Java——排序算法
java排序从大的分类来看,可以分为内排序和外排序:其中,在排序过程中只使用了内存的排序称为内排序;内存和外存结合使用的排序成为外排序。
下面讲的都是内排序。
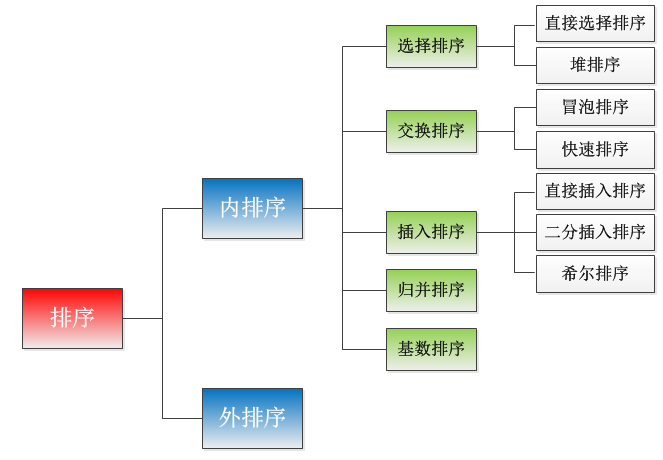
内排序在细分可以这样分:
1、选择排序:直接选择排序,堆排序
2、交换排序:冒泡排序,快速排序
3、插入排序:直接插入排序,二分插入排序,希尔排序
4、归并排序
5、基数排序
是不是觉得这样分类,文字的看着不形象,我也画了一张分类图:
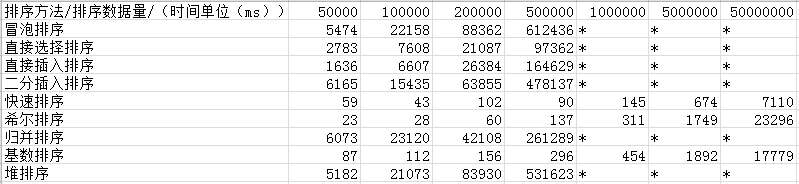
通过测试,我的测试数据(后面数据量大了,有的排序时间太长,我就用*代替了):
通过测试数据来看,不同排序适用于不同的场景,快速排序也不一定是最快的,在数据量比较小的时候,希尔排序反而更快,只是在不断增加数据量的时候,快速排序比较快也很明显。同时,排序也不能只看排序的速度,还需要看它的空间复杂度,即对内存空间利用的要求。例如,快排、归并、堆排序这三者,通过随机数产生数组,它们的时间复杂度可以说是基本一样的,但是当n比较大的时候,你会发现归并排序会比其他两个慢。
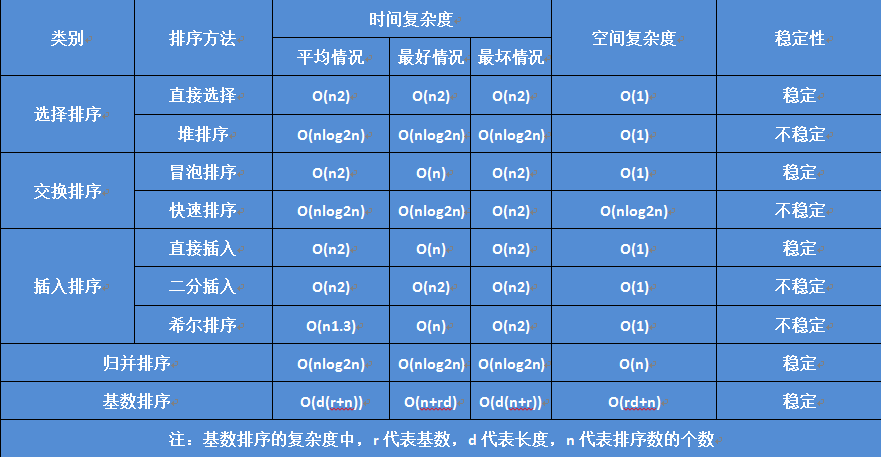
各种排序的时间复杂度、空间复杂度和稳定性,同样图形比较形象:
稳定性:
1、稳定:冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序和基数排序
2、 不稳定:选择排序、快速排序、希尔排序、堆排序
平均时间复杂度
1、O(n^2):直接插入排序,简单选择排序,冒泡排序。
2、在数据量特别大的时候,冒泡排序基本是最慢的。
3、在数据规模较小时(9W内),直接插入排序,简单选择排序差不多。当数据较大时,冒泡排序算法的时间代价最高。性能为O(n^2)的算法基本
上是相邻元素进行比较,基本上都是稳定的。
1、O(nlogn):快速排序,归并排序,希尔排序,堆排序。
2、其中,快排是最好的, 其次是归并和希尔,但数据量特别大的时候,归并排序很容易出现内存溢出的错误,如普通机器n>1000万时。
空间复杂度
1、O(1):冒泡排序、直接插入排序、二分插入排序、希尔排序、直接选择排序、堆排序
2、 O(n):归并排序
3、 O(nlog2n):快速排序
4、O(rd+n):基数排序
排序算法的选择
1、数据规模较小
(1)待排序列基本序的情况下,可以选择直接插入排序;
(2)对稳定性不作要求宜用简单选择排序,对稳定性有要求宜用插入或冒泡
2、数据规模不是很大
(1)完全可以用内存空间,序列杂乱无序,对稳定性没有要求,快速排序,此时要付出log(N)的额外空间。
(2)序列本身可能有序,对稳定性有要求,空间允许下,宜用归并排序
3、数据规模很大
(1)对稳定性有求,则可考虑归并排序。
(2)对稳定性没要求,可以用快速排序。
4、数组初始基本有序的时候,宜用直接插入排序,否则,可以用希尔排序。
下面是实现源码:
- package sort;
- /**
- * Package: sort
- *
- * File: JavaSorts.java
- *
- * Copyright @ 2015 Corpration Name
- *
- */
- public class JavaSorts {
- /**
- * 希尔排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void ShellSort(int[] array){
- int d = array.length;
- do {
- d /= 2; //设置增量,通过设置增量来进行分组,分组后,每一组内采用直接插入排序
- OneShell(array, d);//一个增量对应一趟希尔排序
- } while (d > 1);
- }
- /**
- * 一趟希尔排序
- * @param array
- * @param d
- */
- public static void OneShell(int[] array,int d){
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length - d; i++) {
- int temp = array[i+d]; //array[i+d]的拷贝,每一次插入操作所以插入的值
- if (array[i] > array[i + d]) {
- int j = i;
- //此时分组为:j,j+d,j+2d,j+3d····,组内采用直接插入排序
- while(j >= 0 && array[j] > temp){
- array[j + d] = array[j]; //使用while循环寻找temp能够插入的位置,从右往左寻找,大于temp的往后移动
- j -= d;
- }
- array[j + d] = temp; //插入数据
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 快速排序
- * @param array
- * @param l
- * @param r
- */
- public static void QuickSort(int[] array,int l,int r){
- if (l < r) {
- int i = l,j = r,temp = array[l];
- while(i < j){
- while(i < j && array[j] > temp){
- j--; //从右边开始寻找比temp小的数
- }
- if(i < j){
- array[i++] = array[j]; //找到后,将这个数赋值到i位置上,然后i+1,因为下一轮寻找比temp大的数,从i+1位置开始
- }
- while(i < j && array[i] < temp){
- i++; //从左边寻找比temp大的数
- }
- if(i < j){
- array[j--] = array[i]; //找到后,将这个数赋值到j位置上,然后j-1,因为下一轮寻找比temp小的数从j-1位置开始
- }
- }
- array[i] = temp; //此时比temp小的数都移动到左边,比temp大的数都移动到了右边,最后将temp赋值到中间位置
- QuickSort(array, l, i - 1); //对temp左边的数进行递归
- QuickSort(array, i + 1, r); //对temp右边的数进行递归
- }
- }
- /**
- * 堆排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void HeapSort(int[] array){
