cpu-z for ubuntu 12.04 64bit : cpu-g
wget https://launchpad.net/~phantomas/+archive/ppa/+files/cpu-g_0.9.0_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i cpu-g*.deb http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/620416:discovering-and-monitoring-hardware-in-linux-
Discovering and Monitoring Hardware in Linux
 Exclusive
ExclusiveNothing ever need be a mystery on Linux as it has a large number of excellent utilities for discovering hardware and monitoring hardware health. Here are a handful of good tools for spotting possible hard drive failure, displaying hardware information and monitoring temperatures, fans, voltages, email, music players and more.

GSmartControl provides an excellent graphical interface to smartmontools.
Hard Drive Health
You're probably familiar with the excellent smartmontools for monitoring hard drive health, and getting early warning of possible drive failure. Smartmontools runs tests and reads data on drives that have the Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) system built into them. It's been around seemingly forever, but did you know there is a graphical interface for it? SmartControl puts a nice interface on smartmontools and supports all of its functions.
You can run a short or long self-test with a button click, and GSmartControl is especially valuable for quickly and easily finding log files and reading SMART attributes data, reading test results, and seeing detailed data on your hard drives.
Monitoring and Alerting
It's not fun when your first warning of a failed CPU fan is a melted-down CPU. lm-sensors is still my top choice for monitoring temperatures, fans, and voltages:
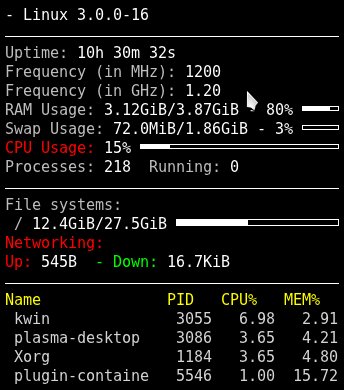
A simple Conky setup.
$ sensors
atk0110-acpi-0
Adapter: ACPI interface
Vcore Voltage: +1.23 V (min = +0.85 V, max = +1.60 V)
+3.3 Voltage: +3.31 V (min = +2.97 V, max = +3.63 V)
+5 Voltage: +4.97 V (min = +4.50 V, max = +5.50 V)
+12 Voltage: +12.15 V (min = +10.20 V, max = +13.80 V)
CPU FAN Speed: 3183 RPM (min = 600 RPM)
CPU Temperature: +44.0°C (high = +60.0°C, crit = +95.0°C)
MB Temperature: +40.0°C (high = +45.0°C, crit = +75.0°C)
I wish for a nice graphical front-end and alerter to lm-sensors; GNOME and KDE release nice ones and then they disappear. Xsensors is simple, the xfce4-sensors-plugin looks great in XFCE, and the KDE4 System Monitor widget is all right, but it's not very configurable and does no alerting. psensor is a rather nice, and it can run as a server for remote monitoring. GKrellM is an old favorite cram-full of features, alerting, and configurability.
Conky takes the prize for most objects supported. In addition to the usual system monitors it monitors email, music players, instant messaging, logfiles, weather forecast, and pretty much anything you want. If there isn't a plugin to do what you want you can write one.
Probing Hardware
It helps to know what is on your system, and you're probably familiar with the lscpi command for getting detailed information on everything connected to the PCI bus. Here are a few options you may not know about:
lspci with no options shows a hardware list with vendor names, chipsets, and device types.
lspci -k displays the kernel driver in use for each device, and available kernel modules, like this example for an Nvidia graphics card:
01:00.0 VGA compatible controller: nVidia Corporation G98 [GeForce 8400 GS] (rev a1)
Subsystem: Micro-Star International Co., Ltd. Device 1162
Kernel driver in use: nvidia
Kernel modules: nvidia_current, nouveau, nvidiafb
lspci -t displays a tree view that shows the relationships between your devices.
The vendor names, chipsets, subsystems, device classes-- all the information displayed by lspci comes from a giant database, the PCI ID Repository. You can update your local copy of this database, /usr/share/misc/pci.ids, by running the update-pciids command as root.
Using dmidecode
dmidecode is a wonderful utility for getting information about everything on your motherboard without opening the case, or booting to the BIOS. If you run dmidecode with no options it spits out pages of data. You can select what you want to see by consulting the DMI types table in man dmidecode. Here are some examples.
How much RAM does your motherboard support?
$ sudo dmidecode -t 16
# dmidecode 2.9
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x0033, DMI type 16, 15 bytes
Physical Memory Array
Location: System Board Or Motherboard
Use: System Memory
Error Correction Type: None
Maximum Capacity: 16 GB
Error Information Handle: Not Provided
Number Of Devices: 4
How much RAM is installed, and in which slots? This example has most of the output snipped:
$ sudo dmidecode -t 17
# dmidecode 2.9
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x0035, DMI type 17, 27 bytes
Memory Device
Total Width: 64 bits
Data Width: 64 bits
Size: 2048 MB
Form Factor: DIMM
Set: None
Locator: DIMM0
Bank Locator: BANK0
Type: DDR2
Type Detail: Synchronous
Speed: 800 MHz (1.2 ns)
What are the onboard devices, such as video, networking, sound?
$ sudo dmidecode -t 10
# dmidecode 2.9
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x002C, DMI type 10, 6 bytes
On Board Device Information
Type: Video
Status: Enabled
Description: ATI
Handle 0x002D, DMI type 10, 6 bytes
On Board Device Information
Type: Ethernet
Status: Enabled
Description: To Be Filled By O.E.M.

The graphical lshw viewer.
