【Java】浅谈Java IO
注意
本文的代码,为了学习方便,简化代码复杂度,未考虑拆包、粘包等情况的处理。所以仅供学习使用,不能用于实际环境。
阻塞IO,BIO
Java1.1发布的IO是BIO。阻塞地连接之后,通过流进行同步阻塞地通讯。
同步阻塞连接
因同步阻塞地监听连接,如果服务端只有单线程进程处理,每个请求必须等待前一请求处理完毕才开始处理新请求。
所以,一般情况下,服务端每接收一个请求,可交派给一个线程处理这个请求,这样,在处理环节实现异步。其逻辑图如下:
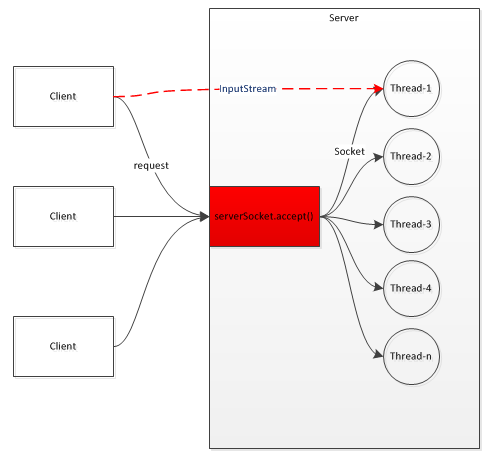
阻塞通讯
客户端与服务端之间的通讯是通过流进行传输的,而流是单向的、阻塞的,即通讯效率依赖于对方以及网络。其逻辑图如下:

代码实例
服务端:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.nicchagil.ioexercise.Constant;
public class MyHelloServer {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyHelloServer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(Constant.SERVER_PORT)) {
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 阻塞接收
new HelloBusinessThread(socket).start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("输入输出异常", e);
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
服务端业务线程:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloBusinessThread extends Thread {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloBusinessThread.class);
Socket socket = null;
public HelloBusinessThread(Socket socket) {
super();
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String result = bufferedReader.readLine();
logger.info("接收一个请求:" + result);
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(outputStream);
printWriter.println("hello");
logger.info("发送一个响应");
printWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
客户端:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.nicchagil.ioexercise.Constant;
public class MyHelloClient {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyHelloClient.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (Socket socket = new Socket(Constant.SERVER_HOST, Constant.SERVER_PORT);) {
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(outputStream);
printWriter.println("hi");
logger.info("发送一个请求");
printWriter.flush();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String result = bufferedReader.readLine();
logger.info("收到一个答复:" + result);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
logger.error("无法找到此主机", e);
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("输入输出异常", e);
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.in.read();
}
}
非阻塞IO,NIO
JDK1.4后,推出了NIO,为非阻塞IO。
其在Unix中依赖select、poll、epoll调用,在JDK1.5 update10之后,使用的是epoll调用。
多路复用器,Selector
多路复用器,通过单线程轮询多条Channel是否就绪,如果就绪,则获取对应的SelectionKey,从中去获取就绪的Channel进行后续的IO操作。
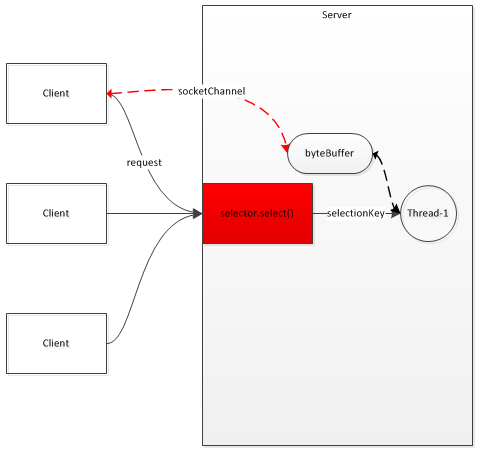
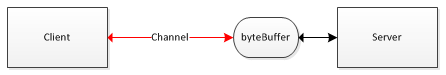
通道与缓冲区,Channel与Buffer
流,是单向的。而通道,是全双工的,即双向的。
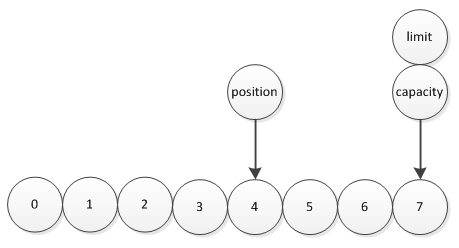
缓冲区有3个属性,position、limit、capacity,分别表示位置、限制位、容量。
比如flip(),翻转缓冲区:
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position; // 将原位置赋予限制位
position = 0; // 位置置0
mark = -1;
return this;
}
加入写入完毕是这样的:
flip()后开始读取是这样的:

比如clear(),清除缓冲区:
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0; // 位置置0
limit = capacity; // 容量赋予限制位
mark = -1;
return this;
}
比如rewind(),重绕缓冲区:
public final Buffer rewind() {
position = 0; // 位置置0
mark = -1;
return this;
}
代码实例
先写一个工具类:
package com.nicchagil.ioexercise.nio.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class NIOUtil {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NIOUtil.class);
/**
* 将信息写入通道
*/
public static void writeToChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel, String message) {
if (message == null || message.trim().length() == 0) {
return;
}
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
bytes = message.getBytes("UTF-8"); // 转换为字节数组
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
throw new RuntimeException(e1);
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length); // 开辟缓冲区
byteBuffer.put(bytes); // 放入缓冲区
byteBuffer.flip(); // 切换读取缓冲区模式
try {
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer); // 写入通道
// logger.info("发送 -> {}", message);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 读取并转换为String
*/
public static String readToString(SocketChannel socketChannel, SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64); // 开辟缓冲区
int readByteNum = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); // 读取数据
/* 有数据 */
if (readByteNum > 0) {
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.remaining()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
return message;
}
/* 无数据,无处理 */
if (readByteNum == 0) {
}
/* 小于零,表示连接已关闭 */
if (readByteNum < 0) {
