pyqt4_应用例子(计算器,对话框,进度条,日历等等)
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程)
http://zetcode.com/gui/pyqt4/layoutmanagement/
zetcode官网
PyQt4 tutorial
This is PyQt4 tutorial. The tutorial is suited for beginners and intermediate programmers. After reading this tutorial, you will be able to program non trivial PyQt4 applications. PyQt5 tutorial is the successor of this tutorial.
目录内容
Table of contents
- Introduction
- First programs
- Menus and toolbars
- Layout management
- Events and signals
- Dialogs
- Widgets
- Widgets II
- Drag & drop
- Drawing
- Custom widgets
- The Tetris game
计算器
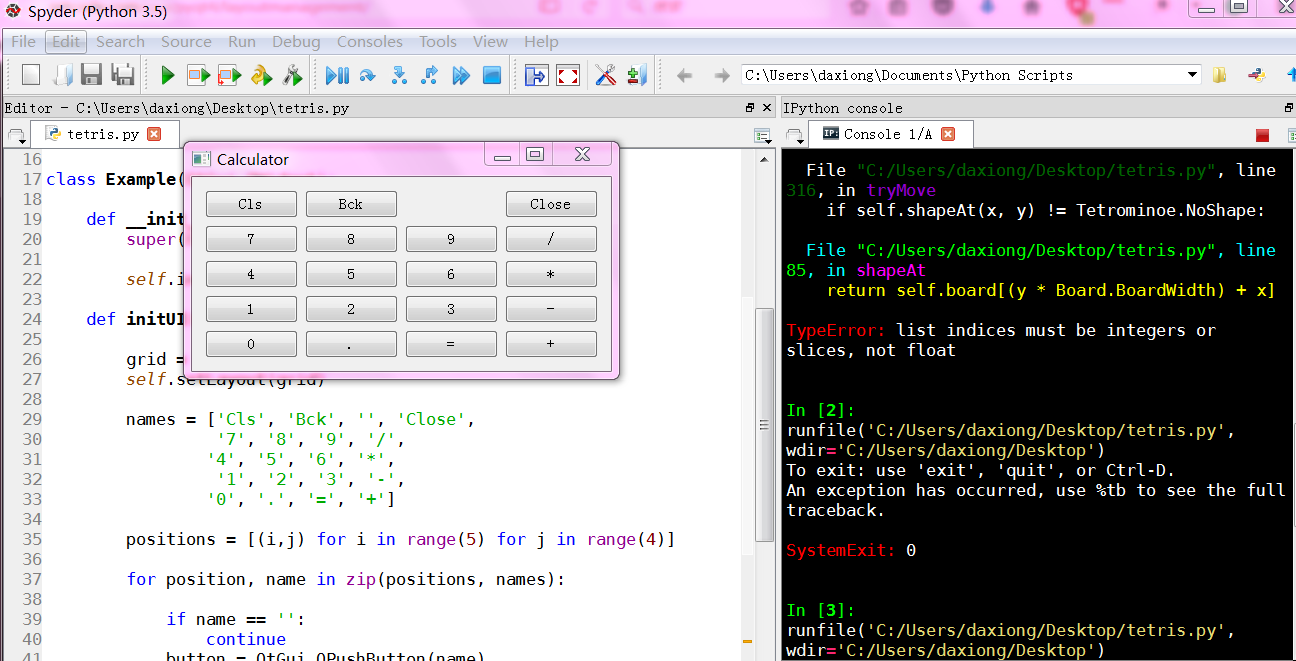
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial In this example, we create a skeleton
of a calculator using a QtGui.QGridLayout. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: July 2014
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): grid = QtGui.QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(grid) names = ['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close',
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+'] positions = [(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)] for position, name in zip(positions, names): if name == '':
continue
button = QtGui.QPushButton(name)
grid.addWidget(button, *position) self.move(300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Calculator')
self.show() def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
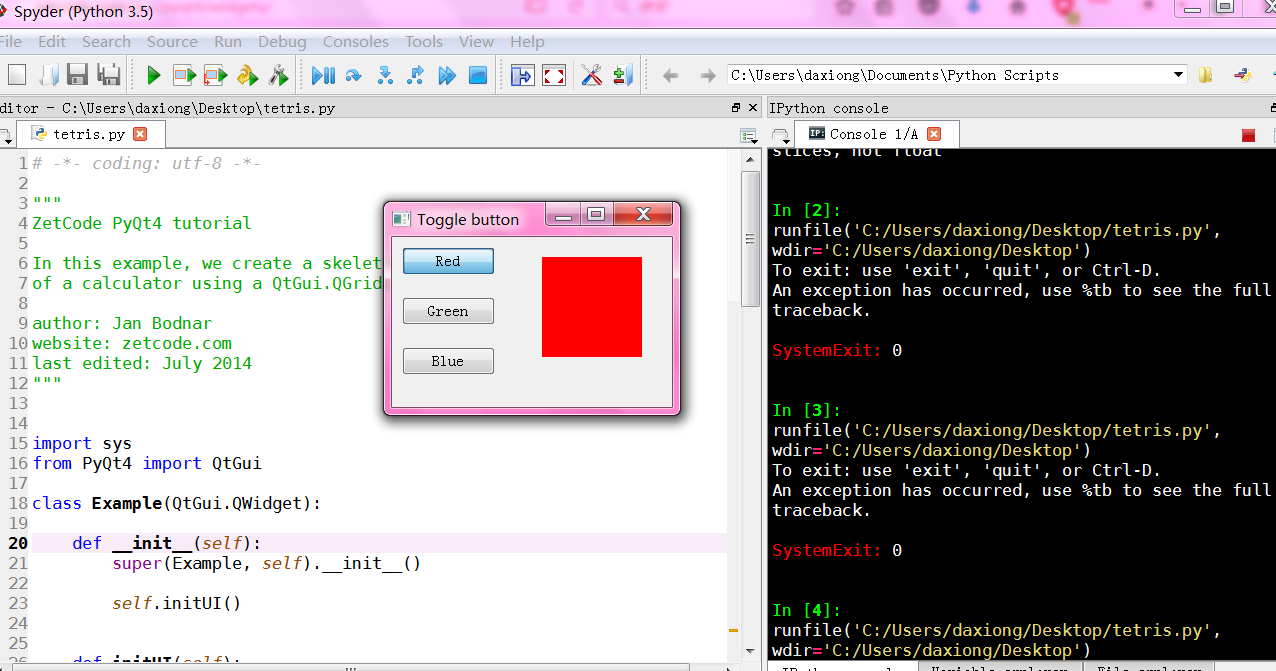
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial In this example, we create three toggle buttons.
