docker+k8s基础篇五
Docker+K8s基础篇(五)
- service资源介绍
- A:service资源的工作特性
- service的使用
- A:service字段介绍
- B:ClusterIP的简单使用
- C:NodePort的简单使用
- D:LoadBalancer和ExternalName
- E:无头service
♣一:service资源介绍
A:service资源的工作特性:
kubernetes的service资源:
在整个k8s集群的节点中pods资源是最小的对象,这些对象是提供真正服务的重要组成部分,当我们需要通过外部进行访问的时候因各pod资源提供的访问端点是不一致的,我们就需要设定一个固定的访问端点来提供访问,这个访问端点,是存在pod至上和控制器之下的中间层,这个中间层将叫service,service会严格依赖k8s上的一个重要组件叫coredns(新版本)和kube-dns(老版本1.11之前的版本),所以我们在部署的时候必需要部署coredes或者kube-dns。
kubernetes要想给客户端提供网络功能,需要依赖于第三方方案,这种方案在新版本中可以通过cni(容器网络插件标准接口)来接入任何遵循这种标准的第三方方案,例如我们使用到的flannel。
kubernetes的三类ip地址:
1:node网络
2:pod网络
node和pod的地址是实际存在且配置了。
3:cluater(集群地址)或者叫做service地址,这种地址是虚拟的地址(virtual ip),这些地址没有出现在接口之上,仅仅只是出现在service的规则当中。
在每个节点之上都工作了kube-proxy组件,这个组件将会实时监视service资源中的变动信息,这个监视是由kube-proxy通过一种固有的方式(watch)请求方式来实现的,一旦service的资源发生变动,kube-proxy都要将其转换为当前节点之上的能够被service调度的规则之上(这个规则可能是iptables或者ipvs规则,取决于service的实现方式)
service的实现方式在k8s上有三种模型:
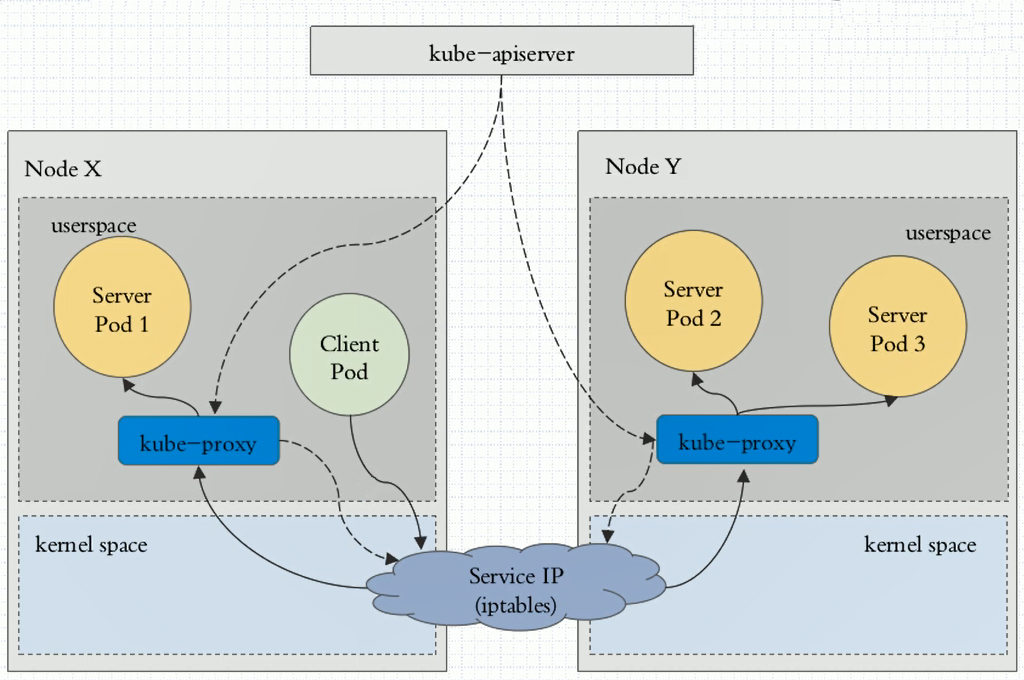
1:userspace(用户空间)
当用户的访问请求会先到达service上,由service将其转换监听在某个套接字上的用户空间内的kube-proxy,接下来kube-proxy处理完成之后再转给service代理至这个service各个相 关联的pod之上,实现调度。
这种模型效率不高,因为用户请求要进过工作在内核上的service转给工作各个“主机”之上用户空间的kube-proxy,kube-proxy将其封装成请求报文发送给内核空间的service资源, 有service的规则在调度至各个pod资源上。
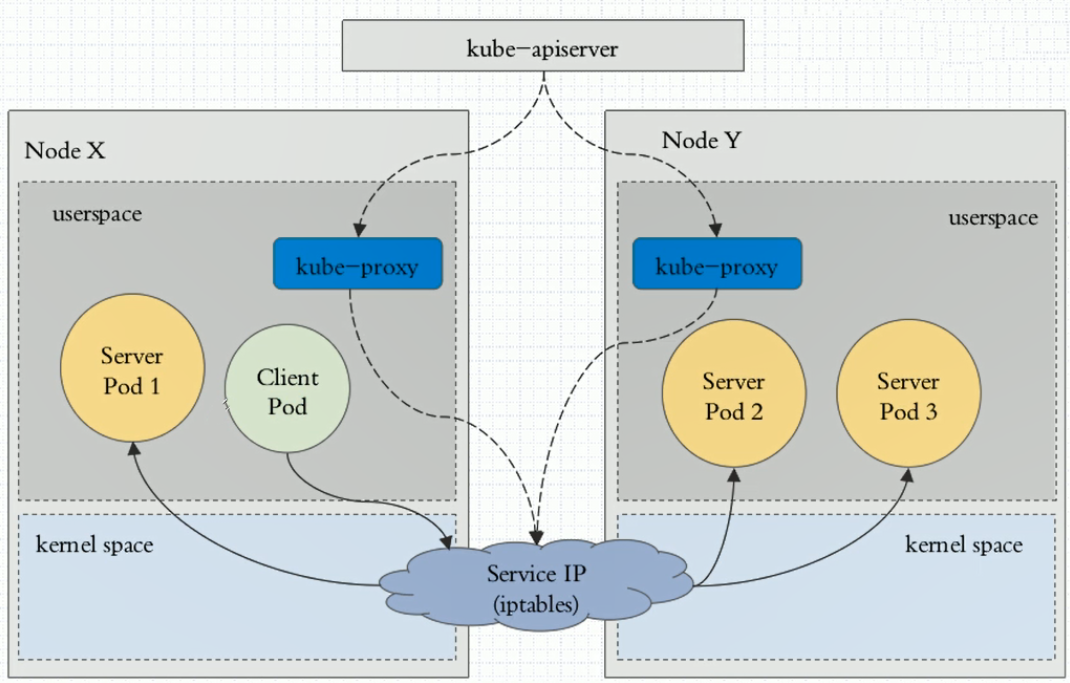
2:iptabeles:
当前用户请求直接请求service的IP,这个请求会被工作在本地内核空间中的service所截取,然后直接调度给相关联的pod,而整个调度都是基于iptables规则来完成的。
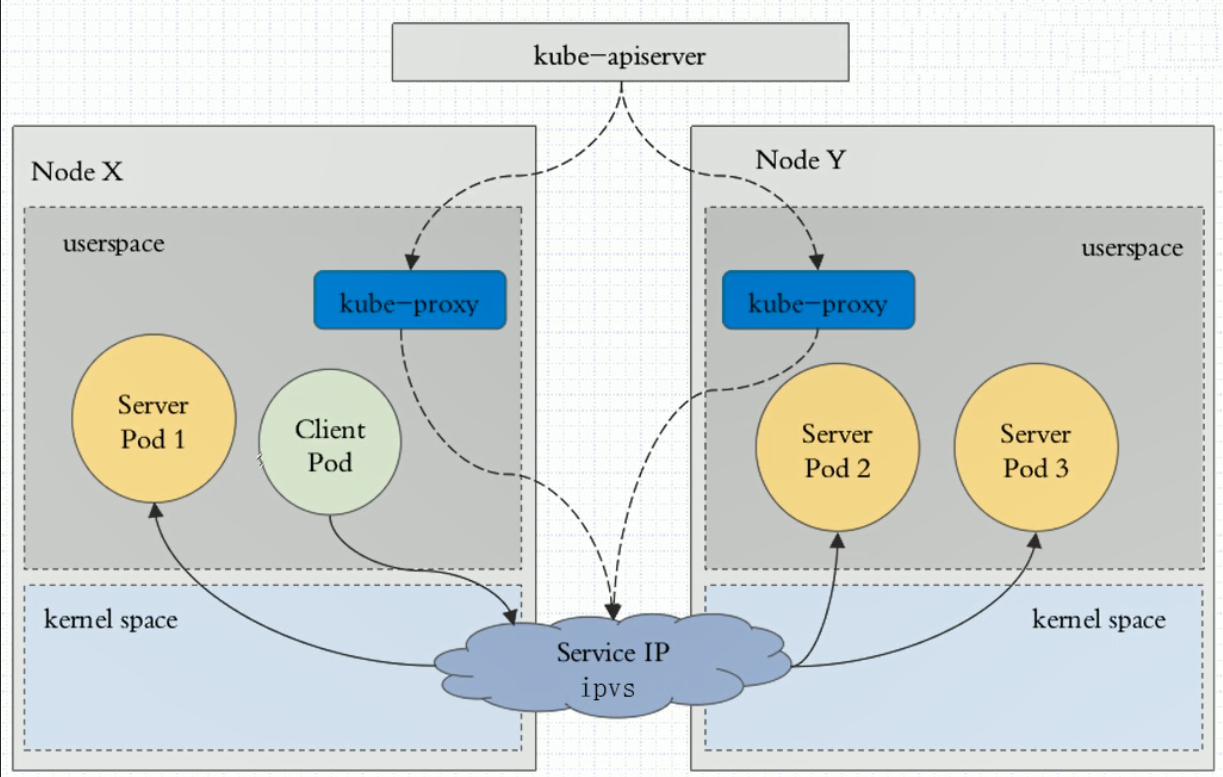
3:ipvs:
和iptables一样,只不过规则换成了ipvs规则。
在配置k8s的时候设定k8s工作在什么模式之下,就会生成对应模式的规则,1.1之前默认是userspace,1.11默认使用的ipvs,如果ipvs没有激活,就会降级为iptables。
当集群中的pods资源发生了改变,这个信息会立马反应到apiservice之上,因为这个改变会直接存储在apiservice的ectd当中,这种变化也会立即触发kube-proxy并发送给service资源中将其转换为iptables或者ipvs规则,这些转换都是动态且实时的。
