Python GIL 多线程机制 (C source code)
最近阅读《Python源码剖析》对进程线程的封装解释:
GIL,Global Interpreter Lock,对于python的多线程机制非常重要,其如何实现的?代码中实现如下:

指向一个void*,C语言中的空指针类型可以指向任意类型。Python建立多线程环境的动作只会执行一次。
PyEval_InitThreads--》PyThread_allocate_lock创建GIL之后,当前线程开始遵守python的多线程机制,即任何调用Python C API之前需要先获得GIL.
也就是代码中PyThread_acquire_lock尝试获取GIL。

static PyMethodDef thread_methods[] = {
{"start_new_thread", (PyCFunction)thread_PyThread_start_new_thread,
METH_VARARGS,
start_new_doc},
{"start_new", (PyCFunction)thread_PyThread_start_new_thread,
METH_VARARGS,
start_new_doc},
{"allocate_lock", (PyCFunction)thread_PyThread_allocate_lock,
METH_NOARGS, allocate_doc},
{"allocate", (PyCFunction)thread_PyThread_allocate_lock,
METH_NOARGS, allocate_doc},
{"exit_thread", (PyCFunction)thread_PyThread_exit_thread,
METH_NOARGS, exit_doc},
{"exit", (PyCFunction)thread_PyThread_exit_thread,
METH_NOARGS, exit_doc},
{"interrupt_main", (PyCFunction)thread_PyThread_interrupt_main,
METH_NOARGS, interrupt_doc},
{"get_ident", (PyCFunction)thread_get_ident,
METH_NOARGS, get_ident_doc},
{"_count", (PyCFunction)thread__count,
METH_NOARGS, _count_doc},
{"stack_size", (PyCFunction)thread_stack_size,
METH_VARARGS,
stack_size_doc},
{NULL, NULL} /* sentinel */
};
/*创建bootstate,并初始化,其保存关于线程的一切信息,如线程过程,和参数等,*/
static PyObject *
thread_PyThread_start_new_thread(PyObject *self, PyObject *fargs)
{
PyObject *func, *args, *keyw = NULL;
struct bootstate *boot;
long ident;
if (!PyArg_UnpackTuple(fargs, "start_new_thread", , ,
&func, &args, &keyw))
return NULL;
if (!PyCallable_Check(func)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"first arg must be callable");
return NULL;
}
if (!PyTuple_Check(args)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"2nd arg must be a tuple");
return NULL;
}
if (keyw != NULL && !PyDict_Check(keyw)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"optional 3rd arg must be a dictionary");
return NULL;
}
boot = PyMem_NEW(struct bootstate, );
if (boot == NULL)
return PyErr_NoMemory();
boot->interp = PyThreadState_GET()->interp;
boot->func = func;
boot->args = args;
boot->keyw = keyw;
boot->tstate = _PyThreadState_Prealloc(boot->interp);
if (boot->tstate == NULL) {
PyMem_DEL(boot);
return PyErr_NoMemory();
}
Py_INCREF(func);
Py_INCREF(args);
Py_XINCREF(keyw);
PyEval_InitThreads(); /* Start the interpreter's thread-awareness */
ident = PyThread_start_new_thread(t_bootstrap, (void*) boot);
if (ident == -) {
PyErr_SetString(ThreadError, "can't start new thread");
Py_DECREF(func);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_XDECREF(keyw);
PyThreadState_Clear(boot->tstate);
PyMem_DEL(boot);
return NULL;
}
return PyInt_FromLong(ident);
}
/*以boot为参数,创建一个原生线程*/
PyThreadState *
_PyThreadState_Prealloc(PyInterpreterState *interp)
{
return new_threadstate(interp, );
}
static PyThreadState *
new_threadstate(PyInterpreterState *interp, int init)
{
PyThreadState *tstate = (PyThreadState *)malloc(sizeof(PyThreadState));
if (_PyThreadState_GetFrame == NULL)
_PyThreadState_GetFrame = threadstate_getframe;
if (tstate != NULL) {
tstate->interp = interp;
tstate->frame = NULL;
tstate->recursion_depth = ;
tstate->tracing = ;