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
- BuildMaxHeap(array, array.length - 1 - i);
- Swap(array, 0, array.length - 1 - i);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 创建最大堆
- * @param array
- * @param lastOneIndex
- */
- public static void BuildMaxHeap(int[] array,int lastOneIndex){
- for (int i = (lastOneIndex - 1)/2; i >= 0; i--) {
- int k = i;
- while(2*k + 1 <= lastOneIndex){
- int bigIndex = 2*k + 1; //bigIndex用于记录一个节点树中最大数的索引
- if (bigIndex < lastOneIndex) { //满足这个条件,说明堆中有array[2*k+2]这个节点
- if (array[bigIndex] < array[bigIndex + 1]) {
- bigIndex++; //若满足这个条件,说明k节点下的右子节点大于左子结点,因而bigIndex加1
- }
- }
- if (array[k] < array[bigIndex]) {
- Swap(array, bigIndex, k); //若k节点小于它其中一个子节点,则与这个子节点交换值
- k = bigIndex; //交换完值后,此时k节点下面的bigIndex节点可能不满足堆的性质,所以赋值给k,重新进入下一轮while循环
- }else {
- break;//若k节点满足堆的性质,则直接跳出循环
- }
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 交换array中array[a]、array[b]
- * @param array
- * @param a
- * @param b
- */
- public static void Swap(int[] array,int a,int b){
- if (a < array.length && b < array.length) {
- int temp = array[a];
- array[a] = array[b];
- array[b] = temp;
- }
- }
- /**
- * 直接插入排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void DirectInsertSort(int[] array){
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
- int temp = array[i + 1];
- if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
- int j = i;
- while(j >= 0 && array[j] > temp){
- array[j + 1] = array[j];
- j--;
- }
- array[j + 1] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 二分插入排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void BinaryInsertSort(int[] array){
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
- int temp = array[i + 1]; //需要插入的数
- if(array[i] > array[i + 1]){
- int l = 0; //有序队列中左边标识
- int r = i; //有序队列中右边标识
- while(l < r){
- int mid = (l + r) / 2; //永远指向l->r中间的那个值,中间值与temp(需要插入的值)比较
- if (array[mid] > temp) {
- r--; //通过while循环,二分折半搜索temp应该插入的位置
- }else {
- l++;
- }
- }
- //运行到这里,l==r,即是temp应该插入的位置是array[l](或者array[r])
- for (int j = i + 1; j > l; j--) {
- array[j] = array[j - 1]; //将l -> i的数都往后移动一位
- }
- array[l] = temp; //将temp插入到l位置
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 直接选择排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void DirectSelectSort(int[] array){
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
- int min = array[i];
- for (int j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
- if (array[j] < min) {
- min = array[j];
- array[j] = array[i];
- array[i] = min;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 冒泡排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void BubbleSort(int[] array){
- int temp = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1; j++) {
- if (array[j] > array[j+1]) {
- temp = array[j];
- array[j] = array[j+1];
- array[j+1] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 归并排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void MergeSort(int[] array){
- int left = 0;
- int right = array.length - 1;