They will control the background color of a
QtGui.QFrame. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: September 2011
""" import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.col = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0) redb = QtGui.QPushButton('Red', self)
redb.setCheckable(True)
redb.move(10, 10) redb.clicked[bool].connect(self.setColor) greenb = QtGui.QPushButton('Green', self)
greenb.setCheckable(True)
greenb.move(10, 60) greenb.clicked[bool].connect(self.setColor) blueb = QtGui.QPushButton('Blue', self)
blueb.setCheckable(True)
blueb.move(10, 110) blueb.clicked[bool].connect(self.setColor) self.square = QtGui.QFrame(self)
self.square.setGeometry(150, 20, 100, 100)
self.square.setStyleSheet("QWidget { background-color: %s }" %
self.col.name()) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170)
self.setWindowTitle('Toggle button')
self.show() def setColor(self, pressed): source = self.sender() if pressed:
val = 255
else: val = 0 if source.text() == "Red":
self.col.setRed(val)
elif source.text() == "Green":
self.col.setGreen(val)
else:
self.col.setBlue(val) self.square.setStyleSheet("QFrame { background-color: %s }" %
self.col.name()) def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
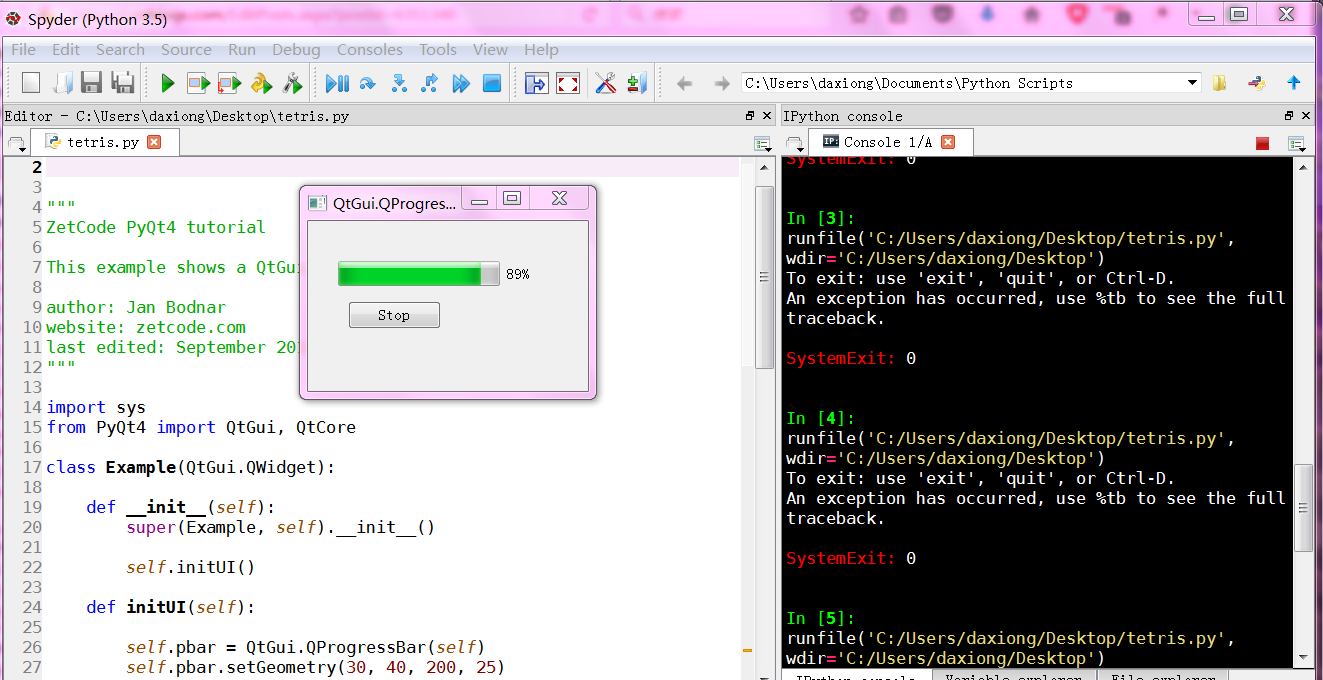
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial This example shows a QtGui.QProgressBar widget. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: September 2011
""" import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.pbar = QtGui.QProgressBar(self)
self.pbar.setGeometry(30, 40, 200, 25) self.btn = QtGui.QPushButton('Start', self)
