转:Scipy入门
Scipy入门
转:http://notes.yeshiwei.com/scipy/getting_started.html
本章节主要内容来自 Getting Started 。翻译的其中一部分,并加入了一些我的心得体会。
3.2.1. 什么是scipy,numpy,matplotlib
| Python: | 是一种广泛意义上的编程语言。它非常适合做交互式的工作,并且足够强大可做大型应用。 |
|---|---|
| Numpy: | 是python的一个扩展,它定义了数组和矩阵,以及作用在它们上面的基本操作。 |
| Scipy: | 是另一个python的扩展包。它利用numpy做更高级的数学,信号处理,优化,统计等等。 |
| Matplotlib: | 是一个作图的python扩展包。 |
3.2.2. 它们能干什么?
Scipy 和它的弟兄们可以做很多事情:
首先,它可以做深度的数学数值计算。做矩阵计算,算特征值,算积分,算微分方程。
Numpy的array 类(实现matrix类的基础)充分考虑了效率,所以它比python本身自带的list数据结构要快很多。 而且,类似他实现了类似matlab里面的矩阵操作,可以省掉很多循环。 例如,通常的Python:
a = range(10000000)
b = range(10000000)
c = []
for i in range(len(a)):
c.append(a[i] + b[i])在几GHz的cpu上这个循环通常需要跑5-10秒。而使用numpy。
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(10000000)
b = np.arange(10000000)
c = a + b不仅易读,而且执行的更快,快很多。
There is a sizeable collection of both generic and application-specific numerical code written in or using numpy and scipy. See the Topical Software index for a partial list. Python 有许多模块可以开发交互应用例如 TraitsUI 和 wxPython 结合scipy,就可以开发出很好的交互式应用了。
Using ipython makes interactive work easy. Data processing, exploration of numerical models, trying out operations on the fly allows to go quickly from an idea to a result (see the article on ipython ).
使用 matplotlib 来画出高质量的图。With it you can turn your data or your models into figures for presentations or articles. No need to do the numerical work in one program, save the data, and plot it with another program.
3.2.3. How to work with scipy
Python is a language, it comes with several user interfaces. There is no single program that you can start and that gives an integrated user experience. Instead of that there are dozens of way to work with python.
The most common is to use the advanced interactive python shell ipython to enter commands and run scripts. Scripts can be written with any text editor.
我的选择是 直接在terminal里面运行,emacs编写。
Neither scipy nor numpy provide, by default, plotting functions. They are just numerical tools. The recommended plotting package is matplotlib.
Under Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux, all these tools are provided by the Enthought Python Distribution . 更多关于安装请查看 Installing 在下面的例子里,除了scipy包,还需要安装ipython和一个图形界面的backend,我安装的是tk。
3.2.4. 学习scipy
这可能是一个比较好的快速上手的教程 Tutorial:tutorial focused on interactive data analysis
中文的教程的话,HYRY Studio 的 用Python做科学计算 以及其 实例集 应该是比较完整的一个中文教程了。
To learn more about the python language, the python tutorial will make you familiar with the python syntax and objects. You can download this tutorial from http://docs.python.org/download.html .
我最早就是直接看的官方手册里面的tutorial学的python,很快就上手了,里面也包括了python的C扩展的教程,在python安装包里面就应该有这个官方手册。
Dave Kuhlman’s course on numpy and scipy is another good introduction: http://www.rexx.com/~dkuhlman/scipy_course_01.html
The Documentation and [“Cookbook”] sections of this site provide more material for further learning.
3.2.5. 先看点简单的例子
这里给出的是用ipython的例子,可以不用显示声明所用数组是numpy里的array。直接用python的交互也是类似的,ipython只是有一些扩展功能,具体介绍请看下章。
3.2.5.1. Interactive work(交互方式)
Let’s look at the Fourier transform of a square window. To do this we are going to use ipython, an interactive python shell. As we want to display our results with interactive plots, we will start ipython with the “-pylab” switch, which enables the interactive use of matplotlib:
$ ipython -pylab
Python 2.5.1 (r251:54863, May 2 2007, 16:27:44)
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
IPython 0.7.3 -- An enhanced Interactive Python.
? -> Introduction to IPython's features.
%magic -> Information about IPython's 'magic' % functions.
help -> Python's own help system.
object? -> Details about 'object'. ?object also works, ?? prints more.
Welcome to pylab, a matplotlib-based Python environment.
For more information, type 'help(pylab)'.
Ipython offers a great many convenience features, such as tab-completion of python functions and a good help system:
In [1]: %logstart
Activating auto-logging. Current session state plus future input saved.
