JDK8下Object类源码理解
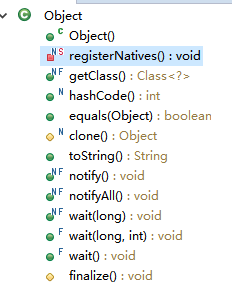
JDK8中Object类提供的方法:
package java.lang; /**
* Class {@code Object} is the root of the class hierarchy.
* Every class has {@code Object} as a superclass. All objects,
* including arrays, implement the methods of this class.
*
* @author unascribed
* @see java.lang.Class
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public class Object { private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
java虚拟机创造对象的一些基本操作:分配内存空间,定义变量,产生this指针等等。
1.子类是否可以继承父类的private属性和方法?
package demo;
public class TestPrivate extends A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestPrivate obj = new TestPrivate();
obj.count; // The field A.count is not visible
obj.out(); // The method out() from the type A is not visible
}
}
class A{
private int count;
private void out(){
System.out.println("A private method");
}
}
子类继承父类,但是父类的private属性和方法仍然属于父类所有,即子类并不具有该private属性和方法(只能看不能用),若想要同样的属性就需要自己重新定义或在父类中设置get,set方法。

2.native关键字解释
(https://www.cnblogs.com/KingIceMou/p/7239668.html)
|
Java平台有个用户和本地C代码进行互操作的API,称为Java Native Interface (Java本地接口)。使用native关键字说明这个方法是原生函数,也就是这个方法是用C/C++语言实现的,并且被编译成了DLL,由java去调用。这些函数的实现体在DLL中,JDK的源代码中并不包含,你应该是看不到的。对于不同的平台它们也是不同的。这也是java的底层机制,实际上java就是在不同的平台上调用不同的native方法实现对操作系统的访问的。 |
|
native是与C++联合开发的时候用的!java自己开发不用的! |
|
1。native 是用做java 和其他语言(如c++)进行协作时用的 |
|
native的意思就是通知操作系统,这个函数你必须给我实现,因为我要使用。 |
|
java是跨平台的语言,既然是跨了平台,所付出的代价就是牺牲一些对底层的控制,而java要实现对底层的控制,就需要一些其他语言的帮助,这个就是native的作用了 |
|
Java不是完美的,Java的不足除了体现在运行速度上要比传统的C++慢许多之外,Java无法直接访问到操作系统底层(如系统硬件等),为此Java使用native方法来扩展Java程序的功能。 |
|
JAVA本地方法适用的情况 2.为了访问一个老的系统或者使用一个已有的库,而这个系统或这个库不是用JAVA编写的 3.为了加快程序的性能,而将一段时间敏感的代码作为本地方法实现。 |
native不能与abstract连用,因为native是有方法体的,只不过不是java语言实现的,而abstract表示没有方法体。
如果一个含有本地方法的类被继承,子类会继承这个本地方法并且可以用java语言重写这个方法(这个似乎看起来有些奇怪),同样的如果一个本地方法被final标识,它被继承后不能被重写。(https://blog.csdn.net/wbl313/article/details/2560690)
/**
* Returns the runtime class of this {@code Object}. The returned
* {@code Class} object is the object that is locked by {@code
* static synchronized} methods of the represented class.
*
* <p><b>The actual result type is {@code Class<? extends |X|>}
* where {@code |X|} is the erasure of the static type of the
* expression on which {@code getClass} is called.</b> For
* example, no cast is required in this code fragment:</p>
*
* <p>
* {@code Number n = 0; }<br>
* {@code Class<? extends Number> c = n.getClass(); }
* </p>
*
* @return The {@code Class} object that represents the runtime
* class of this object.
* @jls 15.8.2 Class Literals
*/
public final native Class<?> getClass();
本地实现,不允许重写。返回运行时的class,由static synchronized方法锁定。
package demo;
public class TestClass extends Aa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Aa a = new TestClass();
a.test();
System.out.println(a.getClass()); // class demo.TestClass
System.out.println(a.getClass().getSuperclass()); // class demo.Aa
System.out.println(a.toString()); // demo.TestClass@139a55
System.out.println("===========================");
TestClass test = new TestClass();
test.test();
System.out.println(test.getClass()); // class demo.TestClass
System.out.println(test.getClass().getSuperclass()); // class demo.Aa
System.out.println(test.toString()); // demo.TestClass@1db9742
}
}
class Aa{
public void test(){
System.out.println(this.getClass()); // class demo.TestClass
System.out.println(super.getClass()); // class demo.TestClass
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSuperclass()); // class demo.Aa
System.out.println(super.getClass().getSuperclass()); // class demo.Aa
System.out.println(this.toString()); // demo.TestClass@139a55
System.out.println(super.toString()); // demo.TestClass@139a55
}
}
/*
class demo.TestClass
class demo.TestClass
class demo.Aa
class demo.Aa
demo.TestClass@139a55
demo.TestClass@139a55
class demo.TestClass
class demo.Aa
demo.TestClass@139a55
===========================
class demo.TestClass
class demo.TestClass
class demo.Aa
class demo.Aa
demo.TestClass@1db9742
demo.TestClass@1db9742
class demo.TestClass
class demo.Aa
demo.TestClass@1db9742
*/
3.为什么this.getClass()和super.getClass()效果相同?
