Seaborn结构化图形绘制(FacetGrid)
结构化图形绘制(FacetGrid)
可实现多行多列个性化绘制图形。
sns.FacetGrid(
data,
row=None,
col=None,
hue=None,
col_wrap=None,
sharex=True,
sharey=True,
height=3,
aspect=1,
palette=None,
row_order=None,
col_order=None,
hue_order=None,
hue_kws=None,
dropna=True,
legend_out=True,
despine=True,
margin_titles=False,
xlim=None,
ylim=None,
subplot_kws=None,
gridspec_kws=None,
size=None,
)
Docstring: Multi-plot grid for plotting conditional relationships.
Init docstring:
Initialize the matplotlib figure and FacetGrid object.
This class maps a dataset onto multiple axes arrayed in a grid of rows
and columns that correspond to *levels* of variables in the dataset.
The plots it produces are often called "lattice", "trellis", or
"small-multiple" graphics.
It can also represent levels of a third varaible with the ``hue``
parameter, which plots different subets of data in different colors.
This uses color to resolve elements on a third dimension, but only
draws subsets on top of each other and will not tailor the ``hue``
parameter for the specific visualization the way that axes-level
functions that accept ``hue`` will.
When using seaborn functions that infer semantic mappings from a
dataset, care must be taken to synchronize those mappings across
facets. In most cases, it will be better to use a figure-level function
(e.g. :func:`relplot` or :func:`catplot`) than to use
:class:`FacetGrid` directly.
The basic workflow is to initialize the :class:`FacetGrid` object with
the dataset and the variables that are used to structure the grid. Then
one or more plotting functions can be applied to each subset by calling
:meth:`FacetGrid.map` or :meth:`FacetGrid.map_dataframe`. Finally, the
plot can be tweaked with other methods to do things like change the
axis labels, use different ticks, or add a legend. See the detailed
code examples below for more information.
See the :ref:`tutorial <grid_tutorial>` for more information.
Parameters
----------
data : DataFrame
Tidy ("long-form") dataframe where each column is a variable and each
row is an observation.
row, col, hue : strings
Variables that define subsets of the data, which will be drawn on
separate facets in the grid. See the ``*_order`` parameters to
control the order of levels of this variable.
col_wrap : int, optional
"Wrap" the column variable at this width, so that the column facets
span multiple rows. Incompatible with a ``row`` facet.
share{x,y} : bool, 'col', or 'row' optional
If true, the facets will share y axes across columns and/or x axes
across rows.
height : scalar, optional
Height (in inches) of each facet. See also: ``aspect``.
aspect : scalar, optional
Aspect ratio of each facet, so that ``aspect * height`` gives the width
of each facet in inches.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
{row,col,hue}_order : lists, optional
Order for the levels of the faceting variables. By default, this
will be the order that the levels appear in ``data`` or, if the
variables are pandas categoricals, the category order.
hue_kws : dictionary of param -> list of values mapping
Other keyword arguments to insert into the plotting call to let
other plot attributes vary across levels of the hue variable (e.g.
the markers in a scatterplot).
legend_out : bool, optional
If ``True``, the figure size will be extended, and the legend will be
drawn outside the plot on the center right.
despine : boolean, optional
Remove the top and right spines from the plots.
margin_titles : bool, optional
If ``True``, the titles for the row variable are drawn to the right of
the last column. This option is experimental and may not work in all
cases.
{x, y}lim: tuples, optional
Limits for each of the axes on each facet (only relevant when
share{x, y} is True.
subplot_kws : dict, optional
Dictionary of keyword arguments passed to matplotlib subplot(s)
methods.
gridspec_kws : dict, optional
Dictionary of keyword arguments passed to matplotlib's ``gridspec``
module (via ``plt.subplots``). Requires matplotlib >= 1.4 and is
ignored if ``col_wrap`` is not ``None``.
See Also
--------
PairGrid : Subplot grid for plotting pairwise relationships.
relplot : Combine a relational plot and a :class:`FacetGrid`.
catplot : Combine a categorical plot and a :class:`FacetGrid`.
lmplot : Combine a regression plot and a :class:`FacetGrid`.
