-showDefaultModulePath`, 2) `pkg-config --variable=moduledir
xorg-server`, or 3) the X library path (see the '--x-library-path'
option) plus either 'modules' (for X servers older than X.Org 7.0) or
'xorg/modules' (for X.Org 7.0 or later).
--x-library-path=X-LIBRARY-PATH
The path under which the NVIDIA X libraries will be installed. If this
option is not specified, nvidia-installer uses the following search order
and selects the first valid directory it finds: 1) `X
-showDefaultLibPath`, 2) `pkg-config --variable=libdir xorg-server`, or
3) the X prefix (see the '--x-prefix' option) plus 'lib' on 32bit
systems, and either 'lib64' or 'lib' on 64bit systems, depending on the
installed Linux distribution.
--x-sysconfig-path=X-SYSCONFIG-PATH
The path under which X system configuration files will be installed. If
this option is not specified, nvidia-installer uses the following search
order and selects the first valid directory it finds: 1) `pkg-config
--variable=sysconfigdir xorg-server`, or 2) /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d.
--opengl-prefix=OPENGL-PREFIX
The prefix under which the OpenGL components of the NVIDIA driver will be
installed; the default is: '/usr'. Only under rare circumstances should
this option be used. The Linux OpenGL ABI
(http://oss.sgi.com/projects/ogl-sample/ABI/) mandates this default
value.
--opengl-libdir=OPENGL-LIBDIR
The path relative to the OpenGL library installation prefix under which
the NVIDIA OpenGL components will be installed. The default is 'lib' on
32bit systems, and 'lib64' or 'lib' on 64bit systems, depending on the
installed Linux distribution. Only under very rare circumstances should
this option be used.
--compat32-chroot=COMPAT32-CHROOT
The top-level prefix (chroot) relative to which the 32bit compatibility
libraries will be installed on Linux/x86-64 systems; this option is unset
by default, the 32bit library installation prefix (see below) and the
32bit library path alone determine the target location. Only under very
rare circumstances should this option be used.
--compat32-prefix=COMPAT32-PREFIX
The prefix under which the 32bit compatibility components of the NVIDIA
driver will be installed; the default is: '/usr'. Only under rare
circumstances should this option be used.
--compat32-libdir=COMPAT32-LIBDIR
The path relative to the 32bit compatibility prefix under which the 32bit
compatibility components of the NVIDIA driver will be installed. The
default is 'lib' or 'lib32', depending on the installed Linux
distribution. Only under very rare circumstances should this option be
used.
--install-compat32-libs, --no-install-compat32-libs
32-bit compatibility libraries may be optionally installed. Setting
--install-compat32-libs will install these libraries. Setting
--no-install-compat32-libs will skip installation of these libraries.
Note: this option will have no effect on -no-compat32.run packages.
--installer-prefix=INSTALLER-PREFIX
The prefix under which the installer binary will be installed; the
default is: '/usr'. Note: please use the '--utility-prefix' option
instead.
--utility-prefix=UTILITY-PREFIX
The prefix under which the NVIDIA utilities (nvidia-installer,
nvidia-settings, nvidia-xconfig, nvidia-bug-report.sh) and the NVIDIA
utility libraries will be installed; the default is: '/usr'.
--utility-libdir=UTILITY-LIBDIR
The path relative to the utility installation prefix under which the
NVIDIA utility libraries will be installed. The default is 'lib' on
32bit systems, and 'lib64' or 'lib' on 64bit systems, depending on the
installed Linux distribution.
--documentation-prefix=DOCUMENTATION-PREFIX
The prefix under which the documentation files for the NVIDIA driver will
be installed. The default is: '/usr'.
--application-profile-path=APPLICATION-PROFILE-PATH
The directory under which default application profiles for the NVIDIA
driver will be installed. The default is: '/usr/share/nvidia'.
--kernel-include-path=KERNEL-INCLUDE-PATH
The directory containing the kernel include files that should be used
when compiling the NVIDIA kernel module. This option is deprecated;
please use '--kernel-source-path' instead.
--kernel-source-path=KERNEL-SOURCE-PATH
The directory containing the kernel source files that should be used when
compiling the NVIDIA kernel module. When not specified, the installer
will use '/lib/modules/`uname -r`/build', if that directory exists.
Otherwise, it will use '/usr/src/linux'.
--kernel-output-path=KERNEL-OUTPUT-PATH
The directory containing any KBUILD output files if either one of the
'KBUILD_OUTPUT' or 'O' parameters were passed to KBUILD when building the
kernel image/modules. When not specified, the installer will assume that
no separate output directory was used.
