第五次编程作业-Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
1.正规化的线性回归
(1)代价函数
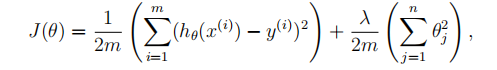
(2)梯度
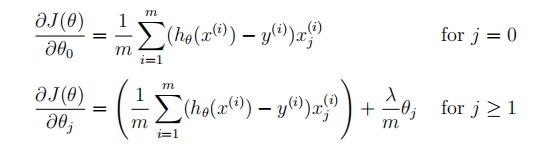
linearRegCostFunction.m
function [J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, lambda)
%LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for regularized linear
%regression with multiple variables
% [J, grad] = LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION(X, y, theta, lambda) computes the
% cost of using theta as the parameter for linear regression to fit the
% data points in X and y. Returns the cost in J and the gradient in grad % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost and gradient of regularized linear
% regression for a particular choice of theta.
%
% You should set J to the cost and grad to the gradient.
%
%求h(θ)
h = X * theta;
J = 1/2/m *((h-y)'*(h-y)) + lambda/2/m*(theta(2:end,:)'*theta(2:end,:));
grad(1,1) = X(:,1)'*(h-y)/m;
grad(2:end,1) = X(:,2:end)'*(h-y)/m +lambda/m * theta(2:end,1);
% =========================================================================
grad = grad(:); end
用fmincg最优的theta来拟合线性回归,画出线性回归函数(在这里是低维度的可以画出来)
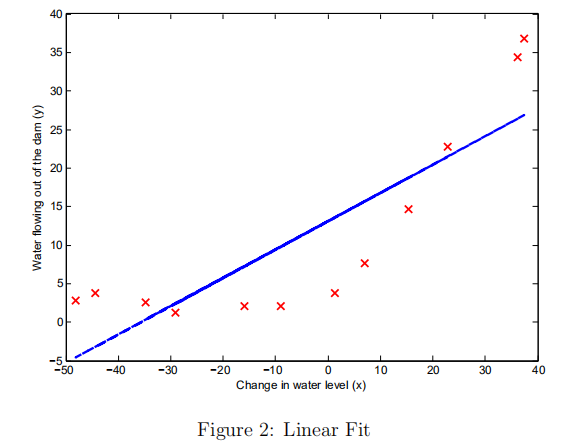
2.偏差与方差
(1)求训练样本的误差代价:
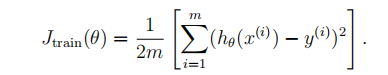
(2)交叉样本集
Jcv
learningCurve.m
function [error_train, error_val] = ...
learningCurve(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda)
%LEARNINGCURVE Generates the train and cross validation set errors needed
%to plot a learning curve
% [error_train, error_val] = ...
% LEARNINGCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda) returns the train and
% cross validation set errors for a learning curve. In particular,
% it returns two vectors of the same length - error_train and
% error_val. Then, error_train(i) contains the training error for
% i examples (and similarly for error_val(i)).
%
% In this function, you will compute the train and test errors for
% dataset sizes from 1 up to m. In practice, when working with larger
% datasets, you might want to do this in larger intervals.
% % Number of training examples
m = size(X, 1); % You need to return these values correctly
error_train = zeros(m, 1);
error_val = zeros(m, 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the cross validation errors in error_val.
% i.e., error_train(i) and
% error_val(i) should give you the errors
% obtained after training on i examples.
%
% Note: You should evaluate the training error on the first i training
% examples (i.e., X(1:i, :) and y(1:i)).
%
% For the cross-validation error, you should instead evaluate on
% the _entire_ cross validation set (Xval and yval).
%
% Note: If you are using your cost function (linearRegCostFunction)
% to compute the training and cross validation error, you should
% call the function with the lambda argument set to 0.
% Do note that you will still need to use lambda when running
% the training to obtain the theta parameters.
%
% Hint: You can loop over the examples with the following:
%
% for i = 1:m
% % Compute train/cross validation errors using training examples
% % X(1:i, :) and y(1:i), storing the result in
% % error_train(i) and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
% % ---------------------- Sample Solution ---------------------- %进行训练的时候,对训练样本i个进行训练得到theta值,再求J for i = 1:m
theta = trainLinearReg(X(1:i,:), y(1:i), lambda);
error_train(i) = linearRegCostFunction(X(1:i,:), y(1:i), theta, 0);
error_val(i) = linearRegCostFunction(Xval, yval,theta,0);
end % ------------------------------------------------------------- % ========================================================================= end
学习曲线如下:

3.多项式回归
(1) 上面学习曲线可以看出来高偏差,欠拟合。采用增加特性来拟合,即多项式如下:

polyFeatures.m
function [X_poly] = polyFeatures(X, p)
%POLYFEATURES Maps X (1D vector) into the p-th power
% [X_poly] = POLYFEATURES(X, p) takes a data matrix X (size m x 1) and
% maps each example into its polynomial features where
% X_poly(i, :) = [X(i) X(i).^2 X(i).^3 ... X(i).^p];
% % You need to return the following variables correctly.
