AtCoder Beginner Contest 144 题解
$cf$ 自闭了,打 $abc$ 散散心
...这个有什么好讲的吗,题目看懂就会做了
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cmath>
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long ll;
- inline int read()
- {
- int x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
- while(ch<''||ch>'') { if(ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar(); }
- while(ch>=''&&ch<='') { x=(x<<)+(x<<)+(ch^); ch=getchar(); }
- return x*f;
- }
- int a,b;
- int main()
- {
- a=read(),b=read();
- if(a>||b>||a<||b<) { printf("-1\n"); return ; }
- printf("%d\n",a*b);
- return ;
- }
A
预处理一下哪些数可以被表示然后查表即可
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cmath>
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long ll;
- inline int read()
- {
- int x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
- while(ch<''||ch>'') { if(ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar(); }
- while(ch>=''&&ch<='') { x=(x<<)+(x<<)+(ch^); ch=getchar(); }
- return x*f;
- }
- const int N=;
- bool vis[N];
- int main()
- {
- for(int i=;i<=;i++)
- for(int j=;j<=;j++) vis[i*j]=;
- int a=read();
- if(vis[a]) printf("Yes\n");
- else printf("No\n");
- return ;
- }
B
C - Walk on Multiplication Table
根号枚举一下因数,设因数为 $x$ ,那么看看走到 $(x,n/x)$ 是不是比较短的路径即可
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cmath>
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long ll;
- inline ll read()
- {
- ll x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
- while(ch<''||ch>'') { if(ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar(); }
- while(ch>=''&&ch<='') { x=(x<<)+(x<<)+(ch^); ch=getchar(); }
- return x*f;
- }
- ll n,ans;
- int main()
- {
- n=read(); int t=sqrt(n);
- ans=n-;
- for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
- {
- if(n%i) continue;
- ans=min(ans,n/i+i-);
- }
- printf("%lld\n",ans);
- return ;
- }
C
对我这个数学不好的人来说很不友好啊...
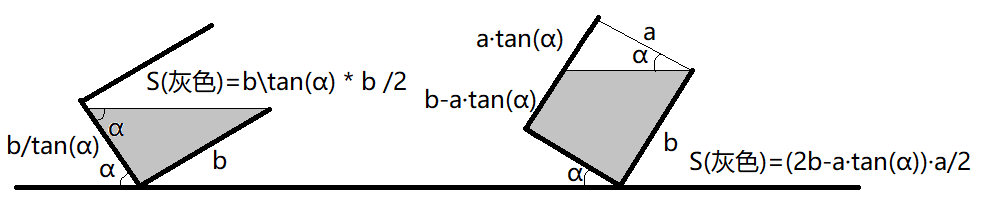
显然二分一下倾斜角看看水是否会倒出来
首先可以把 $x$ 除以 $a$ ,然后就变成平面的问题
然后要特判一下内部是梯形还是三角形就做完了,要注意一下细节,别和我一样把精度设到 $1e-18$ 或者 $-1e18$ ,$\text{2333333}$
放张图比较好理解吧:
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cmath>
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long ll;
- typedef long double ldb;
- inline int read()
- {
- int x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
- while(ch<''||ch>'') { if(ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar(); }
- while(ch>=''&&ch<='') { x=(x<<)+(x<<)+(ch^); ch=getchar(); }
- return x*f;
- }
- const ldb pi=acos(-1.0),eps=1e-;
- ldb a,b,x,ans;
- inline bool check(ldb alp)
- {
- if(a*tan(alp)>=b)
- {
- ldb y=b/tan(alp);
- return y*b/<=x;
- }
- ldb t=b-a*tan(alp);
- return (t+b)*a/<=x;
- }
- int main()
- {
- cin>>a>>b>>x;
- x/=a;
- ldb L=eps,R=pi/-eps;
- while(fabsl(R-L)>eps)
- {
- ldb mid=(L+R)/;
- if(check(mid)) R=mid,ans=mid;
- else L=mid;
- }
- printf("%.12Lf\n",ans/pi*);
- return ;
- }
D
首先容易想到最大的 $A$ 和最小的 $F$ 匹配,次大的和次小的匹配...这样匹配下去
然后考虑如何减一些 $A$ ,显然可以二分答案,那么 $check$ 长这样:
- inline bool check(ll p)//二分的答案p
- {
- ll now=K;
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
- {
- // af<=p , a<=p/f
- if(p/F[i]>=A[i]) continue;
