Apache2 在Linux环境下的安装
安装Apache2:
apt-get install apache2
启动Apache2服务:
service apache2 start
在终端运行启动后,打开浏览器URL访问 http://localhost/ 或 127.0.0.1
显示的网页就是Apache2 Web Server 默认页[It works],由此可以断定Apache2 Web服务器正在运行

Apache的默认网页位于:/var/www/html/index.html ;可以通过编辑index.html文件提供想要的任何信息,可以通过更改文件代码改变html页面的显示方式和内容
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<title>Apache2 Debian Default Page: It works</title>
<style type="text/css" media="screen">
* {
margin: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
} body, html {
padding: 3px 3px 3px 3px; background-color: #D8DBE2; font-family: Verdana, sans-serif;
font-size: 11pt;
text-align: center;
} div.main_page {
position: relative;
display: table; width: 800px; margin-bottom: 3px;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px; border-width: 2px;
border-color: #212738;
border-style: solid; background-color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;
} div.page_header {
height: 99px;
width: 100%; background-color: #F5F6F7;
} div.page_header span {
margin: 15px 0px 0px 50px; font-size: 180%;
font-weight: bold;
} div.page_header img {
margin: 3px 0px 0px 40px; border: 0px 0px 0px;
} div.table_of_contents {
clear: left; min-width: 200px; margin: 3px 3px 3px 3px; background-color: #FFFFFF; text-align: left;
} div.table_of_contents_item {
clear: left; width: 100%; margin: 4px 0px 0px 0px; background-color: #FFFFFF; color: #000000;
text-align: left;
} div.table_of_contents_item a {
margin: 6px 0px 0px 6px;
} div.content_section {
margin: 3px 3px 3px 3px; background-color: #FFFFFF; text-align: left;
} div.content_section_text {
padding: 4px 8px 4px 8px; color: #000000;
font-size: 100%;
} div.content_section_text pre {
margin: 8px 0px 8px 0px;
padding: 8px 8px 8px 8px; border-width: 1px;
border-style: dotted;
border-color: #000000; background-color: #F5F6F7; font-style: italic;
} div.content_section_text p {
margin-bottom: 6px;
} div.content_section_text ul, div.content_section_text li {
padding: 4px 8px 4px 16px;
} div.section_header {
padding: 3px 6px 3px 6px; background-color: #8E9CB2; color: #FFFFFF;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 112%;
text-align: center;
} div.section_header_red {
background-color: #CD214F;
} div.section_header_grey {
background-color: #9F9386;
} .floating_element {
position: relative;
float: left;
} div.table_of_contents_item a,
div.content_section_text a {
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
} div.table_of_contents_item a:link,
div.table_of_contents_item a:visited,
div.table_of_contents_item a:active {
color: #000000;
} div.table_of_contents_item a:hover {
background-color: #000000; color: #FFFFFF;
} div.content_section_text a:link,
div.content_section_text a:visited,
div.content_section_text a:active {
background-color: #DCDFE6; color: #000000;
} div.content_section_text a:hover {
background-color: #000000; color: #DCDFE6;
} div.validator {
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main_page">
<div class="page_header floating_element">
<img src="/icons/openlogo-75.png" alt="Debian Logo" class="floating_element"/>
<span class="floating_element">
Apache2 Debian Default Page
</span>
</div>
<!-- <div class="table_of_contents floating_element">
<div class="section_header section_header_grey">
TABLE OF CONTENTS
</div>
<div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element">
<a href="#about">About</a>
</div>
<div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element">
<a href="#changes">Changes</a>
</div>
<div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element">
<a href="#scope">Scope</a>
</div>
<div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element">
<a href="#files">Config files</a>
</div>
</div>
-->
<div class="content_section floating_element"> <div class="section_header section_header_red">
<div id="about"></div>
It works!
</div>
<div class="content_section_text">
<p>
This is the default welcome page used to test the correct
operation of the Apache2 server after installation on Debian systems.