tstate->use_tracing = ;
tstate->tick_counter = ;
tstate->gilstate_counter = ;
tstate->async_exc = NULL;
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
tstate->thread_id = PyThread_get_thread_ident();
#else
tstate->thread_id = ;
#endif
tstate->dict = NULL;
tstate->curexc_type = NULL;
tstate->curexc_value = NULL;
tstate->curexc_traceback = NULL;
tstate->exc_type = NULL;
tstate->exc_value = NULL;
tstate->exc_traceback = NULL;
tstate->c_profilefunc = NULL;
tstate->c_tracefunc = NULL;
tstate->c_profileobj = NULL;
tstate->c_traceobj = NULL;
tstate->trash_delete_nesting = ;
tstate->trash_delete_later = NULL;
if (init)
_PyThreadState_Init(tstate);
HEAD_LOCK();
tstate->next = interp->tstate_head;
interp->tstate_head = tstate;
HEAD_UNLOCK();
}
return tstate;
}
GIL(NRMUTEX)对象,结构中有4个成员,其中hevent就是Win32平台下的Event内核对象,而thread_id则记录任意时刻获取的GIL的线程ID。
/*
* Lock support. It has too be implemented as semaphores.
* I [Dag] tried to implement it with mutex but I could find a way to
* tell whether a thread already own the lock or not.
*/
PyThread_type_lock
PyThread_allocate_lock(void)
{
PNRMUTEX aLock; dprintf(("PyThread_allocate_lock called\n"));
if (!initialized)
PyThread_init_thread(); aLock = AllocNonRecursiveMutex() ; dprintf(("%ld: PyThread_allocate_lock() -> %p\n", PyThread_get_thread_ident(), aLock)); return (PyThread_type_lock) aLock;
} typedef struct NRMUTEX {
LONG owned ;
DWORD thread_id ;
HANDLE hevent ;
} NRMUTEX, *PNRMUTEX ; PNRMUTEX
AllocNonRecursiveMutex(void)
{
PNRMUTEX mutex = (PNRMUTEX)malloc(sizeof(NRMUTEX)) ;
if (mutex && !InitializeNonRecursiveMutex(mutex))
{
free(mutex) ;
mutex = NULL ;
}
return mutex ;
} BOOL
InitializeNonRecursiveMutex(PNRMUTEX mutex)
{
mutex->owned = - ; /* No threads have entered NonRecursiveMutex */
mutex->thread_id = ;
mutex->hevent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL) ;
return mutex->hevent != NULL ; /* TRUE if the mutex is created */
}
PyThread_acquire_lock尝试获取GIL代码如下:
void
PyEval_InitThreads(void)
{
if (interpreter_lock)
return;
interpreter_lock = PyThread_allocate_lock();
PyThread_acquire_lock(interpreter_lock, );
main_thread = PyThread_get_thread_ident();
}
/*
* Return 1 on success if the lock was acquired
*
* and 0 if the lock was not acquired. This means a 0 is returned
* if the lock has already been acquired by this thread!
*/
int
PyThread_acquire_lock(PyThread_type_lock aLock, int waitflag)
{
int success ; dprintf(("%ld: PyThread_acquire_lock(%p, %d) called\n", PyThread_get_thread_ident(),aLock, waitflag)); success = aLock && EnterNonRecursiveMutex((PNRMUTEX) aLock, (waitflag ? INFINITE : )) == WAIT_OBJECT_0 ; dprintf(("%ld: PyThread_acquire_lock(%p, %d) -> %d\n", PyThread_get_thread_ident(),aLock, waitflag, success)); return success;
}
Windown下调用系统的WaitForSingleObject
DWORD
EnterNonRecursiveMutex(PNRMUTEX mutex, BOOL wait)
{
/* Assume that the thread waits successfully */
DWORD ret ; /* InterlockedIncrement(&mutex->owned) == 0 means that no thread currently owns the mutex */
if (!wait)
{
if (InterlockedCompareExchange(&mutex->owned, , -) != -)
return WAIT_TIMEOUT ;
ret = WAIT_OBJECT_0 ;
}
else
ret = InterlockedIncrement(&mutex->owned) ?