https://www.cnblogs.com/lcchuguo/p/4804990.html
看了上篇给出的解释明白了,关键在于Object类中getClass()的定义:Returns the runtime class of this {@code Object}.规定返回对象的运行时类,即不管调用TestClass对象的this.getClass()还是super.getClass(),去调用的getClass()的对象是TestClass对象,super也是该TestClass对象的super,即TestClass对象.super.getClass(),处于最下面的依然是TestClass实例对象。所以不管是this还是super,它们对应的运行时类都是TestClass。
4. getClass(), .class区别
package demo;
public class TestPrivate extends A{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A obj = new TestPrivate();
System.out.println(obj.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(A.class);
}
}
class A{
private int count;
private void out(){
System.out.println("A private method");
}
}
/*
obj.getClass().getName() 可以定位到Object和Class类中的代码处
A.class无法定位代码
*/
|
getClass() 利用这个方法就可以获得一个实例的类型类。类型类指的是代表一个类型的类,因为一切皆是对象,类型也不例外,在Java使用类型类来表示一个类型。所有的类型类都是Class类的实例; 是一个类的实例所具备的方法,运行时才能确定(反射); 通过返回的Class对象获取Person的相关信息,比如:获取Person的构造方法,方法,属性有哪些等等信息(当我们想要获取Person的信息,比如:获取Person的名字,获取Person的构造函数,获取Person的继承关系等等这些Person的相关信息就不能仅仅只是通过new Person()的方式了。而是需要获取内存中实实在在存在的这个Class Person,通过获取到的。 Person p = new Person(1,”刘德华”); 然后通过cla对象来获取Person的相关信息,因为Class提供了大量的方法来获取类(?extends Object)的信息) |
|
.class 一个类方法,编译时确定 |
5.getClass()返回的是Class类的实例的理解
(https://blog.csdn.net/expect521/article/details/79139829)
同理对于Person类,或者准确的说每个类(除所有类的父类Object)也有两个称呼,既可以称为是类,也可称为变量。参照物不同称呼不同。
参照物: Person的属性id,name 则:Person的称呼是类(Class)
参照物: Class类 则:Person的称呼是变量/属性
例如:
|
String name Class Person name的类型是String,此时 Class Person 的性质和String name一样。 String 等同于 Class,是类。 name 等同于 Person,是对象 / 变量的称呼。 String类下有很多方法供name对象使用,同理Class类下也有很多方法供Person对象使用。 Class类和String类一样,都是继承于Object类,Object是所有类的根类 。 |
6.Class类继承于Object类?

7.Why Object is Super Class in Java?
https://javapapers.com/java/why-object-is-super-class-in-java/
|
①By having the Object as the super class of all Java classes, without knowing the type we can pass around objects using the Object declaration.(通用--未知类型) |
|
②Before generics was introduced, imagine the state of heterogeneous Java collections. A collection class like ArrayList allows to store any type of classes. It was made possible only by Object class hierarchy.(泛型之前--任何类型) |
|
③The other reason would be to bring a common blueprint for all classes and have some list of functions same among them. I am referring to methods like hashCode(), clone(), toString() and methods for threading which is defined in Object class.(通用methods) |
如下示例:
package demo;
public class SuperClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "java";
Class classstr = str.getClass();
System.out.println("the super class of String is ----> " + classstr.getSuperclass());
Object obj = new Object();
Class classobj = obj.getClass();
System.out.println("the super class of Object is ---> " + classobj.getSuperclass());
Class c = classobj.getClass();
System.out.println("the super class of Class is ---> " + c.getSuperclass());
} // end main
} // end SuperClass
/*
the super class of String is ----> class java.lang.Object
the super class of Object is ---> null
the super class of Class is ---> class java.lang.Object
*/
/**
* Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is
* supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by
* {@link java.util.HashMap}.
* <p>
* The general contract of {@code hashCode} is:
* <ul>
* <li>Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during
* an execution of a Java application, the {@code hashCode} method
* must consistently return the same integer, provided no information
* used in {@code equals} comparisons on the object is modified.
* This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an
* application to another execution of the same application.
* <li>If two objects are equal according to the {@code equals(Object)}
* method, then calling the {@code hashCode} method on each of
* the two objects must produce the same integer result.
* <li>It is <em>not</em> required that if two objects are unequal
* according to the {@link java.lang.Object#equals(java.lang.Object)}
* method, then calling the {@code hashCode} method on each of the
* two objects must produce distinct integer results. However, the
* programmer should be aware that producing distinct integer results
* for unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables.
* </ul>
* <p>
* As much as is reasonably practical, the hashCode method defined by
* class {@code Object} does return distinct integers for distinct
* objects. (This is typically implemented by converting the internal
* address of the object into an integer, but this implementation
* technique is not required by the
* Java™ programming language.)
*
* @return a hash code value for this object.
* @see java.lang.Object#equals(java.lang.Object)
* @see java.lang.System#identityHashCode
*/
public native int hashCode();
https://blog.csdn.net/luanlouis/article/details/41547649
Java 中Object对象的hashcode()返回值一定不会是Object对象的内存地址这么简单!(深挖源码)

(https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13860194/what-is-an-internal-address-in-java/13860488#13860488)
从JDK7开始,Object.hashCode()返回的就不再是地址了。
注意this.hashCode()和this.getClass().hashCode()是不同的,见toString()处的测试。
同一对象多次调用应该返回同一个Integer值;equals返回相等,hashCode也应该相等;equals不同,hashCode应该不同(不是必须)------>提升hash tables的性能。对于不同的对象返回不同的Integer。
equals--true,hashCode--true(符合Object规范+hashSet等的规范);hashCode--true,equals不一定true;equals--false,hashCode不一定false。
/**
* Indicates whether some other object is "equal to" this one.
* <p>
* The {@code equals} method implements an equivalence relation
* on non-null object references:
* <ul>
* <li>It is <i>reflexive</i>: for any non-null reference value
* {@code x}, {@code x.equals(x)} should return
* {@code true}.
