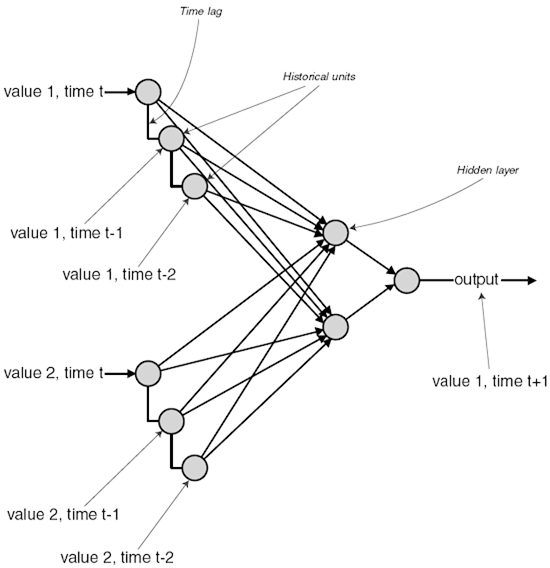
Elman network with additional notes
// Author: John McCullock
// Date: 10-15-05
// Description: Elman Network Example 1.
//http://www.mnemstudio.org/neural-networks-elman.htm
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib> using namespace std; const int maxTests = 10000;
const int maxSamples = 4; const int inputNeurons = 6;
const int hiddenNeurons = 3;
const int outputNeurons = 6;
const int contextNeurons = 3; const double learnRate = 0.2; //Rho.
const int trainingReps = 2000; //beVector is the symbol used to start or end a sequence.
double beVector[inputNeurons] = {1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0}; // 0 1 2 3 4 5
double sampleInput[3][inputNeurons] = {{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0},
{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0},
{0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0}}; //Input to Hidden weights (with biases).
double wih[inputNeurons + 1][hiddenNeurons]; //Context to Hidden weights (with biases).
double wch[contextNeurons + 1][hiddenNeurons]; //Hidden to Output weights (with biases).
double who[hiddenNeurons + 1][outputNeurons]; //Hidden to Context weights (no biases).
double whc[outputNeurons + 1][contextNeurons]; //Activations.
double inputs[inputNeurons];
double hidden[hiddenNeurons];
double target[outputNeurons];
double actual[outputNeurons];
double context[contextNeurons]; //Unit errors.
double erro[outputNeurons];
double errh[hiddenNeurons]; void ElmanNetwork();
void testNetwork();
void feedForward();
void backPropagate();
void assignRandomWeights();
int getRandomNumber();
double sigmoid(double val);
double sigmoidDerivative(double val); int main(){ cout << fixed << setprecision(3) << endl; //Format all the output.
srand((unsigned)time(0)); //Seed random number generator with system time.
ElmanNetwork();
testNetwork(); return 0;
} void ElmanNetwork(){
double err;
int sample = 0;
int iterations = 0;
bool stopLoop = false; assignRandomWeights(); //Train the network.
do { if(sample == 0){
for(int i = 0; i <= (inputNeurons - 1); i++){
inputs[i] = beVector[i];
} // i
} else {
for(int i = 0; i <= (inputNeurons - 1); i++){
inputs[i] = sampleInput[sample - 1][i];
} // i
} //After the samples are entered into the input units, the sample are
//then offset by one and entered into target-output units for
//later comparison.
if(sample == maxSamples - 1){
for(int i = 0; i <= (inputNeurons - 1); i++){
target[i] = beVector[i];
} // i
} else {
for(int i = 0; i <= (inputNeurons - 1); i++){
target[i] = sampleInput[sample][i];
} // i
} feedForward(); err = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i <= (outputNeurons - 1); i++){
err += sqrt(target[i] - actual[i]);
} // i
err = 0.5 * err; if(iterations > trainingReps){
stopLoop = true;
}
iterations += 1; backPropagate(); sample += 1;
if(sample == maxSamples){
sample = 0;
}
} while(stopLoop == false); cout << "Iterations = " << iterations << endl;
} void testNetwork(){
int index;
int randomNumber, predicted;
bool stopTest, stopSample, successful; //Test the network with random input patterns.
stopTest = false;
for(int test = 0; test <= maxTests; test++){ //Enter Beginning string.
inputs[0] = 1.0;
inputs[1] = 0.0;
inputs[2] = 0.0;
inputs[3] = 0.0;
inputs[4] = 0.0;
inputs[5] = 0.0;
cout << "(0) "; feedForward(); stopSample = false;
successful = false;
index = 0; //note:If failed then index start from 0 again
/*However, the nature of this kind of recurrent network is easier to understand (at least to me),
imply by referring to the unit's position in serial order (i.e.; Y0, Y1, Y2, Y3, ...).
