性能优化-Bitmap内存管理及优化
Bitmap作为重要Android应用之一,在很多时候如果应用不当,很容易造成内存溢出,那么这篇文章的目的就在于探讨Bitmap的有效运用及其优化
缓存介绍
当多次发送请求的时候,请求同一内容,为了使资源得到合理利用,那么就需要设置缓存,避免同一内容被多次请求
在这里使用一个Http的缓存策略,对http自带的缓存策略做一个简单的使用介绍,从而引出今天的主角
http自带缓存的使用前提:服务器设置了缓存时间
response.addHeader("Cache-control", "max-age=10"); //HttpServletResponse response
以上代表了在10秒重内不会再请求服务器,此时客户端开启了缓存的话,在10内就不会重复请求了
http自带缓存的策略的使用:
- 打开缓存,Android在默认情况下HttpResponseCache(网络请求响应缓存)是关闭的
try {
File cacheDir = new File(getCacheDir(), "http");//缓存目录,在应用目录的cache文件夹下生成http文件夹
long maxSize = 10 * 1024 * 1024;//缓存大小:byte
HttpResponseCache.install(cacheDir, maxSize );
Log.d(TAG, "打开缓存");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
- 发送请求,这里以向服务器请求一张图片为例
此时,会连接服务器,获取服务器里面的内容
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
BitmapFactory.decodeStream((InputStream) new URL("http://192.168.1.7:8080/test.png").getContent());
Log.d(TAG, "下载图片");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
- 删除缓存,就算现在不删,也要找时间清理
HttpResponseCache cache = HttpResponseCache.getInstalled();
if(cache!=null){
try {
cache.delete();
Log.d(TAG, "清空缓存");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
经过以上步骤,就走完了http缓存的一个流程,在实际应用中,一般会采用自己设计缓存的方法,这里只是引出缓存这个概念
Bitmap优化着手点
在使用Bitmap的时候,容易使得Bitmap超过系统分配的内存阈值,发么此时就产生了常见的OOM报错,因此,优化Bitmap的思路也就在于如何避免OOM的发生
那么避免OOM发生就要从图片本身下手了,常见的处理方式便是将图片进行压缩,常用的压缩算法有三种:
质量压缩
质量压缩是通过同化像素点周围的相近的像素点,从而达到降低文件大小的作用,也就是说其本身的像素多少并没有改变,压缩出来的图片虽然大小发生了改变,但分辨率没有发生改变,而在Bitmap中,其是按照像素大小,即图片的像素多少来计算内存空间的,因此这种方法并不能有效避免OOM,这也就是为何只改变图片大小对于Bitmap的内存使用没有作用的原因
那么质量压缩有什么作用呢?其实它的作用就是减少存储体积,方便传输或者保存尺寸压缩
尺寸压缩的思路就是使用Canvas读取现在的bitmap,然后对其尺寸进行修改,这里是真实的改变了图片的像素大小,所以在Bitmap使用的时候,就会得到改变尺寸后的大小,那么就可以对Bitmap进行有效优化,这种操作一般用于缓存缩略图采样率压缩
设置图片的采样率,降低图片像素,其原理和尺寸压缩类似,不过实现的方式不同
Bitmap的Java层源代码分析
由于Bitmap的底层CPP代码涉及到的东西略多,这里就简单介绍下Java层的源码就好
在Bitmap使用的使用,通常会使用如下三个方法加载来自不同地方的图片
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path)
BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, id)
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is)
那么在BitmapFactory源代码中,这三个方法是怎么处理的呢?
打开源代码,我们可以看到:
public static Bitmap decodeFile(String pathName) {
return decodeFile(pathName, null);
}
···
public static Bitmap decodeResource(Resources res, int id) {
return decodeResource(res, id, null);
}
···
public static Bitmap decodeStream(InputStream is) {
return decodeStream(is, null, null);
}
在这里又传递了一次参数,那么找到这三个传递参数的方法
public static Bitmap decodeFile(String pathName, Options opts) {
Bitmap bm = null;
InputStream stream = null;
try {
stream = new FileInputStream(pathName);
bm = decodeStream(stream, null, opts);
} catch (Exception e) {
/* do nothing.