- ll t=A[i]-p/F[i];
- if(t>now) return ;
- now-=t;
- }
- return ;
- }
分析完代码发现,为了最优一定要 $A$ 从小到大对应匹配 $F$ 从大到小,一种证明大概是这样的:
首先可以发现,对于二分的答案 $p$ ,它需要的 $K$ 为 $\sum_{i=1}^{n}max(A_i-\left \lfloor \frac{p}{F_i}\right \rfloor,0)$
那么式子相当于 $\sum_{i=1}^{n}A_i-\sum_{i=1}^{n}\left \lfloor \frac{p}{F_i}\right \rfloor+\sum_{i=1}^{n}[A_i<\left \lfloor \frac{p}{F_i}\right \rfloor](\left \lfloor \frac{p}{F_i}\right \rfloor-A_i)$
发现如果某种匹配能让最后一项求和尽量小,那么即为最优的
然后问题就变成了给长度为 $n$ 的序列 $A,B$ ,求一种匹配使 $\sum_{i=1}^{n}[A_i<B_i](B_i-A_i)$ 最小
首先对于最大的 $B_x$ ,如果 $A_i,A_j$ 都大于 $B_x$ ,那么 $i,j$ 选那个没影响,如果 $A_i<B<A_j$ 显然要让 $A_j$ 去和 $B_x$ 匹配
因为如果让 $A_i$ 和 $B_x$ 匹配,首先产生的代价一定大于 $A_i$ 和 $B_y,y\neq x$ 匹配的代价,然后 $A_j$ 不管和谁匹配代价都为 $0$,那么综合一下还是要让 $A_j$ 去匹配 $B_x$
如果 $A_i<A_j<B$ ,那么如果 $A_i$ 和 $B_x$ 匹配并且 $A_j$ 和 $B_y$ 匹配,如果 $A_j<B_y$ 那么交换 $i,j$ 对答案没影响
但是如果 $A_j>B_y$ ,自己写一下式子会发现代价大于等于 $A_j$ 和 $B_x$ 匹配,$A_i$ 和 $B_y$ 匹配的代价(这里要再分 $B_y$ 和 $A_i$ 之间的关系讨论)
所以综上,$A$ 中最大的和 $B$ 中最大的匹配,次大的和次大的匹配,这样下去一定不会劣于其他方案
回到原来的问题,因为 $F$ 变成了分母,所以要 $F$ 最小的和 $A$ 最大的匹配
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cmath>
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long ll;
- inline ll read()
- {
- ll x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
- while(ch<''||ch>'') { if(ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar(); }
- while(ch>=''&&ch<='') { x=(x<<)+(x<<)+(ch^); ch=getchar(); }
- return x*f;
- }
- const int N=2e5+;
- const ll INF=1e12;
- ll n,m,A[N],F[N];
- inline bool check(ll p)
- {
- ll now=m;
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
- {
- // af<=p , a<=p/f
- if(p/F[i]>=A[i]) continue;
- ll t=A[i]-p/F[i];
- if(t>now) return ;
- now-=t;
- }
- return ;
- }
- int main()
- {
- n=read(),m=read();
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++) A[i]=read();
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++) F[i]=read();
- sort(A+,A+n+); sort(F+,F+n+);
- reverse(F+,F+n+);
- ll L=,R=INF,ans=;
- while(L<=R)
- {
- ll mid=L+R>>;
- if(check(mid)) R=mid-,ans=mid;
- else L=mid+;
- }
- printf("%lld\n",ans);
- return ;
- }
E
一开始显然会考虑枚举断边然后 $dp$ 一下算代价
设 $f[x]$ 表示从 $x$ 出发最终到达 $n$ 的期望步数,那么转移显然
但是枚举断边复杂度为 $m$,总复杂度为 $m(n+m)$ ,不太行
考虑枚举点,对于某个点 $u$ ,它有若干的出边 $(u,v_i)$
考虑断掉哪条从 $u$ 出发的边是最优的,显然是 $f[v_i]$ 最大的那个,所以只要考虑断最大的那个即可
那么枚举点的复杂度为 $n$ ,总复杂度为 $n(n+m)$,记得如果某个点没法走到 $n$ ,那么期望步数为 $INF$
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cmath>
- #include<vector>
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long ll;
- typedef double db;
- inline int read()
- {
- int x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
- while(ch<''||ch>'') { if(ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar(); }
- while(ch>=''&&ch<='') { x=(x<<)+(x<<)+(ch^); ch=getchar(); }
- return x*f;
- }
- const int N=,INF=1e9;
- int n,m,a[N*N],b[N*N];
- vector <int> V[N];
- db f[N],ans;
- inline db calc(int p)
- {
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++) f[i]=;
- f[n]=;
- for(int i=n-;i>=;i--)
- {
- int len=V[i].size();
- if(p==i&&len==) { f[i]=INF; continue; }
- db t=1.0/(len-(p==i)),mx=;
- for(int j=;j<len;j++)
- {
- int v=V[i][j]; mx=max(mx,(f[v]+)*t);
- f[i]+=(f[v]+)*t;
- }
- if(p==i) f[i]-=mx;