--kernel-install-path=KERNEL-INSTALL-PATH
The directory in which the NVIDIA kernel module should be installed. The
default value is either '/lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/drivers/video'
(if '/lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel' exists) or '/lib/modules/`uname
-r`/video'.
--proc-mount-point=PROC-MOUNT-POINT
The mount point for the proc file system; if not specified, then this
value defaults to '/proc' (which is normally correct). The mount point
of the proc filesystem is needed because the contents of '<proc
filesystem>/version' is used when identifying if a precompiled kernel
interface is available for the currently running kernel. This option
should only be needed in very rare circumstances.
--log-file-name=LOG-FILE-NAME
File name of the installation log file (the default is:
'/var/log/nvidia-installer.log').
--tmpdir=TMPDIR
Use the specified directory as a temporary directory when generating
transient files used by the installer; if not given, then the following
list will be searched, and the first one that exists will be used:
$TMPDIR, /tmp, ., $HOME.
--ui=UI
Specify what user interface to use, if available. Valid values for UI
are 'ncurses' (the default) or 'none'. If the ncurses interface fails to
initialize, or 'none' is specified, then a simple printf/scanf interface
will be used.
-c, --no-ncurses-color
Disable use of color in the ncurses user interface.
--no-nvidia-modprobe
Skip installation of 'nvidia-modprobe', a setuid root utility which
nvidia-installer installs by default. nvidia-modprobe can be used by
user-space NVIDIA driver components to load the NVIDIA kernel module, and
create the NVIDIA device files, when those components run without
sufficient privileges to do so on their own, e.g., the CUDA driver run
within the permissions of a non-privileged user. This utility is only
needed if other means of loading the NVIDIA kernel module and creating
the NVIDIA device files are unavailable.
-k KERNEL-NAME, --kernel-name=KERNEL-NAME
Build and install the NVIDIA kernel module for the non-running kernel
specified by KERNEL-NAME (KERNEL-NAME should be the output of `uname -r`
when the target kernel is actually running). This option implies
'--no-precompiled-interface'. If the options '--kernel-install-path' and
'--kernel-source-path' are not given, then they will be inferred from
KERNEL-NAME; eg: '/lib/modules/KERNEL-NAME/kernel/drivers/video/' and
'/lib/modules/KERNEL-NAME/build/', respectively.
-n, --no-precompiled-interface
Disable use of precompiled kernel interfaces.
--no-abi-note
The NVIDIA OpenGL libraries contain an OS ABI note tag, which identifies
the minimum kernel version needed to use the library. This option causes
the installer to remove this note from the OpenGL libraries during
installation.
--no-rpms
Normally, the installer will check for several rpms that conflict with
the driver (specifically: NVIDIA_GLX and NVIDIA_kernel), and remove them
if present. This option disables this check.
-b, --no-backup
During driver installation, conflicting files are backed up, so that they
can be restored when the driver is uninstalled. This option causes the
installer to simply delete conflicting files, rather than back them up.
-r, --no-recursion
Normally, nvidia-installer will recursively search for potentially
conflicting libraries under the default OpenGL and X server installation
locations. With this option set, the installer will only search in the
top-level directories.
-K, --kernel-module-only
Install a kernel module only, and do not uninstall the existing driver.
This is intended to be used to install kernel modules for additional
kernels (in cases where you might boot between several different
kernels). To use this option, you must already have a driver installed,
and the version of the installed driver must match the version of this
kernel module.
--no-kernel-module
Install everything but the kernel module, and do not remove any existing,
possibly conflicting kernel modules. This can be useful in some DEBUG
environments. If you use this option, you must be careful to ensure that
a NVIDIA kernel module matching this driver version is installed
separately.
--no-x-check
Do not abort the installation if nvidia-installer detects that an X
server is running. Only under very rare circumstances should this option
be used.
--precompiled-kernel-interfaces-path=PRECOMPILED-KERNEL-INTERFACES-PATH
Before searching for a precompiled kernel interface in the .run file,
search in the specified directory.
-z, --no-nouveau-check
Normally, nvidia-installer aborts installation if the nouveau kernel
driver is in use. Use this option to disable this check.
-Z, --disable-nouveau
If the nouveau kernel module is detected by nvidia-installer, the
installer offers to attempt to disable nouveau. The default action is to
not attempt to disable nouveau; use this option to change the default
action to attempt to disable nouveau.