♣二:service的使用:
A:service字段介绍:
[root@www kubeadm]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 77m
在我们初始化集群的时候已然帮忙创建了一个名称叫kubernetes的service资源,这个资源很重要,是保证我们service和集群节点之间联系的,而且10.96.0.1是面向集群内部的地址。
[root@www kubeadm]# kubectl explain svc 也是包含5个一级字段
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 DESCRIPTION:
Service is a named abstraction of software service (for example, mysql)
consisting of local port (for example 3306) that the proxy listens on, and
the selector that determines which pods will answer requests sent through
the proxy. FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#resources kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#types-kinds metadata <Object>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#metadata spec <Object>
Spec defines the behavior of a service.
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status status <Object>
Most recently observed status of the service. Populated by the system.
Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status [root@www kubeadm]# kubectl explain svc.spec.ports(ports是用于把那个端口和后端的容器端口建立关联关系)
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: ports <[]Object> DESCRIPTION:
The list of ports that are exposed by this service. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#virtual-ips-and-service-proxies ServicePort contains information on service's port. FIELDS:
name <string>
The name of this port within the service. This must be a DNS_LABEL. All
ports within a ServiceSpec must have unique names. This maps to the 'Name'
field in EndpointPort objects. Optional if only one ServicePort is defined
on this service. nodePort <integer>
The port on each node on which this service is exposed when type=NodePort
or LoadBalancer. Usually assigned by the system. If specified, it will be
allocated to the service if unused or else creation of the service will
fail. Default is to auto-allocate a port if the ServiceType of this Service
requires one. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#type-nodeport port <integer> -required- service的端口
The port that will be exposed by this service. protocol <string> node端口
The IP protocol for this port. Supports "TCP", "UDP", and "SCTP". Default
is TCP. targetPort <string> pods端口
Number or name of the port to access on the pods targeted by the service.
Number must be in the range 1 to 65535. Name must be an IANA_SVC_NAME. If
this is a string, it will be looked up as a named port in the target Pod's
container ports. If this is not specified, the value of the 'port' field is
used (an identity map). This field is ignored for services with
clusterIP=None, and should be omitted or set equal to the 'port' field.
More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#defining-a-service [root@www kubeadm]# kubectl explain svc.spec.selector (我们需要关联到哪些pods资源上)
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 FIELD: selector <map[string]string> DESCRIPTION:
Route service traffic to pods with label keys and values matching this
selector. If empty or not present, the service is assumed to have an
external process managing its endpoints, which Kubernetes will not modify.
