23、springboot与缓存(1)
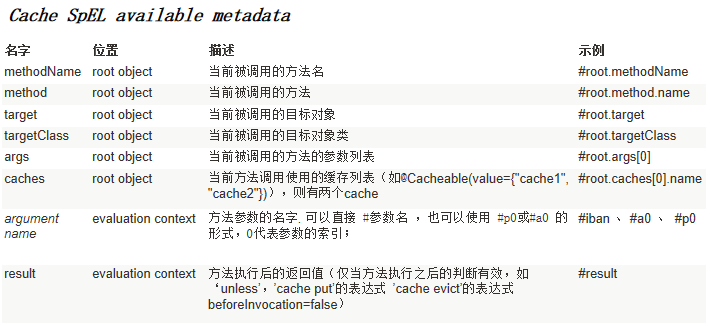
一、JSR107
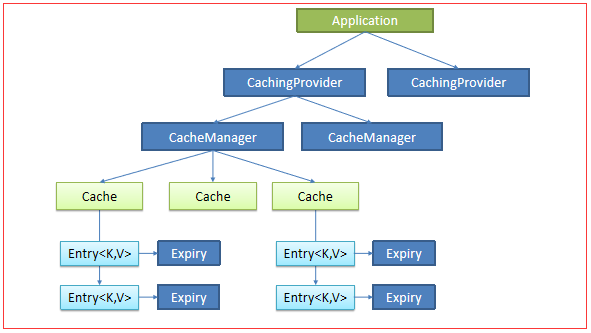
使用比较麻烦
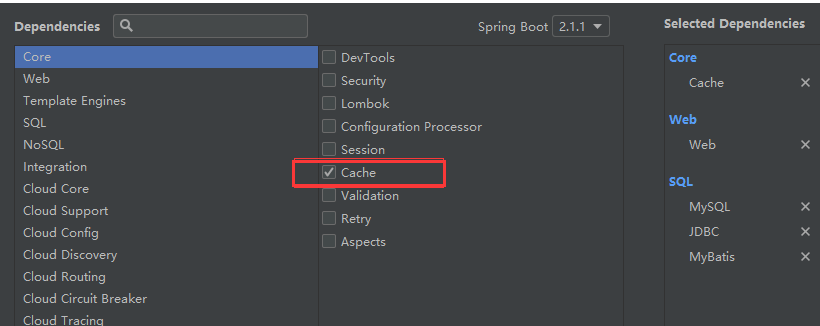
二、Spring缓存抽象
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
...}
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender; //性别 1男 0女
private Integer dId;
...}
public interface EmployeeMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}")
Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
@Update("UPDATE employee SET lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},d_id=#{dId} WHERE id=#{id}")
public void updateEmp(Employee employee);
@Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}")
public void deleteEmpById(Integer id);
@Insert("INSERT INTO employee(lastName,email,gender,d_id) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})")
public void insertEmployee(Employee employee);
@Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE lastName = #{lastName}")
Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName);
}
@Service
public class EmpService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询:" + id +"员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
}
@Controller
public class EmpController { @Autowired
EmpService empService; @ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee getEmp(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){
Employee emp = empService.getEmp(id);
return emp;
}
}
测试:
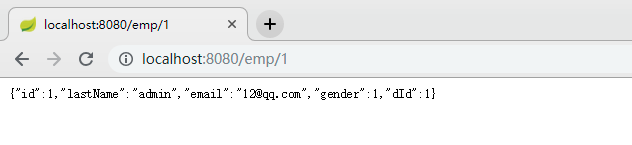
使用缓存:
在主程序中:开启缓存
@MapperScan("com.example.springbootcache.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbootCacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
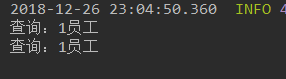
此时页面连续请求两次:
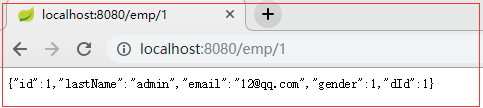
@Cacheable
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询:" + id +"员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}