-X, --run-nvidia-xconfig
nvidia-installer can optionally invoke the nvidia-xconfig utility. This
will update the system X configuration file so that the NVIDIA X driver
is used. The pre-existing X configuration file will be backed up. At
the end of installation, nvidia-installer will ask the user if they wish
to run nvidia-xconfig; the default response is 'no'. Use this option to
make the default response 'yes'. This is useful with the
'--no-questions' or '--silent' options, which assume the default values
for all questions.
--force-selinux=FORCE-SELINUX
Linux installations using SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) require that
the security type of all shared libraries be set to 'shlib_t' or
'textrel_shlib_t', depending on the distribution. nvidia-installer will
detect when to set the security type, and set it using chcon(1) on the
shared libraries it installs. If the execstack(8) system utility is
present, nvidia-installer will use it to also clear the executable stack
flag of the libraries. Use this option to override nvidia-installer's
detection of when to set the security type. Valid values for
FORCE-SELINUX are 'yes' (force setting of the security type), 'no'
(prevent setting of the security type), and 'default' (let
nvidia-installer decide when to set the security type).
--selinux-chcon-type=SELINUX-CHCON-TYPE
When SELinux support is enabled, nvidia-installer will try to determine
which chcon argument to use by first trying 'textrel_shlib_t', then
'texrel_shlib_t', then 'shlib_t'. Use this option to override this
detection logic.
--no-sigwinch-workaround
Normally, nvidia-installer ignores the SIGWINCH signal before it forks to
execute commands, e.g. to build the kernel module, and restores the
SIGWINCH signal handler after the child process has terminated. This
option disables this behavior.
--no-cc-version-check
The NVIDIA kernel module should be compiled with the same compiler that
was used to compile the currently running kernel. The layout of some
Linux kernel data structures may be dependent on the version of gcc used
to compile it. The Linux 2.6 kernel modules are tagged with information
about the compiler and the Linux kernel's module loader performs a strict
version match check. nvidia-installer checks for mismatches prior to
building the NVIDIA kernel module and aborts the installation in case of
failures. Use this option to override this check.
--no-distro-scripts
Normally, nvidia-installer will run scripts from /usr/lib/nvidia before
and after installing or uninstalling the driver. Use this option to
disable execution of these scripts.
--no-opengl-files
Do not install any of the OpenGL-related driver files.
--kernel-module-source-prefix=KERNEL-MODULE-SOURCE-PREFIX
Specify a path where the source directory for the kernel module will be
installed. Default: install source directory at /usr/src
--kernel-module-source-dir=KERNEL-MODULE-SOURCE-DIR
Specify the name of the directory where the kernel module sources will be
installed. Default: directory name is "nvidia-VERSION"
--no-kernel-module-source
Skip installation of the kernel module source.
--dkms
nvidia-installer can optionally register the NVIDIA kernel module
sources, if installed, with DKMS, then build and install a kernel module
using the DKMS-registered sources. This will allow the DKMS
infrastructure to automatically build a new kernel module when changing
kernels. During installation, if DKMS is detected, nvidia-installer will
ask the user if they wish to register the module with DKMS; the default
response is 'no'. This option will bypass the detection of DKMS, and
cause the installer to attempt a DKMS-based installation regardless of
whether DKMS is present.
--module-signing-secret-key=MODULE-SIGNING-SECRET-KEY
Specify a path to a private key to use for signing the NVIDIA kernel
module. The corresponding public key must also be provided.
--module-signing-public-key=MODULE-SIGNING-PUBLIC-KEY
Specify a path to a public key to use for verifying the signature of the
NVIDIA kernel module. The corresponding private key must also be
provided.
--module-signing-script=MODULE-SIGNING-SCRIPT
Specify a path to a program to use for signing the NVIDIA kernel module.
The program will be called with the arguments: program-name <HASH>
<PRIVATEKEY> <PUBLICKEY> <MODULE>; if the program returns an error
status, it will be called again with the arguments: program-name
<PRIVATEKEY> <PUBLICKEY> <MODULE>. Default: use the "sign-file" script in
the kernel source directory.
--module-signing-key-path=MODULE-SIGNING-KEY-PATH
Specify a path where signing keys generated by nvidia-installer will be
installed. Default: install keys to '/usr/share/nvidia'.
--module-signing-hash=MODULE-SIGNING-HASH
Specify a cryptographic hash algorithm to use for signing kernel modules.
This requires a module signing tool that allows explicit selection of the
hash algorithm, and the hash algorithm name must be recognizable by the
module signing tool. Default: select a hash algorithm automatically,
based on the kernel's configuration.
--module-signing-x509-hash=MODULE-SIGNING-X509-HASH
Specify a cryptographic hash algorithm to use for signing X.509
certificates generated by nvidia-installer. The hash algorithm name must
be one of the message digest algorithms recognized by the x509(1)
command.