Filename : ipython_log.py
Mode : rotate
Output logging : False
Raw input log : False
Timestamping : False
State : active
This activates logging of the session to a file. The format of the log file allows it to be simply executed as a python script at a later date, or edited into a program. Ipython also keeps track of all inputs and outputs (and makes them accessible in the lists called In and Out), so that you can start the logging retroactively:
In [2]: from scipy import *
Since numpy and scipy are not built into python, you must explicitly tell python to load their features. Scipy provides numpy so it is not necessary to import it when importing scipy.
Now to the actual math:
In [3]: a = zeros(1000)
In [4]: a[:100]=1
The first line simply makes an array of 1000 zeros, as you might expect; numpy defaults to making these zeros double-precision floating-point numbers, but if I had wanted single-precision or complex numbers, I could have specified an extra argument to zeros. The second line sets the first hundred entries to 1.
I next want to take the Fourier transform of this array. Scipy provides a fft function to do that:
In [5]: b = fft(a)
In order to see what b looks like, I’ll use the matplotlib library. If you started ipython with the “-pylab” you do not need to import matplotlib. Elsewhere you can import it with: “from pylab import * ”, but you will not have interactive functionality (the plots displays as you create them):
In [6]: plot(abs(b))
Out[6]: [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D instance at 0xb7b9144c>]
In [7]: show()
这里要在新窗口中显示图片需要设置matplotlib的backends。我用的是TkAgg,这需要安装tk
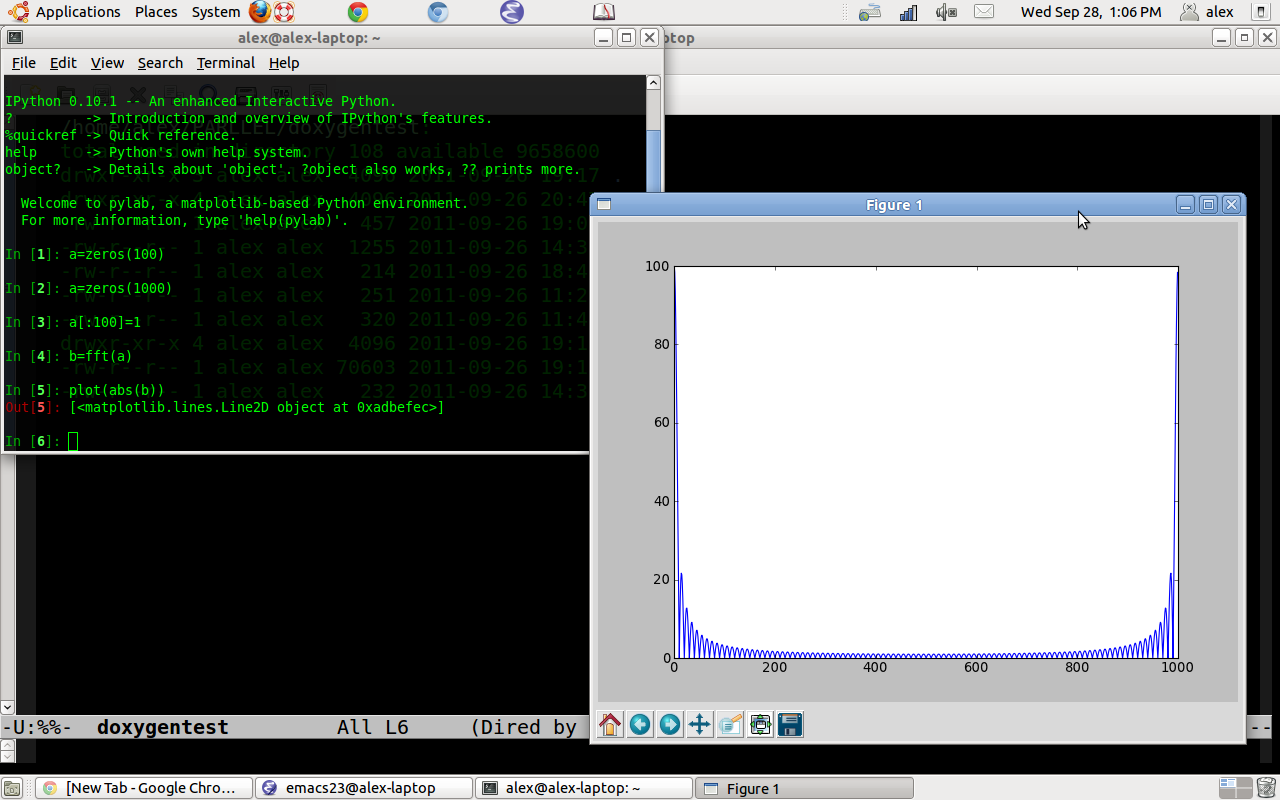
This brings up a window showing the graph of b. The show command on input “[7]” is not necessary if you started ipython with the “-pylab” switch.