/* Some thread owns the mutex, let's wait... */
WaitForSingleObject(mutex->hevent, INFINITE) : WAIT_OBJECT_0 ; mutex->thread_id = GetCurrentThreadId() ; /* We own it */
return ret ;
}
Linux下则使用互斥锁metux和lock机制,条件等待机制一起使用。
先由本线程调用status = pthread_mutex_lock( &thelock->mut )锁住,mutex保持锁定状态,并在线程挂起进入等待前解锁。
然后status = pthread_cond_wait(&thelock->lock_released,&thelock->mut);
之后status = pthread_mutex_unlock( &thelock->mut );
int
PyThread_acquire_lock(PyThread_type_lock lock, int waitflag)
{
int success;
pthread_lock *thelock = (pthread_lock *)lock;
int status, error = ; dprintf(("PyThread_acquire_lock(%p, %d) called\n", lock, waitflag)); status = pthread_mutex_lock( &thelock->mut );
CHECK_STATUS("pthread_mutex_lock[1]");
success = thelock->locked == ; if ( !success && waitflag ) {
/* continue trying until we get the lock */ /* mut must be locked by me -- part of the condition
* protocol */
while ( thelock->locked ) {
status = pthread_cond_wait(&thelock->lock_released,
&thelock->mut);
CHECK_STATUS("pthread_cond_wait");
}
success = ;
}
if (success) thelock->locked = ;
status = pthread_mutex_unlock( &thelock->mut );
CHECK_STATUS("pthread_mutex_unlock[1]"); if (error) success = ;
dprintf(("PyThread_acquire_lock(%p, %d) -> %d\n", lock, waitflag, success));
return success;
}

python创建子线程过程:
多线程环境初始化之后,python开始创建底层平台的原生线程。主线程通过调用 thread_PyThread_start_new_thread-》PyThread_start_new_thread完成子线程的工作,返回子线程的ID。子线程的ID只有被激活才能从子线程中获取,因此主线程等待这个子线程的ID,一旦子线程设置好ID,就会设法唤醒主线程。至此,主线程和子线程开始分道扬镳。主线程在返回子线程ID之后,继续执行后续的字节码。
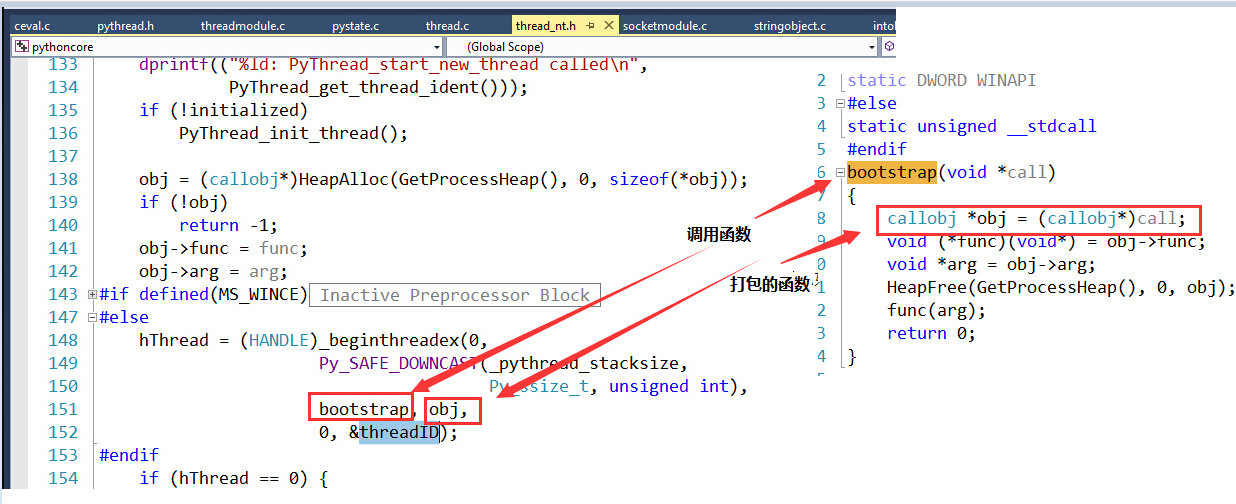
PyThread_start_new_thread传入的func是函数t_bootstrap,而arg则是bootstate结构体boot。而boot中保存着程序中所定义的线程信息。PyThread_start_new_thread首先将func和arg都打包到一个类型为callobj结构体中。
创建好子线程之后,其开始与主线程对GIL竞争。在t_bootstrap中调用PyEval_AcquireThread申请GIL,成功之后就申请到GIL,接下来子线程调用PyEval_CallObjectWithKeywords并最终调用我们熟悉的函数PyEval_EvalFrameEx,也就是python的字节码执行引擎。之后执行完毕,进行清理扫尾工作PyThreadState_DeleteCurrent释放GIL。
