HDU 2490 Parade(DPの单调队列)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)
Description
When seeing his Citizens, Panagola always waves his hands. He may get tired and need a break. So please never make Panagola travel in a same west-east road for more than k minutes. If it takes p minutes to pass a love-hate zone, we say the length of that love-hate zone is p. Of course you know every love-hate zone’s length.
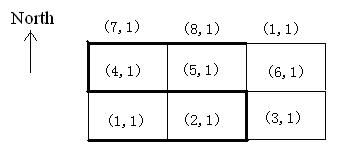
The figure below illustrates the case in sample input. In this figure, a best route is marked by thicker lines.
Input
The first line contains three integers: n, m and k.(0<n<=100,0<m<=10000, 0<=k<=3000000)
The next n+1 lines stands for n + 1 west-east roads in north to south order. Each line contains m integers showing the welcome values of the road’s m love-hate zones, in west to east order.
The last n+1 lines also stands for n + 1 west-east roads in north to south order. Each line contains m integers showing the lengths (in minutes) of the road's m love-hate zones, in west to east order.
Output
题目大意:有一个n*m的矩阵,只能沿着边走,只能往左、往右或往上走,在同一行只能沿一个方向走(走了左边就不能返回走右边了)。打横的边都有一个权值(可能为负数)和一个长度,每行走过的长度不能超过k,打竖的边没有权值和长度。先要从最下面的任意一个点开始,走到最上面的任意一个点,问最大权值和为多少(答案不超过$2^{31}-1$,虽然题目不是这么说的)。
思路:一看就是动态规划,每一行只和上一行的状态有关。因为习惯从小到大循环我们从上往下走,反正都一样。设dp[i][j]为走到第 i 行第 j 个点的最大权值(已往左往右走完),那么dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][x] + sum(welcome[i][y])),distance(x, y) ≤ k,y in [x, i]。其中distance和sum(welcome[i][y])可以预处理出来(如sum[i]代表1~i的和,distance(i, j) = sum[j] - sum[i],i ≤ j),平均到处理每个dp[i][j]身上时间复杂度为O(1)。但是这样计算dp数组,时间复杂度高达$O(nm^2)$。
现假设我们从左到右走,那么dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x] + sum_welcome[y]) = dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x]) + sum_welcome[y],那么对每一个j,所用的dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x]都是一样的,这里很容易能想到单调队列优化(如果你知道单调队列的话)。每次把队列末尾小于dp[i - 1][j] - sum_welcome[j]弹出,把队头distance(i, x) > k的弹出,队头就是最佳的dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x]。优化完时间复杂度为$O(nm)$,已经是读入数据的复杂度了。(这里不介绍单调队列)
PS:可恶这题居然不让人在线非要我把整个矩阵一起读进来……
代码(1078MS,可恶啊C++又比G++快一倍):
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; const int MAXN = ;
const int MAXM = ; int wel[MAXN][MAXM], len[MAXN][MAXM];
int sum_w[MAXM], sum_l[MAXM];
int a[MAXM], b[MAXM], head, tail;
int dp[][MAXM];
int n, m, k, cur; inline void insert(int x, int y) {
while(head != tail && a[tail - ] < x) --tail;
a[tail] = x; b[tail] = y; ++tail;
} void solve() {
memset(dp, , sizeof(dp));
cur = ;
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
cur ^= ;
memset(dp[cur], , sizeof(dp[cur])); sum_w[] = sum_l[] = ;
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) sum_w[j] = sum_w[j - ] + wel[i][j];
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) sum_l[j] = sum_l[j - ] + len[i][j];
head = tail = ;
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) {
insert(dp[cur ^ ][j] - sum_w[j], sum_l[j]);
while(k < sum_l[j] - b[head]) ++head;
dp[cur][j] = max(dp[cur][j], a[head] + sum_w[j]);
} sum_w[m] = sum_l[m] = ;
for(int j = m; j > ; --j) sum_w[j - ] = sum_w[j] + wel[i][j];
for(int j = m; j > ; --j) sum_l[j - ] = sum_l[j] + len[i][j];
head = tail = ;
for(int j = m; j >= ; --j) {
insert(dp[cur ^ ][j] - sum_w[j], sum_l[j]);
while(k < sum_l[j] - b[head]) ++head;
dp[cur][j] = max(dp[cur][j], a[head] + sum_w[j]);
}
}
} int main() {
while(scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k) != EOF) {
if(n == && m == && k == ) break;
++n;
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) scanf("%d", &wel[i][j]);
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) scanf("%d", &len[i][j]);
solve();
int ans = ;
for(int i = ; i <= m; ++i) ans = max(ans, dp[cur][i]);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
HDU 2490 Parade(DPの单调队列)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)的更多相关文章
- HDU 3401 Trade dp+单调队列优化
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3401 Trade Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others)Mem ...