self.btn.move(40, 80)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.doAction) self.timer = QtCore.QBasicTimer()
self.step = 0 self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170)
self.setWindowTitle('QtGui.QProgressBar')
self.show() def timerEvent(self, e): if self.step >= 100: self.timer.stop()
self.btn.setText('Finished')
return self.step = self.step + 1
self.pbar.setValue(self.step) def doAction(self): if self.timer.isActive():
self.timer.stop()
self.btn.setText('Start') else:
self.timer.start(100, self)
self.btn.setText('Stop') def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
下拉菜单

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.lbl = QtGui.QLabel("Ubuntu", self) combo = QtGui.QComboBox(self)
combo.addItem("Ubuntu")
combo.addItem("Mandriva")
combo.addItem("Fedora")
combo.addItem("Red Hat")
combo.addItem("Gentoo") combo.move(50, 50)
self.lbl.move(50, 150) combo.activated[str].connect(self.onActivated) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 200)
self.setWindowTitle('QtGui.QComboBox')
self.show() def onActivated(self, text): self.lbl.setText(text)
self.lbl.adjustSize() def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
拖动技术
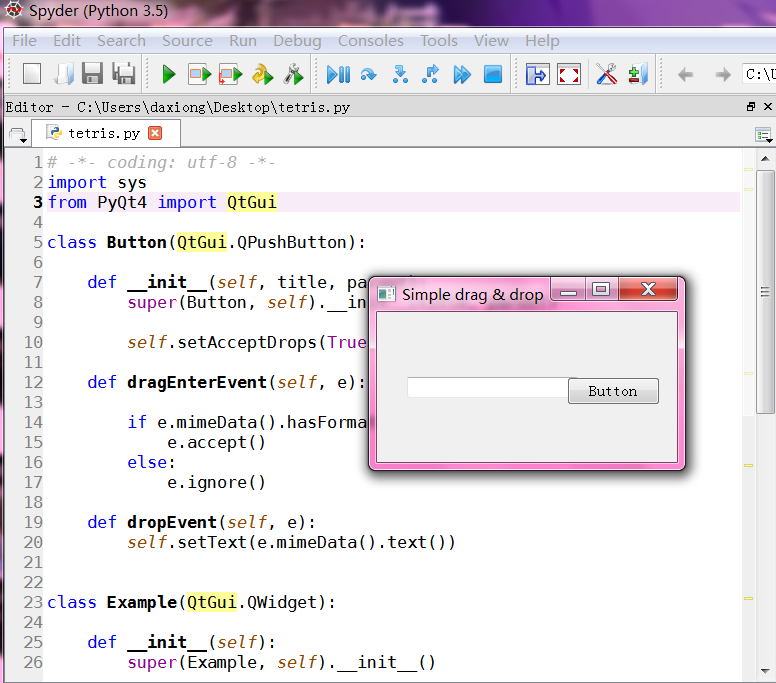
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui class Button(QtGui.QPushButton): def __init__(self, title, parent):
super(Button, self).__init__(title, parent) self.setAcceptDrops(True) def dragEnterEvent(self, e): if e.mimeData().hasFormat('text/plain'):
e.accept()
else:
e.ignore() def dropEvent(self, e):