NIOUtil.cancelSelectionKey(selectionKey);
socketChannel.close();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 取消/关闭SelectionKey
*/
public static void cancelSelectionKey(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
if (selectionKey == null) {
return;
}
selectionKey.cancel(); // 取消SelectionKey
if (selectionKey.channel() != null) {
try {
selectionKey.channel().close(); // 关闭通道
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
服务端:
package com.nicchagil.ioexercise.nio.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.nicchagil.ioexercise.Constant;
import com.nicchagil.ioexercise.nio.util.NIOUtil;
public class NIOServer {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
public NIOServer() throws Exception {
selector = Selector.open(); // 多路复用器
/* 配置通道 */
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(Constant.SERVER_HOST, Constant.SERVER_PORT), 512); // 监听的主机、端口,和挂起的最大连接数
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); // 通道绑定多路复用器,并监听“连接”事件
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = null;
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = null;
SelectionKey selectionKey = null;
while (true) {
try {
this.logger.info("polling...");
selector.select(); // 阻塞轮询,当轮询通道中有IO就绪时,返回
selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); // 获取就绪通道的SelectionKey
this.logger.info("当前就绪的通道数 -> {}", selectionKeys.size());
iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
selectionKey = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
try {
this.handle(selectionKey); // 处理该通道业务
} catch (IOException e) {
this.logger.error("通道{}出现异常:{}", selectionKey, e);
NIOUtil.cancelSelectionKey(selectionKey);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
this.logger.error("多路复用监听出现异常", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 处理通道业务
*/
public void handle(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) { // 无效快速失败
this.logger.info("连接无效");
return;
}
/* 连接事件 */
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
this.accept(selectionKey);
}
/* 读取事件 */
else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel(); // 转换为连接Socket
String message = NIOUtil.readToString(socketChannel, selectionKey);
this.logger.info("message -> {}", message);
if (message != null) {
NIOUtil.writeToChannel(socketChannel, "hi, client");
}
}
}
/**
* 接受连接
*/
private void accept(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
this.logger.info("开始连接事件");
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel)selectionKey.channel(); // 转换为服务器Socket
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); // 接收一个连接
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 非阻塞
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); // 通道绑定多路复用器,并监听“读取”事件
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new NIOServer();
}
}
客户端:
package com.nicchagil.ioexercise.nio.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.nicchagil.ioexercise.Constant;
import com.nicchagil.ioexercise.nio.util.NIOUtil;
public class NIOClient {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private Selector selector; // 多路复用器
private SocketChannel socketChannel; // 通道
public NIOClient() throws IOException {
this.selector = Selector.open(); // 多路复用器
/* 配置通道 */
this.socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
this.socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 非阻塞
/* 连接服务器 */
this.connect();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = null;
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = null;
SelectionKey selectionKey = null;
while (true) {
try {
this.selector.select(); // 阻塞轮询,当轮询通道中有IO就绪时,返回
selectionKeys = this.selector.selectedKeys(); // 获取就绪通道的SelectionKey
iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
selectionKey = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
try {
this.handle(selectionKey); // 处理该通道业务
} catch (IOException e) {
this.logger.error("通道{}出现异常:{}", selectionKey, e);
NIOUtil.cancelSelectionKey(selectionKey);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
this.logger.error("多路复用监听出现异常", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 连接服务器
*/
public void connect() throws IOException {
boolean connect = this.socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(Constant.SERVER_HOST, Constant.SERVER_PORT));
if (connect) { // 连接成功