t_bootstrap 看上去似乎子线程一直执行到释放GIL,他们是如何激活多线程机制的呢?答案在于函数PyEval_EvalFrameEx中,python内部维护的模拟中断时钟不断激活线程的调度机制,从而实现子线程和主线程的切换。
执行秩序: thread_PyThread_start_new_thread-》PyThread_start_new_thread-》bootstrap--》t_bootstrap
t_bootstrap 代码:
static void
t_bootstrap(void *boot_raw)
{
struct bootstate *boot = (struct bootstate *) boot_raw;
PyThreadState *tstate;
PyObject *res; tstate = boot->tstate;
tstate->thread_id = PyThread_get_thread_ident();
_PyThreadState_Init(tstate);
PyEval_AcquireThread(tstate);
nb_threads++;
res = PyEval_CallObjectWithKeywords(
boot->func, boot->args, boot->keyw);
if (res == NULL) {
if (PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_SystemExit))
PyErr_Clear();
else {
PyObject *file;
PyObject *exc, *value, *tb;
PyErr_Fetch(&exc, &value, &tb);
PySys_WriteStderr(
"Unhandled exception in thread started by ");
file = PySys_GetObject("stderr");
if (file)
PyFile_WriteObject(boot->func, file, 0);
else
PyObject_Print(boot->func, stderr, 0);
PySys_WriteStderr("\n");
PyErr_Restore(exc, value, tb);
PyErr_PrintEx(0);
}
}
else
Py_DECREF(res);
Py_DECREF(boot->func);
Py_DECREF(boot->args);
Py_XDECREF(boot->keyw);
PyMem_DEL(boot_raw);
nb_threads--;
PyThreadState_Clear(tstate);
PyThreadState_DeleteCurrent();
PyThread_exit_thread();
}
完成打包之后,调用Win32下的创建thread API 函数CreateThread或者_beginthreadex ,然后通过bootstrap调用我们定义的函数(例如自己的test.py中的def testThread 函数)
函数打包,调用代码:
Python GIL 多线程机制 (C source code)的更多相关文章
- python多线程机制
Python中的线程从一开始就是操作系统的原生线程.而Python虚拟机也同样使用一个全局解释器锁(Global Interpreter Lock,GIL)来互斥线程多Python虚拟机的使用. GI ...
- convert source code files to pdf format in python
import os import sys def find_file(root_dir, type): dirs_pool = [root_dir] dest_pool = [] def scan_d ...
- python GIL 全局锁,多核cpu下的多线程性能究竟如何?
python GIL 全局锁,多核cpu下的多线程性能究竟如何?GIL全称Global Interpreter Lock GIL是什么? 首先需要明确的一点是GIL并不是Python的特性,它是在实现 ...
