shiro密码的比对,密码的MD5加密,MD5盐值加密,多个Relme
有具体问题的可以参考之前的关于shiro的博文,关于shiro的博文均是一次工程的内容
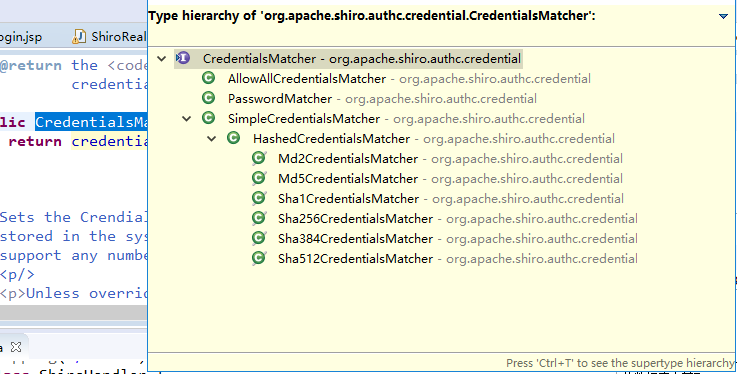
使用其提供的接口实现
<!--
.配置Realm
.1直接实现Realm接口的bean
-->
<bean id="jdbcRealm" class="com.MrChengs.shiro.realms.ShiroRealm">
<property name="credentialsMatcher">
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher"> <!-- 加密的方法 -->
<property name="hashAlgorithmName" value="MD5"></property> <!-- 指定加密的次数 -->
<property name="hashIterations" value=""></property>
</bean>
</property> </bean>
看源码:
public SimpleHash(String algorithmName, Object source, Object salt, int hashIterations)
throws CodecException, UnknownAlgorithmException {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(algorithmName)) {
throw new NullPointerException("algorithmName argument cannot be null or empty.");
}
this.algorithmName = algorithmName;
this.iterations = Math.max(DEFAULT_ITERATIONS, hashIterations);
ByteSource saltBytes = null;
if (salt != null) {
saltBytes = convertSaltToBytes(salt);
this.salt = saltBytes;
}
ByteSource sourceBytes = convertSourceToBytes(source);
hash(sourceBytes, saltBytes, hashIterations);
}
测试加密:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hash="MD5";
Object cred = "";
Object salt = null;
int hashInter = ;
//加密的类
System.out.println(new SimpleHash(hash, cred, salt, hashInter));
}
fc1709d0a95a6be30bc5926fdb7f22f4
MD5盐值加密
//盐值
ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username);
此时放置的不在是明文的密码
ShiroRealm.java
//6.根据用户的情况来构建AuthenticationInfo并且返回
//以下信息是从数据库中获取的
//principal:认证的实体信息,可以是username,也可以是数据表对应的实体对象
Object principal = username;
//credentials:密码
Object credentials = null;
if("user".equals(username)){
//计算后user密码为123456的盐值
credentials = "2044dc18864ca3bc408359a0fb13c2a7";
}else if("admin".equals(username)){
//计算和admin密码为123456的盐值
credentials = "30beaf2a87d54ebe889cfccc076247ad";
} //realmName:当前realm对象为name,调用父类的getName()方法即可
String realmName = getName(); //盐值
ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username); SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = null;//new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, realmName);
info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, credentialsSalt, realmName);
return info;
}
盐值的计算:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hash="MD5";
Object cred = "";
Object salt = "admin";
int hashInter = ;
//加密的类
System.out.println(new SimpleHash(hash, cred, salt, hashInter));
//new SimpleHash(algorithmName, source, salt, hashIterations)
}
在测试中,只有用户名为user/admin 密码为123456才能成功登陆
多Realm
创建新的类
SecondRealm。java
public class SecondRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm {
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken arg0) throws AuthenticationException {
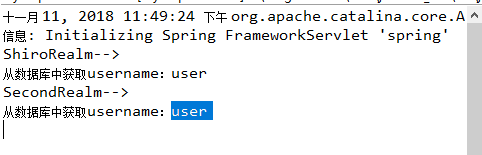
System.out.println("SecondRealm-->");
//1.把AuthenticationToken转为UsernamePasswordToken
UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) arg0;
//2.从UsernamePasswordToken获取username
String username = upToken.getUsername();
//3.调用数据库的方法,从数据库查询username对应的用户记录
System.out.println("从数据库中获取username:" + username);
//4.若用户不存在可以抛出异常 UnKnownAccountException异常
if("unknow".equals(username)){
throw new UnknownAccountException("username 不存在");
}
//5.根据用户信息的清空决定是否需要抛出其他的异常
if("monster".equals(username)){
throw new LockedAccountException("用户被锁定");
}
//6.根据用户的情况来构建AuthenticationInfo并且返回
//以下信息是从数据库中获取的
//principal:认证的实体信息,可以是username,也可以是数据表对应的实体对象
Object principal = username;
//credentials:密码
Object credentials = null;
if("user".equals(username)){
credentials = "6e3be0247455b9298f47eac8e57a07214ef84115";
}else if("admin".equals(username)){
credentials = "ff9633d047eaaf9861984ed86e5f73f904647716";
}
//realmName:当前realm对象为name,调用父类的getName()方法即可
String realmName = getName();
//盐值
ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username);
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = null;//new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, realmName);
info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, credentialsSalt, realmName);
