kaggle 实战 (2): CNN 手写数字识别
文章目录
Tensorflow 官方示例
import tensorflow as tf
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train),(x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=tf.nn.softmax)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
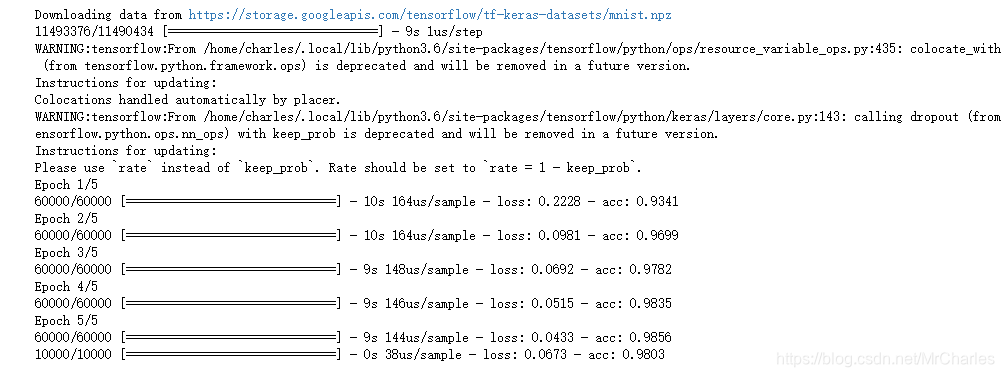
这个本身精度不高,我们可以改变结构提升精度
CNN
from __future__ import division, print_function, absolute_import
# Import MNIST data
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data/", one_hot=False)
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Training Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
num_steps = 2000
batch_size = 128
# Network Parameters
num_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28)
num_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
dropout = 0.25 # Dropout, probability to drop a unit
# Create the neural network
def conv_net(x_dict, n_classes, dropout, reuse, is_training):
# Define a scope for reusing the variables
with tf.variable_scope('ConvNet', reuse=reuse):
# TF Estimator input is a dict, in case of multiple inputs
x = x_dict['images']
# MNIST data input is a 1-D vector of 784 features (28*28 pixels)
# Reshape to match picture format [Height x Width x Channel]
# Tensor input become 4-D: [Batch Size, Height, Width, Channel]
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
# Convolution Layer with 32 filters and a kernel size of 5
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(x, 32, 5, activation=tf.nn.relu)
# Max Pooling (down-sampling) with strides of 2 and kernel size of 2
conv1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv1, 2, 2)
# Convolution Layer with 64 filters and a kernel size of 3
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(conv1, 64, 3, activation=tf.nn.relu)
# Max Pooling (down-sampling) with strides of 2 and kernel size of 2
conv2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv2, 2, 2)
# Flatten the data to a 1-D vector for the fully connected layer
fc1 = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(conv2)
# Fully connected layer (in tf contrib folder for now)
fc1 = tf.layers.dense(fc1, 1024)
# Apply Dropout (if is_training is False, dropout is not applied)
fc1 = tf.layers.dropout(fc1, rate=dropout, training=is_training)
# Output layer, class prediction
out = tf.layers.dense(fc1, n_classes)
return out
# Define the model function (following TF Estimator Template)
def model_fn(features, labels, mode):
# Build the neural network
# Because Dropout have different behavior at training and prediction time, we
# need to create 2 distinct computation graphs that still share the same weights.
logits_train = conv_net(features, num_classes, dropout, reuse=False, is_training=True)
logits_test = conv_net(features, num_classes, dropout, reuse=True, is_training=False)
# Predictions
pred_classes = tf.argmax(logits_test, axis=1)
pred_probas = tf.nn.softmax(logits_test)
# If prediction mode, early return
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode, predictions=pred_classes)
# Define loss and optimizer
loss_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=logits_train, labels=tf.cast(labels, dtype=tf.int32)))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss_op, global_step=tf.train.get_global_step())
# Evaluate the accuracy of the model
acc_op = tf.metrics.accuracy(labels=labels, predictions=pred_classes)
# TF Estimators requires to return a EstimatorSpec, that specify
# the different ops for training, evaluating, ...
estim_specs = tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(
mode=mode,
predictions=pred_classes,
loss=loss_op,
train_op=train_op,
eval_metric_ops={'accuracy': acc_op})
return estim_specs
# Build the Estimator
model = tf.estimator.Estimator(model_fn)
# Define the input function for training
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={'images': mnist.train.images}, y=mnist.train.labels,
batch_size=batch_size, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True)
# Train the Model
model.train(input_fn, steps=num_steps)
# Evaluate the Model
# Define the input function for evaluating
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={'images': mnist.test.images}, y=mnist.test.labels,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
# Use the Estimator 'evaluate' method
model.evaluate(input_fn)
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)
#test=pd.read_csv('./input/test.csv')
import numpy
from numpy import genfromtxt
my_data = numpy.double(genfromtxt('./input/test.csv', delimiter=','))
# Prepare the input data
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={'images': numpy.float32(my_data[1:,:])}, shuffle=False)
# Use the model to predict the images class
preds2 = list(model.predict(input_fn))
Submission = pd.DataFrame({
"ImageId": range(1, len(preds2)+1),
"Label": preds2
})
Submission.to_csv("cnnMnistSubmission.csv", index=False)
Submission.head(5)
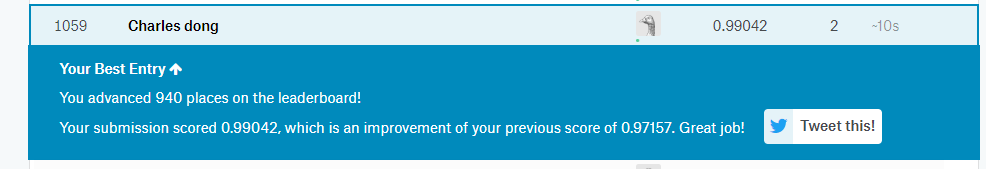
提交结果
kaggle 实战 (2): CNN 手写数字识别的更多相关文章
- Kaggle竞赛丨入门手写数字识别之KNN、CNN、降维
引言 这段时间来,看了西瓜书.蓝皮书,各种机器学习算法都有所了解,但在实践方面却缺乏相应的锻炼.于是我决定通过Kaggle这个平台来提升一下自己的应用能力,培养自己的数据分析能力. 我个人的计划是先从 ...
