Java的I/O系统
1.File类
File类既能代表一个特定文件的名称,又能代表一个目录下的一组文件的名称。
如果我们调用不带参数的list()方法,便可以获得此File对象包含的全部列表。然而,如果我们想获得一个受限列表,例如,想得到所有扩展名为.java的文件,那么我们就要用到“目录过滤器”,这个类告诉我们怎样显示符合条件的File对象。
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class DirList3 {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
File path = new File(".");
String[] list;
if(args.length == 0){
list = path.list();
}else{
list = path.list(new FilenameFilter() {
private Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(args[0]);
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return pattern.matcher(name).matches();
}
});
}
Arrays.sort(list, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
for(String dirItem : list){
System.out.println(dirItem);
}
}
}
File类不仅仅只代表存在的文件或目录。也可以用File对象来创建新的目录或尚不存在的整个目录路径。我们还可以查看文件的特性(例如,大小、最后修改日期、读/写),检查某个File对象代表的是一个文件还是一个目录,并可以删除文件。
import java.io.*;
public class MakeDirectories {
private static void usage() {
System.err.println(
"Usage:MakeDirectories path1 ...\n" +
"Creates each path\n" +
"Usage:MakeDirectories -d path1 ...\n" +
"Deletes each path\n" +
"Usage:MakeDirectories -r path1 path2\n" +
"Renames from path1 to path2");
System.exit(1);
}
private static void fileData(File f) {
System.out.println(
"Absolute path: " + f.getAbsolutePath() +
"\n Can read: " + f.canRead() +
"\n Can write: " + f.canWrite() +
"\n getName: " + f.getName() +
"\n getParent: " + f.getParent() +
"\n getPath: " + f.getPath() +
"\n length: " + f.length() +
"\n lastModified: " + f.lastModified());
if(f.isFile()){
System.out.println("It's a file");
}else if(f.isDirectory()){
System.out.println("It's a directory");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length < 1){
usage();
}
if(args[0].equals("-r")) {
if(args.length != 3){
usage();
}
File old = new File(args[1]),rname = new File(args[2]);
old.renameTo(rname);
fileData(old);
fileData(rname);
return; // Exit main
}
int count = 0;
boolean del = false;
if(args[0].equals("-d")) {
count++;
del = true;
}
count--;
while(++count < args.length) {
File f = new File(args[count]);
if(f.exists()) {
System.out.println(f + " exists");
if(del) {
System.out.println("deleting..." + f);
f.delete();
}
}else { // Doesn't exist
if(!del) {
f.mkdirs();
System.out.println("created " + f);
}
}
fileData(f);
}
}
}
2.字节流
编程语言的I/O类库中常使用流这个抽象概念,它代表任何有能力产出数据的数据源对象或者是有能力接收数据的接收端对象。
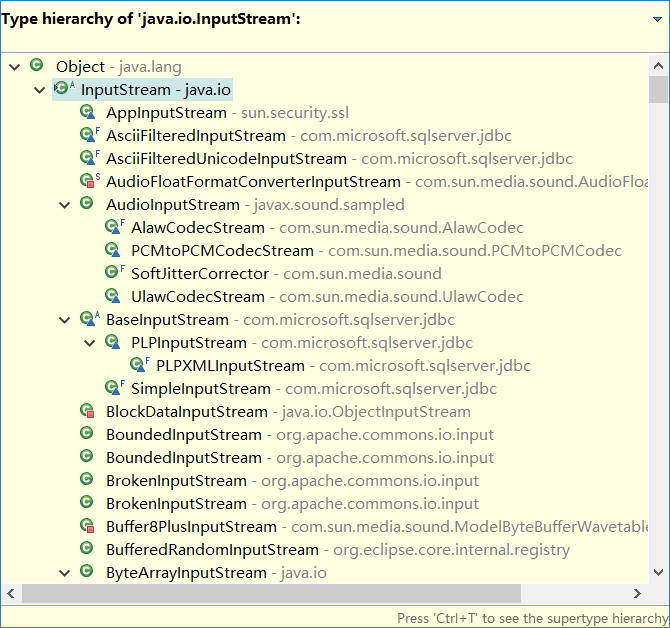
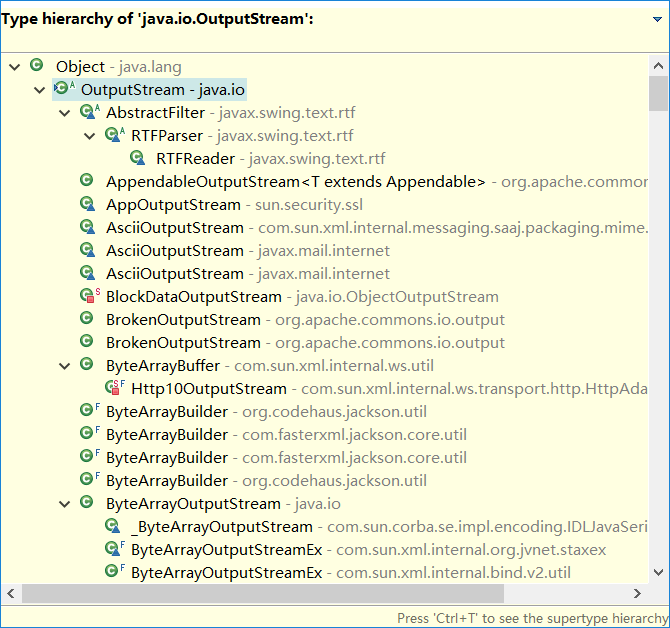
