caffe-ssd使用预训练模型做目标检测
首先参考https://www.jianshu.com/p/4eaedaeafcb4
这是一个傻瓜似的目标检测样例,目前还不清楚图片怎么转换,怎么验证,后续继续跟进
- 模型测试
(1)图片数据集上测试
python examples/ssd/score_ssd_pascal.py
输出为
I0505 ::27.929069 caffe.cpp:] Finetuning from models/VGGNet/VOC0712/SSD_300x300/VGG_VOC0712_SSD_300x300_iter_120000.caffemodel
I0505 ::28.052016 net.cpp:] Ignoring source layer mbox_loss
I0505 ::28.053956 caffe.cpp:] Starting Optimization
I0505 ::28.053966 solver.cpp:] Solving VGG_VOC0712_SSD_300x300_train
I0505 ::28.053969 solver.cpp:] Learning Rate Policy: multistep
I0505 ::28.197612 solver.cpp:] Iteration , loss = 1.45893
I0505 ::28.197657 solver.cpp:] Iteration , Testing net (#)
I0505 ::28.213793 net.cpp:] Ignoring source layer mbox_loss
I0505 ::04.390517 solver.cpp:] Test net output #: detection_eval = 0.570833
I0505 ::04.414819 solver.cpp:] Optimization Done.
I0505 ::04.414847 caffe.cpp:] Optimization Done. 作者:Ericzhang922
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/4eaedaeafcb4
來源:简书
简书著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。
可以看到图片数据集上的检测结果为57.0833%。利用python examples/ssd/ssd_detect.py可以用单张图片测试检测效果(注意文件内加载文件的路径,如果报错修改为绝对路径):

可以得到如下结果
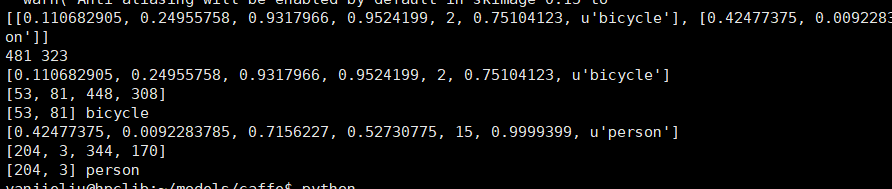
然后来看ssd_detect.py中的代码
#encoding=utf8
'''
Detection with SSD
In this example, we will load a SSD model and use it to detect objects.
''' import os
import sys
import argparse
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
# Make sure that caffe is on the python path:
caffe_root = './'
os.chdir(caffe_root)
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.join(caffe_root, 'python'))
import caffe from google.protobuf import text_format
from caffe.proto import caffe_pb2 def get_labelname(labelmap, labels):
num_labels = len(labelmap.item)
labelnames = []
if type(labels) is not list:
labels = [labels]
for label in labels:
found = False
for i in xrange(0, num_labels):
if label == labelmap.item[i].label:
found = True
labelnames.append(labelmap.item[i].display_name)
break
assert found == True
return labelnames class CaffeDetection:
def __init__(self, gpu_id, model_def, model_weights, image_resize, labelmap_file):
caffe.set_device(gpu_id)
caffe.set_mode_gpu() self.image_resize = image_resize
# Load the net in the test phase for inference, and configure input preprocessing.
self.net = caffe.Net(model_def, # defines the structure of the model
model_weights, # contains the trained weights
caffe.TEST) # use test mode (e.g., don't perform dropout)
# input preprocessing: 'data' is the name of the input blob == net.inputs[0]
self.transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': self.net.blobs['data'].data.shape})
self.transformer.set_transpose('data', (2, 0, 1))
self.transformer.set_mean('data', np.array([104, 117, 123])) # mean pixel
# the reference model operates on images in [0,255] range instead of [0,1]
self.transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255)
# the reference model has channels in BGR order instead of RGB
self.transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2, 1, 0)) # load PASCAL VOC labels
file = open(labelmap_file, 'r')
self.labelmap = caffe_pb2.LabelMap()
text_format.Merge(str(file.read()), self.labelmap) def detect(self, image_file, conf_thresh=0.5, topn=5):
'''
SSD detection
'''
# set net to batch size of 1
# image_resize = 300
self.net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, 3, self.image_resize, self.image_resize)
image = caffe.io.load_image(image_file) #Run the net and examine the top_k results
transformed_image = self.transformer.preprocess('data', image)
self.net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformed_image # Forward pass.
detections = self.net.forward()['detection_out'] # Parse the outputs.