return info;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hash="SHA1";
Object cred = "";
Object salt = "user";
int hashInter = ;
//加密的类
System.out.println(new SimpleHash(hash, cred, salt, hashInter));
//new SimpleHash(algorithmName, source, salt, hashIterations)
}
}
加密方式是SHA1
<!--
.配置SecurityManager
-->
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/> <!-- 此时这个属性需要注释使用下面的属性配置
<property name="realm" ref="jdbcRealm"/>
-->
<property name="authenticator" ref="autheniicator"></property> </bean>
<!-- 认证器 -->
<bean id="autheniicator" class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator">
<property name="realms">
<list>
<ref bean="jdbcRealm"/>
<ref bean="SecondRealm"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean> <!--
.配置Realm
.1直接实现Realm接口的bean
-->
<bean id="jdbcRealm" class="com.MrChengs.shiro.realms.ShiroRealm">
<property name="credentialsMatcher">
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher"> <!-- 加密的方法 -->
<property name="hashAlgorithmName" value="MD5"></property> <!-- 指定加密的次数 -->
<property name="hashIterations" value=""></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean> <bean id="SecondRealm" class="com.MrChengs.shiro.realms.SecondRealm">
<property name="credentialsMatcher">
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher"> <!-- 加密的方法 -->
<property name="hashAlgorithmName" value="SHA1"></property> <!-- 指定加密的次数 -->
<property name="hashIterations" value=""></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
执行的顺序和list的顺序有关
<bean id="autheniicator" class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator">
<property name="realms">
<list>
<ref bean="jdbcRealm"/>
<ref bean="SecondRealm"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
shiro密码的比对,密码的MD5加密,MD5盐值加密,多个Relme的更多相关文章
- Java和JS MD5加密-附盐值加密demo
JAVA和JS的MD5加密 经过测试:字母和数据好使,中文不好使. 源码如下: ** * 类MD5Util.java的实现描述: * */public class MD5Util { // 获得MD5 ...
- Spring Security中的MD5盐值加密
在 spring Security 文档中有这么一句话: "盐值的原理非常简单,就是先把密码和盐值指定的内容合并在一起,再使用md5对合并后的内容进行演算,这样一来,就算密码是一个很常见的字 ...
- c# MD5及盐值加密
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Security.Cryptography;u ...
- c# MD5盐值加密
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Security.Cryptograph ...
- shiro盐值加密并验证
在数据表中存的密码不应该是123456,而应该是123456加密之后的字符串,而且还要求这个加密算法是不可逆的,即由加密后的字符串不能反推回来原来的密码,如果能反推回来那这个加密是没有意义的.著名的加 ...
- MD5盐值加密
加密思路 思路解析:(数据解析过程基于16进制来处理的,加密后为16进制字符串) 加密阶段: 对一个字符串进行MD5加密,我们需要使用到MessageDigest(消息摘要对象),需要一个盐值(sal ...
- shiro 密码的MD5盐值加密
- hashlib 文件校验,MD5动态加盐返回加密后字符
hashlib 文件校验 # for循环校验 import hashlib def check_md5(file): ret = hashlib.md5() with open(file, mode= ...
- 给MD5加上salt随机盐值加密算法实现密码安全的php实现
给MD5加上salt随机盐值加密算法实现密码安全的php实现 如果直接对密码进行散列,那么黑客可以对通过获得这个密码散列值,然后通过查散列值字典(例如MD5密码破解网站),得到某用户的密码.加上sal ...
随机推荐
- BAT的关于程序员的那些事
前言 你是否早有进入BAT公司的想法,但却因为对其不了解而在门外彷徨? 你是否想把技术团队打造成像BAT这些超级互联网公司,但却无从下手? 你是否已经进入了BAT,但是不知道如何晋升而苦恼? 那这篇文 ...
- Bitbucket 关联 VS
1.双击已经建立好的仓库 - 克隆仓库-目标路径选择一个空的文件夹,点击克隆 2.把已经建立好的项目拷贝的到刚刚那个空目录里面 3.在VS里面打开新路径下面的项目,点击提交即可; 我安装了Bitbuc ...
- .net EF框架-实现增删改查
声明一个EF上下文对象 Model dbContext = new Model(); 添加操作(向表中插入一条数据) //声明一个表的实体 Contact contact = new Contact( ...
- T-SQL语句创建表
USE E_Market --指定当前所操作的数据库 GO CREATE TABLE 表名 ( BID int identity (1,1)NOT NULL, BNAME varch ...
- C++运行符重载、友元函数
Complex.h #pragma once #include <iostream> using namespace std; //表示一个复数 class Complex { priva ...
- split 将字符串分割成字符串数组
list_name = list_name.split(","); split() 方法用于把一个字符串分割成字符串数组. 语法 stringObject.split(separa ...
- java导入excle表格,并且对表格进行相应的修改,并对表格数据进行整理,最后导出本地表格等一系列操作
1.首先创建一个java项目 完成效果如下图所示 2.导入以下jar包 3.代码如下 其中行和列的操作是根据需求自动划分的 public class auto_date { private stati ...
- @media print样式 关于table断页
<html> <head> <style> @media print { table { page-break-after:auto } tr { page-bre ...
- 第3章 css属性color的RGBA值
颜色之RGBA RGB是一种色彩标准,是由红(R).绿(G).蓝(B)的变化以及相互叠加来得到各式各样的颜色.RGBA是在RGB的基础上增加了控制alpha透明度的参数. 语法: color:rgba ...
- RegExp.prototype.exec()使用技巧
RegExp.prototype.exec() exec() 方法在一个指定字符串中执行一个搜索匹配.返回一个结果数组或 null. 如果你只是为了判断是否匹配(true或 false),可以使用 R ...