Java类库中的I/O类分成输入和输出两部分。
与输入有关的所有类都应该从InputStream继承,而与输出有关的所有类都应该从OutputStream继承。
3.字符流
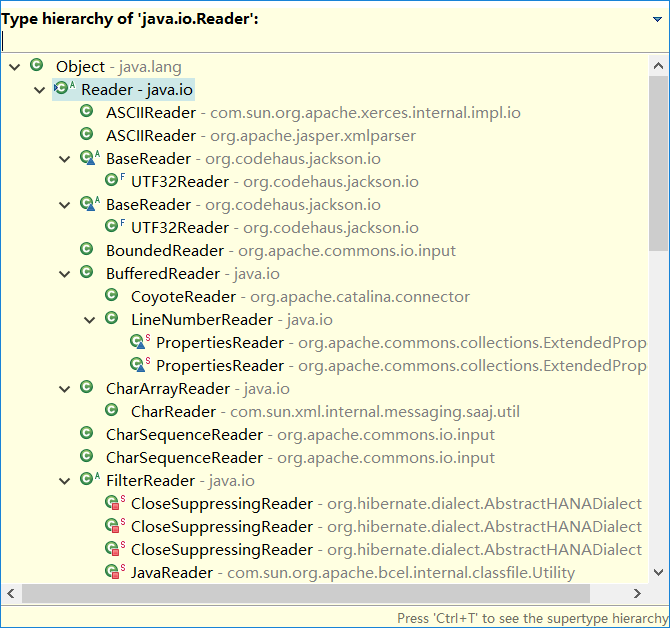
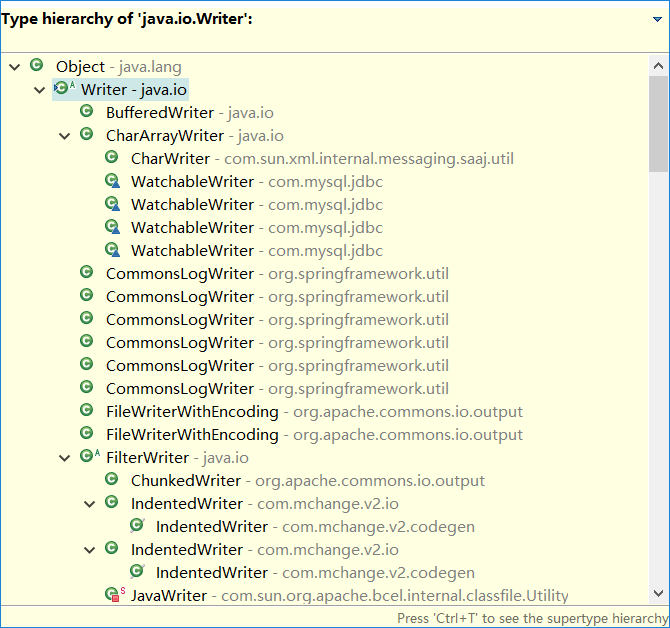
Reader和Writer提供兼容Unicode与面向字符的I/O功能。
有时我们必须把来自于“字节”层次结构中的类和“字符”层次结构中的类结合起来使用。为了实现这个目的,要用到适配器类:InputStreamReader可以把InputStream转换为Reader,而OutputStreamWriter可以把OututStream转换为Writer。
4.I/O流的典型使用方式
4.1 缓冲输入文件
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedInputFile {
// Throw exceptions to console:
public static String read(String filename) throws IOException {
// Reading input by lines:
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
String s;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while((s = in.readLine())!= null){
sb.append(s + "\n");
}
in.close();
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.print(read("BufferedInputFile.java"));
}
}
4.2 从内存输入
public class MemoryInput {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StringReader in = new StringReader(BufferedInputFile.read("MemoryInput.java"));
int c;
while((c = in.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)c);
}
}
}
4.3 格式化的内存输入
public class FormattedMemoryInput {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try {
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(BufferedInputFile.read("FormattedMemoryInput.java").getBytes()));
while(true){
System.out.print((char)in.readByte());
}
}catch(EOFException e) {
System.err.println("End of stream");
}
}
}
public class TestEOF {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("TestEOF.java")));
while(in.available() != 0){
System.out.print((char)in.readByte());
}
}
}
4.4 基本的文件输入
import java.io.*;
public class BasicFileOutput {
static String file = "BasicFileOutput.out";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new StringReader(BufferedInputFile.read("BasicFileOutput.java")));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)));
// Here's the shortcut:
//PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(file);
int lineCount = 1;
String s;
while((s = in.readLine()) != null ){
out.println(lineCount++ + ": " + s);
}
out.close();
// Show the stored file:
System.out.println(BufferedInputFile.read(file));
}
}
4.5 存储和恢复数据
import java.io.*;
public class StoringAndRecoveringData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Data.txt")));
out.writeDouble(3.14159);
out.writeUTF("That was pi");
out.writeDouble(1.41413);