If you can read this page, it means that the Apache HTTP server installed at
this site is working properly. You should <b>replace this file</b> (located at
<tt>/var/www/html/index.html</tt>) before continuing to operate your HTTP server.
</p> <p>
If you are a normal user of this web site and don't know what this page is
about, this probably means that the site is currently unavailable due to
maintenance.
If the problem persists, please contact the site's administrator.
</p> </div>
<div class="section_header">
<div id="changes"></div>
Configuration Overview
</div>
<div class="content_section_text">
<p>
Debian's Apache2 default configuration is different from the
upstream default configuration, and split into several files optimized for
interaction with Debian tools. The configuration system is
<b>fully documented in
/usr/share/doc/apache2/README.Debian.gz</b>. Refer to this for the full
documentation. Documentation for the web server itself can be
found by accessing the <a href="/manual">manual</a> if the <tt>apache2-doc</tt>
package was installed on this server. </p>
<p>
The configuration layout for an Apache2 web server installation on Debian systems is as follows:
</p>
<pre>
/etc/apache2/
|-- apache2.conf
| `-- ports.conf
|-- mods-enabled
| |-- *.load
| `-- *.conf
|-- conf-enabled
| `-- *.conf
|-- sites-enabled
| `-- *.conf
</pre>
<ul>
<li>
<tt>apache2.conf</tt> is the main configuration
file. It puts the pieces together by including all remaining configuration
files when starting up the web server.
</li> <li>
<tt>ports.conf</tt> is always included from the
main configuration file. It is used to determine the listening ports for
incoming connections, and this file can be customized anytime.
</li> <li>
Configuration files in the <tt>mods-enabled/</tt>,
<tt>conf-enabled/</tt> and <tt>sites-enabled/</tt> directories contain
particular configuration snippets which manage modules, global configuration
fragments, or virtual host configurations, respectively.
</li> <li>
They are activated by symlinking available
configuration files from their respective
*-available/ counterparts. These should be managed
by using our helpers
<tt>
a2enmod,
a2dismod,
</tt>
<tt>
a2ensite,
a2dissite,
</tt>
and
<tt>
a2enconf,
a2disconf
</tt>. See their respective man pages for detailed information.
</li> <li>
The binary is called apache2. Due to the use of
environment variables, in the default configuration, apache2 needs to be
started/stopped with <tt>/etc/init.d/apache2</tt> or <tt>apache2ctl</tt>.
<b>Calling <tt>/usr/bin/apache2</tt> directly will not work</b> with the
default configuration.
</li>
</ul>
</div> <div class="section_header">
<div id="docroot"></div>
Document Roots
</div> <div class="content_section_text">
<p>
By default, Debian does not allow access through the web browser to
<em>any</em> file apart of those located in <tt>/var/www</tt>,
<a href="http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/mod_userdir.html" rel="nofollow">public_html</a>
directories (when enabled) and <tt>/usr/share</tt> (for web
applications). If your site is using a web document root
located elsewhere (such as in <tt>/srv</tt>) you may need to whitelist your
document root directory in <tt>/etc/apache2/apache2.conf</tt>.
</p>
<p>
The default Debian document root is <tt>/var/www/html</tt>. You
can make your own virtual hosts under /var/www. This is different
to previous releases which provides better security out of the box.
</p>
</div> <div class="section_header">
<div id="bugs"></div>
Reporting Problems
</div>
<div class="content_section_text">
<p>
Please use the <tt>reportbug</tt> tool to report bugs in the
Apache2 package with Debian. However, check <a
href="http://bugs.debian.org/cgi-bin/pkgreport.cgi?ordering=normal;archive=0;src=apache2;repeatmerged=0"
rel="nofollow">existing bug reports</a> before reporting a new bug.
</p>
<p>
Please report bugs specific to modules (such as PHP and others)
to respective packages, not to the web server itself.