- MergeSortRecursive(array, left, right);
- }
- /**
- * 归并排序的递归方法
- * @param array
- * @param left
- * @param right
- */
- public static void MergeSortRecursive(int[] array,int left,int right){
- if (left >= right) {
- return; //递归的停止判断,没有这个判断会报StackOverflowError
- }
- int mid = (left + right)/2;
- MergeSortRecursive(array, left, mid);
- MergeSortRecursive(array, mid+1, right);
- Merge(array, left, mid, right);
- }
- /**
- * 归并排序中合并方法
- * @param array
- * @param left
- * @param mid
- * @param right
- */
- public static void Merge(int[] array,int left,int mid,int right){
- int r_left = mid + 1; //需要合并数组中右边数组第一个数索引
- int[] tempArray = new int[array.length];//一个临时数组,用于合并时暂时存储
- int newIndex = left; //临时数组索引
- int tempLeft = left; //合并完了以后,用于复制数组的索引
- while(left <= mid && r_left <= right){ //将部分的数放入到临时数组中
- if (array[left] < array[r_left]) {
- tempArray[newIndex++] = array[left++];
- }else {
- tempArray[newIndex++] = array[r_left++];
- }
- }
- while (left <= mid) {
- tempArray[newIndex++] = array[left++]; //将左边还剩余的数放入临时数组(若需要合并的左边还剩余数)
- }
- while(r_left <= right){
- tempArray[newIndex++] = array[r_left++];//将右边还剩余的数放入临时数组(若需要和并的右边还剩余数)
- }
- while(tempLeft <= right){
- array[tempLeft] = tempArray[tempLeft++]; //将临时数组复制到array
- }
- }
- /**
- * 基数排序
- * @param array
- */
- public static void RadixSort(int[] array){
- int bits = FindMaxBit(array); //得到数组中最大的那个数的位数
- for (int i = 0; i < bits; i++) {
- OneBitSort(array, i+1); //一位基数的排序
- }
- }
- /**
- * 一位基数的排序
- * @param array
- * @param bit
- */
- public static void OneBitSort(int[] array,int bit){
- int[] tempArray = new int[array.length];
- int index = 0;
- int tempIndex = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
- if (FindBitNum(array[j], bit) == i) {
- tempArray[index++] = array[j];
- }
- }
- }
- while(tempIndex < array.length){
- array[tempIndex] = tempArray[tempIndex++]; //复制数组
- }
- }
- /**
- * 得到某个数某一位的数(例如:num=1234,n=2,FindBitNum(1234,2)=3)
- * @param num
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static int FindBitNum(int num,int n){
- int key1 = (int)Math.pow(10, n);
- int key2 = (int)Math.pow(10, n-1);
- num %= key1;
- num /= key2;
- return num;
- }
- /**
- * 得到一个数组中最大数的位数
- * @param array
- * @return
- */
- public static int FindMaxBit(int[] array){
- if (array == null || array.length ==0) {
- return 0;
- }
- int max = array[0];
- for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
- if (array[i] > max) {
- max = array[i];
- }
- }
- int bit = 0;
- while(max / 10 != 0 || max % 10 != 0){
- max /= 10;
- bit++;
- }
- return bit;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("冒泡排序:"+SortThreads.getBubbleSortTime());
- System.out.println("直接选择排序:"+SortThreads.getDirSelectSortTime());
- System.out.println("直接插入排序:"+SortThreads.getDirInsertSortTime());
- System.out.println("二分插入排序:"+SortThreads.getBinaryInsertSortTime());
- System.out.println("快速排序:"+SortThreads.getQuickSortTime());
- System.out.println("希尔排序:"+SortThreads.getShellSortTime());