out.writeUTF("Square root of 2");
out.close();
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("Data.txt")));
System.out.println(in.readDouble());
// Only readUTF() will recover the
// Java-UTF String properly:
System.out.println(in.readUTF());
System.out.println(in.readDouble());
System.out.println(in.readUTF());
}
}
4.6 读写随机访问文件
import java.io.*;
public class UsingRandomAccessFile {
static String file = "rtest.dat";
static void display() throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
System.out.println("Value " + i + ": " + rf.readDouble());
}
System.out.println(rf.readUTF());
rf.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
rf.writeDouble(i*1.414);
}
rf.writeUTF("The end of the file");
rf.close();
display();
rf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
rf.seek(5*8);
rf.writeDouble(47.0001);
rf.close();
display();
}
}
5.标准I/O
从标准输入中读取
按照标准I/O模型,Java提供了System.in、System.out和System.err。
import java.io.*;
public class Echo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader stdin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s;
while((s = stdin.readLine()) != null && s.length()!= 0){
System.out.println(s);
}
// An empty line or Ctrl-Z terminates the program
}
}
将System.out转换成PrintWriter
import java.io.*;
public class ChangeSystemOut {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(System.out, true);
out.println("Hello, world");
}
}
标准I/O重定向
import java.io.*;
public class Redirecting {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream console = System.out;
BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("Redirecting.java"));
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.out")));
//setIn(InputStream)、setOut(PrintStream)和setErr(PrintStream)对标准输入、输出和错误I/O流进行重定向。
System.setIn(in);
System.setOut(out);
System.setErr(out);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s;
while((s = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(s);
}
out.close(); // Remember this!
System.setOut(console);
}
}
6.NIO
相关阅读:Java的NIO
Java的I/O系统的更多相关文章
- JAVA中获取当前系统时间及格式转换
JAVA中获取当前系统时间 一. 获取当前系统时间和日期并格式化输出: import java.util.Date;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; publi ...
- java中的io系统详解 - ilibaba的专栏 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET
java中的io系统详解 - ilibaba的专栏 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET 亲,“社区之星”已经一周岁了! 社区福利快来领取免费参加MDCC大会机会哦 Tag功能介绍—我们 ...