</p>
</div> </div>
</div>
<div class="validator">
</div>
</body>
</html>
index.html 默认内容
若是想让浏览器浏览我们想要的HTML内容,可以在该目录下添加新的HTML文件【添加新的HTML网页】:
<! index2.html >
<html>
<body>
<h1> 第一个Apache-Web中的HTML页面 </h1> <p> Hello ! Apache ! </p> <p> Is you to </p>
</body>
</html>
然后打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost/ 或 127.0.0.1 并没有看见自己的网站,依旧是apache默认的网页,这是因为index.html是默认第一加载的页面,此时的真实完整的URL是: http://localhost/index.html ;若想访问自己添加的页面,则需要改变URL:http://localhost/index2.html
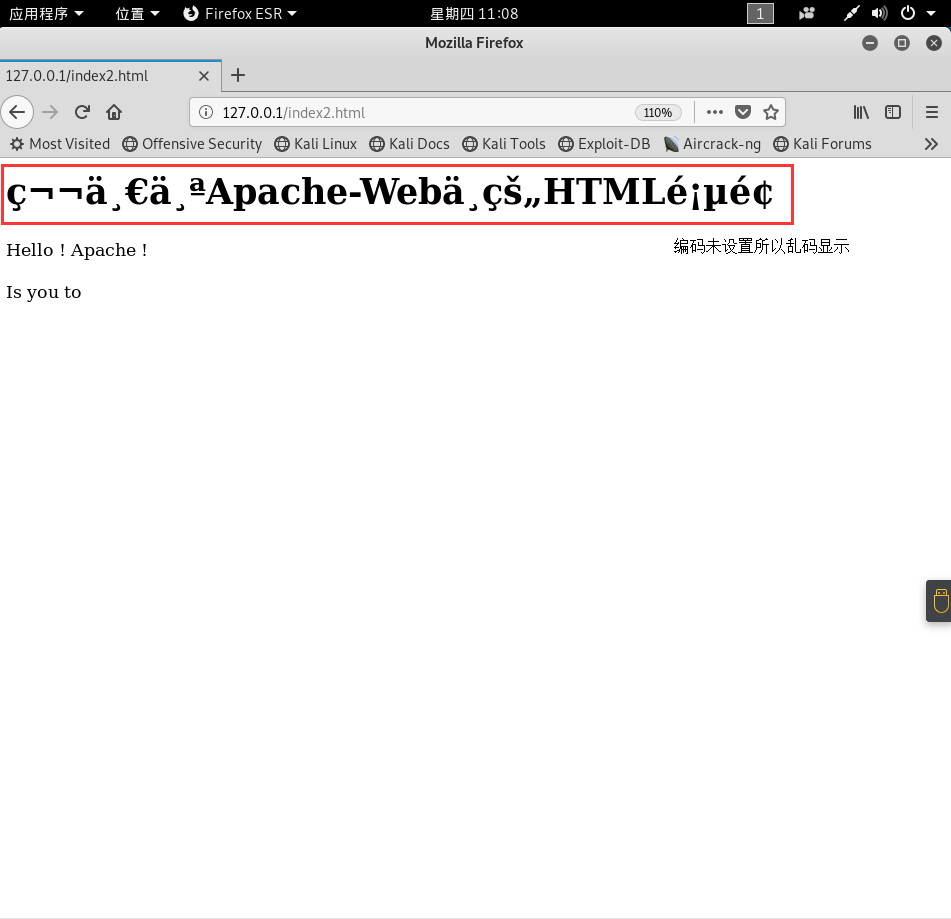
`
——————
至此,Apache的简单安装运行介绍完毕!
如果需要关闭服务:service apache2 stop
如果需要重启服务:serivce apache2 restart
Apache2 在Linux环境下的安装的更多相关文章
- 全世界最详细的图形化VMware中linux环境下oracle安装(二)【weber出品必属精品】
<ORACLE 10.2.05版本的升级补丁安装> 首先我们解压 $ unzip p8202632_10205_LINUX.zip 解压后我们会发现多出了个文件夹,他是:Disk1,进入D ...
- 全世界最详细的图形化VMware中linux环境下oracle安装(一)【weber出品必属精品】
安装流程:前期准备工作--->安装ORACLE软件--->安装升级补丁--->安装odbc创建数据库--->安装监听器--->安装EM <前期准备工作> 安装 ...