If the exception happened on open, bm will be null.
*/
Log.e("BitmapFactory", "Unable to decode stream: " + e);
} finally {
if (stream != null) {
try {
stream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// do nothing here
}
}
}
return bm;
}
在decodeFile()方法中,将传入文件转化成了流,送到了decodeStream()进行处理,其他就没做什么了,那么我们再看看decodeResource()做了啥
public static Bitmap decodeResource(Resources res, int id, Options opts) {
Bitmap bm = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
final TypedValue value = new TypedValue();
is = res.openRawResource(id, value);
bm = decodeResourceStream(res, value, is, null, opts);
} catch (Exception e) {
/* do nothing.
If the exception happened on open, bm will be null.
If it happened on close, bm is still valid.
*/
} finally {
try {
if (is != null) is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (bm == null && opts != null && opts.inBitmap != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Problem decoding into existing bitmap");
}
return bm;
}
由以上代码看出,decodeResource()也只是中转,把参数设置好,传到decodeResourceStream()中去了,那么顺藤摸瓜,看一看这个方法里干了啥,于是我们找到了这个方法
public static Bitmap decodeResourceStream(Resources res, TypedValue value,
InputStream is, Rect pad, Options opts) {
if (opts == null) {
opts = new Options();
}
if (opts.inDensity == 0 && value != null) {
final int density = value.density;
if (density == TypedValue.DENSITY_DEFAULT) {
opts.inDensity = DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT;
} else if (density != TypedValue.DENSITY_NONE) {
opts.inDensity = density;
}
}
if (opts.inTargetDensity == 0 && res != null) {
opts.inTargetDensity = res.getDisplayMetrics().densityDpi;
}
return decodeStream(is, pad, opts);
}
查看代码发现,这里其实也没有干嘛,设置了Options参数,这里涉及到一个像素密度和分辨率的转化问题,其中,DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT = 160,这个问题网上有很多讨论,这里简明说明一下
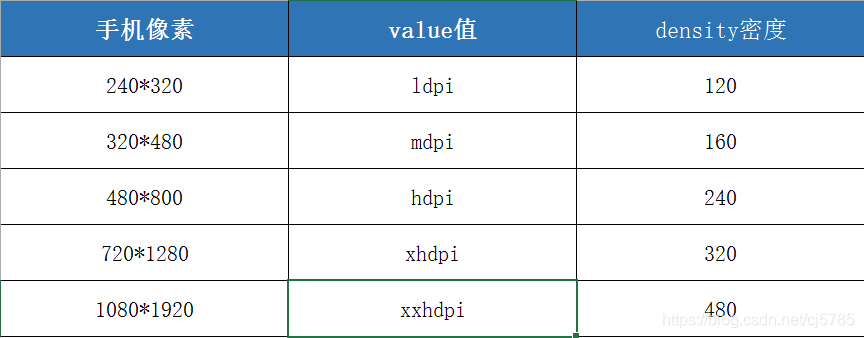
px = dp * Density
详细介绍可以参阅此文:dpi、dip、分辨率、屏幕尺寸、px、density关系以及换算
综合上面的分析,所有的线索都指向了decodeStream()这个方法,那么我们就来看看这个方法干了啥吧
public static Bitmap decodeStream(InputStream is, Rect outPadding, Options opts) {
// we don't throw in this case, thus allowing the caller to only check
// the cache, and not force the image to be decoded.