* <li>It is <i>symmetric</i>: for any non-null reference values
* {@code x} and {@code y}, {@code x.equals(y)}
* should return {@code true} if and only if
* {@code y.equals(x)} returns {@code true}.
* <li>It is <i>transitive</i>: for any non-null reference values
* {@code x}, {@code y}, and {@code z}, if
* {@code x.equals(y)} returns {@code true} and
* {@code y.equals(z)} returns {@code true}, then
* {@code x.equals(z)} should return {@code true}.
* <li>It is <i>consistent</i>: for any non-null reference values
* {@code x} and {@code y}, multiple invocations of
* {@code x.equals(y)} consistently return {@code true}
* or consistently return {@code false}, provided no
* information used in {@code equals} comparisons on the
* objects is modified.
* <li>For any non-null reference value {@code x},
* {@code x.equals(null)} should return {@code false}.
* </ul>
* <p>
* The {@code equals} method for class {@code Object} implements
* the most discriminating possible equivalence relation on objects;
* that is, for any non-null reference values {@code x} and
* {@code y}, this method returns {@code true} if and only
* if {@code x} and {@code y} refer to the same object
* ({@code x == y} has the value {@code true}).
* <p>
* Note that it is generally necessary to override the {@code hashCode}
* method whenever this method is overridden, so as to maintain the
* general contract for the {@code hashCode} method, which states
* that equal objects must have equal hash codes.
*
* @param obj the reference object with which to compare.
* @return {@code true} if this object is the same as the obj
* argument; {@code false} otherwise.
* @see #hashCode()
* @see java.util.HashMap
*/
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
和non-null对象引用的等值判断。具有自反性、对称性、传递性和一致性。对于任何non-null引用x,x.equals(null)--false。大多数实现遵循规则:x.equals(y)--true,当且仅当x==y。需要重写,注意和hashCode方法之间的约束。
8. 为什么equals和hashCode方法要定义在Object类中而不是单独的接口?
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/8113752/why-equals-and-hashcode-were-defined-in-object


(还不理解chaos到底指什么??)
/**
* Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning
* of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general
* intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote>
* will be true, and that the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements.
* While it is typically the case that:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement.
* <p>
* By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling
* {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except
* {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that
* {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.
* <p>
* By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent
* of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,
* it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned
* by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means
* copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"
* of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these
* objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only
* primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually
* the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone}
* need to be modified.
* <p>
* The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a
* specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does
* not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a
* {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays
* are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that
* the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]}
* is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.
* Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this
* object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of
* the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the
* contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method
* performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
* <p>
* The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface
* {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object
* whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an
* exception at run time.
*
* @return a clone of this instance.
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not
* support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses
* that override the {@code clone} method can also
* throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot
* be cloned.
* @see java.lang.Cloneable
*/
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
方法有protected修饰,所以子类实现需要覆盖此方法并实现Cloneable接口,才能在外部实现clone功能。
|
重写 |
|
①被复制的类需要实现Cloneable接口(否则抛异常),该接口为标记接口,不含任何方法 ②覆盖clone(),访问修饰符设为public。方法中调用super.clone()方法得到需要的复制对象 |
创建并返回该对象的一个副本。副本精确的定义取决于该对象的副本。常x.clone() != x ----true,x.getClass() == x.clone().getClass() ---true(不是绝对的约束),通常有x.equals(x.clone()) --true(也不是绝对约束)。返回的副本应该有对应所有副本的引用(super.clone)----> x.getClass() == x.clone().getClass() ---true。
返回的副本和调用的对象独立。
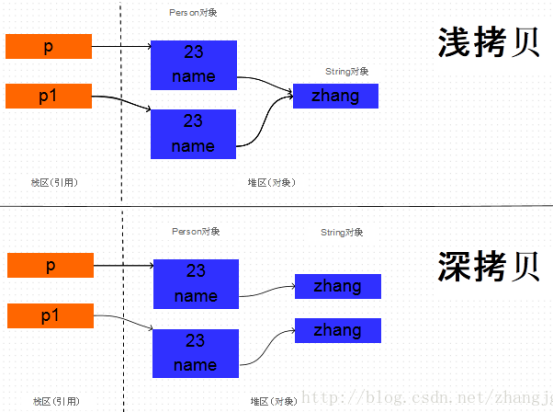
在某些场景中,我们需要获取到一个对象的拷贝用于某些处理。这时候就可以用到Java中的Object.clone方法进行对象复制,得到一个一模一样的新对象。但是在实际使用过程中会发现:当对象中含有可变的引用类型属性时,在复制得到的新对象对该引用类型属性内容进行修改,原始对象响应的属性内容也会发生变化,这就是"浅拷贝"的现象。方法说明也表示该方法是“浅拷贝”(Thus, this method performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.)
9.关于创建对象的两种方式(new,clone),clone与引用复制,浅拷贝与深拷贝
(https://blog.csdn.net/it_zkc/article/details/73733527)
创建对象的两种方式:
|
①new 找new后面类的类型,按此类型分配内存,进行初始化(声明、初始化块、构造器),通过this返回新创建对象的引用 |
|
②clone 分配内存,大小与调用clone方法的对象一样,将调用对象的各个值赋给新创建对象 |
浅拷贝与深拷贝:
/**
* Returns a string representation of the object. In general, the
* {@code toString} method returns a string that
* "textually represents" this object. The result should
* be a concise but informative representation that is easy for a
* person to read.
* It is recommended that all subclasses override this method.
* <p>
* The {@code toString} method for class {@code Object}
* returns a string consisting of the name of the class of which the
* object is an instance, the at-sign character `{@code @}', and
* the unsigned hexadecimal representation of the hash code of the
* object. In other words, this method returns a string equal to the
* value of:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
* </pre></blockquote>
*
* @return a string representation of the object.