det_label = detections[0,0,:,1]
det_conf = detections[0,0,:,2]
det_xmin = detections[0,0,:,3]
det_ymin = detections[0,0,:,4]
det_xmax = detections[0,0,:,5]
det_ymax = detections[0,0,:,6] # Get detections with confidence higher than 0.6.
top_indices = [i for i, conf in enumerate(det_conf) if conf >= conf_thresh] top_conf = det_conf[top_indices]
top_label_indices = det_label[top_indices].tolist()
top_labels = get_labelname(self.labelmap, top_label_indices)
top_xmin = det_xmin[top_indices]
top_ymin = det_ymin[top_indices]
top_xmax = det_xmax[top_indices]
top_ymax = det_ymax[top_indices] result = []
for i in xrange(min(topn, top_conf.shape[0])):
xmin = top_xmin[i] # xmin = int(round(top_xmin[i] * image.shape[1]))
ymin = top_ymin[i] # ymin = int(round(top_ymin[i] * image.shape[0]))
xmax = top_xmax[i] # xmax = int(round(top_xmax[i] * image.shape[1]))
ymax = top_ymax[i] # ymax = int(round(top_ymax[i] * image.shape[0]))
score = top_conf[i]
label = int(top_label_indices[i])
label_name = top_labels[i]
result.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label, score, label_name])
return result def main(args):
'''main '''
detection = CaffeDetection(args.gpu_id,
args.model_def, args.model_weights,
args.image_resize, args.labelmap_file)
result = detection.detect(args.image_file)
print result img = Image.open(args.image_file)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
width, height = img.size
print width, height
for item in result:
xmin = int(round(item[0] * width))
ymin = int(round(item[1] * height))
xmax = int(round(item[2] * width))
ymax = int(round(item[3] * height))
draw.rectangle([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax], outline=(255, 0, 0))
draw.text([xmin, ymin], item[-1] + str(item[-2]), (0, 0, 255))
print item
print [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]
print [xmin, ymin], item[-1]
img.save('detect_result.jpg') def parse_args():
'''parse args'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--gpu_id', type=int, default=0, help='gpu id')
parser.add_argument('--labelmap_file',
default='data/VOC0712/labelmap_voc.prototxt')
parser.add_argument('--model_def',
default='models/VGGNet/VOC0712/SSD_300x300/deploy.prototxt')
parser.add_argument('--image_resize', default=300, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--model_weights',
default='models/VGGNet/VOC0712/SSD_300x300/'
'VGG_VOC0712_SSD_300x300_iter_120000.caffemodel')
parser.add_argument('--image_file', default='examples/images/fish-bike.jpg')
return parser.parse_args() if __name__ == '__main__':
main(parse_args())
首先看传参这部分
def parse_args():
'''parse args'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--gpu_id', type=int, default=0, help='gpu id')
parser.add_argument('--labelmap_file',
default='data/VOC0712/labelmap_voc.prototxt')
parser.add_argument('--model_def',
default='models/VGGNet/VOC0712/SSD_300x300/deploy.prototxt')
parser.add_argument('--image_resize', default=300, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--model_weights',
default='models/VGGNet/VOC0712/SSD_300x300/'
'VGG_VOC0712_SSD_300x300_iter_120000.caffemodel')
parser.add_argument('--image_file', default='examples/images/fish-bike.jpg')
return parser.parse_args()
通过这部分的代码,我们可以看到进行检测时与训练时不一样,不需要对图片格式进行转换,直接输入原始图片就可以
所以,利用此命令 python ./examples/ssd/ssd_detect.py --image_file examples/images/fish-bike.jpg 可以指定用来检测的图片,
根据自己图片的位置,调整参数 python ./examples/ssd/ssd_detect.py --image_file ~/dataset/img_test/p1.jpg ,又因为需要进行时间统计,所以对代码进行修改。加入时间统计的函数,如下
#encoding=utf8
'''
Detection with SSD
In this example, we will load a SSD model and use it to detect objects.
''' import os
import sys
import argparse
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import time
# Make sure that caffe is on the python path:
caffe_root = './'
os.chdir(caffe_root)
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.join(caffe_root, 'python'))
import caffe from google.protobuf import text_format
from caffe.proto import caffe_pb2 def get_labelname(labelmap, labels):
num_labels = len(labelmap.item)
labelnames = []
if type(labels) is not list:
labels = [labels]
for label in labels:
found = False
for i in xrange(0, num_labels):
if label == labelmap.item[i].label:
found = True
labelnames.append(labelmap.item[i].display_name)
break
assert found == True
return labelnames class CaffeDetection:
def __init__(self, gpu_id, model_def, model_weights, image_resize, labelmap_file):
caffe.set_device(gpu_id)