if (is == null) {
return null;
}
Bitmap bm = null;
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_GRAPHICS, "decodeBitmap");
try {
if (is instanceof AssetManager.AssetInputStream) {
final long asset = ((AssetManager.AssetInputStream) is).getNativeAsset();
bm = nativeDecodeAsset(asset, outPadding, opts);
} else {
bm = decodeStreamInternal(is, outPadding, opts);
}
if (bm == null && opts != null && opts.inBitmap != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Problem decoding into existing bitmap");
}
setDensityFromOptions(bm, opts);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_GRAPHICS);
}
return bm;
}
看一看上面的代码,先是判断了输出流,然后新建Bitmap对象,之后开始写入跟踪信息,这里可以忽略这个写入跟踪信息的玩意儿,下一步就是校验输入流的来源,是assets里面的,还是其他的,因为位置不一样,其处理方法不一样,这里的nativeDecodeAsset()方法就是JNI的方法了,而decodeStreamInternal又是啥呢?再往下看看
private static Bitmap decodeStreamInternal(InputStream is, Rect outPadding, Options opts) {
// ASSERT(is != null);
byte [] tempStorage = null;
if (opts != null) tempStorage = opts.inTempStorage;
if (tempStorage == null) tempStorage = new byte[DECODE_BUFFER_SIZE];
return nativeDecodeStream(is, tempStorage, outPadding, opts);
}
这里就是设置了一个数组,以供JNI使用,然后又传递到了JNI里面去了,也就是说这里调用了两个JNI的方法,一个是assets目录,一个是非assets目录
private static native Bitmap nativeDecodeStream(InputStream is, byte[] storage,
Rect padding, Options opts);
private static native Bitmap nativeDecodeAsset(long nativeAsset, Rect padding, Options opts);
那么JNI中做了什么事情呢?
static jobject nativeDecodeStream(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jobject is, jbyteArray storage,
jobject padding, jobject options) {
jobject bitmap = NULL;
std::unique_ptr<SkStream> stream(CreateJavaInputStreamAdaptor(env, is, storage));
if (stream.get()) {
std::unique_ptr<SkStreamRewindable> bufferedStream(
SkFrontBufferedStream::Create(stream.release(), SkCodec::MinBufferedBytesNeeded()));
SkASSERT(bufferedStream.get() != NULL);
bitmap = doDecode(env, bufferedStream.release(), padding, options);
}
return bitmap;
}
nativeDecodeAsset()处理与其类似,这里就不再展开了,这篇文章进行了详细分析:android 图片占用内存大小及加载解析
那么,Java层代码到此分析结束,在Java层,其最终调用的就是decodeStream()方法了
decodeStream()方法参数分析
由上面的代码分析,我们已经知道,BitmapFactory的调用参数可以设置的由三个InputStream,Rect和Options
那么Options又有什么参数可以设置呢?
inDensity:bitmap的像素密度
inTargetDensity:bitmap输出的像素密度
质量压缩实现方法
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(imageFile.getAbsolutePath(), options);
public void qualitCompress(Bitmap bmp, File file){
int quality = 50; //0~100
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
bmp.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, quality, baos); //图片格式可以选择JPEG,PNG,WEBP
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(baos.toByteArray());
fos.flush();
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
尺寸压缩的实现方法
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(imageFile.getAbsolutePath(), options);
public static void sizeCompress(Bitmap bmp,File file){
int ratio = 4; //缩小的倍数
Bitmap result = Bitmap.createBitmap(bmp.getWidth() / ratio, bmp.getHeight() / ratio,
Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);//这里设置的是Bitmap的像素格式
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(result);
RectF rect = new RectF(0, 0, bmp.getWidth() / ratio, bmp.getHeight() / ratio);
canvas.drawBitmap(bmp, null, rect, null); //通过Canvas重新画入
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
result.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, 100, baos);
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(baos.toByteArray());
fos.flush();
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
采样率压缩的实现方法
public static void rateCompress(String filePath, File file){
int inSampleSize = 8; //设置采样率,数值越大,像素越低
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false; //为true的时候不会真正加载图片,而是得到图片的宽高信息
options.inSampleSize = inSampleSize; //采样率
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(filePath, options);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG, 100 ,baos); // 把压缩后的数据存放到baos中
try {
if(file.exists()){
file.delete();
} else {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(baos.toByteArray());
fos.flush();
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
总结
以上就是系统自带的压缩算法实现Bitmap的处理
质量压缩:适合网络传输
尺寸压缩和采样率压缩:适合生成缩略图
性能优化-Bitmap内存管理及优化的更多相关文章
- Android性能优化:谈话Bitmap内存管理和优化
最近除了那些忙着项目开发的事情,目前正在准备我的论文.短的时间没有写博客,今晚难得想总结.只要有一点时间.因此,为了凑合用,行.唠叨罗嗦,直接进入正题. 从事Android自移动终端的发展,想必是常常 ...