self.setText(e.mimeData().text()) class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): edit = QtGui.QLineEdit('', self)
edit.setDragEnabled(True)
edit.move(30, 65) button = Button("Button", self)
button.move(190, 65) self.setWindowTitle('Simple drag & drop')
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 150) def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
ex.show()
app.exec_() if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
绘图
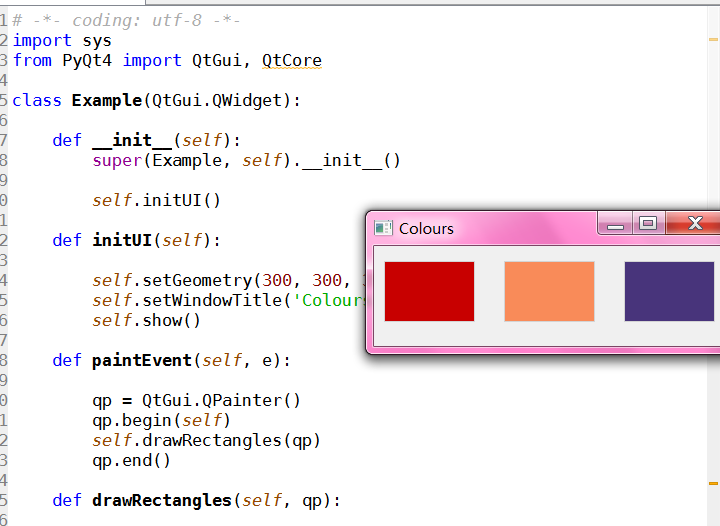
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial This example draws three rectangles in three
different colours. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: September 2011
""" import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 100)
self.setWindowTitle('Colours')
self.show() def paintEvent(self, e): qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawRectangles(qp)
qp.end() def drawRectangles(self, qp): color = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0)
color.setNamedColor('#d4d4d4')
qp.setPen(color) qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(200, 0, 0))
qp.drawRect(10, 15, 90, 60) qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(255, 80, 0, 160))
qp.drawRect(130, 15, 90, 60) qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(25, 0, 90, 200))
qp.drawRect(250, 15, 90, 60) def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
其它例子
Screenshots
Here you can see some of the screenshots from the e-book.

俄罗斯方块

pyqt4_应用例子(计算器,对话框,进度条,日历等等)的更多相关文章
- 使用Uploadify实现上传图片生成缩略图例子,实时显示进度条
不了解Uploadify的,先看看前一篇详细说明 http://www.cnblogs.com/XuebinDing/archive/2012/04/26/2470995.html Uploadify ...