*/
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
之前在getClass()时看到this.toString()和super.toString()效果使一样的,都是返回了this对应的类的toString。
10.为什么this.toString()和super.toString()返回相同?
看Object对toString()的默认实现,getClass()前有默认this调用,即第一步为this.getClass()返回了this运行时的类,即调用this和super的toString方法返回一样是因为这里的getClass(),它们都得到了运行时类,所以在“@”前面的应该相同,再看“@”后面的Integer.toHexString(hashCode()),我们看它们的hashCode()的测试
package demo;
public class TestClass extends Aa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Aa a = new TestClass();
System.out.println("++++++++++++++ a ++++++++++++");
a.test();
a.testSSuer();
System.out.println("class--" + a.getClass().getName() + " hashCode--" + a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println("===========================");
Aa aa = new Aa();
System.out.println("++++++++++++++++++++ aa ++++++++++++++++");
aa.test();
System.out.println("class--" + aa.getClass().getName() + " hashCode--" + aa.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println("===========================");
TestClass test = new TestClass();
System.out.println("++++++++++++++++ test ++++++++++++++");
test.test();
test.testSSuer();
System.out.println("class--" + test.getClass().getName() + " hashCode--" + test.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println("===========================");
TestClass test2 = new TestClass();
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++ test2 ++++++++++++");
test2.test();
test2.testSSuer();
System.out.println("class--" + test2.getClass().getName() + " hashCode--" + test2.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
class Aa{
private int count;
private Object obj;
// setter and getter methods
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public Object getObj() {
return obj;
}
public void setObj(Object obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
// test methods
public void test(){
System.out.println(this.toString());
System.out.println(super.toString());
System.out.println(this.hashCode());
System.out.println(super.hashCode());
testSuper();
}
private void testSuper() {
System.out.println("************* super *************");
System.out.println("class----" + this.getClass().getSuperclass().getName());
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSuperclass().hashCode());
System.out.println();
}
public void testSSuer(){
System.out.println("+++++++++ SSuper ++++++++");
System.out.println("class----" + this.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass().getName());
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass().hashCode());
System.out.println();
}
}
/*
++++++++++++++ a ++++++++++++
demo.TestClass@139a55
demo.TestClass@139a55
1284693
1284693
************* super *************
class----demo.Aa
31168322
+++++++++ SSuper ++++++++
class----java.lang.Object
17225372
class--demo.TestClass hashCode--27134973
===========================
++++++++++++++++++++ aa ++++++++++++++++
demo.Aa@52e922
demo.Aa@52e922
5433634
5433634
************* super *************
class----java.lang.Object
17225372
class--demo.Aa hashCode--31168322
===========================
++++++++++++++++ test ++++++++++++++
demo.TestClass@25154f
demo.TestClass@25154f
2430287
2430287
************* super *************
class----demo.Aa
31168322
+++++++++ SSuper ++++++++
class----java.lang.Object
17225372
class--demo.TestClass hashCode--27134973
===========================
+++++++++++++++++ test2 ++++++++++++
demo.TestClass@10dea4e
demo.TestClass@10dea4e
17689166
17689166
************* super *************
class----demo.Aa
31168322
+++++++++ SSuper ++++++++
class----java.lang.Object
17225372
class--demo.TestClass hashCode--27134973
*/
可以看到this和super的hashCode()返回值一样,但是通过this.getClass().hashCode()的返回值又和它们不同,且this.getClass().getSuperClass().hashCode()又和它们不一样,这是为什么呢?
我们观察到一个现象:通过对象调用的hashCode()会返回不同的值,但是通过getClass().hashCode()会返回一致的结果,getClass()返回了对象的类,再通过类调用hashCode方法返回值是相同的,但是在Class类中并没有重写hashCode方法,所以Object中对对象的类的处理是不同的(运行在windows下),本地方法实现时做了区别对待?其实不是的,因为类Object、Aa、TestClass在Aa a = new TestClass();时就已经加载到内存中了,相当于一个类对象,即一个Class对象,在以后再new Object、Aa、TestClass时就不用再加载一次类了,所以通过getClass()方法返回了内存中加载的类,再在加载类中调用hashCode()返回的就是加载类相关的信息(包含了地址但不完全是地址)。
现在又回到了那个问题上,为什么this.hashCode()和super.hashCode()返回一样?
着手点:super关键字,继承的内存图
为什么子类不能通过super来调用父类的private属性或方法?super和this能调用的属性和方法一样,除过super调用构造器及其在父类和子类中存在一样方法时调用父类方法,super还有什么用?
https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390836899
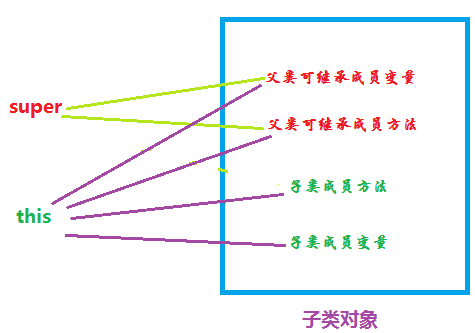
从图中可知,压根没有父类对象,只有子类对象,而且this完全引用这个对象,super只是引用了这个对象中从父类继承来的成员,也就是说,除了super不能访问子类定义的成员之外,super和this是同一个对象。 |
|
我觉得是这样的,new子类对象时,先开辟一片内存空间,先给父类的成员变量安排好内存单元,然后子类自己的数据接着来分配给予内存单元,相当于父类数据与子类数据合租一个房子,房子是子类的。 |
|
一个对象可以理解为一个房子,而一个类只是规定了什么地方要放什么东西,比如客厅要放沙发,餐厅要有餐桌。 |
因为Aa和TestClass类都没有重写hashCode函数,所以super和this都可以调用hashCode(),由于hashCode需要地址信息而this和super是一样的(一栋房子的地址),所以它们返回的hashCode()是相同的。即它们调用的toString()也是一样的。
查看Integer.toHexString()方法:
public static String toHexString(int i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 4);
}
/**
* Convert the integer to an unsigned number.