- redis性能优化、内存分析及优化
redis性能优化.内存分析及优化 1.优化网络延时 2.警惕执行时间长的操作 3.优化数据结构.使用正确的算法 4.考虑操作系统和硬件是否影响性能 5.考虑持久化带来的开销 5.1 RDB 全量持久 ...
- iOS性能优化之内存管理:Analyze、Leaks、Allocations的使用和案例代码
最近接了个小任务,和公司的iOS小伙伴们分享下instruments的具体使用,于是有了这篇博客...性能优化是一个很大的话题,这里讨论的主要是内存泄露部分. 一. 一些相关概念 很多人应该比较了解这 ...
- Android 内存管理之优化建议
OOM(OutOfMemory)转:http://hukai.me/android-performance-oom/ 前面我们提到过使用getMemoryClass()的方法可以得到Dalvik He ...
- oracle基础——内存管理、优化
内存图解: 自动管理:11g:AMM 10g:ASMM SGA(system global area):由所有服务进程和后台进程共享 PGA(program global area): 由每个服务 ...
- Oracle性能优化之内存管理
Oracle实例中的内存使用分为两类:程序全局区(program global area, PGA)和系统全局区(system global area, SGA).前者专门供每个会话使用,后者由所有O ...
- iOS内存管理和优化 from 刘延军
- android bitmap的内存分配和优化
首先Bitmap在Android虚拟机中的内存分配,在Google的网站上给出了下面的一段话 大致的意思也就是说,在Android3.0之前,Bitmap的内存分配分为两部分,一部分是分配在Dalvi ...
- android 管理Bitmap内存 - 开发文档翻译
由于本人英文能力实在有限,不足之初敬请谅解 本博客只要没有注明“转”,那么均为原创,转贴请注明本博客链接链接 Managing Bitmap Memory 管理Bitmap内存 In additi ...
随机推荐
- Flume实时监控目录sink到hdfs,再用sparkStreaming监控hdfs的这个目录,对数据进行计算
目标:Flume实时监控目录sink到hdfs,再用sparkStreaming监控hdfs的这个目录,对数据进行计算 1.flume的配置,配置spoolDirSource_hdfsSink.pro ...
- bzoj 2430: [Poi2003]Chocolate 贪心
发现每一次切割都会使另一方向所有切割次数++. 而每一刀的代价就是 cost*切割次数,故贪心按照cost从大到小排序即可. #include <bits/stdc++.h> #defin ...
- dp * 3
cf 467 C 从序列中选出 \(k\) 段连续的 \(m\) 个数 最大化总和 \(f_{i, j}\) 表示前 \(i\) 个位置中选出了 \(j\) 段 转移显然 #include <b ...
- linux系列(十五):tail命令
1.命令格式: tail[必要参数][选择参数][文件] 2.命令功能: 用于显示指定文件末尾内容,不指定文件时,作为输入信息进行处理.常用查看日志文件. 3.命令参数: -f 循环读取 -q 不显示 ...
- NetworkX系列教程(10)-算法之二:最小/大生成树问题
小书匠 Graph 图论 重头戏部分来了,写到这里我感觉得仔细认真点了,可能在NetworkX中,实现某些算法就一句话的事,但是这个算法是做什么的,用在什么地方,原理是怎么样的,不清除,所以,我决定 ...
- RabbitMQ的安装和管理
c:\Program Files (x86)\RabbitMQ Server\rabbitmq_server-3.5.1\sbin>------------------------------- ...
- centos7mongo集群
1.安装 cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb.repo << EOF[mongodb-org-3.6]name=MongoDB Repositorybase ...
- Python中一些高效的数据操作
列表统计 chars = ["a", "b", "a", "c", "a", "d&quo ...
- linux 编写定时任务,查询服务是否挂掉
shell 脚本 #!/bin/bash a=`netstat -unltp|grep fdfs|wc -l` echo "$a" if [ "$a" -ne ...
- Hadoop zookeeper hbase spark phoenix (HA)搭建过程
环境介绍: 系统:centos7 软件包: apache-phoenix-4.14.0-HBase-1.4-bin.tar.gz 下载链接:http://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apac ...