caffe.set_mode_gpu() self.image_resize = image_resize
# Load the net in the test phase for inference, and configure input preprocessing.
self.net = caffe.Net(model_def, # defines the structure of the model
model_weights, # contains the trained weights
caffe.TEST) # use test mode (e.g., don't perform dropout)
# input preprocessing: 'data' is the name of the input blob == net.inputs[0]
self.transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': self.net.blobs['data'].data.shape})
self.transformer.set_transpose('data', (2, 0, 1))
self.transformer.set_mean('data', np.array([104, 117, 123])) # mean pixel
# the reference model operates on images in [0,255] range instead of [0,1]
self.transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255)
# the reference model has channels in BGR order instead of RGB
self.transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2, 1, 0)) # load PASCAL VOC labels
file = open(labelmap_file, 'r')
self.labelmap = caffe_pb2.LabelMap()
text_format.Merge(str(file.read()), self.labelmap) def detect(self, image_file, conf_thresh=0.5, topn=5):
'''
SSD detection
'''
# set net to batch size of 1
# image_resize = 300
self.net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, 3, self.image_resize, self.image_resize)
image = caffe.io.load_image(image_file) #Run the net and examine the top_k results
transformed_image = self.transformer.preprocess('data', image)
self.net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformed_image # Forward pass.
detections = self.net.forward()['detection_out'] # Parse the outputs.
det_label = detections[0,0,:,1]
det_conf = detections[0,0,:,2]
det_xmin = detections[0,0,:,3]
det_ymin = detections[0,0,:,4]
det_xmax = detections[0,0,:,5]
det_ymax = detections[0,0,:,6] # Get detections with confidence higher than 0.6.
top_indices = [i for i, conf in enumerate(det_conf) if conf >= conf_thresh] top_conf = det_conf[top_indices]
top_label_indices = det_label[top_indices].tolist()
top_labels = get_labelname(self.labelmap, top_label_indices)
top_xmin = det_xmin[top_indices]
top_ymin = det_ymin[top_indices]
top_xmax = det_xmax[top_indices]
top_ymax = det_ymax[top_indices] result = []
for i in xrange(min(topn, top_conf.shape[0])):
xmin = top_xmin[i] # xmin = int(round(top_xmin[i] * image.shape[1]))
ymin = top_ymin[i] # ymin = int(round(top_ymin[i] * image.shape[0]))
xmax = top_xmax[i] # xmax = int(round(top_xmax[i] * image.shape[1]))
ymax = top_ymax[i] # ymax = int(round(top_ymax[i] * image.shape[0]))
score = top_conf[i]
label = int(top_label_indices[i])
label_name = top_labels[i]
result.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label, score, label_name])
return result def main(args):
'''main '''
start = time.time()
detection = CaffeDetection(args.gpu_id,
args.model_def, args.model_weights,
args.image_resize, args.labelmap_file) result = detection.detect(args.image_file)
end = time.time()
print('time:\n')
print str(end-start) with open('./mcode/ssd_outputs.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write('\n')
f.write(str(end-start)) print result img = Image.open(args.image_file)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
width, height = img.size
print width, height
for item in result:
xmin = int(round(item[0] * width))
ymin = int(round(item[1] * height))
xmax = int(round(item[2] * width))
ymax = int(round(item[3] * height))
draw.rectangle([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax], outline=(255, 0, 0))
draw.text([xmin, ymin], item[-1] + str(item[-2]), (0, 0, 255))
print item
print [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]
print [xmin, ymin], item[-1]
img.save('detect_result.jpg') def parse_args():
'''parse args'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--gpu_id', type=int, default=0, help='gpu id')
parser.add_argument('--labelmap_file',
default='data/VOC0712/labelmap_voc.prototxt')
parser.add_argument('--model_def',
default='models/VGGNet/VOC0712/SSD_300x300/deploy.prototxt')
parser.add_argument('--image_resize', default=300, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--model_weights',
default='models/VGGNet/VOC0712/SSD_300x300/'
'VGG_VOC0712_SSD_300x300_iter_120000.caffemodel')
parser.add_argument('--image_file', default='examples/images/fish-bike.jpg')
return parser.parse_args() if __name__ == '__main__':
main(parse_args())
将文件修改后的文件放在/caffe/mcode/文件夹中,执行 python ./mcode/ssd_detect.py --image_file ~/dataset/img_test/p1.jpg
在weiliu89/caffe开源了三款数据集的fine-tuning模型,PASCAL VOC models、COCO models、ILSVRC models。
PASCAL VOC models:20分类
COCO models:80分类
ILSVRC models:1000分类
目前默认的模型应该是由vgg16搭建而来
caffe-ssd使用预训练模型做目标检测的更多相关文章
- tensorflow利用预训练模型进行目标检测(一):安装tensorflow detection api
一.tensorflow安装 首先系统中已经安装了两个版本的tensorflow,一个是通过keras安装的, 一个是按照官网教程https://www.tensorflow.org/install/ ...