*/
private static String toUnsignedString0(int val, int shift) {
// assert shift > 0 && shift <=5 : "Illegal shift value";
int mag = Integer.SIZE - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(val);
int chars = Math.max(((mag + (shift - 1)) / shift), 1);
char[] buf = new char[chars]; formatUnsignedInt(val, shift, buf, 0, chars); // Use special constructor which takes over "buf".
return new String(buf, true);
}
Integer.SIZE = 32
public static int numberOfLeadingZeros(int i) {
// HD, Figure 5-6
if (i == 0)
return 32;
int n = 1;
if (i >>> 16 == 0) { n += 16; i <<= 16; }
if (i >>> 24 == 0) { n += 8; i <<= 8; }
if (i >>> 28 == 0) { n += 4; i <<= 4; }
if (i >>> 30 == 0) { n += 2; i <<= 2; }
n -= i >>> 31;
return n;
}
/**
* Format a long (treated as unsigned) into a character buffer.
* @param val the unsigned int to format
* @param shift the log2 of the base to format in (4 for hex, 3 for octal, 1 for binary)
* @param buf the character buffer to write to
* @param offset the offset in the destination buffer to start at
* @param len the number of characters to write
* @return the lowest character location used
*/
static int formatUnsignedInt(int val, int shift, char[] buf, int offset, int len) {
int charPos = len;
int radix = 1 << shift;
int mask = radix - 1;
do {
buf[offset + --charPos] = Integer.digits[val & mask];
val >>>= shift;
} while (val != 0 && charPos > 0); return charPos;
}
每四位和1111做&运算,根据digits对应的值赋值。(先从第四位开始)
/**
* All possible chars for representing a number as a String
*/
final static char[] digits = {
'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' ,
'6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,
'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' ,
'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' ,
'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' ,
'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z'
};
/**
* Wakes up a single thread that is waiting on this object's
* monitor. If any threads are waiting on this object, one of them
* is chosen to be awakened. The choice is arbitrary and occurs at
* the discretion of the implementation. A thread waits on an object's
* monitor by calling one of the {@code wait} methods.
* <p>
* The awakened thread will not be able to proceed until the current
* thread relinquishes the lock on this object. The awakened thread will
* compete in the usual manner with any other threads that might be
* actively competing to synchronize on this object; for example, the
* awakened thread enjoys no reliable privilege or disadvantage in being
* the next thread to lock this object.
* <p>
* This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
* of this object's monitor. A thread becomes the owner of the
* object's monitor in one of three ways:
* <ul>
* <li>By executing a synchronized instance method of that object.
* <li>By executing the body of a {@code synchronized} statement
* that synchronizes on the object.
* <li>For objects of type {@code Class,} by executing a
* synchronized static method of that class.
* </ul>
* <p>
* Only one thread at a time can own an object's monitor.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
* the owner of this object's monitor.
* @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll()
* @see java.lang.Object#wait()
*/
public final native void notify();
不能被重写。唤醒该对象monitor中等待的单线程。有多个线程则选择一个唤醒。在实现时选择是任意且灵活的。
执行该方法的线程唤醒在对象的等待池中等待的一个线程,JVM从对象的等待池中随机选择一个线程,把它转到对象的锁池中。该方法的调用,会从所有正在等待obj对象锁的线程中,唤醒其中的一个(选择算法依赖于不同实现),被唤醒的线程此时加入到了obj对象锁的争夺之中,然而该notify方法的执行线程此时并未释放obj的对象锁,而是离开synchronized代码块时释放。因此在notify方法之后,synchronized代码块结束之前,所有其他被唤醒的,等待obj对象锁的线程依旧被阻塞(https://my.oschina.net/fengheju/blog/169695)
|
https://blog.csdn.net/vk5176891/article/details/53945677 |
|
三个方法都必须在synchronized 同步关键字所限定的作用域中调用,否则会报错java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException ,意思是因为没有同步,所以线程对对象锁的状态是不确定的,不能调用这些方法。 |
|
wait 表示持有对象锁的线程A准备释放对象锁权限,释放cpu资源并进入等待。 notify 表示持有对象锁的线程A准备释放对象锁权限,通知jvm唤醒某个竞争该对象锁的线程X。线程A synchronized 代码作用域结束后,线程X直接获得对象锁权限,其他竞争线程继续等待(即使线程X同步完毕,释放对象锁,其他竞争线程仍然等待,直至有新的notify ,notifyAll被调用)。 notifyAll 表示持有对象锁的线程A准备释放对象锁权限,通知jvm唤醒所有竞争该对象锁的线程,线程A synchronized 代码作用域结束后,jvm通过算法将对象锁权限指派给某个线程X,所有被唤醒的线程不再等待。线程X synchronized 代码作用域结束后,之前所有被唤醒的线程都有可能获得该对象锁权限,这个由JVM算法决定。 |
|
wait有三个重载方法,同时必须捕获非运行时异常InterruptedException。 wait() 进入等待,需要notify ,notifyAll才能唤醒 wait(long timeout) 进入等待,经过timeout 超时后,若未被唤醒,则自动唤醒 wait(timeout, nanos) 进入等待,经过timeout 超时后,若未被唤醒,则自动唤醒。相对wait(long timeout) 更加精确时间。 |
为何这三个不是Thread类声明中的方法,而是Object类中声明的方法?https://www.cnblogs.com/csuwater/p/5411693.html
为何这三个不是Thread类声明中的方法,而是Object类中声明的方法(当然由于Thread类继承了Object类,所以Thread也可以调用者三个方法)?其实这个问题很简单,由于每个对象都拥有monitor(即锁),所以让当前线程等待某个对象的锁,当然应该通过这个对象来操作了。而不是用当前线程来操作,因为当前线程可能会等待多个线程的锁,如果通过线程来操作,就非常复杂了。
/**
* Wakes up all threads that are waiting on this object's monitor. A
* thread waits on an object's monitor by calling one of the
* {@code wait} methods.