- HDU - 3415(DP + 单调队列)
链接:HDU - 3415 题意:给出一个包含 n 个数的环,求满足长度大于 0 小于等于 k 的最大区间和. 题解:将数组加倍,形成环.求一个前缀和sum.枚举每一个sum[i],以 i 结尾的最大 ...
- HDU 5945 题解(DP)(单调队列)
题面: Fxx and game Time Limit: 3000/1500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/65536 K (Java/Others) T ...
- hdu 4123 树形DP+单调队列
http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/problem/25790 这题基本同poj 3162 要注意mx,mx2,vx,vx2每次都要初始化 #include <iostr ...
- HDU 4749 Parade Show 2013 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Nanjing Online
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4749 题目大意:给一个原序列N,再给出一个序列M,问从N中一共可以找出多少个长度为m的序列,序列中的数 ...
- HDU 2494/POJ 3930 Elevator(模拟)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)
Description Too worrying about the house price bubble, poor Mike sold his house and rent an apartmen ...
- HDU 2492 Ping pong(数学+树状数组)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)
Description N(3<=N<=20000) ping pong players live along a west-east street(consider the street ...
- HDU 2491 Priest John's Busiest Day(贪心)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)
Description John is the only priest in his town. October 26th is the John's busiest day in a year be ...
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(暴力+最小生成树)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)
Description For a tree, which nodes and edges are all weighted, the ratio of it is calculated accord ...
随机推荐
- c++11线程创建的三种方法
一.用一个初始函数创建一个线程 直接看代码:注意c++在运行一个可执行程序的时候(创建了一个进程),会自动的创建一个主线程,这个主线程和进程同生共死,主线程结束,进程也就结束了. #include & ...
- vue2.0 移动端,下拉刷新,上拉加载更多插件,修改版
在[实现丰盛]的插件基础修改[vue2.0 移动端,下拉刷新,上拉加载更多 插件], 1.修改加载到尾页面,返回顶部刷新数据,无法继续加重下一页 2.修改加载完成文字提示 原文链接:http://ww ...
- Spring Security学习笔记(一)
认证和权限控制 AuthenticationManager是认证的主要接口,它只有一个authenticate方法,可以做3件事情. 返回一个认证信息(Authentication),表示认证成功 抛 ...
- Flask的request和session是从哪里来的?
因为之前一直在项目中使用django, 所以在学习Flask的过程中, 难免对吧django和Flask进行对比, 这一次我发现Flask中的request和session并没有想象的那么简单, 所以 ...
- MySQL至TiDB复制延迟监控
因生产环境mysql中有较多复杂sql且运行效率低,因此采用tidb作为生产环境的从库进行部分慢sql及报表的读写分离.其中MySQL至TIDB采用Syncer工具同步.关于TIDB的安装及Synce ...
- linux 下的torrent下载器qBitTorrent
BT下载利器--Qbittorrent完全攻 Ubuntu使用命令安装qBittorrent的方法 源码下载
- 实验6 shell程序设计一(2)
编写一段bash shell程序, 根据键盘输入的学生成绩,显示相应的成绩登等级, 其中 60分以下为"Failed!", 60-69分为"Passed!", ...
- Jetson tx2 串口通信
主要参考了这篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/zomb1e0117/article/details/85157014 其中需要注意的是最后的时候cutecom端口需要把设备改为:/d ...
- 【8086汇编-Day8】实验九
Lab1 代码 ; 在屏幕上输出内存单元中的十进制两位数 assume cs:code, ds:data data segment db db , ; 前一个字节用于保存商,后一个字节用于保存余数 d ...
- NoSQL入门第三天——Redis配置文件与持久化
一.解析Redis配置文件redis.conf (Linux下配置多于编码) 1.它在哪 由于我是在root的家目录下载安装的,默认的安装位置就是: conf就在这里: 根据经验,出厂的conf永远不 ...