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
NIOUtil.writeToChannel(socketChannel, "hi, server");
} else { // 连接失败
this.socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
}
/**
* 处理通道业务
*/
public void handle(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) { // 无效快速失败
// this.logger.info("连接无效");
return;
}
/* 连接事件 */
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {
this.connect(selectionKey);
}
/* 读取事件 */
else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel(); // 转换为连接Socket
String message = NIOUtil.readToString(socketChannel, selectionKey);
this.logger.info("message -> {}", message);
}
}
/**
* 连接
*/
private void connect(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException {
if (socketChannel.finishConnect()) { // 完成连接
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
NIOUtil.writeToChannel(socketChannel, "hi, server");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new NIOClient();
}
}
异步IO,AIO
JDK1.7提供了NIO 2.0,包含异步IO,对应UNIX网络编程的AIO。
它是真正的异步非阻塞IO,不需多路复用器轮询,操作完成回调CompletionHandler接口(从代码上可以看到,有好几个处理器实现CompletionHandler,比如连接处理器、读取处理器、发送处理器)。
代码实例
首先将一些重复的代码提到一个公用类中:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class AIOUtil {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AIOUtil.class);
/**
* 通过通道发送消息
* @param socketChannel 异步套接字通道
* @param message 消息
*/
public static void write(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, String message) {
byte[] bytes = message.getBytes();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
byteBuffer.put(bytes);
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer, byteBuffer, new WriteHandler(socketChannel)); // 写消息
}
/**
* 关闭通道
* @param socketChannel 异步套接字通道
*/
public static void close(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel) {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("关闭套接字通道异常:{}", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
服务器入口类:
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import com.nicchagil.ioexercise.Constant;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(); // 服务器套接字通道
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(Constant.SERVER_PORT)); // 监听端口
/*
* 接收一个连接,此方法初始一个异步操作来接收一个连接。
* 处理器参数是一个完成处理器,当接收到连接或连接失败时被回调完成处理器。
* 为了能并发处理新连接,完成处理器并不是被初始线程直接调用。
*/
serverSocketChannel.accept(serverSocketChannel, new AcceptHandler()); // 接收一个连接
System.in.read();
}
}
接收连接处理器:
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 接收连接处理器
*/
public class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel> {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel) {
serverSocketChannel.accept(serverSocketChannel, this); // 服务器Socket继续接收请求
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
/*
* 从通道中读取字节到缓冲区,此方法初始一个异步读取操作,从通道中读取字节到缓冲区。
* 处理器参数是一个完成处理器,读取完成或失败时被调用。
* 读取的字节数会传递给处理器,如没有可读取的字节,则传递-1。
*/
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer, byteBuffer, new ReadHandler(socketChannel)); // 读取消息
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel attachment) {
this.logger.error("接收连接异常:{}", exc);
}
}
读取消息处理器:
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 读取消息处理器
*/
public class ReadHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel;
public ReadHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel) {
this.socketChannel = socketChannel;
}
/**
* 读取消息
*/
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {
byteBuffer.flip(); // 翻转缓冲区
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.remaining()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
try {
String message = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
this.logger.info("接收到消息 -> {}", message);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
this.logger.info("接收消息异常:{}", e);
}
// 向客户端发送消息
AIOUtil.write(socketChannel, "hi, client");
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
this.logger.info("接收消息异常");
AIOUtil.close(socketChannel);
}
}
发送消息处理器:
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* 发送消息处理器
*/
public class WriteHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel;
public WriteHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel) {
this.socketChannel = socketChannel;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) {
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buffer, buffer, this);
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