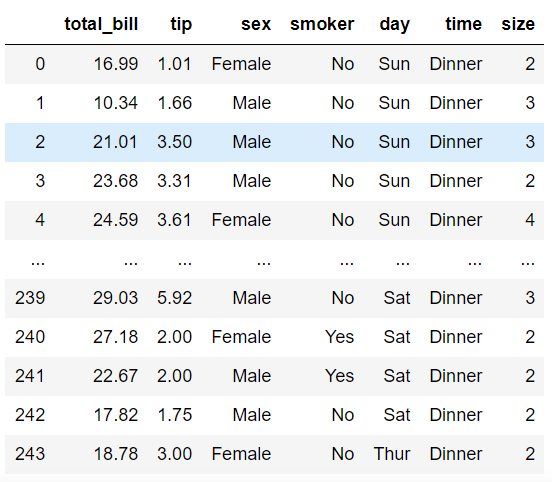
#导入数据
tips = sns.load_dataset('tips', data_home='./seaborn-data')
tips
#设置风格
sns.set_style('white')
#col设置网格的分类列,row设置分类行
ax = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', row='sex')
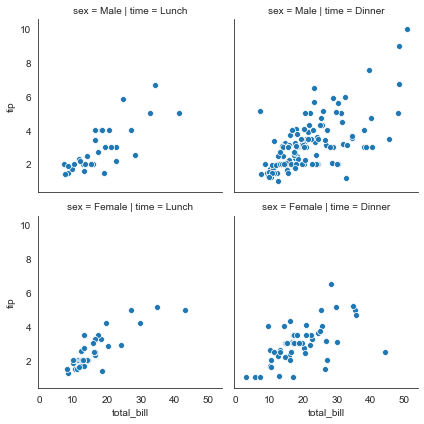
散点图
ax = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', row='sex')
#利用map方法在网格内绘制散点图sns.scatterplot = plt.scatter,sns的散点图更美观
ax = ax.map(sns.scatterplot, 'total_bill', 'tip')
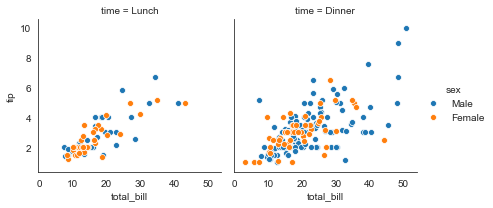
#hue设置分类绘制
ax = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', hue='sex')
ax = ax.map(sns.scatterplot, 'total_bill', 'tip')
#添加图例
ax = ax.add_legend()
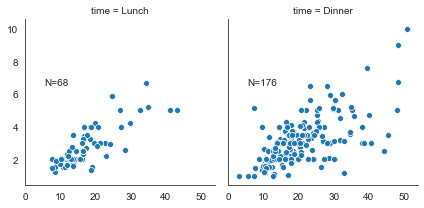
#定义一个文本函数
def annotate(data, **kws):
n = len(data)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.text(.1, .6, f"N={n}", transform=ax.transAxes)
ax = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time')
ax = ax.map(sns.scatterplot, 'total_bill', 'tip')
#添加文本标签
ax = ax.map_dataframe(annotate)
#其它参数
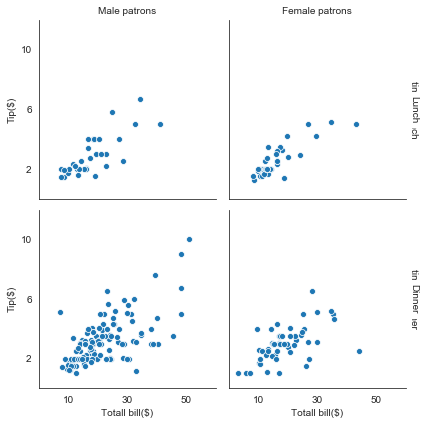
#margin_titles设置边缘标头
ax = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='sex', row='time', margin_titles=True)
ax.map(sns.scatterplot, 'total_bill', 'tip')
#set_axis_labels设置x轴和y轴标签
ax.set_axis_labels('Totall bill($)', 'Tip($)')
#set_titles设置标头(会出现重叠现象)
ax.set_titles(col_template='{col_name} patrons', row_template='{row_name}')