X_poly = zeros(numel(X), p); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Given a vector X, return a matrix X_poly where the p-th
% column of X contains the values of X to the p-th power.
%
%
for i=1:p
X_poly(:,i) = X.^i;
end
% ========================================================================= end
(2) 画出学习曲线
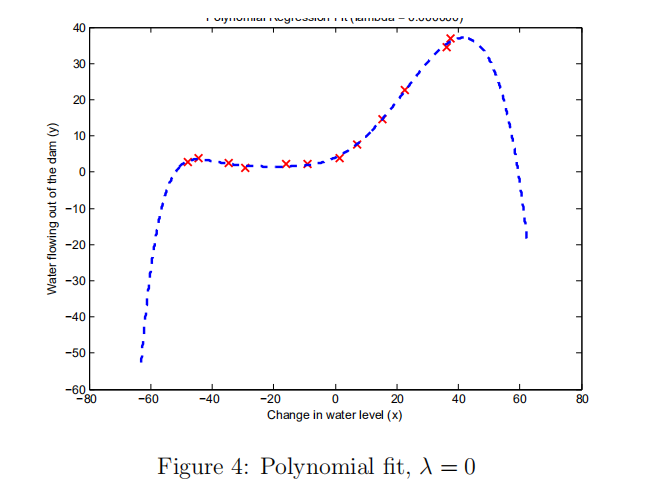
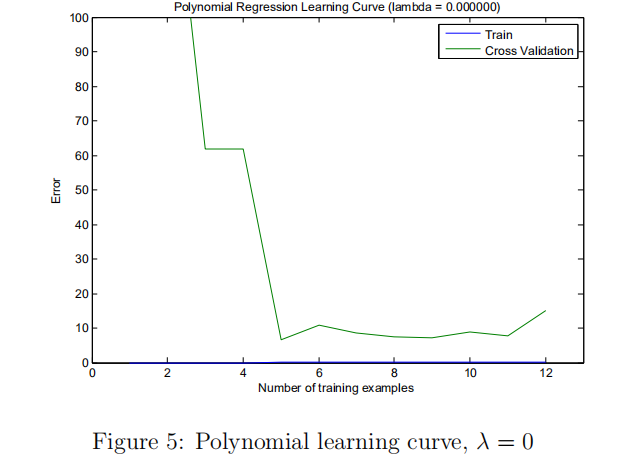
(2)可以看出出现了高方差,过拟合。选择一个好的正则化参数lambda。
利用交叉验证集来选择合适的lambda,选择最小的Jcv对应的lambda。(在这里求代价误差的时候就不用加正则化项了)
trainLinearReg.m
function [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
validationCurve(X, y, Xval, yval)
%VALIDATIONCURVE Generate the train and validation errors needed to
%plot a validation curve that we can use to select lambda
% [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
% VALIDATIONCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval) returns the train
% and validation errors (in error_train, error_val)
% for different values of lambda. You are given the training set (X,
% y) and validation set (Xval, yval).
% % Selected values of lambda (you should not change this)
lambda_vec = [0 0.001 0.003 0.01 0.03 0.1 0.3 1 3 10]'; % You need to return these variables correctly.
error_train = zeros(length(lambda_vec), 1);
error_val = zeros(length(lambda_vec), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the validation errors in error_val. The
% vector lambda_vec contains the different lambda parameters
% to use for each calculation of the errors, i.e,
% error_train(i), and error_val(i) should give
% you the errors obtained after training with
% lambda = lambda_vec(i)
%
% Note: You can loop over lambda_vec with the following:
%
% for i = 1:length(lambda_vec)
% lambda = lambda_vec(i);
% % Compute train / val errors when training linear
% % regression with regularization parameter lambda
% % You should store the result in error_train(i)
% % and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
%
for i = 1:length(lambda_vec)
lambda = lambda_vec(i);
theta = trainLinearReg(X, y, lambda); %10x1选择最优的theta
error_train(i,1) = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, 0);
error_val(i,1) = linearRegCostFunction(Xval, yval, theta, 0);
end % ========================================================================= end
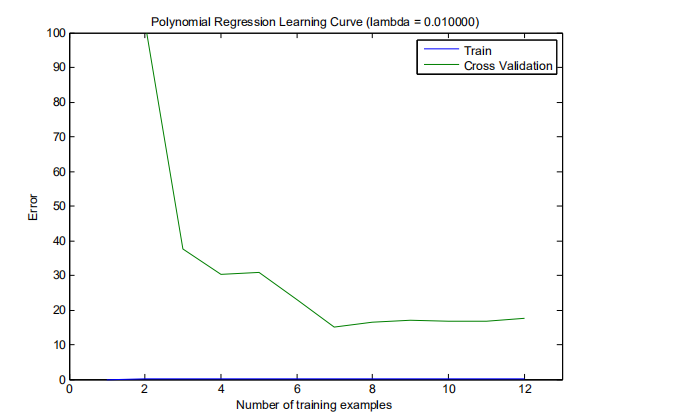
(3)计算测试集代价误差3.8599,(根据上面得到的最优的λ= 3)
(4)画出学习曲线
第五次编程作业-Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance的更多相关文章
- Andrew Ng机器学习 五:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
背景:实现一个线性回归模型,根据这个模型去预测一个水库的水位变化而流出的水量. 加载数据集ex5.data1后,数据集分为三部分: 1,训练集(training set)X与y: 2,交叉验证集(cr ...