this.logger.info("发送消息异常");
AIOUtil.close(socketChannel);
}
}
Netty,NIO框架
NIO的API太过复杂,开发者极容易出错,所以如果有一个NIO框架对我们项目的开发有好处,而Netty是一个优秀的NIO框架。
代码实例
首先定义了些常量:
public interface Constant {
String HOST = "127.0.0.1";
Integer PORT = 60000;
String DELIMITER = "<!#%&(@$^*)>";
}
服务端与服务端入口:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.nicchagil.nettyexercise.common.Constant;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class MyServer {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private Integer port;
public MyServer(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 事件循环群组
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); // 启动类
serverBootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) // 指定事件循环群组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 指定通道类型
.localAddress(this.port) // 指定监听端口
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { // 指定通道初始化器
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline channelPipeline = ch.pipeline();
/* 分隔符方式分包 */
ByteBuf delimiterByteBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(Constant.DELIMITER.getBytes());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, delimiterByteBuf)); // 指定单条消息最大长度和分隔符
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
channelPipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler()); // 指定数据入站处理器
}
});
ChannelFuture cf = serverBootstrap.bind().sync(); // 服务器同步绑定
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync(); // 关闭服务器通道
} finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync(); // 释放线程池资源
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new MyServer(Constant.PORT).start();
}
}
服务端处理器:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
public static AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger();
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
this.logger.info("通道被激活");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
this.logger.info("第{}次读取信息 -> {}", counter.incrementAndGet(), msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
this.logger.info("读取完成");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("ok...", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// channelFuture.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable throwable) throws Exception {
this.logger.error("出现异常 -> {}", throwable);
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端与客户端入口:
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.nicchagil.nettyexercise.common.Constant;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class MyClient {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private final String host;
private final int port;
public MyClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(this.host, this.port))
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.connect().sync();
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new MyClient(Constant.HOST, Constant.PORT).start();
System.in.read();
}
}
客户端处理器:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.nicchagil.nettyexercise.common.Constant;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class MyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
this.logger.info("通道被激活");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, Netty, abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwsyz, 123456" + Constant.DELIMITER, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
this.logger.info("读取信息 -> {}", msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
this.logger.info("读取完成");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable throwable) throws Exception {
this.logger.error("出现异常 -> {}", throwable);
ctx.close();
}
}
【Java】浅谈Java IO的更多相关文章
- 浅谈Java的throw与throws
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/luoweifu/article/details/10721543 我进行了一些加工,不是本人原创但比原博主要更完善~ 浅谈Java异常 以前虽然知道一 ...
- !! 浅谈Java学习方法和后期面试技巧
浅谈Java学习方法和后期面试技巧 昨天查看3303回复33 部落用户大酋长 下面简单列举一下大家学习java的一个系统知识点的一些介绍 一.java基础部分:java基础的时候,有些知识点是非常重要 ...
- 浅谈JAVA中如何利用socket进行网络编程(二)
转自:http://developer.51cto.com/art/201106/268386.htm Socket是网络上运行的两个程序间双向通讯的一端,它既可以接受请求,也可以发送请求,利用它可以 ...
- 浅谈Java中的equals和==(转)
浅谈Java中的equals和== 在初学Java时,可能会经常碰到下面的代码: 1 String str1 = new String("hello"); 2 String str ...
- 浅谈Java中的对象和引用
浅谈Java中的对象和对象引用 在Java中,有一组名词经常一起出现,它们就是“对象和对象引用”,很多朋友在初学Java的时候可能经常会混淆这2个概念,觉得它们是一回事,事实上则不然.今天我们就来一起 ...