- CNN 手写数字识别
1. 知识点准备 在了解 CNN 网络神经之前有两个概念要理解,第一是二维图像上卷积的概念,第二是 pooling 的概念. a. 卷积 关于卷积的概念和细节可以参考这里,卷积运算有两个非常重要特性, ...
- 卷积神经网络CNN 手写数字识别
1. 知识点准备 在了解 CNN 网络神经之前有两个概念要理解,第一是二维图像上卷积的概念,第二是 pooling 的概念. a. 卷积 关于卷积的概念和细节可以参考这里,卷积运算有两个非常重要特性, ...
- Keras cnn 手写数字识别示例
#基于mnist数据集的手写数字识别 #构造了cnn网络拟合识别函数,前两层为卷积层,第三层为池化层,第四层为Flatten层,最后两层为全连接层 #基于Keras 2.1.1 Tensorflow ...
- pytorch CNN 手写数字识别
一个被放弃的入门级的例子终于被我实现了,虽然还不太完美,但还是想记录下 1.预处理 相比较从库里下载数据集(关键是经常失败,格式也看不懂),更喜欢直接拿图片,从网上找了半天,最后从CSDN上下载了一个 ...
- keras框架的CNN手写数字识别MNIST
参考:林大贵.TensorFlow+Keras深度学习人工智能实践应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2018. 首先在命令行中写入 activate tensorflow和jupyter notebo ...
- kaggle 实战 (1): PCA + KNN 手写数字识别
文章目录 加载package read data PCA 降维探索 选择50维度, 拆分数据为训练集,测试机 KNN PCA降维和K值筛选 分析k & 维度 vs 精度 预测 生成提交文件 本 ...
- 深度学习之PyTorch实战(3)——实战手写数字识别
上一节,我们已经学会了基于PyTorch深度学习框架高效,快捷的搭建一个神经网络,并对模型进行训练和对参数进行优化的方法,接下来让我们牛刀小试,基于PyTorch框架使用神经网络来解决一个关于手写数字 ...
- keras和tensorflow搭建DNN、CNN、RNN手写数字识别
MNIST手写数字集 MNIST是一个由美国由美国邮政系统开发的手写数字识别数据集.手写内容是0~9,一共有60000个图片样本,我们可以到MNIST官网免费下载,总共4个.gz后缀的压缩文件,该文件 ...
随机推荐
- spring boot下WebSocket消息推送
WebSocket协议 WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通讯的协议.WebSocket通信协议于2011年被IETF定为标准RFC 6455,并由RFC7936补充规范.WebSo ...
- 如何删除github里的项目
1.登录github网站后,就会看到如下画面,在头像下面有个你的项目资源这一栏,假如我要删除名为“hhh”的项目,现在鼠标点进这个项目里面 2.进去后点setting 点进去后,默认是选择了OPtio ...
- 匈牙利算法实战codevs1022覆盖
1022 覆盖 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 大师 Master 题解 查看运行结果 题目描述 Description 有一个N×M的单位方格中 ...
- Java 整型数组只有一个整数是只出现一次的,其余都出现两次
package writtenExamination; /** * @author lindaZ * @date 2015年10月22日 * @todo 找出数组中仅出现一次的数,其余数字出现两次 * ...
- nginx-rtmp-module 指令详解
译序:截至 Jul 8th,2013 官方公布的最新 Nginx RTMP 模块 nginx-rtmp-module 指令详解. Core rtmp 语法:rtmp { ... } 上下文:根 描述: ...
- linux下alsa架构音频驱动播放wav格式文件
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <alsa/asoundl ...
- mysql的下载
怎样从Mysql官网下载mysql.tar.gz版本的安装包 原创 2016年10月20日 21:06:41 10854 今天学习在Linux上部署项目,用到了Mysql,因此想要下载适用 ...
- 笔记54 Mybatis快速入门(五)
Mybatis中注解的使用 1.XML方式的CRUD 新增加接口CategoryMapper ,并在接口中声明的方法上,加上注解对比配置文件Category.xml,其实就是把SQL语句从XML挪到了 ...
- Tools: windbg 使用指南
windbg使用 符号表C:\Symbols; SRV*C:\Symbols*http://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols 系统变量_NT_SYMBOL_PAT ...
- C# - *.dll vs *.lib (动态链接库 vs 静态链接库)
静态库 库(Library)就是一段编译好的二进制代码,加上头文件就可以使用. 静态链接库(Windows 下的*.lib, Linux & Mac 下的 .a).之所以叫做静态,是因为静态库 ...