#坐标上下限和刻度设置
ax.set(xlim=(0,60), ylim=(0, 12), xticks=[10, 30, 50], yticks=[2, 6, 10])
#存储图片
ax.savefig('facet_plot.png')
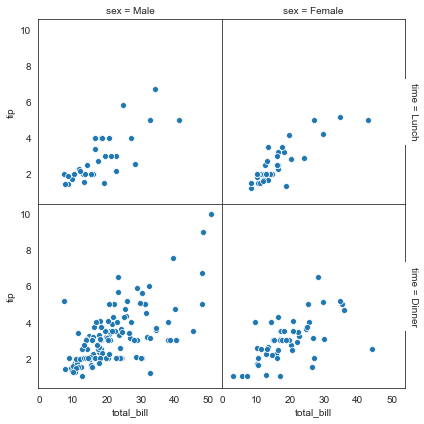
#despine设置是否显示上和右边框线
ax = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='sex', row='time', margin_titles=True, despine=False)
ax.map(sns.scatterplot, 'total_bill', 'tip')
#设置图形间隔
ax.fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0, hspace=0)
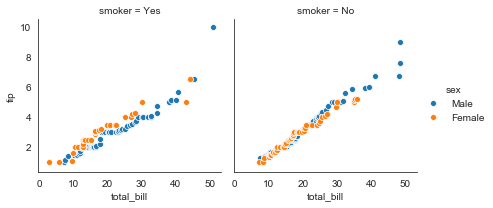
#QQ图:检验样本数据概率分布(例如正态分布)的方法,直观的表示观测值与预测值之间的差异,或两个数之间的差异
from scipy import stats
#定义QQ图函数
def qqplot(x, y, **kwargs):
_, xr = stats.probplot(x, fit=False) #拟合概率图
_, yr = stats.probplot(y, fit=False)
sns.scatterplot(xr, yr, **kwargs) #**kwargs表示关键字参数,可以用字典形式传入参数
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='smoker', hue='sex')
g = g.map(qqplot, 'total_bill', 'tip')
g = g.add_legend()
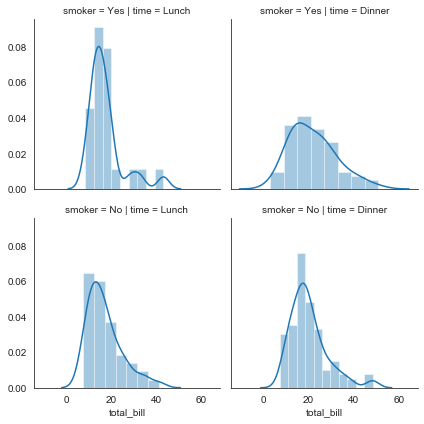
直方图
#直方图
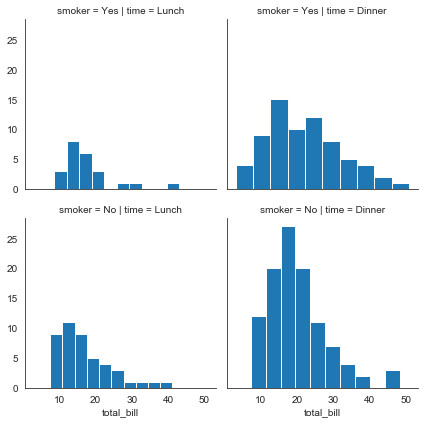
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', row='smoker')
g = g.map(plt.hist, 'total_bill')
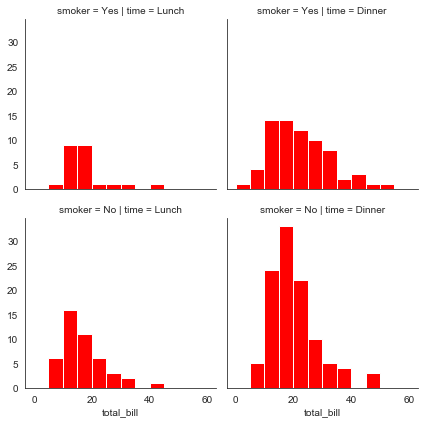
#bins设置直方图个数,color设置颜色
bins = np.arange(0, 65, 5)
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', row='smoker')
g = g.map(plt.hist, 'total_bill', bins=bins, color='r')
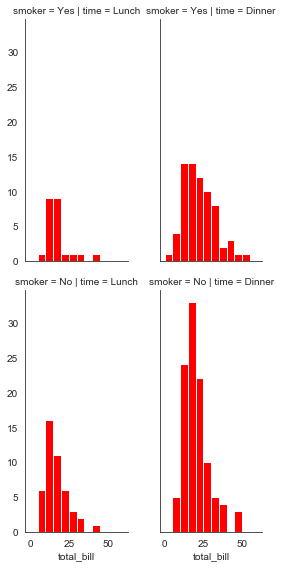
#height设置高度,aspece设宽高比
bins = np.arange(0, 65, 5)