Only applies to types ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer. Ignored if
type is ExternalName. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/ spec.clusterIP(指定固定的ip,创建之后无法改变) [root@www kubeadm]# kubectl explain svc.spec.type (service的类型)
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 FIELD: type <string> DESCRIPTION:
type determines how the Service is exposed. Defaults to ClusterIP. Valid
options are ExternalName, ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer.
"ExternalName" maps to the specified externalName. "ClusterIP" allocates a
cluster-internal IP address for load-balancing to endpoints. Endpoints are
determined by the selector or if that is not specified, by manual
construction of an Endpoints object. If clusterIP is "None", no virtual IP
is allocated and the endpoints are published as a set of endpoints rather
than a stable IP. "NodePort" builds on ClusterIP and allocates a port on
every node which routes to the clusterIP. "LoadBalancer" builds on NodePort
and creates an external load-balancer (if supported in the current cloud)
which routes to the clusterIP. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#publishing-services-service-types
service资源的字段介绍
svc.spec.type字段类型:
类型一共分为4种:
1:ExternalName(把集群外部的服务引入到集群内部直接使用);
2:ClusterIP;
3:NodePort(接入外部);
4:LoadBalancer(支持lbaas负载均衡的一键调度)
B:ClusterIP的简单使用:
[root@www TestYaml]# cat redis-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: redis
clusterIP: 10.98.98.98 (指定ip创建的时候需要注意网段和地址冲突问题)
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl apply -f redis-svc.yaml
service/redis created
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 102m
redis ClusterIP 10.98.98.98 <none> 6379/TCP 14s 可以看到redis的ip和端口是配置文件指定的ip和端口
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl describe svc redis
Name: redis
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"redis","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"clusterIP":"10.98.98.98","...
Selector: app=redis
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.98.98.98
Port: <unset> 6379/TCP 指定的service端口
TargetPort: 6379/TCP 指定的pod端口
Endpoints: <none>
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
这里需要说明的是service不会直接到pod,而是需要进过中间层Endpoints的,Endpoints也是k8s上标准的对象,再由Endpoints关联至pods资源上。
ClusterIP案例
C:NodePort的简单使用:
[root@www TestYaml]# cat NodePort.svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: myapp
clusterIP: 10.99.99.99
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8088
targetPort: 8088
nodePort: 30008 从30000到32767之间的都可以,默认是动态分配的
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl apply -f NodePort.svc.yaml
service/myapp created
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 125m
myapp NodePort 10.99.99.99 <none> 8088:30008/TCP 22s service的8088端口映射成node上的30008
redis ClusterIP 10.98.98.98 <none> 6379/TCP 23m
通过此种方式创建的pod就可以在外部直接访问了,只不过要进过好几级转换,先是port,再是protocol,在转换到targetPort上。
NodePort案例
D:LoadBalancer和ExternalName:
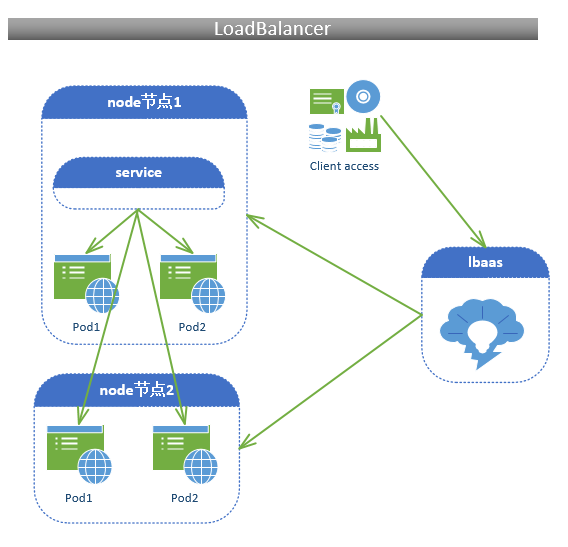
如果购买了阿里云平台的环境虚拟机(带ibaas负载均衡服务),你在上面搭建了一共k8s的集群服务,k8s会自动去调用云平台的ibaas服务,用软件的方式去把用户的访问请求负载调度至后端的任意一个node节点上,在由节点上的service服务再负载调度至后端的任意一个pod之上,整个过程都是自动的,而且是两级负载均衡调度。
ExternalName:
我们在构建pods的时候本来就是层级关系的,例如db被tomcat访问,tomcat被nginx访问,这种被访问的形式本身就是一种client的存在,那如果是我们的nginx服务在集群外部的某台集群上,想nginx能访问到集群内部的tomcat就需要使用ExternalName,在创建yaml文件的时候ExternalName是一个真实有效且能被dns所解析的服务名,然后用户的访问请求走外部的nginx,nginx在发送请求报文给集群内部的nodeIP到service,有service调度到后端的pod(tomcat),pod在返回给service,最后返回到nginx上,实现访问,但是此种方式用的不多。
[root@www kubeadm]# kubectl explain svc.spec.externalName (externalName只能是类型为ExternalName的时候才有效)
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 FIELD: externalName <string> DESCRIPTION:
externalName is the external reference that kubedns or equivalent will
return as a CNAME record for this service. No proxying will be involved.