* <p>
* The awakened threads will not be able to proceed until the current
* thread relinquishes the lock on this object. The awakened threads
* will compete in the usual manner with any other threads that might
* be actively competing to synchronize on this object; for example,
* the awakened threads enjoy no reliable privilege or disadvantage in
* being the next thread to lock this object.
* <p>
* This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
* of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
* description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
* a monitor.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
* the owner of this object's monitor.
* @see java.lang.Object#notify()
* @see java.lang.Object#wait()
*/
public final native void notifyAll();
唤醒该对象monitor中的所有线程
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until either another thread invokes the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object, or a
* specified amount of time has elapsed.
* <p>
* The current thread must own this object's monitor.
* <p>
* This method causes the current thread (call it <var>T</var>) to
* place itself in the wait set for this object and then to relinquish
* any and all synchronization claims on this object. Thread <var>T</var>
* becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies dormant
* until one of four things happens:
* <ul>
* <li>Some other thread invokes the {@code notify} method for this
* object and thread <var>T</var> happens to be arbitrarily chosen as
* the thread to be awakened.
* <li>Some other thread invokes the {@code notifyAll} method for this
* object.
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt() interrupts}
* thread <var>T</var>.
* <li>The specified amount of real time has elapsed, more or less. If
* {@code timeout} is zero, however, then real time is not taken into
* consideration and the thread simply waits until notified.
* </ul>
* The thread <var>T</var> is then removed from the wait set for this
* object and re-enabled for thread scheduling. It then competes in the
* usual manner with other threads for the right to synchronize on the
* object; once it has gained control of the object, all its
* synchronization claims on the object are restored to the status quo
* ante - that is, to the situation as of the time that the {@code wait}
* method was invoked. Thread <var>T</var> then returns from the
* invocation of the {@code wait} method. Thus, on return from the
* {@code wait} method, the synchronization state of the object and of
* thread {@code T} is exactly as it was when the {@code wait} method
* was invoked.
* <p>
* A thread can also wake up without being notified, interrupted, or
* timing out, a so-called <i>spurious wakeup</i>. While this will rarely
* occur in practice, applications must guard against it by testing for
* the condition that should have caused the thread to be awakened, and
* continuing to wait if the condition is not satisfied. In other words,
* waits should always occur in loops, like this one:
* <pre>
* synchronized (obj) {
* while (<condition does not hold>)
* obj.wait(timeout);
* ... // Perform action appropriate to condition
* }
* </pre>
* (For more information on this topic, see Section 3.2.3 in Doug Lea's
* "Concurrent Programming in Java (Second Edition)" (Addison-Wesley,
* 2000), or Item 50 in Joshua Bloch's "Effective Java Programming
* Language Guide" (Addison-Wesley, 2001).
*
* <p>If the current thread is {@linkplain java.lang.Thread#interrupt()
* interrupted} by any thread before or while it is waiting, then an
* {@code InterruptedException} is thrown. This exception is not
* thrown until the lock status of this object has been restored as
* described above.
*
* <p>
* Note that the {@code wait} method, as it places the current thread
* into the wait set for this object, unlocks only this object; any
* other objects on which the current thread may be synchronized remain
* locked while the thread waits.
* <p>
* This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
* of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
* description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
* a monitor.
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait in milliseconds.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value of timeout is
* negative.
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
* the owner of the object's monitor.
* @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the
* current thread before or while the current thread
* was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted
* status</i> of the current thread is cleared when
* this exception is thrown.
* @see java.lang.Object#notify()
* @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll()
*/
public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
执行了该方法的线程释放对象的锁,JVM会把该线程放到对象的等待池中。该线程等待其它线程唤醒。该方法的调用,使得调用该方法的执行线程(T1)放弃obj的对象锁并阻塞,直到别的线程调用了obj的notifyAll方法、或者别的线程调用了obj的notify方法且JVM选择唤醒(T1),被唤醒的线程(T1)依旧阻塞在wait方法中,与其它的线程一起争夺obj的对象锁,直到它再次获得了obj的对象锁之后,才能从wait方法中返回。(除了notify方法,wait还有带有时间参数的版本,在等待了超过所设时间之后,T1线程一样会被唤醒,进入到争夺obj对象锁的行列;另外中断可以直接跳出wait方法)(https://my.oschina.net/fengheju/blog/169695)
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object, or
* some other thread interrupts the current thread, or a certain
* amount of real time has elapsed.
* <p>
* This method is similar to the {@code wait} method of one
* argument, but it allows finer control over the amount of time to
* wait for a notification before giving up. The amount of real time,
* measured in nanoseconds, is given by:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* 1000000*timeout+nanos</pre></blockquote>
* <p>
* In all other respects, this method does the same thing as the
* method {@link #wait(long)} of one argument. In particular,
* {@code wait(0, 0)} means the same thing as {@code wait(0)}.