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', row='smoker', height=4, aspect=.5)
g = g.map(plt.hist, 'total_bill', bins=bins, color='r')
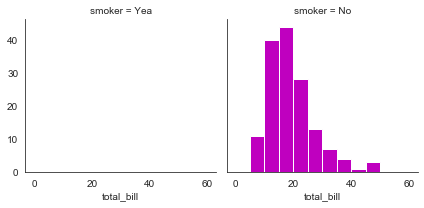
#col_order设置显示顺序
bins = np.arange(0, 65, 5)
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='smoker', col_order=['Yea', 'No'])
g = g.map(plt.hist, 'total_bill', bins=bins, color='m')
直方密度图
#直方密度图
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', row='smoker')
g = g.map(sns.distplot, 'total_bill')
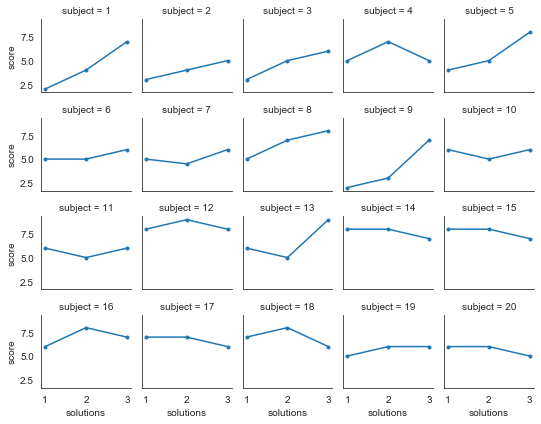
折线图
#导入数据
att = sns.load_dataset('attention', data_home='./seaborn-data')
#col_wrap设置列数,height设置高度,marker设置标记点样式
g = sns.FacetGrid(att, col='subject', col_wrap=5, height=1.5)
g = g.map(plt.plot, 'solutions', 'score', marker='.')
Seaborn结构化图形绘制(FacetGrid)的更多相关文章
- d3.js 之SVG:矢量化图形绘制
SVG Scalable Vector Graphics 是一个成熟的W3C标准,被设计用来在web和移动平台 上展示可交互的图形.和HTML类似,SVG也支持CSS和JavaScript.尽管可以使 ...
- seaborn线性关系数据可视化:时间线图|热图|结构化图表可视化
一.线性关系数据可视化lmplot( ) 表示对所统计的数据做散点图,并拟合一个一元线性回归关系. lmplot(x, y, data, hue=None, col=None, row=None, p ...
- CMM模型,结构化开发方法和面向对象开发方法的比较,UML(统一建模语言),jackson开发方法
CMM模型 一.CMM简介 CMM,英文全称为Capability Maturity Model for Software,即:软件成熟度模型. CMM的核心是把软件开发视为一个过程.它是对于软件在定 ...
- 【Windows编程】系列第五篇:GDI图形绘制
上两篇我们学习了文本字符输出以及Unicode编写程序,知道如何用常见Win32输出文本字符串,这一篇我们来学习Windows编程中另一个非常重要的部分GDI图形绘图.Windows的GDI函数包含数 ...