Must be a valid RFC-1123 hostname (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1123) and
requires Type to be ExternalName.
[root@www kubeadm]#
externalName字段说明
[root@www kubeadm]# kubectl explain svc.spec.sessionAffinity(svc还支持sessionAffinity)
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 FIELD: sessionAffinity <string> DESCRIPTION:
Supports "ClientIP" and "None". Used to maintain session affinity. Enable
client IP based session affinity. Must be ClientIP or None. Defaults to
None. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#virtual-ips-and-service-proxies
这里的session支持两种,一个是ClientIP,将来自同一个ip访问的请求始终调度到同一个pod上。
None就是默认的随机调度。
sessionAffinity字段说明
E:无头service:
无头service,即值创建service的时候不指定clusterIP,此时用户的访问请求不再是访问clusterIP而是转而访问pod上的ip
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl explain svc.spec.clusterIP
KIND: Service
VERSION: v1 FIELD: clusterIP <string> DESCRIPTION:
clusterIP is the IP address of the service and is usually assigned randomly
by the master. If an address is specified manually and is not in use by
others, it will be allocated to the service; otherwise, creation of the
service will fail. This field can not be changed through updates. Valid
values are "None", empty string (""), or a valid IP address. "None" can be
specified for headless services when proxying is not required. Only applies
to types ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer. Ignored if type is
ExternalName. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#virtual-ips-and-service-proxies
在指定clusterIP的时候可以指定为none(格式是""即可)
案例:
[root@www TestYaml]# cat NodePort.svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: myapp
clusterIP: None 不指定ip
ports:
- port: 8088
targetPort: 8088
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 81m
myapp ClusterIP None <none> 8088/TCP 9s 可以看到ip是none标记
[root@www TestYaml]# kubectl get svc -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 83m 我们直接去解析coredns的ip就能直接看到pod ip的解析记录
[root@www TestYaml]# dig -t A myapp.default.svc.cluster.local. @10.96.0.10 我们直接解析coredns的ip看看下解析记录 ; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-74.el7_6.1 <<>> -t A myapp.default.svc.cluster.local. @10.96.0.10
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 60422
;; flags: qr aa rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;myapp.default.svc.cluster.local. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION:
myapp.default.svc.cluster.local. 5 IN A 10.244.2.9 可以看到这里有三个记录,ip分别是2.9,2.8,1.8
myapp.default.svc.cluster.local. 5 IN A 10.244.2.8
myapp.default.svc.cluster.local. 5 IN A 10.244.1.8 ;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 10.96.0.10#53(10.96.0.10)
;; WHEN: 日 7月 14 11:29:23 CST 2019
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 201 [root@www TestYaml]# kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
myapp-9758dcb6b-hl957 1/1 Running 0 4m6s 10.244.2.8 www.kubernetes.node1.com <none> <none>
myapp-9758dcb6b-z8rk6 1/1 Running 0 4m6s 10.244.2.9 www.kubernetes.node1.com <none> <none>
myapp-9758dcb6b-zl5jt 1/1 Running 0 4m6s 10.244.1.8 www.kubernetes.node2.com <none> <none>
上面的2.9,2.8,1.8对应的ip就是pod的ip,这样我们得出的结论就是当service没有clusterip的时候就会通过coredns来解析并转发到后端的pod之上。
无头service案例
service很好用,但是也是存在缺陷的,当面我们创建了service的时候,用户访问需要进行两级转换,如果是阿里云的lbaas则是两级调度,其实我们看到的是两级转换,但是落到ipvs或者iptebles之上就是四层调度。因为ipvs和iptables都是四层的,如果我们建立的是https服务的话,例如https对应的名称是myapp,那么你的每一个myapp都要配置成htpps的主机,因为ipvs或者iptables自身是无法卸载https会话的。
kubernetes还有一种引入外部流量的方式,叫ingress(是一种7层调度器)将外部的流量引入到内部来,但是也是无法脱离service的工作,必需要用pod7层功能的应用来调度,起能提供的应用有nginx,haprxoy等。在kubernetes之上应用比较多的是nginx,当然还有别的应用有各自相应的优势。
docker+k8s基础篇五的更多相关文章
- docker+k8s基础篇一
Docker+K8s基础篇(一) docker的介绍 A:为什么是docker B:k8s介绍 docker的使用 A:docker的安装 B:docker的常用命令 C:docker容器的启动和操作 ...