--no-check-for-alternate-installs
Maintainers of alternate driver installation methods can report the
presence and/or availability of an alternate driver installation to
nvidia-installer. Setting this option skips the check for alternate
driver installations.
--no-unified-memory
Do not install the NVIDIA Unified Memory kernel module. This kernel
module is required for CUDA on 64-bit systems, and if it is not
installed, the CUDA driver and CUDA applications will not be able to run.
The '--no-unified-memory' option should only be used to work around
failures to build or install the Unified Memory kernel module on systems
that do not need to run CUDA.
--no-drm
Do not install the nvidia-drm kernel module. This kernel module provides
several features, including X11 autoconfiguration, support for PRIME, and
DRM-KMS. The latter is used to support modesetting on windowing systems
that run independently of X11. The '--no-drm' option should only be used
to work around failures to build or install the nvidia-drm kernel module
on systems that do not need these features.
-j CONCURRENCY-LEVEL, --concurrency-level=CONCURRENCY-LEVEL
Set the concurrency level for operations such as building the kernel
module which may be parallelized on SMP systems. By default, this will be
set to the number of detected CPUs, or to '1', if nvidia-installer fails
to detect the number of CPUs. Systems with a large number of CPUs will
have the default concurrency level limited to 32; setting a higher level
on the command line will override this limit.
--force-libglx-indirect
If the package includes a libglvnd-based OpenGL library, then always
install a libGLX_indirect.so.0 symlink, overwriting one if it exists.
--no-libglx-indirect
Do not install a libGLX_indirect.so.0 symlink.
--install-libglvnd, --no-install-libglvnd
If the package includes a libglvnd-based OpenGL library, then it will try
to determine whether the libglvnd libraries are already available, and
will install them if they're not. Use --install-libglvnd to always
install the libglvnd libraries, overwriting any that already exist. Use
--no-install-libglvnd to exclude the libglvnd libraries, even if they
appear to be missing.
--glvnd-glx-client, --no-glvnd-glx-client
By default, the NVIDIA GLX driver will be installed with the new GLVND
architecture, to support coexisting with other GLVND-compliant GLX
drivers. However, some applications which do not conform to the Linux
OpenGL ABI may not be fully compatible with a GLVND-based GLX driver. The
--no-glvnd-glx-client option will select a non-GLVND GLX client library
(libGL.so.1), which may help to avoid compatibility issues with such
applications.
--glvnd-egl-config-path=GLVND-EGL-CONFIG-PATH
If the package includes a libglvnd-based EGL library, then install the
EGL vendor library config file to this directory. If the libglvnd
libraries are already present, then by default the installer will try to
determine the path by running `pkg-config --variable=datadir libglvnd`.
If that fails, then it will default to /usr/share/glvnd/egl_vendor.d.
--glvnd-egl-client, --no-glvnd-egl-client
By default, the NVIDIA EGL driver will be installed with the new GLVND
architecture, to support coexisting with other GLVND-compliant EGL
drivers. However, some applications may not be fully compatible with a
GLVND-based EGL driver. The --no-glvnd-egl-client option will select a
non-GLVND EGL client library, which may help to avoid compatibility
issues with such applications.
--egl-external-platform-config-path=EGL-EXTERNAL-PLATFORM-CONFIG-PATH
If the package includes an EGL external platform library, then install
the EGL external platform library config file to this directory. Defaults
to /usr/share/egl/egl_external_platform.d.
--override-file-type-destination=OVERRIDE-FILE-TYPE-DESTINATION
Override the default destination for a file type. This option takes an
argument in the form of '<FILE_TYPE>:<destination>', where <FILE_TYPE> is
a file type from the installer .manifest file, and <destination> is an
absolute path to the directory where files of that type should be
installed. This option may be given multiple times in order to override
the destinations for multiple file types. Use of this option takes
precedence over any other options that might otherwise influence the
destination of the specified file type.
--skip-depmod
Don't run the depmod(1) utility after modifying kernel modules. This
should only be used in cases where depmod(1) will be run separately after
running nvidia-installer.
Ubuntu18.04安装 NVIDIA驱动的更多相关文章
- ubuntu18.04安装nvidia驱动总结经验
本人电脑是 DELL Inspiron 3670, 系统装的是ubuntu18.04, 显卡使用的是GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, 在安装nividia显卡的时候花费两天时间,感受颇深,顾总 ...