* <p>
* The current thread must own this object's monitor. The thread
* releases ownership of this monitor and waits until either of the
* following two conditions has occurred:
* <ul>
* <li>Another thread notifies threads waiting on this object's monitor
* to wake up either through a call to the {@code notify} method
* or the {@code notifyAll} method.
* <li>The timeout period, specified by {@code timeout}
* milliseconds plus {@code nanos} nanoseconds arguments, has
* elapsed.
* </ul>
* <p>
* The thread then waits until it can re-obtain ownership of the
* monitor and resumes execution.
* <p>
* As in the one argument version, interrupts and spurious wakeups are
* possible, and this method should always be used in a loop:
* <pre>
* synchronized (obj) {
* while (<condition does not hold>)
* obj.wait(timeout, nanos);
* ... // Perform action appropriate to condition
* }
* </pre>
* This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
* of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
* description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
* a monitor.
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait in milliseconds.
* @param nanos additional time, in nanoseconds range
* 0-999999.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value of timeout is
* negative or the value of nanos is
* not in the range 0-999999.
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
* the owner of this object's monitor.
* @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the
* current thread before or while the current thread
* was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted
* status</i> of the current thread is cleared when
* this exception is thrown.
*/
public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
if (timeout < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
} if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
} if (nanos > 0) {
timeout++;
} wait(timeout);
}
源码直接简单加1??
|
https://www.zhihu.com/question/41808470/answer/137420141 |
|
主要点在于知道 timeout的单位为毫秒, 参数nanos 的单位为纳秒, 1毫秒 = 1000 微秒 = 1000 000 纳秒 其主要作用应该在能更精确控制等待时间(尤其在高并发时,毫秒的时间节省也是很值得的) |
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object.
* In other words, this method behaves exactly as if it simply
* performs the call {@code wait(0)}.
* <p>
* The current thread must own this object's monitor. The thread
* releases ownership of this monitor and waits until another thread
* notifies threads waiting on this object's monitor to wake up
* either through a call to the {@code notify} method or the
* {@code notifyAll} method. The thread then waits until it can
* re-obtain ownership of the monitor and resumes execution.
* <p>
* As in the one argument version, interrupts and spurious wakeups are
* possible, and this method should always be used in a loop:
* <pre>
* synchronized (obj) {
* while (<condition does not hold>)
* obj.wait();
* ... // Perform action appropriate to condition
* }
* </pre>
* This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
* of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
* description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
* a monitor.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
* the owner of the object's monitor.
* @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the
* current thread before or while the current thread
* was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted
* status</i> of the current thread is cleared when
* this exception is thrown.
* @see java.lang.Object#notify()
* @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll()
*/
public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {
wait(0);
}
/**
* Called by the garbage collector on an object when garbage collection
* determines that there are no more references to the object.
* A subclass overrides the {@code finalize} method to dispose of
* system resources or to perform other cleanup.
* <p>
* The general contract of {@code finalize} is that it is invoked
* if and when the Java™ virtual
* machine has determined that there is no longer any
* means by which this object can be accessed by any thread that has
* not yet died, except as a result of an action taken by the
* finalization of some other object or class which is ready to be
* finalized. The {@code finalize} method may take any action, including
* making this object available again to other threads; the usual purpose
* of {@code finalize}, however, is to perform cleanup actions before
* the object is irrevocably discarded. For example, the finalize method
* for an object that represents an input/output connection might perform
* explicit I/O transactions to break the connection before the object is
* permanently discarded.
* <p>
* The {@code finalize} method of class {@code Object} performs no
* special action; it simply returns normally. Subclasses of
* {@code Object} may override this definition.
* <p>
* The Java programming language does not guarantee which thread will
* invoke the {@code finalize} method for any given object. It is
* guaranteed, however, that the thread that invokes finalize will not
* be holding any user-visible synchronization locks when finalize is
* invoked. If an uncaught exception is thrown by the finalize method,
* the exception is ignored and finalization of that object terminates.
* <p>
* After the {@code finalize} method has been invoked for an object, no
* further action is taken until the Java virtual machine has again
* determined that there is no longer any means by which this object can
* be accessed by any thread that has not yet died, including possible
* actions by other objects or classes which are ready to be finalized,
* at which point the object may be discarded.
* <p>
* The {@code finalize} method is never invoked more than once by a Java
* virtual machine for any given object.
* <p>
* Any exception thrown by the {@code finalize} method causes
* the finalization of this object to be halted, but is otherwise
* ignored.