So for the purpose of this illustration, I'll just use strings of numbers like: 0, 3, 5, 2, 0,
where 0 refers to Y0, 3 refers to Y3, 5 refers to Y5, etc. Each string begins and ends with a terminal symbol; I'll use 0 for this example.*/
randomNumber = 0;
predicted = 0; do { for(int i = 0; i <= 5; i++){
cout << actual[i] << " ";
if(actual[i] >= 0.3){
//The output unit with the highest value (usually over 3.0)
//is the network's predicted unit that it expects to appear
//in the next input vector.
//For example, if the 3rd output unit has the highest value,
//the network expects the 3rd unit in the next input to
//be 1.0
//If the actual value isn't what it expected, the random
//sequence has failed, and a new test sequence begins.
predicted = i;
}
} // i
cout << "\n"; randomNumber = getRandomNumber(); //Enter a random letter. index += 1; //Increment to the next position.
if(index == 5){
stopSample = true;
} else {
cout << "(" << randomNumber << ") ";
} for( i = 0; i <= 5; i++){
if(i == randomNumber){//note:i==randomNumber&&i == predicted then succeed
inputs[i] = 1.0;
if(i == predicted){
successful = true;
//for(int k=0;k<5;k++)//have a look;
// cout<<"\nTang :the sequence is:"<<inputs[k]<<'\t';
//cout<<endl;
} else {
//Failure. Stop this sample and try a new sample.
stopSample = true;
}
} else {
inputs[i] = 0.0;
}
} // i feedForward(); } while(stopSample == false); //Enter another letter into this sample sequence. if((index > 4) && (successful == true)){ //note: stop the iteration until success a sequence matching success at least 5 times.
//If the random sequence happens to be in the correct order,
//the network reports success.
cout << "Success." << endl;
cout << "Completed " << test << " tests." << endl;
stopTest = true;
break;
} else {
cout << "Failed." << endl;
if(test > maxTests){
stopTest = true;
cout << "Completed " << test << " tests with no success." << endl;
break;
}
}
} // Test
} void feedForward(){
double sum; //Calculate input and context connections to hidden layer.
for(int hid = 0; hid <= (hiddenNeurons - 1); hid++){
sum = 0.0;
//from input to hidden...
for(int inp = 0; inp <= (inputNeurons - 1); inp++){
sum += inputs[inp] * wih[inp][hid];
} // inp
//from context to hidden...
for(int con = 0; con <= (contextNeurons - 1); con++){
sum += context[con] * wch[con][hid];
} // con
//Add in bias.
sum += wih[inputNeurons][hid];
sum += wch[contextNeurons][hid];
hidden[hid] = sigmoid(sum);
} // hid //Calculate the hidden to output layer.
for(int out = 0; out <= (outputNeurons - 1); out++){
sum = 0.0;
for(int hid = 0; hid <= (hiddenNeurons - 1); hid++){
sum += hidden[hid] * who[hid][out];
} // hid //Add in bias.
sum += who[hiddenNeurons][out];
actual[out] = sigmoid(sum);
} // out //Copy outputs of the hidden to context layer.
for(int con = 0; con <= (contextNeurons - 1); con++){
context[con] = hidden[con];
} // con } void backPropagate(){ //Calculate the output layer error (step 3 for output cell).
for(int out = 0; out <= (outputNeurons - 1); out++){
erro[out] = (target[out] - actual[out]) * sigmoidDerivative(actual[out]);
} // out //Calculate the hidden layer error (step 3 for hidden cell).
for(int hid = 0; hid <= (hiddenNeurons - 1); hid++){
errh[hid] = 0.0;
for(int out = 0; out <= (outputNeurons - 1); out++){
errh[hid] += erro[out] * who[hid][out];
} // out
errh[hid] *= sigmoidDerivative(hidden[hid]);
} // hid //Update the weights for the output layer (step 4).
for( out = 0; out <= (outputNeurons - 1); out++){
for(int hid = 0; hid <= (hiddenNeurons - 1); hid++){
who[hid][out] += (learnRate * erro[out] * hidden[hid]);
} // hid
//Update the bias.
who[hiddenNeurons][out] += (learnRate * erro[out]);
} // out //Update the weights for the hidden layer (step 4).
for( hid = 0; hid <= (hiddenNeurons - 1); hid++){
for(int inp = 0; inp <= (inputNeurons - 1); inp++){
wih[inp][hid] += (learnRate * errh[hid] * inputs[inp]);
} // inp
//Update the bias.
wih[inputNeurons][hid] += (learnRate * errh[hid]);
} // hid } void assignRandomWeights(){ for(int inp = 0; inp <= inputNeurons; inp++){
for(int hid = 0; hid <= (hiddenNeurons - 1); hid++){
//Assign a random weight value between -0.5 and 0.5
wih[inp][hid] = -0.5 + double(rand()/(RAND_MAX + 1.0));
} // hid
} // inp for(int con = 0; con <= contextNeurons; con++){
for(int hid = 0; hid <= (hiddenNeurons - 1); hid++){
//Assign a random weight value between -0.5 and 0.5
wch[con][hid] = -0.5 + double(rand()/(RAND_MAX + 1.0));
} // hid
} // con for(int hid = 0; hid <= hiddenNeurons; hid++){
for(int out = 0; out <= (outputNeurons - 1); out++){
//Assign a random weight value between -0.5 and 0.5
who[hid][out] = -0.5 + double(rand()/(RAND_MAX + 1.0));
} // out
} // hid for(int out = 0; out <= outputNeurons; out++){
for(int con = 0; con <= (contextNeurons - 1); con++){
//These are all fixed weights set to 0.5
whc[out][con] = 0.5;
} // con
} // out } int getRandomNumber(){
//Generate random value between 0 and 6.