And much, much more, which is all detailed in the man page.
Using lshw
The lshw command also gives a detailed peek inside your PC, and you can invoke its graphical view with lshw -X (left). It's a little weird to navigate, but everything is there.
I like the way lshw presents information. It includes details like filesystem types and sizes, bus information, and capabilities. It has a couple of nice extras: the -sanitize option scrubs IP addresses, serial numbers, and other identifiers, and the -class option lets you choose categories such as volume and disk for block devices, memory, and display. Run lshw -short to see what the categories are. Here is an abbreviated example:
$ sudo lshw -short
H/W path Device Class Description
=====================================================
/0/33/2 memory 2GiB DIMM DDR2 Synchronous 800 MHz (1.2 ns
/0/33/3 memory DIMM [empty]
/0/100/a/0 eth0 network RTL8111/8168B PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet
/0/100/11/0 /dev/sda disk 2TB SAMSUNG HD204UI
/0/100/11/0/1 /dev/sda1 volume 1651GiB EXT4 volume
/0/100/11/0/2 /dev/sda2 volume 211GiB EXT4 volume
/0/100/11/1 /dev/sdb disk 640GB WDC WD6401AALS-0
/0/100/11/1/1 /dev/sdb1 volume 27GiB EXT4 volume
/0/100/11/1/2 /dev/sdb2 volume 1907MiB Linux swap volume
/0/100/11/0.0.0 /dev/cdrom2 disk iHAS424 B
/1 wlan0 network Wireless interface
cpu-z for ubuntu 12.04 64bit : cpu-g的更多相关文章
- Ubuntu 12.04 64bit 配置完android 5.0编译环境后出现“could not write bytes: Broken pipe.”而无法进入输入帐号密码的登陆界面
Ubuntu 12.04 64bit 配置完android 5.0编译环境后出现“could not write bytes: Broken pipe.”而无法进入输入帐号密码的登陆界面.上网问了问百 ...
- Ubuntu 12.04 64bit GCC交叉编译器制作 原创
...
- build linaro 4.8 on ubuntu 12.04 64bit
安装必要的软件 sudo apt-get build-dep gcc binutils gdb sudo apt-get install curl gawk sudo apt-get install ...
- mark ubuntu 16.04 64bit + cpu only install mtcnn
大神代码链接 称之为MTCNN人脸检测算法,同时有大神已经GitHub上开源了其基于caffe的C++ API 的源代码,https://github.com/DaFuCoding/MTCNN_Caf ...
- 在Ubuntu 12.04 - 64bit中安装CodeSourcery时提示错误
安装时提示错误,Your 64-bit Linux host is missing the 32-bit libraries requied to install and use Sourcery C ...
- Ubuntu 12.04 64bit 安装编译GCC 4.1.2 绝对原创
1. 下载并解压源代码: wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/gnu/gcc/gcc-4.1.2/gcc-4.1.2.tar.bz2 tar jxvf gcc-4.1.2. ...
- ubuntu 12.04 64bit 安装 teamviewer 8.0
1. 在http://www.teamviewer.com下载teamviewer_linux_x64.deb 2.sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux_x64.deb 3.如果 ...
- Windows XP硬盘安装Ubuntu 12.04双系统图文详解
Windows XP硬盘安装Ubuntu 12.04双系统图文详解 Ubuntu 12.04 LTS版本于2012年4月26日发布,趁着五一放假,赶紧在自己的Windows XP的电脑上安装下Ubun ...
- Ubuntu 12.04 安装MySQL
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yhLinux/p/4012689.html 本文适合新手入门. 本文是对 Ubuntu 12.04 环境下安装 MySQL 的记录,通过这两天 ...
随机推荐
- ros 充电topic
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding=utf- import rospy from std_msgs.msg import String i= def talker(): glo ...
- js,jq获取父,兄弟,子节点整理
js获取节点 父: parentNode 获取已知节点的父节点. 子: childNodes; 得到全部子节点 children 得到全部子节点 firstChild 获得第一个子节点 lastChi ...
- php中if(\$a==\$b)和if(\$a=\$b)什么区别?
<?php // if($a==$b)和if($a=$b)什么区别? $a = 1; $b = 1; if ($a == $b) { // 通过 echo '通过'.PHP_EOL; } if ...
- 求文件的hash值(基于SHA3的Hash)
import hashlib import tkinter from tkinter import filedialog import pyperclip def fileHash(fileName) ...
- aar的使用(module或者library)
引入: 1. android studio正常的module引用aar文件需要配置如下: ① 在module的build.gradle的android节点下 repositories { flatDi ...
- 学习笔记40—endnote点点滴滴
1.在endnote中,如果引用书籍时,需要作者名称后面加“逗号”,作者名称才不会缩写, 比如: 1) 加“逗号”之前: 2)加“逗号”之后
- Qt的QVariant类
QStandardItemModel类中的函数 bool setData(const QModelIndex &index, const QVariant &value, int ro ...
- go build 和 go install
环境:Win10 + GO1.9.2 1.区别 ①go build:编译go源码生成一个可执行文件:使用-o参数可以指定生成的可执行文件名称,如go build -o test.exe ②go ins ...
- lua --- 点号 和 冒号
冒号的作用:1.定义函数时,给函数添加隐藏的第一个参数 self2.调用函数时,默认把当前调用者作为第一个参数传递进去 如 a:b(c) 可以理解为 a.b(a, c) 以下是用点号的定义和调用函数的 ...
- C#获取路径中最后一个文件夹的名字
using System; using System.IO; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(stri ...