- System.out.println("归并排序:"+SortThreads.getMergeSortTime());
- System.out.println("基数排序:"+SortThreads.getRadixSortTime());
- System.out.println("堆排序:"+SortThreads.getHeapSortTime());
- }
- }
对于这些排序算法,我对它们的排序速度比较感兴趣,所以自己也测试了一下,数组是通过随机数产生的,我测的时候每一个数是不大于4位数,即不大于10000。
ProduceRandomNum.java产生随机数的数组:
- package sort;
- import java.util.Random;
- /**
- * Package: sort
- *
- * File: SortRunnable.java
- *
- * Copyright @ 2015 Corpration Name
- *
- */
- public class ProduceRandomNum{
- public synchronized static int[] RandomArray(int num,int n){
- Random random = new Random();
- int[] array = new int[num];
- for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
- array[i] = random.nextInt((int)Math.pow(10, n));
- }
- return array;
- }
- }
SortThreads.java测试排序的时间的方法,封装都一个类中,这个类我一直想把它写成多线程的方式(即是将这些排序一起运行),但是后面没有找到一个好的方法,所以后面就用了这种最笨的方法,有好办法的大神一定要指出来。
- package sort;
- /**
- * Package: sort
- *
- * File: SortThreads.java
- *
- * Copyright @ 2015 Corpration Name
- *
- */
- public class SortThreads {
- private static final int arrayNum = 500000;
- private static final int bit = 4;
- public static long getBubbleSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.BubbleSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getQuickSortTime(){
- int[] array = ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit);
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.QuickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getDirSelectSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.DirectSelectSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getDirInsertSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.DirectInsertSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getBinaryInsertSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.BinaryInsertSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getShellSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.ShellSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getMergeSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.MergeSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getRadixSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.RadixSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- public static long getHeapSortTime(){
- long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- JavaSorts.HeapSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
- long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
- return newTime - oldTime;
- }
- }
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/u014039577/article/details/49667643
Java——排序算法的更多相关文章
- 常用Java排序算法
常用Java排序算法 冒泡排序 .选择排序.快速排序 package com.javaee.corejava; public class DataSort { public DataSort() { ...
- Java排序算法之直接选择排序
Java排序算法之直接选择排序 基本过程:假设一序列为R[0]~R[n-1],第一次用R[0]和R[1]~R[n-1]相比较,若小于R[0],则交换至R[0]位置上.第二次从R[1]~R[n-1]中选 ...
- java排序算法(一):概述
java排序算法(一)概述 排序是程序开发中一种非常常见的操作,对一组任意的数据元素(活记录)经过排序操作后,就可以把它们变成一组按关键字排序的一组有序序列 对一个排序的算法来说,一般从下面三个方面来 ...