- }
- return f[];
- }
- int main()
- {
- n=read(),m=read();
- for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
- {
- a[i]=read(),b[i]=read();
- V[a[i]].push_back(b[i]);
- }
- ans=calc();
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
- ans=min(ans,calc(i));
- printf("%.9lf\n",ans);
- return ;
- }
F
AtCoder Beginner Contest 144 题解的更多相关文章
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 154 题解
人生第一场 AtCoder,纪念一下 话说年后的 AtCoder 比赛怎么这么少啊(大雾 AtCoder Beginner Contest 154 题解 A - Remaining Balls We ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 153 题解
目录 AtCoder Beginner Contest 153 题解 A - Serval vs Monster 题意 做法 程序 B - Common Raccoon vs Monster 题意 做 ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 177 题解
AtCoder Beginner Contest 177 题解 目录 AtCoder Beginner Contest 177 题解 A - Don't be late B - Substring C ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 184 题解
AtCoder Beginner Contest 184 题解 目录 AtCoder Beginner Contest 184 题解 A - Determinant B - Quizzes C - S ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 173 题解
AtCoder Beginner Contest 173 题解 目录 AtCoder Beginner Contest 173 题解 A - Payment B - Judge Status Summ ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 172 题解
AtCoder Beginner Contest 172 题解 目录 AtCoder Beginner Contest 172 题解 A - Calc B - Minor Change C - Tsu ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 169 题解
AtCoder Beginner Contest 169 题解 这场比赛比较简单,证明我没有咕咕咕的时候到了! A - Multiplication 1 没什么好说的,直接读入两个数输出乘积就好了. ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 148 题解
目录 AtCoder Beginner Contest 148 题解 前言 A - Round One 题意 做法 程序 B - Strings with the Same Length 题意 做法 ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 151 题解报告
总的来说,这次的题目比较水,然而菜菜的我并没有把所有题目都做完,话不多说,直接来干货: A:Next Alphabet 题目链接:https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc151/ ...
随机推荐
- ios编译库文件时出现的问题
1. 警告:directory not found for option "xxxxxxxx" 文件路径未找到 选择工程, 编译的 (targets) 选择 Build Setti ...
- python将py文件转换为pyc
python -m py_compile lib/ylpy.py python -m py_compile lib/ylpy.py python 一个.py文件如何调用另一个.py文件中的类和函数 A ...
- ArcGIS超级工具SPTOOLS-制图篇
1.1 梯形接幅表的创建 视频:https://weibo.com/tv/v/Hvq9KzKKQ?fid=1034:4374886702060760 根据一个图层范围,生成接幅表,支持地图比例尺有1 ...
- cmder的segmentation fault错误修复
Segmentation fault 现场还原 问题出现的原因是我在 cmder的命令行里执行了cmder /register ALL命令,本意是把cmder放到右键菜单里去的 但我没想到的是,各种不 ...
- c# 线程异步处理
public class AsyncHelper { private static readonly TaskFactory _myTaskFactory = new TaskFactory(Canc ...
- Qt编写安防视频监控系统7-全屏切换
一.前言 全屏切换这个功能点属于简单的,一般会做到右键菜单中,也提供了快捷键比如alt+enter来触发,恢复全屏则按esc即可,全屏处理基本上都是隐藏通道面板以外的窗体,保持最大化展示,由于采用了模 ...
- STM32第二章I/O端口应用
STM32F10xxx系列中,有7个I/O端口,每个端口有两个32位配置寄存器(GPIOx_CRL,GPIOx_CRH),两个32位数据寄存器(GPIOx_IDR和GPIOx_ODR),一个32位置位 ...
- 安装ELectron失败解决方案
npm安装Electron解决方案 Electron使用npm安装时,因为是国外的镜像源,所以速度会非常慢.而使用cnpm如下命令进行安装时,又会出现安装失败的问题: npm install elec ...
- linux下使用openssl和md5sum加密文件或者字符串
#openssl //在终端中输入openssl后回车. OpenSSL> md5 //输入md5后回车 123456 //接着输入123456,不要输入回车.然后按3次ctr ...
- Shell脚本中怎么实现用户切换实现操作
当我们在服务器上面疯狂的进行操作的时候,我们用shell脚本来帮我们来完成一些基本的任务,但是一些命令或者一些操作需要我们不断切换用户来实现的话,在shell脚本就不那么好实现了,那么我们在shell ...
