C++解析(31):自定义内存管理(完)
0.目录
1.遗失的关键字mutable
2.new / delete
3.new[] / delete[]
4.小结
5.C++语言学习总结
1.遗失的关键字mutable
笔试题:
统计对象中某个成员变量的访问次数
遗失的关键字:
- mutable是为了突破const函数的限制而设计的
- mutable成员变量将永远处于可改变的状态
- mutable在实际的项目开发中被严禁滥用
mutable的深入分析:
- mutable成员变量破坏了只读对象的内部状态
- const成员函数保证只读对象的状态不变性
- mutable成员变量的出现无法保证状态不变性
示例1——使用mutable实现成员变量的访问统计:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int m_value;
mutable int m_count;
public:
Test(int value = 0)
{
m_value = value;
m_count = 0;
}
int getValue() const
{
m_count++;
return m_value;
}
void setValue(int value)
{
m_count++;
m_value = value;
}
int getCount() const
{
return m_count;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test t;
t.setValue(100); // 满足普通对象
cout << "t.m_value = " << t.getValue() << endl;
cout << "t.m_count = " << t.getCount() << endl;
const Test ct(200); // 满足只读对象
cout << "ct.m_value = " << ct.getValue() << endl;
cout << "ct.m_count = " << ct.getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
t.m_value = 100
t.m_count = 2
ct.m_value = 200
ct.m_count = 1
示例2——不使用mutable实现成员变量的访问统计:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int m_value;
int * const m_pCount;
/* mutable int m_count; */
public:
Test(int value = 0) : m_pCount(new int(0))
{
m_value = value;
/* m_count = 0; */
}
int getValue() const
{
/* m_count++; */
*m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1;
return m_value;
}
void setValue(int value)
{
/* m_count++; */
*m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1;
m_value = value;
}
int getCount() const
{
/* return m_count; */
return *m_pCount;
}
~Test()
{
delete m_pCount;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test t;
t.setValue(100); // 满足普通对象
cout << "t.m_value = " << t.getValue() << endl;
cout << "t.m_count = " << t.getCount() << endl;
const Test ct(200); // 满足只读对象
cout << "ct.m_value = " << ct.getValue() << endl;
cout << "ct.m_count = " << ct.getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
t.m_value = 100
t.m_count = 2
ct.m_value = 200
ct.m_count = 1
2.new / delete
面试题:
new关键字创建出来的对象位于什么地方?
被忽略的事实:
new / delete的本质是C++预定义的操作符
C++对这两个操作符做了严格的行为定义:
- new:
- 获取足够大的内存空间(默认为堆空间)
- 在获取的空间中调用构造函数创建对象
- delete:
- 调用析构函数销毁对象
- 归还对象所占用的空间(默认为堆空间)
在C++中能够重载new / delete操作符:
- 全局重载(不推荐)
- 局部重载(针对具体类进行重载)
重载new / delete的意义在于改变动态对象创建时的内存分配方式
new / delete 的重载方式:
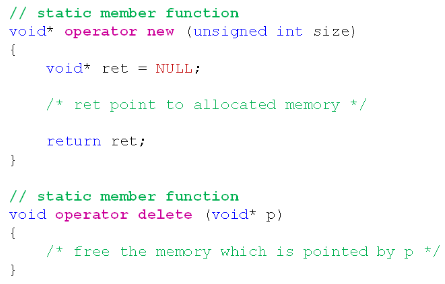
(new和delete默认就是静态成员函数,不管你写不写static。)
示例——静态存储区中创建动态对象:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
static const unsigned int COUNT = 4;
static char c_buffer[];
static char c_map[];
int m_value;
public:
void* operator new (unsigned long size)
{
void* ret = NULL;
for(int i=0; i<COUNT; i++)
{
if( !c_map[i] )
{
c_map[i] = 1;
ret = c_buffer + i * sizeof(Test);
cout << "succeed to allocate memory: " << ret << endl;
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
void operator delete (void* p)
{
if( p != NULL )
{
char* mem = reinterpret_cast<char*>(p);
int index = (mem - c_buffer) / sizeof(Test);
int flag = (mem - c_buffer) % sizeof(Test);
if( (flag == 0) && (0 <= index) && (index < COUNT) )
{
c_map[index] = 0;
cout << "succeed to free memory: " << p << endl;
}
}
}
};
char Test::c_buffer[sizeof(Test) * Test::COUNT] = {0};
char Test::c_map[Test::COUNT] = {0};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test* pt = new Test;
delete pt;
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
succeed to allocate memory: 0x601380
succeed to free memory: 0x601380
(可以看到new和delete的重载函数确实被调用了。)
示例——进一步试验:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
cout << "===== Test Single Object =====" << endl;
Test* pt = new Test;
delete pt;
cout << "===== Test Object Array =====" << endl;
Test* pa[5] = {0};
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
pa[i] = new Test;
cout << "pa[" << i << "] = " << pa[i] << endl;
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << "delete " << pa[i] << endl;
delete pa[i];
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
===== Test Single Object =====
succeed to allocate memory: 0x6013a0
succeed to free memory: 0x6013a0
===== Test Object Array =====
succeed to allocate memory: 0x6013a0
pa[0] = 0x6013a0
succeed to allocate memory: 0x6013a4
pa[1] = 0x6013a4
succeed to allocate memory: 0x6013a8
pa[2] = 0x6013a8
succeed to allocate memory: 0x6013ac
pa[3] = 0x6013ac
pa[4] = 0
delete 0x6013a0
succeed to free memory: 0x6013a0
delete 0x6013a4
succeed to free memory: 0x6013a4
delete 0x6013a8
succeed to free memory: 0x6013a8
delete 0x6013ac
succeed to free memory: 0x6013ac
delete 0
(因为c_buffer的空间只能创建4个对象,因此for循环中的第5个对象就没有空间了,于是返回了空指针。)
(可以使用这个方法加上二阶构造模式就可以将单例模式推广到多例模式!)