I notice that it would look nicer if I shifted b around to put zero frequency in the center. I can do this by concatenating the second half of b with the first half, but I don’t quite remember the syntax for concatenate:
In [8]: concatenate?
Type: builtin_function_or_method
Base Class: <type 'builtin_function_or_method'>
String Form: <built-in function concatenate>
Namespace: Interactive
Docstring:
concatenate((a1, a2, ...), axis=0)
Join arrays together.
The tuple of sequences (a1, a2, ...) are joined along the given axis
(default is the first one) into a single numpy array.
Example:
>>> concatenate( ([0,1,2], [5,6,7]) )
array([0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7])
In [9]: f=arange(-500,500,1)
In [10]: grid(True)
In [11]: plot(f,abs(concatenate((b[500:],b[:500]))))
Out[11]: [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D instance at 0xb360ca4c>]
In [12]: show()

This brings up the graph I wanted. I can also pan and zoom, using a set of interactive controls, and generate postscript output for inclusion in publications (If you want to learn more about plotting, you are advised to read the matplotlib tutorial ).
3.2.5.2. Running a script(脚本方式)
When you are repeating the same work over and over, it can be useful to save the commands in a file and run it as a script in ipython. You can quit the current ipython session using “ctrl-D” and edit the file ipython_log.py. When you want to execute the instructions in this file you can open a new ipython session an enter the command “%run -i ipython_log.py”. 这里ipython将刚才的命令记录在了ipython_log.py中了。
It can also be handy to try out a few commands in ipython, while editing a script file. This allows to try the script line by line on some simple cases before saving it and running it.
3.2.5.3. Some notes about importing
用import 加载程序包的时候的一点细节,值得注意一下,关乎加载的效率。
The following is not so important for you if you are just about to start with scipy & friends and you shouldn’t worry about it. But it’s good to keep it in mind when you start to develop some larger applications.
For interactive work (in ipython) and for smaller scripts it’s ok to use:
from scipy import *
This has the advantage of having all functionallity in the current namespace ready to go. However, for larger programs/packages it is advised to import only the functions or modules that you really need. Lets consider the case where you (for whatever reason) want to compare numpy’s and scipy’s fft functions. In your script you would then write:
#!python numbers=disable
# import from module numpy.fft
from numpy.fft import fft
# import scipy's fft implementation and rename it;
# Note: `from scipy import fft` actually imports numpy.fft.fft (check with
# `scipy.fft?` in Ipython or look at .../site-packages/scipy/__init__.py)
from scipy.fftpack import fft as scipy_fft
The advantage is that you can, when looking at your code, see explicitly what you are importing, which results in clear and readable code. Additionally, this is often faster than importing everything with:
import *
especially if you import from a rather large package like scipy.
However, if you use many different numpy functions, the import statement would get very long if you import everything explicitly. But instead of using “import *” you can import the whole package:
#!python numbers=disable
from numpy import * # bad
from numpy import abs, concatenate, sin, pi, dot, amin, amax, asarray, cov, diag, zeros, empty, exp, eye, kaiser # very long
import numpy # good
# use numpy.fft.fft() on array 'a'
b = numpy.fft.fft(a)
This is ok since usually:
import numpy
is quite fast. Scipy, on the other hand, is rather big (has many subpackages). Therefore:
from scipy import *
can be slow on the first import (all subsequent import statements will be executed faster because no re-import is actually done). That’s why the importing of subpackages (like scipy.fftpack) is disabled by default if you say import scipy, which then is as fast as import numpy. If you want to use, say scipy.fftpack, you have to import it explicitly (which is a good idea anyway). If you want to load all scipy subpackges at once, you will have to do:
import scipy;
scipy.pkgload()
For interactive sessions with Ipython, you can invoke it with the scipy profile:
ipython -p scipy
which reads the scipy profile rc file (usually ~/.ipython/ipythonrc-scipy) and loads all of scipy for you. For a ready-to-go interactive environment with scipy and matplotlib plotting, you would use something like:
ipython -pylab -p scipy
For a general overview of package structuring and “pythonic” importing conventions, take a look at this part of the Python tutorial
转:Scipy入门的更多相关文章
- [技术干货-算子使用] mindspore.scipy 入门使用指导
1. MindSpore框架的SciPy模块 SciPy 是基于NumPy实现的科学计算库,主要用于数学.物理学.生物学等科学以及工程学领域.诸如高阶迭代,线性代数求解等都会需要用到SicPy.Sci ...
- Python数据分析与可视化(经典学习资料)
Numpy:来存储和处理大型矩阵,比Python自身的嵌套列表(nested list structure)结构要高效的多,本身是由C语言开发.这个是很基础的扩展,其余的扩展都是以此为基础.数据结构为 ...