- python3应用例子01(进度条)
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import sysimport time def bar(num, total): rate = num / ...
- android学习笔记20——ProgressDialog进度条对话框
ProgressDialog==>进度条对话框 ProgressDialog本身就代表一个进度条对话框,程序只需要创建ProgressDialog实例,并将其显示出来就是一个进度条对话框:开发者 ...
- 关于JFace中的进度条对话框(ProgressMonitorDialog类)
在Windows操作系统中,最常用的进度条对话框就是文件复制时的弹出框,如果想让用户愉快的使用你开发 的软件,那么在执行某个较长时间的操作时候,就应该弹出一个进度条提示框,告诉用户程序正在做什么. 做 ...
- android 对话框中的进度条 (ProgressDialog)
from:http://byandby.iteye.com/blog/817214 显然要定义对话框进度条就要用ProgressDialog,首先我们需要创建ProgressDialog对象,当然这里 ...
- Android -- ProgressBar(进度条的使用)
我们在开发程序是经常会需要软件全屏显示.自定义标题(使用按钮等控件)和其他的需求,今天这一讲就是如何控制Android应用程序的窗体显示. requestWindowFeature可以设置的值有:(具 ...
- Android的ProgressBar以及自定义进度条
1.xml文件 activity_main.xml <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/an ...
- android:异步任务asyncTask介绍及异步任务下载图片(带进度条)
为什么要用异步任务? 在android中仅仅有在主线程才干对ui进行更新操作.而其他线程不能直接对ui进行操作 android本身是一个多线程的操作系统,我们不能把全部的操作都放在主线程中操作 .比方 ...
- Android开发 ---构建对话框Builder对象,消息提示框、列表对话框、单选提示框、多选提示框、日期/时间对话框、进度条对话框、自定义对话框、投影
效果图: 1.activity_main.xml 描述: a.定义了一个消息提示框按钮 点击按钮弹出消息 b.定义了一个选择城市的输入框 点击按钮选择城市 c.定义了一个单选提示框按钮 点击按钮选择某 ...
- Dialog详解(包括进度条、PopupWindow、自定义view、自定义样式的对话框)
Dialog详解(包括进度条.PopupWindow.自定义view.自定义样式的对话框) Android中提供了多种对话框,在实际应用中我们可能会需要修改这些已有的对话框.本实例就是从实际出发, ...
随机推荐
- Promise.all请求失败重发功能的实现
写爬虫时遇到用Promise.all同时请求多个页面,不可避免的会遇到某些请求失败的情况,这时可以实现一个"重发失败请求"的功能. Promise.all(task).then() ...
- Python学习二
list [ ] Python内置的一种数据类型是列表:list.list是一种有序的集合,可以随时添加和删除其中的元素 classmates = ['Michael', 'Bob', 'Tracy ...
- CentOS中Intel i350T4驱动安装
2015.3.31 在linux*中直接按解决方法中安装i350驱动即可 *************************************************************** ...
- 剑指offer:用两个栈实现队列
题目描述: 用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作. 队列中的元素为int类型. 思路: 可以用stack1来存所有入队的数.在出队操作中,首先将stack1中的元素清空,转移到sta ...
- C#简单窗体应用程序(一)
使用C#创建控制台应用程序的基本步骤: (1)创建项目: (2)用户界面设计: (3)属性设置: (4)编写程序代码: (5)保存.调试.运行: 例题:创建一个Windows窗体应用程序,在窗体中添加 ...
- Git查看与修改用户名、邮箱(转载)
用户名和邮箱的作用: 用户名和邮箱地址相当于你的身份标识,是本地Git客户端的一个变量,不会随着Git库而改变. 每次commit都会用用户名和邮箱纪录. github的contributions跟你 ...
- 关于js typeof 的理解
- SqlServer日期时间函数
-- 判断是否当天,createdate为日期字段 -- ╔════════════════════╗ -- ============================================= ...
- UVAlive4255_Guess
题目很好很有意思. 告诉你n个序列中,任意一个连续子序列的和与0相比较的结果. 构造一个满足条件的序列. 对于从x->y这一段的和,如果大于0,那么sum[x]>sum[y-1],显然我们 ...
- java super
用法: 1.子类构造器里面默认调用父类构造器 2.调用父类的属性,方法