面试题:
如何在指定的地址上创建C++对象?
解决方案:
- 在类中重载new / delete操作符
- 在new的操作符重载函数中返回指定的地址
- 在delete操作符重载中标记对应的地址可用
示例——自定义动态对象的存储空间:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
static unsigned int c_count;
static char* c_buffer;
static char* c_map;
int m_value;
public:
static bool SetMemorySource(char* memory, unsigned int size)
{
bool ret = false;
c_count = size / sizeof(Test);
ret = (c_count && (c_map = reinterpret_cast<char*>(calloc(c_count, sizeof(char)))));
if( ret )
{
c_buffer = memory;
}
else
{
free(c_map);
c_map = NULL;
c_buffer = NULL;
c_count = 0;
}
return ret;
}
void* operator new (unsigned long size)
{
void* ret = NULL;
if( c_count > 0 )
{
for(int i=0; i<c_count; i++)
{
if( !c_map[i] )
{
c_map[i] = 1;
ret = c_buffer + i * sizeof(Test);
cout << "succeed to allocate memory: " << ret << endl;
break;
}
}
}
else
{
ret = malloc(size);
}
return ret;
}
void operator delete (void* p)
{
if( p != NULL )
{
if( c_count > 0 )
{
char* mem = reinterpret_cast<char*>(p);
int index = (mem - c_buffer) / sizeof(Test);
int flag = (mem - c_buffer) % sizeof(Test);
if( (flag == 0) && (0 <= index) && (index < c_count) )
{
c_map[index] = 0;
cout << "succeed to free memory: " << p << endl;
}
}
else
{
free(p);
}
}
}
};
unsigned int Test::c_count = 0;
char* Test::c_buffer = NULL;
char* Test::c_map = NULL;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char buffer[12] = {0};
Test::SetMemorySource(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
cout << "===== Test Single Object =====" << endl;
Test* pt = new Test;
delete pt;
cout << "===== Test Object Array =====" << endl;
Test* pa[5] = {0};
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
pa[i] = new Test;
cout << "pa[" << i << "] = " << pa[i] << endl;
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << "delete " << pa[i] << endl;
delete pa[i];
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
===== Test Single Object =====
succeed to allocate memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d0
succeed to free memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d0
===== Test Object Array =====
succeed to allocate memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d0
pa[0] = 0x7ffc6b2823d0
succeed to allocate memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d4
pa[1] = 0x7ffc6b2823d4
succeed to allocate memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d8
pa[2] = 0x7ffc6b2823d8
pa[3] = 0
pa[4] = 0
delete 0x7ffc6b2823d0
succeed to free memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d0
delete 0x7ffc6b2823d4
succeed to free memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d4
delete 0x7ffc6b2823d8
succeed to free memory: 0x7ffc6b2823d8
delete 0
delete 0
3.new[] / delete[]
new[] / delete[] 与 new / delete 完全不同:
- 动态对象数组创建通过 new[] 完成
- 动态对象数组的销毁通过 delete[] 完成
- new[] / delete[] 能够被重载,进而改变内存管理方式
new[] / delete[] 的重载方式:

注意事项:
- new[]实际需要返回的内存空间可能比期望的要多
- 对象数组占用的内存中需要保存数组信息
- 数组信息用于确定构造函数和析构函数的调用次数
示例——动态数组的内存管理:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int m_value;
public:
Test()
{
m_value = 0;
}
~Test() { }
void* operator new (unsigned long size)
{
cout << "operator new: " << size << endl;
return malloc(size);
}
void operator delete (void* p)
{
cout << "operator delete: " << p << endl;
free(p);
}
void* operator new[] (unsigned long size)
{
cout << "operator new[]: " << size << endl;
return malloc(size);
}
void operator delete[] (void* p)
{
cout << "operator delete[]: " << p << endl;
free(p);
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test* pt = NULL;
pt = new Test;
delete pt;
pt = new Test[5];
delete[] pt;
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
[root@bogon Desktop]# g++ test.cpp
[root@bogon Desktop]# ./a.out
operator new: 4
operator delete: 0x150a010
operator new[]: 28
operator delete[]: 0x150a030
4.小结
- new / delete 的本质为操作符
- 可以通过全局函数重载 new / delete (不推荐)
- 可以针对具体的类重载 new / delete
- new[] / delete[] 与 new / delete 完全不同
- new[] / delete[] 也是可以被重载的操作符
- new[] 返回的内存空间可能比期望的要多
5.C++语言学习总结
本系列学习的是“经典”C++语言:
“经典”指的是什么?