- Defining Python Source Code Encodings
Defining the Encoding Python will default to ASCII as standard encoding if no other encoding hints a ...
- [ Python - 11 ] 多线程及GIL全局锁
1. GIL是什么? 首先需要明确的一点是GIL并不是python的特性, 它是在实现python解析器(Cpython)时所引入的一个概念. 而Cpython是大部分环境下默认的python执行环境 ...
- UI5 Source code map机制的细节介绍
在我的博客A debugging issue caused by source code mapping里我介绍了在我做SAP C4C开发时遇到的一个曾经困扰我很久的问题,最后结论是这个问题由于Jav ...
- Source Code Structure - Python 源码目录结构
Source Code Structure - Python 源码目录结构 Include 目录包含了 Python 提供的所有头文件, 如果用户需要用 C 或 C++ 编写自定义模块扩展 Pytho ...
- Python使用import导入模块时报ValueError: source code string cannot contain null bytes的解决方案
老猿在导入一个Python模块时报错: >>> import restartnet.py Traceback (most recent call last): File " ...
- Python GIL(Global Interpreter Lock)
一,介绍 定义: In CPython, the global interpreter lock, or GIL, is a mutex that prevents multiple native t ...
随机推荐
- MSSQL 跨服器调用存储过程
A库 CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[A_P_Test] AS BEGIN SELECT * FROM dbo.A_LoadData END B库 在B中调用A库存储过程 注:是同一 ...
- Http状态码笔记
1,503 服务器不可用. HTTP Error 503错误的解释:web服务器不能处理HTTP请求,可能是临时超载或者是服务器进行维护.这意味着你需要忍耐一下,等待服务器的临时处理.在这种状态下,一 ...
- PHP与apache环境配置
最近想了解一些网页后台的东西,在看Luke Welling,laura Thomson的<php与mysql web开发>,书中环境配置的部分很庞杂,网上的各种教程也很乱,搞了一下午终于成 ...
- c#向数据库插入较大数据(SqlBulkCopy)
因为要向数据库添加一些数据,数据量较大 1.使用sql语句批量提交速度较慢 2.用事物批量提交,速度一般 3.用SqlBulkCopy方法写入数据,速度较快 /// <summary> / ...
- MySQL(Percona Server) 5.6 主从复制
MySQL(Percona Server) 5.6.15 主库:192.168.2.21 从库:192.168.2.22 例如我们同步的数据库为:test. 如果需要同步多个数据库下面会有说明. My ...
- 前端开发与SEO
前端开发中通过一些小习惯,可以有利于SEO,本着蚊子再小也是肉的原则,能抓住自然不能忽略. 1.控制首页链接数量,不能过多,也不要太少.更不要为了凑数而添加 2.扁平化层次,力争跳转三次可以到任何页面 ...
- PHP 使用 password_hash() 给密码加密
PHP >= 5.5 时,可以使用 password_hash() 和 password_verify() 来对用户的密码进行加密和验证,例如在用户注册(加密存储)和登陆(验证): <?p ...
- C# 方法返回值的个数
方法返回值类型总的来说分为值类型,引用类型,Void 有些方法显示的标出返回值 public int Add(int a,int b) { return a+b; } 有些方法隐式的返回返回值,我们可 ...
- mysql中影响myisam引擎写入性能的三项设置
一.LOW_PRIORITY1.对于myisam默认是写操作优先,读操作滞后.通过该项更改,可以使读操作优先,写操作在有空闲的时候再写入.但该项可能在理论上造成,写被永远阻塞. SQL语句中使用示例: ...
- 一起来做chrome扩展《AJAX请求》
chrome在一次更新之后,出于安全考虑,完全的禁止了content_script从https向http发起ajax请求,即使正常情况下也会在console里给出提示.这对于WEB来讲是好事,但对于扩 ...