- 图形绘制 Canvas Paint Path 详解
图形绘制简介 Android中使用图形处理引擎,2D部分是android SDK内部自己提供,3D部分是用Open GL ES 1.0.大部分2D使用的api都在android.grap ...
- XHTML 结构化:使用 XHTML 重构网站
http://www.w3school.com.cn/xhtml/xhtml_structural_01.asp 我们曾经为本节撰写的标题是:"XHTML : 简单的规则,容易的方针.&qu ...
- 结构化您的Python工程
我们对于"结构化"的定义是您关注于怎样使您的项目最好地满足它的对象性,我们 需要去考虑如何更好地利用Python的特性来创造简洁.高效的代码.在实践层面, "结构化&qu ...
- (转)GPU图形绘制管线
摘抄“GPU Programming And Cg Language Primer 1rd Edition” 中文名“GPU编程与CG语言之阳春白雪下里巴人”第二章. 图形绘制管线描述GPU渲染流程, ...
- 妙味,结构化模块化 整站开发my100du
********************************************************************* 重要:重新审视的相关知识 /* 妙味官网:www.miaov ...
- Python中的结构化数据分析利器-Pandas简介
Pandas是python的一个数据分析包,最初由AQR Capital Management于2008年4月开发,并于2009年底开源出来,目前由专注于Python数据包开发的PyData开发tea ...
随机推荐
- Jmeter 之常数吞吐量作用
一 添加方法: 线程组右键->添加->定时器-> 常数吞吐量定时器 二 作用: 常数吞吐量定时器的作用: 设置最大的吞吐量不超过设置的值 注意:如果线程能发送的请求远远低于设置的 ...
- centos 7与8修改主机名的各种方法
hostname 查看当前系统主机名,知道当前主机名为localhost 当然在centos7特地添加了hostnamectl命令查看,修改主机名 使用hostnamectl set-hostname ...
- 【MongoDB详细步骤】(内附源码)
第01章-MongoDB 1.安装和启动(docker方式) 1.1.拉取镜像 docker pull mongo:4.4.8 1.2.创建和启动容器 docker run -d --restart= ...
- golang开发_goroutine在项目中的使用姿势
很多初级的Gopher在学习了goroutine之后,在项目中其实使用率不高,尤其一些跨语言过来的人,对并发编程理解不深入,可能很多人只知道go func(),或者掌控不够,谨慎一些,尽量少使用或者不 ...
- Java面向对象(下)--static/final/代码块/抽象/接口/内部类
目录 1 关键字:static 2 理解main方法的语法 3 类的成员之四:代码块 4关键字:final 5 抽象类与抽象方法 6 接口(interface) 7 类的成员之五:内部类 static ...
- k8s标签的增删改查和选择器
在 Kubernetes(K8s)中,标签(Label)是与资源对象相关联的键值对,用于实现多维度的资源分组管理功能.下面是关于 Kubernetes 标签的增删改查操作的简要说明: 查询标签 (查) ...
- XXL-JOB初探
参考:欢迎点击原文:https://www.xuxueli.com/xxl-job/(官方) https://blog.csdn.net/f2315895270/article/details/104 ...
- RAG 范式、技术和趋势
这里分享同济大学 Haofen Wang的关于检索增强生成的报告:<Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Paradigms, Technologies, ...
- 爬虫实战:从HTTP请求获取数据解析社区
在过去的实践中,我们通常通过爬取HTML网页来解析并提取所需数据,然而这只是一种方法.另一种更为直接的方式是通过发送HTTP请求来获取数据.考虑到大多数常见服务商的数据都是通过HTTP接口封装的,因此 ...
- npm ERR! code ENOENT npm ERR! syscall open npm ERR! path C:\Users\shuzi\Desktop\保密文件项目\test-ui/package.json npm ERR! errno -4058
打开一个新的项目,因为当前项目文件夹下没有npm,"dev": "npm run start:dev",所以所以没有展示对应的运行图,如下图: 打开一个新的前端 ...