*
* @throws Throwable the {@code Exception} raised by this method
* @see java.lang.ref.WeakReference
* @see java.lang.ref.PhantomReference
* @jls 12.6 Finalization of Class Instances
*/
protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
空方法且可以抛出任何异常。子类重写。
这是GC清理对象之前所调用的清理方法,是回调方法,我们可以覆盖这个方法写一些清理的代码,GC会自动扫描没有引用的对象,即对象赋值为null;可以通过调用System.runFinalization()或System.runFinalizersOnExit()强制GC清理该对象前调用finalize()方法,GC有时不会调用对象的finalize()方法(由JVM决定)
|
访问垃圾收集在对象上当垃圾收集这确定这个对象上没有更多的引用时可能会触发finalize方法 |
|
一个子类重写了finalize方法处理系统资源或者执行其它的清理也就是调用System.gc可能会触发 |
|
这个一般的合约规定finalize,如果Java虚拟机已经确定这不再有任何意味这个对象能通过任何一个尚未死亡的线程访问的方法调用,除非是由于最后确定的其它对象或类的准备工作所采取的行动 |
|
finalize方法可以采取任何行动,包括使此对象再次可用于其它线程,finalize的通常是在对象不可撤销地丢弃之前执行清楚动作.例如:表示输入输出连接的对象的finalize方法可能会在对象被永久丢弃之前执行显式I/O事务来中断连接 |
|
Java规范确保调用finalize的线程在调用finalize方法时不会持有任何用户可见的同步锁 |
|
如果finalize方法抛出未捕获的异常,则会忽略该异常,并终止该对象的定类。 |
|
finalize方法不会被任何对象调用多次 |
|
finalize方法抛出的任何异常都会导致该对象的终止被停止,否则就忽略 |
调用对象,new对象,非new对象?(只负责回收堆内存中对象);是否与C++中的析构函数相同?(不同,析构函数一定会执行--释放回收,但finalize函数不一定会执行);finalize的其他用途?(判断对象在清理时是否安全释放)https://www.jianshu.com/p/e1b2db7bafce
JDK8下Object类源码理解的更多相关文章
- Thread类源码剖析
目录 1.引子 2.JVM线程状态 3.Thread常用方法 4.拓展点 一.引子 说来也有些汗颜,搞了几年java,忽然发现竟然没拜读过java.lang.Thread类源码,这次特地拿出来晒一晒. ...
- Java集合---Array类源码解析
Java集合---Array类源码解析 ---转自:牛奶.不加糖 一.Arrays.sort()数组排序 Java Arrays中提供了对所有类型的排序.其中主要分为Prim ...
- Java集合---Arrays类源码解析
一.Arrays.sort()数组排序 Java Arrays中提供了对所有类型的排序.其中主要分为Primitive(8种基本类型)和Object两大类. 基本类型:采用调优的快速排序: 对象类型: ...
- Cocos2d-X3.0 刨根问底(六)----- 调度器Scheduler类源码分析
上一章,我们分析Node类的源码,在Node类里面耦合了一个 Scheduler 类的对象,这章我们就来剖析Cocos2d-x的调度器 Scheduler 类的源码,从源码中去了解它的实现与应用方法. ...
- Caffe源码理解2:SyncedMemory CPU和GPU间的数据同步
目录 写在前面 成员变量的含义及作用 构造与析构 内存同步管理 参考 博客:blog.shinelee.me | 博客园 | CSDN 写在前面 在Caffe源码理解1中介绍了Blob类,其中的数据成 ...
- Java并发编程笔记之Unsafe类和LockSupport类源码分析
一.Unsafe类的源码分析 JDK的rt.jar包中的Unsafe类提供了硬件级别的原子操作,Unsafe里面的方法都是native方法,通过使用JNI的方式来访问本地C++实现库. rt.jar ...
- 基于SpringBoot的Environment源码理解实现分散配置
前提 org.springframework.core.env.Environment是当前应用运行环境的公开接口,主要包括应用程序运行环境的两个关键方面:配置文件(profiles)和属性.Envi ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Startup的注册及运行
原文:.NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Startup的注册及运行 写在前面 开发.NET Core应用,直接映入眼帘的就是Startup类和Program类,它们是.NET Core应用程 ...
- 深入源码理解Spring整合MyBatis原理
写在前面 聊一聊MyBatis的核心概念.Spring相关的核心内容,主要结合源码理解Spring是如何整合MyBatis的.(结合右侧目录了解吧) MyBatis相关核心概念粗略回顾 SqlSess ...
随机推荐
- 百度站内搜索https不可用切换api搜索,加上谷歌api站内搜索
google推https几年了,百度开始宣传全面https,但是,百度站内搜索 自己的服务却不走https,接口报错.百度分享也是. 然后采用http://search.zhoulujun.cn/cs ...
- html5 旋转导航练习
ul{ list-style: none; font-size: 24px; font-weight: bold; }a{ text-decoration: none;}li{ ...
- linux下列出所有连接到你的Server的IP地址
linux下列出所有连接到你的Server的IP地址 最近要做一个检查所有连接到主机的IP的脚本,google到一篇老外写的文章 <List all IP addresses connected ...
- Cron表达式解析
每一个域可出现的字符如下:Seconds: 可出现 ", - * /" 四个字符,有效范围为0-59的整数Minutes: 可出 ...
- vue.js国际化vue-i18n插件的使用问题,在模版文本、组件方法、jsf方法里的使用
vue.js国际化vue-i18n插件的使用问题,在模版文本.组件方法.jsf方法里的使用 1.在文本里使用{{$t("xxx")}} <span>{{$t(" ...
- SNMP理解
前两天项目要求一个附加功能,远程监视服务器的运行状况,要定期监视指定端口,指定业务,还包括服务器的磁盘空间,内存,CPU使用率等等.这头俩事还好说,ping和telnet也就搞定了,实在不行就开个so ...
- hive的常见判断与抽样函数
.If函数:if和case差不多,都是处理单个列的查询结果 语法: if(boolean testCondition, T valueTrue, T valueFalseOrNull) 返回值: T ...
- WSDL文件
WSDL: <!--一次webservice调用,其实并不是方法调用,而是发送SOAP消息 ,即xml片段--> <!--以上一篇中的wsdl文档为例,这里我将注释写到文档中 --& ...
- lnmp 系统500 报错
分析点: 1 文件目录权限不足 如果日志缓存目录没有写入权限 chmod -R 775 目录 2 lnmp 一键安装包 查看.user.ini ,其中open_basedir 不要设置到public ...
- HAproxy指南之haproxy实现动静分离(案例篇)
HAproxy指南之haproxy实现动静分离(案例篇) 转自 https://blog.51cto.com/blief/1751806 实际应用环境中,往往需要根据业务请求将相关不同请求跳转 ...