- 浅谈Java中的equals和==
浅谈Java中的equals和== 在初学Java时,可能会经常碰到下面的代码: String str1 = new String("hello"); String str2 = ...
- 浅谈JAVA集合框架
浅谈JAVA集合框架 Java提供了数种持有对象的方式,包括语言内置的Array,还有就是utilities中提供的容器类(container classes),又称群集类(collection cl ...
- 浅谈java性能分析
浅谈java性能分析,效能分析 在老师强烈的要求下做了效能分析,对上次写过的词频统计的程序进行分析以及改进. 对于效能分析:我个人很浅显的认为就是程序的运行效率,代码的执行效率等等. java做性能测 ...
- 浅谈Java中的深拷贝和浅拷贝(转载)
浅谈Java中的深拷贝和浅拷贝(转载) 原文链接: http://blog.csdn.net/tounaobun/article/details/8491392 假如说你想复制一个简单变量.很简单: ...
- 浅谈Java中的深拷贝和浅拷贝
转载: 浅谈Java中的深拷贝和浅拷贝 假如说你想复制一个简单变量.很简单: int apples = 5; int pears = apples; 不仅仅是int类型,其它七种原始数据类型(bool ...
随机推荐
- HDU1575-Tr 【矩阵快速幂】(模板题)
<题目链接> 题目大意: A为一个方阵,则Tr A表示A的迹(就是主对角线上各项的和),现要求Tr(A^k)%9973. Input 数据的第一行是一个T,表示有T组数据. 每组数据的第 ...
- HDU1789 Doing Homework again 做作业【贪心】
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/HDU-1789 题目大意: 给出N个作业的截至日期,和N个作业不交所扣掉的分数,要求输出扣除分数做少的方案. 解析: 与上一道销售商品 ...
- Hash值破解工具(findmyhash与hash-identifier破解Hash值)
Hash值破解工具(findmyhash与hash-identifier破解Hash值) 前言: Kali Linux提供各种哈希密文破解工具,如hashcat.john.rainbows.不论哪一种 ...
- Python爬虫之PyQuery使用(六)
Python爬虫之PyQuery使用 PyQuery简介 pyquery能够通过选择器精确定位 DOM 树中的目标并进行操作.pyquery相当于jQuery的python实现,可以用于解析HTML网 ...
- 智能优化 之 下山单纯形法 C++
单纯形法简介在其他网站上都可以查到,我就不多说了 我们主要说方法 它主要解决的是局部最优解的问题 利用多边形进行求解的,若有n个变量,则利用n+1边形 我们这里以两个变量为例,求解第三维度的最优解 例 ...
- C# 组件模组引用第三方组件问题
对接上一文章由于是动态加载指定程序集,会把当前目录下所有dll都加载进来.如果像sqlite这种第三组件调用了由C.C++非.net语言所以生成的Dll.因为自动生成的原因.会把非C#生成的dll都加 ...
- 10.16 NOIP模拟赛
目录 2018.10.16 NOIP模拟赛 A 购物shop B 期望exp(DP 期望 按位计算) C 魔法迷宫maze(状压 暴力) 考试代码 C 2018.10.16 NOIP模拟赛 时间:2h ...
- Codechef October Challenge 2018 游记
Codechef October Challenge 2018 游记 CHSERVE - Chef and Serves 题目大意: 乒乓球比赛中,双方每累计得两分就会交换一次发球权. 不过,大厨和小 ...
- python:函数中五花八门的参数形式(茴香豆的『回』字有四种写法)
毫不夸张的说,python语言中关于函数参数的使用,是我见过最为灵活的,随便怎么玩都可以,本文以数学乘法为例,演示几种不同的传参形式: 一.默认参数 def multiply1(x, y): retu ...
- 细说ASP.NET Windows身份认证
上篇博客我谈到了一些关于ASP.NET Forms身份认证方面的话题,这次的博客将主要介绍ASP.NET Windows身份认证. Forms身份认证虽然使用广泛,不过,如果是在 Windows Ac ...