- C++ 98/03 标准在实际工程中的常用特性
- 大多数企业的产品开发中需要使用的C++技能
C++语言的学习需要重点在于以下几个方面:
- C语言到C++的改进有哪些?
- 面向对象的核心是什么?
- 操作符重载的本质是什么?
- 模板的核心意义是什么?
- 异常处理的使用方式是什么?
C++解析(31):自定义内存管理(完)的更多相关文章
- 31 (OC)* 内存管理
31 (OC) 内存管理 一:内存管理黄金法则. 如果对一个对象使用了alloc.[Mutable]copy,retain,那么你必须使用相应的realease或者autorelease 二:内存管 ...
- OpenHarmony3.1 Release版本关键特性解析——Enhanced SWAP内存管理
樊成阳 华为技术有限公司内核专家 陈杰 华为技术有限公司内核专家 OpenAtom OpenHarmony(以下简称"OpenHarmony")是面向全场景泛终端设备的操作系统,终 ...
- C++中的自定义内存管理
1,问题: 1,new 关键字创建出来的对象位于什么地方? 1,位于堆空间: 2,有没有可能位于其它地方? 1,有: 2,通过一些方式可以使动态创建的对象位于静态存储区: 3,这个存储区在程序结束后释 ...
- delphi 自定义内存管理
1.主要通过GetMemoryManager来hook原来的内存管理. 2.通过SetMemoryManager来设置你自己的新的内存管理,可以用一个内存池来优化和管理程序的内存调用情况. proce ...
- 《Effective C++》内存管理
如果global new-hander没有成功配置,会抛出一个std::bad_alloc的exception. #include<iostream> #include<new> ...
- GC与显式内存管理
C++复兴的话题至今已被鼓吹两年有余,Herb Sutter和Bjarne Stroustrup等大牛们也为C++带来了大步伐的革新.然而,从这两年的效果而言,C++的复兴并没有发生.一方面随着世界经 ...
- lua内存管理
本文内容基于版本:Lua 5.3.0 Lua内存管理器规则 Lua允许用户自定义内存管理器,并在创建Lua虚拟机(lua_State实例)时传入.当然自定义内存管理器必须遵循Lua已定义的一些行为规则 ...
- 特定于类的内存管理---《C++必知必会》 条款36
我们可以量身定制 operator new 和 operator delete 用于某个类类型,而不是必须使用标准版的 operator new 和 operator delete. 注意:我们不可以 ...
- libevent源码学习(2):内存管理
目录 内存管理函数 函数声明 event-config.h 函数定义 event_mm_malloc_ event_mm_calloc_ event_mm_strdup_ event_mm_reall ...
随机推荐
- MySQL入门篇(四)之MySQL主从复制
一.MySQL主从复制原理 随机站点访问量的鞥集啊,单台的MySQL服务器压力也不断地增加,此时需要对MySQL进行优化,如果在MySQL优化无明显改善时期,可以使用高可用.主从复制.读写分离.分库分 ...
- MVC捕获数据保存时的具体字段验证错误代码
////捕获验证错误代码 //try //{ // // 调试写数据库 //} //catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx) //{ //}
- OpenCL入门:(二:用GPU计算两个数组和)
本文编写一个计算两个数组和的程序,用CPU和GPU分别运算,计算运算时间,并且校验最后的运算结果.文中代码偏多,原理建议阅读下面文章,文中介绍了OpenCL相关名词概念. http://opencl. ...
- 《Node.js核心技术教程》读书笔记---思维导图版
书薄,挺经看!
- Spring单元测试集成H2数据库
项目源代码在:Spring-H2测试 H2简介 H2数据库是一种由Java编写的,极小,速度极快,可嵌入式的数据库.非常适合用在单元测试等数据不需要保存的场景下面. 以下时其官网的介绍: {% blo ...
- ES数据备份到HDFS
1.准备好HDFS(这里我是本机测试) 2.es 安装repository-hdfs插件 (如es为多节点需在每个节点都安装插件) elasticsearch-plugin install repos ...
- RNN: Feed Forward, Back Propagation Through Time and Truncated Backpropagation Through Time
原创作品,转载请注明出处哦~ 了解RNN的前向.后向传播算法的推导原理是非常重要的,这样, 1. 才会选择正确的激活函数: 2. 才会选择合适的前向传播的timesteps数和后向传播的timeste ...
- eclipse提示找不到dubbo.xsb报错
需要下载一个dubbo.xsb文件到本地,并在eclipse中配置 下载路径:下载链接 下载方法: a).带开链接 b).点击[Raw]按钮 c). 右键->另存为 在eclipse中配置xsb ...
- PCA(主成分析)
PCA通过将高维空间向量映射到低维,对于数据进行处理
- UUID.randomUUID()简单介绍
UUID含义是通用唯一识别码 (Universally Unique Identifier),这 是一个软件建构的标准,也是被开源软件基金会 (Open Software Foundation, OS ...