- tensorflow利用预训练模型进行目标检测(二):预训练模型的使用
一.运行样例 官网链接:https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/object_detection/object_detect ...
- tensorflow利用预训练模型进行目标检测(三):将检测结果存入mysql数据库
mysql版本:5.7 : 数据库:rdshare:表captain_america3_sd用来记录某帧是否被检测.表captain_america3_d用来记录检测到的数据. python模块,包部 ...
- tensorflow利用预训练模型进行目标检测(四):检测中的精度问题以及evaluation
一.tensorflow提供的evaluation Inference and evaluation on the Open Images dataset:https://github.com/ten ...
- (转)如何用TensorLayer做目标检测的数据增强
数据增强在机器学习中的作用不言而喻.和图片分类的数据增强不同,训练目标检测模型的数据增强在对图像做处理时,还需要对图片中每个目标的坐标做相应的处理.此外,位移.裁剪等操作还有可能使得一些目标在处理后只 ...
- 使用Faster R-CNN做目标检测 - 学习luminoth代码
像玩乐高一样拆解Faster R-CNN:详解目标检测的实现过程 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/M_i38L2brq69BYzmaPeJ9w 直接参考开源目标检测代码lumin ...
- caffe SSD目标检测lmdb数据格式制作
一.任务 现在用caffe做目标检测一般需要lmdb格式的数据,而目标检测的数据和目标分类的lmdb格式的制作难度不同.就目标检测来说,例如准备SSD需要的数据,一般需要以下几步: 1.准备图片并标注 ...
- [目标检测]SSD原理
1 SSD基础原理 1.1 SSD网络结构 SSD使用VGG-16-Atrous作为基础网络,其中黄色部分为在VGG-16基础网络上填加的特征提取层.SSD与yolo不同之处是除了在最终特征图上做目标 ...
- 【目标检测】SSD:
slides 讲得是相当清楚了: http://www.cs.unc.edu/~wliu/papers/ssd_eccv2016_slide.pdf 配合中文翻译来看: https://www.cnb ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ 4033 树形DP
http://blog.csdn.net/mirrorgray/article/details/51123741 安利队长blog- 树形dp吧,状态挺显然的,dp[x][j]表示以x为根的子树中,选 ...
- Install opencv on Centos
研究centos 有很长一段时间了,一直没有写过这方面的感觉,今天在看到网友的一篇文章时,结合亲身体会就下面安装opencv的一些步骤与大家共享. CentOS OpenCV已被广泛应用但是也在不断的 ...
- Web-数据库-mysql篇
DDL创造 create 修改 alter 删除 dorp DML插入 insert 删除 delete 更新 updateDQLselect from where MySQL与JDBC 一.用 ...
- hihoCoder挑战赛31
#1595 : Numbers 时间限制:8000ms 单点时限:1000ms 内存限制:256MB 描述 给定n个整数常数c[1], c[2], ..., c[n]和一个整数k.现在需要给2k个整数 ...
- svn SSL 错误:Key usage violation in certificate has been detected
CentOS/RHEL yum 安装的 subversion 是 1.6.11 版本,连VisualSVN服务器时会有"Key usage violation"的错误 将subve ...
- js 关于时间
var myDate = new Date(); myDate.getYear(); //获取当前年份(2位) myDate.getFullYear(); //获取完整的年份(4位,1970-???? ...
- java真实面试题(2)
1,递归算法的实行过程,一般来说,可以分为()和()两个阶段,若一个问题的求解既可以用递归也可以用递推时,则往往用(),因为().贪婪法是一种()的算法. 答:递归算法分为递推和回归两个阶段,递推效率 ...
- centos7安装nginx(基础篇)
安装所需环境 Nginx 是 C语言 开发,建议在 Linux 上运行,当然,也可以安装 Windows 版本,本篇则使用 CentOS 7 作为安装环境. 一. gcc 安装安装 nginx 需要先 ...
- CSS背景图怎么自适应全屏(手机或者电脑)
#demo{ background-img:url(../bg.png); --(1)适用于上半部分背景图片,下半部分纯色 将背景图像等比缩放到完全覆盖屏幕,背景图有可能超出屏幕(容器) backgr ...
- python笔记3----第一个小爬虫
1.先看看要爬的网站有没有爬虫协议,可以看该网站有没有robots.txt,如豆瓣的: 2.requests模块:[requests是第三方,代码比python自带的urllib模块简单] 先加载re ...