- [JAVA] java_实例 获得系统字体
这个代码可以帮助理解java是如何获取系统字体并设置文字字体: import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.JComb ...
- 使用apache daemon让java程序在unix系统上以服务方式运行
通过使用apache_commons_daemon,可以让Java程序在unix系统上以服务器的方式运行. 当然,通过wrapper也是可以达到这样的目的,wrapper还可以指定java应用中用到的 ...
- Java电器商场小系统--简单的java逻辑
//商场类public class Goods { int no; //编号 String name; //商品名称 double price; //商品价格 int number; //商品数量 / ...
- Java高并发秒杀系统API之SSM框架集成swagger与AdminLTE
初衷与整理描述 Java高并发秒杀系统API是来源于网上教程的一个Java项目,也是我接触Java的第一个项目.本来是一枚c#码农,公司计划部分业务转java,于是我利用业务时间自学Java才有了本文 ...
- 《Java程序设计》win10系统学前准备
<Java程序设计>win10系统学前准备 Git的安装 在https://gitforwindows.org/中下载git for windows,下载完成后进行安装.当安装进行到这一步 ...
- Java中在java.sql.Date的系统时间上加上30天并写入oracle
在java.sql.Date的系统时间上加上30天,并写入oracle 思路:通过 Calendar.getInstance() 获得对象,然后 add() 方法添加 时间,再通过 new java. ...
- Appium(JAVA)Windows 7系统搭建及示例运行
Appium(JAVA)Windows 7系统搭建及示例运行 分类: Appium 2014-11-14 17:44 4323人阅读 评论(2) 收藏 举报 1.搭建Android环境 http:// ...
- OSGI 面向Java的动态模型系统
OSGI (面向Java的动态模型系统) OSGi(Open Service Gateway Initiative)技术是Java动态化模块化系统的一系列规范.OSGi一方面指维护OSGi规范的OSG ...
随机推荐
- 企业服务总线ESB
# 企业服务总线ESB 由中间件技术实现并支持SOA的一组基础架构,支持异构环境中的服务.消息以及基于事件的交互,并且具有适当的服务级别和可管理性. 通过使用ESB,可以在几乎不更改代码的情况下,以一 ...
- 高可用OpenStack(Queen版)集群-16.Nova集成Ceph
参考文档: Install-guide:https://docs.openstack.org/install-guide/ OpenStack High Availability Guide:http ...
- 【CentOS 7】nginx配置web服务器
1,安装过程 [root@VM_1_14_centos ~]# cd /data/ [root@VM_1_14_centos data]# wget http://nginx.org/download ...
- JavaScript学习(2)call&apply&bind&eval用法
javascript学习(2)call&apply&bind&eval用法 在javascript中存在这样几种特别有用的函数,能方便我们实现各种奇技淫巧.其中,call.bi ...
- python基础_字符编码
字符编码的历史 阶段一:现代计算机起源于美国,最早诞生也是基于英文考虑的ASCII 阶段二:为了满足中文,中国人定制了GBK 阶段三:各国有各国的标准,就会不可避免地出现冲突,结果就是,在多语言混合的 ...
- MyForm_参考django的Form组建
fork wupeiqi:https://github.com/fat39/Tyrion 组件说明:https://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/p/5938916.html
- learning of a previous team
作为一个软件工程团队,离不开下面三个要素:支持,即分享.责任和合作. 分享是出色技术团队的另一个关键要素,它是团队的基石之一.只有通过分享,团队才有可能实现1+1 > 2这种效应,分享也是让团 ...
- java中的互斥锁和信号量的区别
互斥锁和信号量都是操作系统中为并发编程设计基本概念,互斥锁和信号量的概念上的不同在于,对于同一个资源,互斥锁只有0和1 的概念,而信号量不止于此.也就是说,信号量可以使资源同时被多个线程访问,而互斥锁 ...
- Scrum 5.0(继4.0)
一,组员任务完成情况 首页设计初步完成但是需要优化界面,只能简单的输出信息和在首页进行登录.界面极其简单. 鸡汤版面设计有困难,问题在于用何种形式来管理用户的数据上传,但是经过小组间的讨论确定设计方向 ...
- PAT 甲级 1126 Eulerian Path
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805349851185152 In graph theory, an Eu ...