@Cacheable(cacheNames ="e" )
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询:" + id +"员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
此时刷新很多遍依然只打印一次
三、缓存原理

@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({CacheManager.class})
@ConditionalOnBean({CacheAspectSupport.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {CacheManager.class},
name = {"cacheResolver"}
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({CacheProperties.class})
@AutoConfigureAfter({CouchbaseAutoConfiguration.class, HazelcastAutoConfiguration.class, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class, RedisAutoConfiguration.class}) //给容器导入一些组件
@Import({CacheAutoConfiguration.CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
... public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length]; for(int i = ; i < types.length; ++i) {
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
} return imports;
}
}
}
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata)中的return imports;
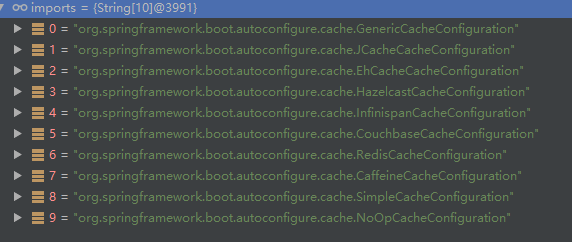
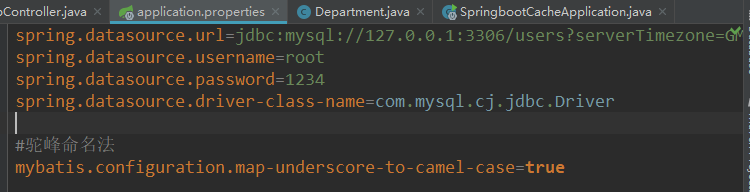
在配置文件中:判断那个缓存是生效的
debug=true
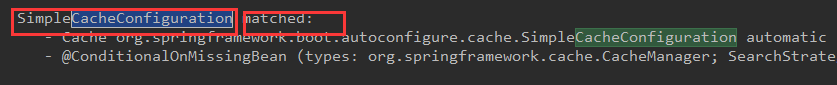
由图可知是SimpleCacheConfiguration 缓存类

@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({CacheManager.class})
@Conditional({CacheCondition.class})
class SimpleCacheConfiguration {
private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;
private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker; SimpleCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker) {
this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties;
this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker;
} @Bean
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager() {
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
} return (ConcurrentMapCacheManager)this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager);
}
}

@Nullable
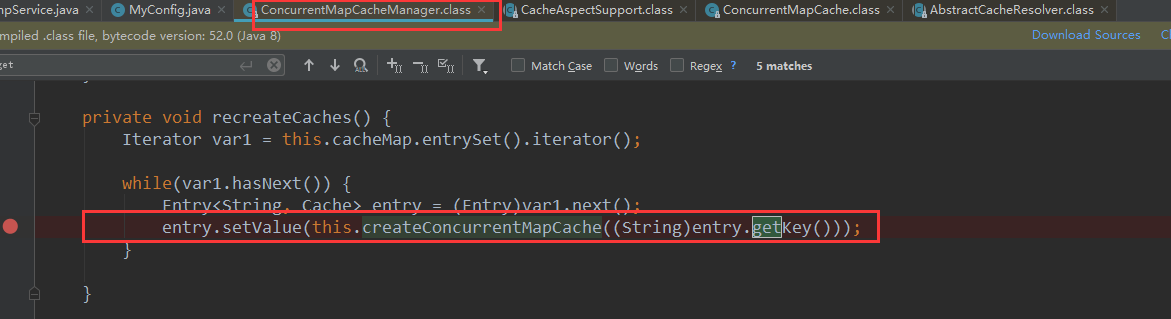
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
ConcurrentMap var3 = this.cacheMap;
synchronized(this.cacheMap) {
cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
cache = this.createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
按照名字取获取,如果为空则会创建一个缓存
运行流程:


其属性的使用:
key:数据库使用的key

此时的key就是 方法名+id; 即 getEmp[1]
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean("MyKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object... objects) {
//Objects事获得其输入的cache中的属性值
return method.getName() +"[" + Arrays.asList(objects).toString()+"]";
}
};
}
}
断点位置:
可以看到debug进入时的值: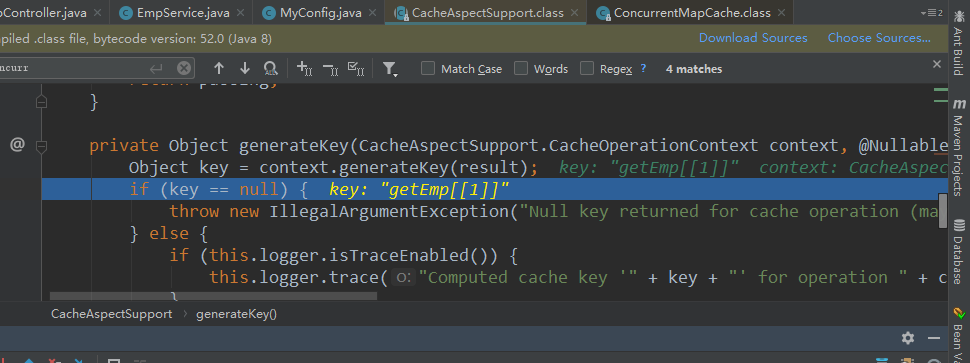
cacheManager:指定缓存管理器
condition:

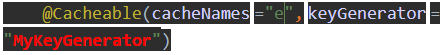
@Cacheable(cacheNames ="e", keyGenerator = "MyKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1")
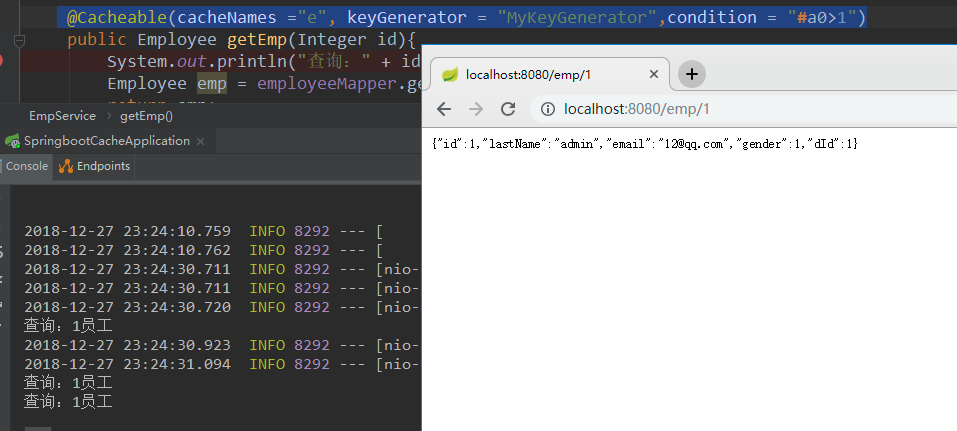
此时查询一次打印一次