- CheeseZH: Stanford University: Machine Learning Ex5:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
源码:https://github.com/cheesezhe/Coursera-Machine-Learning-Exercise/tree/master/ex5 Introduction: In ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias/Variance
作业文件: machine-learning-ex5 1. 正则化线性回归 在本次练习的前半部分,我们将会正则化的线性回归模型来利用水库中水位的变化预测流出大坝的水量,后半部分我们对调试的学习算法进行 ...
- ufldl学习笔记与编程作业:Linear Regression(线性回归)
ufldl学习笔记与编程作业:Linear Regression(线性回归) ufldl出了新教程,感觉比之前的好.从基础讲起.系统清晰,又有编程实践. 在deep learning高质量群里面听一些 ...
- 【模式识别与机器学习】——PART2 机器学习——统计学习基础——Regularized Linear Regression
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/jianxinzhou/p/4083921.html 1. The Problem of Overfitting (1) 还是来看预测房价的这个例 ...
- Regularized Linear Regression with scikit-learn
Regularized Linear Regression with scikit-learn Earlier we covered Ordinary Least Squares regression ...
- ufldl学习笔记和编程作业:Softmax Regression(softmax回报)
ufldl学习笔记与编程作业:Softmax Regression(softmax回归) ufldl出了新教程.感觉比之前的好,从基础讲起.系统清晰,又有编程实践. 在deep learning高质量 ...
- ufldl学习笔记与编程作业:Softmax Regression(vectorization加速)
ufldl学习笔记与编程作业:Softmax Regression(vectorization加速) ufldl出了新教程,感觉比之前的好.从基础讲起.系统清晰,又有编程实践. 在deep learn ...
- ufldl学习笔记与编程作业:Logistic Regression(逻辑回归)
ufldl学习笔记与编程作业:Logistic Regression(逻辑回归) ufldl出了新教程,感觉比之前的好,从基础讲起.系统清晰,又有编程实践. 在deep learning高质量群里面听 ...
随机推荐
- POJ 2533 - Longest Ordered Subsequence - [最长递增子序列长度][LIS问题]
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2533 Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Description A numeric se ...
- 跨界!Omi 发布多端统一框架 Omip 打通小程序与 Web 腾讯开源 2月28日
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/z5qm-2bHk_BCJAwaodrMIg 跨界!Omi 发布多端统一框架 Omip 打通小程序与 Web 腾讯开源 2月28日
- Sessions Hang on row cache lock
Sessions Hang on "row cache lock" (dc_objects) While Creating & Dropping a Table Concu ...
- linux 逆向映射
逆向映射用于建立物理内存页和使用该页的进程的对应页表项之间的联系,在换出页时以便更新所有涉及的进程.得到物理页基址后,根据pfn_to_page可以将页框转换为page实例,page实例中的mappi ...
- #pragma pack的使用
#pragma pack的作用 程序编译器对变量的存储带有一定随机性,而pragma pack是一种字节对齐方法,采用人为设定的方式将存储数据按一定格式排布.百科中提到了其一种作用:有的平台每次读都是 ...
- js DateTime函数
---恢复内容开始--- 一.js获取当前日期时间var myDate = new Date();myDate.getYear(); //获取当前年份(2位)myDate.getFull ...
- 【托业】【跨栏】TEST06
26-30 26 27 28 28 29 30
- Oracle 10g RAC OCR、Voting disk更换
环境:OEL 5.7 + Oracle 10.2.0.5 RAC 需求:更换存储,OCR.Voting disk同时需要更换到新存储. 1.替换OCR 2.替换voting disk 1.替换OCR ...
- 与图论的邂逅03:Lengauer-Tarjan
回想一下,当我们在肝无向图连通性时,我们会遇到一个神奇的点——它叫割点.假设现在有一个无向图,它有一个割点,也就是说把割点删了之后图会分成两个联通块A,B.设点u∈A,v∈B,在原图中他们能够互相到达 ...
- Kafka笔记5(内部工作原理)
集群成员关系: Kafka使用zookeeper维护集群成员信息,每个broker拥有唯一标识符,这个标识符可以在配置文件里指定也可以自动生成,会注册到Zookeeper的/brokers/ids路径 ...