return int(6*rand()/(RAND_MAX + 1.0));
} double sigmoid(double val){
return (1.0 / (1.0 + exp(-val)));
} double sigmoidDerivative(double val){
return (val * (1.0 - val));
}
Elman network with additional notes的更多相关文章
- 论文笔记之:Progressive Neural Network Google DeepMind
Progressive Neural Network Google DeepMind 摘要:学习去解决任务的复杂序列 --- 结合 transfer (迁移),并且避免 catastrophic f ...
- 详解循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network)
本文结构: 模型 训练算法 基于 RNN 的语言模型例子 代码实现 1. 模型 和全连接网络的区别 更细致到向量级的连接图 为什么循环神经网络可以往前看任意多个输入值 循环神经网络种类繁多,今天只看最 ...
- Heterogeneous Self-Organizing Network for Access and Backhaul
This application discloses methods for creating self-organizing networks implemented on heterogeneou ...
- Real-time storage area network
A cluster of computing systems is provided with guaranteed real-time access to data storage in a sto ...
- Gitlab的搭建
从网上看了一大堆的资料,最终选定按照github上的文档来搭建,虽然本人英文不好,就这样看着 这个博客弯曲完全是拷贝过来的,只为了做个笔记 原文地址:https://github.com/gitlab ...
- CentOS6.5Minimal安装Gitlab7.5
文章出处:http://www.restran.net/2015/04/09/gilab-centos-installation-note/ 在 CentOS 6.5 Minimal 系统环境下,用源 ...
- Windows Server 2008 HPC 版本介绍以及的Pack
最近接触了下 这个比较少见的 Windows Server版本 Windows Server 2008 HPC 微软官方的介绍 http://www.microsoft.com/china/hpc/ ...
- 【Caffe 测试】Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe
Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe We will assume that you have Caffe successfully compiled. If not, ...
- rsync Backups for Windows
Transfer your Windows Backups to an rsync server over SSH rsync.net provides cloud storage for offsi ...
随机推荐
- ajax的发展
ajax(Asynchronous Javascript and XML)异步javascrip和XMl. ajax只是一种web交互方法.在客户端(浏览器)和服务区段之间传输少量的信息.从而为用户提 ...
- react 也就这么回事 02 —— JSX 插值表达式、条件渲染以及列表渲染
我们已经学会了 React 创建元素和渲染元素 ReactDOM.render(<div>Hello React!</div>, document.getElementById ...
- windows mysql数据存储路径更改
背景:之前服务器磁盘很小,随着数据量的不断增加,磁盘不够,所以新申请了更大的磁盘,然后需要将旧路径下的数据迁移到新磁盘上. 1.任务管理器-打开服务,找到mysql的启动项,停止服务,属性查看可执行文 ...
- 【axios三部曲】一、使用axios
axios作为一个基于promise的网络请求库,它同时支持浏览器和node环境,是我们开发中常用的一个库 它的一些特性: 从浏览器发出XMLHttpRequests 从node.js发出http ...
- 什么,有狗快跑!慢着,这次手把手教你怎么过安全狗!(sql注入篇)
前言 在记忆里上次绕安全狗还是在上次,开开心心把自己之前绕过狗的payload拿出来,发现全部被拦截了,事情一下子就严肃起来了,这就开整. 环境 本次环境如下sqli-lab的sql注入靶场 网站安全 ...
- 使用jvisualvm监控k8s内java项目
资源文件yaml配置 -javaagent:/usr/skywalking/agent/skywalking-agent.jar -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dja ...
- 【C# .Net GC】条件自动垃圾回收 HandleCollector类
条件自动回收 达到指定条件后自动执行GC回收垃圾. GC中的方法AddMemoryPressure和RemoveMemoryPressure 本机资源有时会消耗大量内存,但用于包装它的托管对象只占用很 ...
- 60天shell脚本计划-6/12-渐入佳境
--作者:飞翔的小胖猪 --创建时间:2021年2月21日 --修改时间:2021年2月25日 说明 每日上传更新一个shell脚本,周期为60天.如有需求的读者可根据自己实际情况选用合适的脚本,也可 ...
- html实现随机验证码
代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <!-- head --> <head> <title>图片登录验证</titl ...
- Spark分区数、task数目、core数目、worker节点数目、executor数目梳理
Spark分区数.task数目.core数目.worker节点数目.executor数目梳理 spark隐式创建由操作组成的逻辑上的有向无环图.驱动器执行时,它会把这个逻辑图转换为物理执行计划,然后将 ...