- docker+k8s基础篇四
Docker+K8s基础篇(四) pod控制器 A:pod控制器类型 ReplicaSet控制器 A:ReplicaSet控制器介绍 B:ReplicaSet控制器的使用 Deployment控制器 ...
- docker+k8s基础篇三
Docker+K8s基础篇(三) kubernetes上的资源 A:k8s上的常用资源 Pod的配置清单 A:Pod上的清单定义 B:Pod创建资源的方法 C:spec下其它字段的介绍 Pod的生命周 ...
- docker+k8s基础篇二
Docker+K8s基础篇(二) docker的资源控制 A:docker的资源限制 Kubernetes的基础篇 A:DevOps的介绍 B:Kubernetes的架构概述 C:Kubernetes ...
- 小白学Docker之基础篇
系列文章: 小白学Docker之基础篇 小白学Docker之Compose 小白学Docker之Swarm PS: 以下是个人作为新手小白学习docker的笔记总结 1. docker是什么 百科上的 ...
- Docker之基础篇
小白学Docker之基础篇 系列文章: 小白学Docker之基础篇 小白学Docker之Compose 小白学Docker之Swarm PS: 以下是个人作为新手小白学习docker的笔记总结 1 ...
- C#基础篇五值类型和引用类型
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace P01M ...
- Hybrid APP基础篇(五)->JSBridge实现示例
说明 JSBridge实现示例 目录 前言 参考来源 楔子 JS实现部分 说明 实现 Android实现部分 说明 JSBridge类 实现 Callback类 实现 Webview容器关键代码 实现 ...
- Python基础篇(五)
bool用于判断布尔值的结果是True还是False >>> bool("a") True >>> bool(3) True >>& ...
随机推荐
- npm包之npm-check-updates
检查npm的依赖包是否有比较新的版本 安装 npm i -g npm-check-updates 使用 ncu --help // 查看相关命令 ncu // 检查当前项目中有没有哪些依赖包可更新 n ...
- ImportError: cannot import name HTTPSHandler
原因在于openssl,openssl-devel两个文件包未正确安装.用下来的命令来安装: 2 yum install openssl -y yum install openssl-devel -y ...
- wiki with 35(dp+矩阵快速幂)
Problem J. Wiki with 35Input file: standard input Time limit: 1 secondOutput file: standard output M ...
- 学习Spring-Data-Jpa(十五)---Auditing与@MappedSuperclass
1.Auditing 一般我们针对一张表的操作需要记录下来,是谁修改的,修改时间是什么,Spring-Data为我们提供了支持. 1.1.在实体类中使用Spring-Data为我们提供的四个注解(也可 ...
- Kali Linux 2019.4中文乱码解决
1.先换源deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kali kali-rolling main non-free contribdeb-src http://mirrors.ali ...
- 分类模型的性能评价指标(Classification Model Performance Evaluation Metric)
二分类模型的预测结果分为四种情况(正类为1,反类为0): TP(True Positive):预测为正类,且预测正确(真实为1,预测也为1) FP(False Positive):预测为正类,但预测错 ...
- 干货 | 10分钟教你用column generation求解vehicle routing problems
OUTLINE 前言 VRPTW description column generation Illustration code reference 00 前言 此前向大家介绍了列生成算法的详细过程, ...
- 【转】Java 8新特性(四):新的时间和日期API
Java 8另一个新增的重要特性就是引入了新的时间和日期API,它们被包含在java.time包中.借助新的时间和日期API可以以更简洁的方法处理时间和日期. 在介绍本篇文章内容之前,我们先来讨论Ja ...
- OpenFOAM——高空腔内的湍流自然对流
本算例来自<ANSYS Fluid Dynamics Verification Manual>中的VMFL052: Turbulent Natural Convection Inside ...
- hotspot编译
"AA=="1",==", /usr/bin/make -s VERBOSE="-s" LOG_LEVEL="warn" ...