- java排序算法(十):桶式排序
java排序算法(十):桶式排序 桶式排序不再是一种基于比较的排序方法,它是一种比较巧妙的排序方式,但这种排序方式需要待排序的序列满足以下两个特征: 待排序列所有的值处于一个可枚举的范围之类: 待排序 ...
- java排序算法(九):归并排序
java排序算法(九):归并排序
- java排序算法(八):希尔排序(shell排序)
java排序算法(八):希尔排序(shell排序) 希尔排序(缩小增量法)属于插入类排序,由shell提出,希尔排序对直接插入排序进行了简单的改进,它通过加大插入排序中元素之间的间隔,并在这些有间隔的 ...
- java排序算法(七):折半插入排序
java排序算法(七):折半插入排序 折半插入排序法又称为二分插入排序法,是直接插入排序法的改良版本,也需要执行i-1趟插入.不同之处在于第i趟插入.先找出第i+1个元素应该插入的位置.假设前i个数据 ...
- java排序算法(六):直接插入排序
java排序算法(六):直接插入排序 直接插入排序的基本操作就是将待的数据元素按其关键字的大小插入到前面的有序序列中 直接插入排序时间效率并不高,如果在最坏的情况下,所有元素的比较次数的总和为(0+1 ...
- java排序算法(五):快速排序
java排序算法(五):快速排序 快速排序是一个速度非常快的交换排序算法,它的基本思路很简单,从待排的数据序列中任取一个数据(如第一个数据)作为分界值,所有比它小的元素放到左边.所有比它大的元素放到右 ...
- java排序算法(四):冒泡排序
java排序算法(四):冒泡排序 冒泡排序是计算机的一种排序方法,它的时间复杂度是o(n^2),虽然不及堆排序.快速排序o(nlogn,底数为2).但是有两个优点 1.编程复杂度很低.很容易写出代码 ...
随机推荐
- [原题复现]2018护网杯(WEB)easy_tornado(模板注入)
简介 原题复现: 考察知识点:模板注入 线上平台:https://buuoj.cn(北京联合大学公开的CTF平台) 榆林学院内可使用信安协会内部的CTF训练平台找到此题 [护网杯 2018]eas ...
- 还不懂spring中的bean的话,你一定得好好看看这篇文章
bean的作用域 bean的生命周期 bean的装配 代码 实体类 package com; import java.util.List; public class User { private St ...
- CorelDRAW常用工具之手绘工具
对于平面设计师来说,一个好用顺手的手绘工具是必不可少的,CorelDRAW的手绘工具能将手绘笔触转换成平滑的线条或者形状. 1.基础操作 CorelDRAW的手绘工具组包含手绘.2点线.贝塞尔.钢笔. ...
- 使用ABBYY FineReader 手动校正文档复杂结构
ABBYY FineReader 15(Windows系统)拥有强大的OCR识别功能,能对扫描仪或者数码相机等光学工具获取的图像进行识别,解析其中的文本.图像.表格.条形码等,方便用户进一步获取图像中 ...
- 宝塔Linux面板基础命令
安装宝塔Centos安装脚本 yum install -y wget && wget -O install.sh http://download.bt.cn/install/insta ...
- jmeter多用户登录并发测试
在使用Jmeter进行性能测试时,我们通常会需要配置多个不同用户进行并发测试,这里简单介绍一下配置方法. 1.运行Jmeter.bat, 在打开的测试计划中右键添加一个线程组: 2.在线程组下添加录 ...
- P6823 「EZEC-4」zrmpaul Loves Array
发现进行一次排序后先前的操作都无效了,所以只需做最后一次排序后的操作.翻转操作打个翻转标记,互换操作根据翻转标记即可. 时间复杂度 \(O\left(n+m\right)\). code: #incl ...
- Java基础教程——List(列表)
集合概述 Java中的集合,指一系列存储数据的接口和类,可以解决复杂的数据存储问题. 导包:import java.util.*; 简化的集合框架图如下: List·列表 ArrayList List ...
- VB的使用
一.今天讲解VB的使用,明天讲解VC与VB的相互调用: 1.指针是什么? 不需要去找什么标准的定义,它就是一个32位整数,在C语言和在VB里都可以用Long类型来表示.在32位Windows平台 ...
- Event Loop - 事件队列
Event Loop 定义: event - 事件 loop - 循环,既然叫事件循环,那么循环的点在哪? 循环的是一个又一个的任务队列,这些任务队列由宏任务和微任务构成 两条原则 一次处理一个任务 ...