23、springboot与缓存(1)的更多相关文章
- 带着新人学springboot的应用03(springboot+mybatis+缓存 下)
springboot+mybatis+缓存,基本的用法想必是会了,现在说一说内部大概的原理. 稍微提一下mybatis,只要导入了mybatis的依赖,那么有个自动配置类就会生效,你可以去mybati ...
- SpringBoot 与缓存
1. JSR107 Java Caching 定义了5个核心接口: CachingProvider:定义了创建,配置,获取,管理和控制多个CacheManager; CacheManager:定义了创 ...
- SpringBoot 整合缓存Cacheable实战详细使用
前言 我知道在接口api项目中,频繁的调用接口获取数据,查询数据库是非常耗费资源的,于是就有了缓存技术,可以把一些不常更新,或者经常使用的数据,缓存起来,然后下次再请求时候,就直接从缓存中获取,不需要 ...
- springboot redis 缓存对象
只要加入spring-boot-starter-data-redis , springboot 会自动识别并使用redis作为缓存容器,使用方式如下 gradle加入依赖 compile(" ...
- springboot~hazelcast缓存中间件
缓存来了 在dotnet平台有自己的缓存框架,在java springboot里当然了集成了很多,而且缓存的中间件也可以进行多种选择,向redis, hazelcast都是分布式的缓存中间件,今天主要 ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用02(springboot+mybatis+缓存 中)
继续接着上一节,大家应该知道驼峰命名法吧!就是我们javabean中属性一般命名是lastName,userName这种类型的,而数据库中列名一般都是last_name,user_name这种的,要让 ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用01(springboot+mybatis+缓存 上)
上一篇结束,第一次做一个这么长的系列,很多东西我也是没有说到,也许是还没有想到,哈哈哈,不过基本的东西还是说的差不多了的.假如以后碰到了不会的,随便查查资料配置一下就ok. 咳,还有大家如果把我前面的 ...
- SpringBoot Redis缓存 @Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut
文章来源 https://blog.csdn.net/u010588262/article/details/81003493 1. pom.xml <dependency> <gro ...
- springboot Redis 缓存
1,先整合 redis 和 mybatis 步骤一: springboot 整合 redis 步骤二: springboot 整合 mybatis 2,启动类添加 @EnableCaching 注解, ...
随机推荐
- UbuntuServer 16.04 with LNMP搭建WordPress
前几天弄了个腾讯云服务器,一时新鲜,就想着在上面搭建一个wordpress博客,前后搞了四五天,各种度娘谷歌,各种错误,不过还好,最终总算是被我搭建出来了!不啰嗦,书归正传,下面开始搭建! 目录: 一 ...
- JDBC数据库连接池
用户每次请求都需要向数据库获得链接,而数据库创建连接通常需要消耗相对较大的资源,创建时间也较长.假设网站一天10万访问量,数据库服务器就需要创建10万次连接,极大的浪费数据库的资源,并且极易造成数据库 ...
- 洛谷P3384 树链剖分
如题,已知一棵包含N个结点的树(连通且无环),每个节点上包含一个数值,需要支持以下操作: 操作1: 格式: 1 x y z 表示将树从x到y结点最短路径上所有节点的值都加上z 操作2: 格式: 2 x ...
- Linux(Ubuntu)下MySQL的安装
1)首先检查系统中是否已经安装了MySQL 在终端里面输入 sudo netstat -tap | grep mysql 若没有反映,没有显示已安装结果,则没有安装.若如下显示,则表示已经安装 2)如 ...
- 关于构造器和Serlvet的知识点
关于java的构造器方法: 1.java构造方法可以有任何的访问修饰符:public.protected.private或者没有修饰(通常被package或者friendly调用)但是不能有非访问性质 ...
- alembic 数据库管理
alembic简介 Alembic是SQLAlchemy作者编写的Python数据库迁移工具 安装 pip install alembic alembic 操作流程 初始化 alembic init ...
- 闭包&执行环境和作用域
闭包 执行环境和作用域参考:<javascript高级程序设计(第3版)>4.2节
- 毕向东_Java基础视频教程第19天_IO流(18~19)
第19天-18-IO流(流操作规律 - 1) 通过三个步骤来明确"流操作"的规律: 明确数据流的"源和目的" 源, 输入流: InputStream/Reade ...
- Word操作总结
1.竖向选择 Notepad中:先把鼠标光标放在起始位置,然后同时按 Alt+Ctrl 或Alt+shift键,然后移动鼠标选取内容. Word中只能用Alt+Shift .
- java获取文件大小的方法
目前Java获取文件大小的方法有两种: 1.通过file的length()方法获取: 2.通过流式方法获取: 通过流式方法又有两种,分别是旧的java.io.*中FileInputStream的ava ...