- 【科研民工笔记2】Ubuntu 16.04 安装nvidia驱动
我的主机是2060的显卡,用的是安装在U盘中的Ubuntu,开机进入后,因为没有安装驱动,所以界面看以来比较大. 通过手动方式,成功安装驱动,最终成功的方案使用的是run文件安装的方式. 1.手动下载 ...
- # Ubuntu16.04安装nvidia驱动+CUDA+cuDNN
Ubuntu16.04安装nvidia驱动+CUDA+cuDNN 准备工作 1.查看GPU是否支持CUDA lspci | grep -i nvidia 2.查看Linux版本 uname -m &a ...
- Ubuntu16.04安装NVIDIA驱动时的一些坑与解决方案
这几天在新购置的笔记本上部署工作环境,在安装NVIDIA驱动的时候遇到了不少坑,重装了很多次,在Ubuntu论坛以及其他资料源看了很多大牛的分析,最终终于解决了一个又一个问题,过程比较艰辛,所以决定写 ...
- Ubuntu16.04安装NVIDIA驱动、实现GPU加速
NVIDIA驱动前前后后装了好几遍,下面把个人的经验分享下,大家仅供参考. 老规矩,先引用师兄的(最详细)https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_23853639/article/de ...
- Ubuntu 16.04安装NVIDIA驱动后循环登录问题
问题描述 最近买了两块NVIDIA Titan X Pascal显卡装到了服务器(运行Ubuntu 16.04)上.为了使用这两块GPU显卡,首先需要安装显卡驱动,安装方式为 #安装一个依赖文件,并更 ...
- Ubuntu18.04安装NVIDIA显卡驱动
1. 查看GPU型号 lspci | grep -i nvidia 我是 GeForce GTX 960M 2. NVIDIA官网下载驱动: https://www.nvidia.com/Downlo ...
- Ubuntu 14.04 安装nVidia驱动后不能进入图形界面的恢复过程
想要解决Ubuntu14.04的风扇不停的转的问题.由于ubuntu本身不支持双显卡切换,导致集显独显都处于开启状态,发热量和耗电量居高不下. 1. 安装驱动过程 参考[1]中的步骤,做了如下的操作. ...
- ubuntu18.04 安装显卡驱动
1.使用PPA仓库进行自动化安装 sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa && sudo apt update 2.查询所有u ...
随机推荐
- iis管理器的程序应用池中没有Asp.NET v4.0
然后 windows + r 输入 cmd 然后输入CD C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319 然后 输入 aspnet_regiis.exe ...
- Unity Shader概述
一.概述 在Unity中需要配合使用材质和Unity Shader才能达到需要的效果.常见的流程:(1)创建一个材质:(2)创建一个Unity Shader,并把它赋给创建的材质:(3)把材质赋给要渲 ...
- UE4 RHI(2)
在上篇简单说明RHI的作用后, 我们在引擎中探索一下RHI的种种细节与实现. 在解决方案资源管理器中搜索RHI, 会有这些文件: (1)对应不同运行平台的PlatformDynamicRHI.cpp( ...
- CISC和RISC的区别
转载于http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9d5430ce0100x5pb.html RISC(Reduced Instruction Set Computer)和CISC( ...
- 今天发现一个Window系统服务增删改查神器:NSSM
官网地址:https://nssm.cc Win10系统下这个:https://nssm.cc/ci/nssm-2.24-101-g897c7ad.zip 官方的帮助,英语的,可以大概看一下: htt ...
- sql回显注入(满满的干货)
三种注入poc where user_id = 1 or 1=1 where user_id = '1' or '1'='1' where user_id =" 1 "or &qu ...
- 【VS开发】【计算机视觉】OpenCV读写xml文件《C版本》
一些简单的XML读写操作,记之于笔记以备忘 主要功能: 1. 创建XML 2. 向XML中存储或者是读取Int float型基本数据 3. 通过创建XML元素,存取复杂的结构如:结构体.矩阵 代码如下 ...
- 【算法集中营】CRC16 三种算法及c实现
标准CRC生成多项式如下表: 名称 生成多项式 简记式* 标准引用 CRC-4 x4+x+1 3 ...
- 2019牛客暑期多校训练营(第六场)-E Androgynos (构造题)
题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/886/E 题意:给出n,求能否构造一个含n个顶点的简单无向图,且它的补图与它同构. 思路:首先要满足与其补图同构,同 ...
- [转帖]加强Linux服务器安全的20项建议
加强Linux服务器安全的20项建议 2017-10-19 22:15:01作者:Linux编辑稿源:系统极客 https://ywnz.com/linuxyffq/99.html 一般情况下用 Li ...