- 干货 | 请收下这份2018学习清单:150个最好的机器学习,NLP和Python教程
机器学习的发展可以追溯到1959年,有着丰富的历史.这个领域也正在以前所未有的速度进化.在之前的一篇文章中,我们讨论过为什么通用人工智能领域即将要爆发.有兴趣入坑ML的小伙伴不要拖延了,时不我待! 在 ...
- 利用python进行数据分析——(一)库的学习
总结一下自己对python常用包:Numpy,Pandas,Matplotlib,Scipy,Scikit-learn 一. Numpy: 标准安装的Python中用列表(list)保存一组值,可以用 ...
- [笔记]我的Linux入门之路 - 05.Eclipse的Python开发环境搭建与Numpy、Scipy库安装
一.Python环境 直接终端查询下python安装没:python --version Python 2.7.12 Ubuntu竟然已经装了Python2.7,那就好说了.不然自己装和装jdk差不多 ...
- Linux入门(10)——Ubuntu16.04使用pip3和pip安装numpy,scipy,matplotlib等第三方库
安装Python3第三方库numpy,scipy,matplotlib: sudo apt install python3-pip pip3 install numpy pip3 install sc ...
- Tensorflow机器学习入门——AttributeError: module 'scipy.misc' has no attribute 'toimage'
这个bug的解决办法: import cv2 # scipy.misc.toimage(image_array).save('cifar10_data/raw/%d.jpg' % i) cv2.imw ...
- IRIS数据集的分析-数据挖掘和python入门-零门槛
所有内容都在python源码和注释里,可运行! ########################### #说明: # 撰写本文的原因是,笔者在研究博文“http://python.jobbole.co ...
- Python之路【第一篇】:Python简介和入门
python简介: 一.什么是python Python(英国发音:/ pa θ n/ 美国发音:/ pa θɑ n/),是一种面向对象.直译式的计算机程序语言. 每一门语言都有自己的哲学: pyth ...
随机推荐
- 成都Uber优步司机奖励政策(1月17日)
滴快车单单2.5倍,注册地址:http://www.udache.com/ 如何注册Uber司机(全国版最新最详细注册流程)/月入2万/不用抢单:http://www.cnblogs.com/mfry ...
- 谁说接口不能有代码?—— Kotlin接口简介(KAD 26)
作者:Antonio Leiva 时间:Jun 6, 2017 原文链接:https://antonioleiva.com/interfaces-kotlin/ 与Java相比,Kotlin接口允许你 ...
- TPO-15 C2 Performance on a biology exam
TPO-15 C2 Performance on a biology exam 第 1 段 1.Listen to part of a conversation between a Student a ...
- Unity编辑器 - 资源修改立即写入磁盘AssetDataBase.SaveAssets()
Unity编辑器 - 资源修改立即写入磁盘AssetDataBase.SaveAssets() 在编写编辑器时,如果需要修改Unity序列化资源(如Prefab,美术资源,ScriptableObje ...
- Java开发工程师(Web方向) - 03.数据库开发 - 第5章.MyBatis
第5章--MyBatis MyBatis入门 Abstract: 数据库框架的工作原理和使用方法(以MyBatis为例) 面向对象的世界与关系型数据库的鸿沟: 面向对象世界中的数据是对象: 关系型数据 ...
- 关于html2canvas清晰度
最近有个小项目 需要生成海报让用户去分享~~~vue做的,海报通过html2canvas 生成. 遇到的最大问题是生成图片的清晰度~~网上找了好多方法. 放大倍数!~网上找的~~ var cntEle ...
- mysql 各种存储引擎的特点
- Struts2(九.初始化用户列表时显示用户照片数目)
1.userlist.jsp //显示每个用户照片的数目(遍历每个用户) $(".picture").each(function(i,e){ $.post("${page ...
- Python高级编程-序列化
在程序运行的过程中,所有的变量都是在内存中,比如,定义一个dict: dict1 = {'name': 'Rob', 'age': 19, 'score': 90} 可以随时修改变量,比如把age改成 ...
- wpa_supplicant之eloop_run分析
部分内容转自http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20273473-id-3128151.html 重要结构体!!! struct eloop_sock { int sock; ...