- Linux 环境下 Lua 安装(转)
系统环境:CentOS-6.2-x86_64. Lua 是嵌入式脚本语言,应用场景很广泛. 引自官网:Lua is used in many products and projects around ...
- 基础--Redis在Linux环境下的安装
1. 安装redis服务 1.1 检查安装依赖程序 yum install gcc-c++yum install -y tclyum install wget 1.1.1 下载redis安装包 (或者 ...
- LINUX环境下SVN安装与配置(利用钩子同步开发环境与测试环境)
安装采用YUM一键安装: 1.环境Centos 6.6 2.安装svnyum -y install subversion 3.配置 建立版本库目录mkdir /www/svndata svnserve ...
- Linux环境下mysql安装并配置远程访问
环境:centOS 1.下载mysql安装文件 [root@localhost ~]# wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-community-release-el ...
- linux环境下redis安装
本篇文章主要说明的是Linux环境下redis数据库的安装: 首先进入目标目录: 下载安装包,执行命令: wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-4. ...
- Linux环境下Oracle安装参数设置
前面讲了虚拟机的设置和OracleLinux的安装,接下来我们来说下Oracle安装前的准备工作.1.系统信息查看系统信息查看首先服务器ip:192.168.8.120服务器系统:Oracle Lin ...
- Redis在linux环境下的安装
下载Redis安装包 wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.2.9.tar.gz 解压Redis安装包 tar -zxvf redis-3.2. ...
随机推荐
- 页面QQ临时对话的实现
一.开通QQ服务 点我进入QQ推广官网>然后点击推广工具即可后面自己看中文 二.页面a标签 <a target="_blank" href="http://w ...
- Python中使用cutecharts实现简单的手绘风格的图表
场景 效果 cutecharts的Github: https://github.com/chenjiandongx/cutecharts 注: 博客: https://blog.csdn.net/ba ...
- SpringCloud(七):springcloud-config统一管理配置中心
前言: Spring Cloud Config组件是独立的,不需要注册到eureka.config工作原理是把读取目标到配置拉取到本地缓存一份然后供给其他客户端使用,所以一旦config启动成功,可以 ...
- Python Web(三)
Infi-chu: http://www.cnblogs.com/Infi-chu/ 一.Django母版渲染 1.创建母版文件 base.html <!DOCTYPE html> < ...
- MAC本地生成SSH KEY的方法
由于时间原因,直接转载,后期有空再来好好整理一下,大家先凑合着用哈: 参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/wangjunling888/article/details/5111565 ...
- RCA:收单设备调用云端接口频繁超时排查总结
研发中心/王鹏 2019年7月 关键词:OKHTTP,安卓,连接复用,开源软件BUG 一.背景知识: OKHTTP已是安卓项目中被广泛使用的网络请求开源库,它有如下特性: 1.支持HTTP/2,允许所 ...
- Android进阶之绘制-自定义View完全掌握(二)
这是自定义View系列的第二篇博客,我们继续来学习关于自定义View的知识. 今天我们来实现一下广告条案例. 我们要实现的是这样的一个效果. 要想实现这样的效果,我们可以借助ViewPager控件,然 ...
- MySql 字段分组拼接
drop table if exists T_Test; create table T_Test select 'A' parent, 'A1' child union all select 'A', ...
- GO 使用静态链接库编译 生成可执行文件 使用第三方 .a 文件,无源码构造
go build 和 go install 都需要使用源码来进行编译.但是有时候我们只有.a或者.so文件.并不能获取到第三方库的源码,这时我们需要静态链接库编译的技巧: 上图是实验前的文件分布. 使 ...
- JavaScript调用mysql查询bigint数据精度失真解决方案
最近我遇上了如题这个问题,后端用node.js写了一个读取mysql数据的接口,之前使用了很久都没发现什么问题,在查询订单表的订单ID时返回的值却是错的 正确的值是 19102818002800002 ...
