JAVA自学笔记24
JAVA自学笔记24
1、能使用同步代码块就使用同步代码块,除非锁对象是this,就可以考虑使用同步方法。静态方法的锁是类的字节码对象。
2、JDK5新特性
1)接口Lock
void Lock()//获取锁
void unlock()//释放锁
ReentrantLock:实现类
public class SellTicketDemo{
public stsatic void main(String args[]){
Thread t1=new Thread(st,"窗口1");
Thread t2=new Thread(st,"窗口2");
Thread t3=new Thread(st,"窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
publlic class SellTicket implements Runnable{
private int tickets=100;
//定义锁对象
private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
public void run(){
//加锁
try{
lock.lock();
if(tickets>0){
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在卖"+(tickets--)+"张票")
})
finally{//解锁
lock.unlock();}//避免程序出现错误而无法解锁
}
}2)死锁问题
①同步弊端:效率低,容易产生死锁问题。如果出现了同步嵌套,就容易出现死锁问题
②是指两个或者两个以上的线程在执行过程中,因争夺资源产生的一种相互等待的现象。
public class MyLock{
//创建两把锁对象
public static final Object ObjA=new Object();
public static final Object ObjB=new Object();
}
public class DieLock extends Thread{
private boolean flag;
public DieLock(boolean flag){
this.flag=flag;
public void run(){
if(flag){
Synchronized(MyLock.objA){
System.out.println("if objA");
Synchronized(MyLock.objB){
System.out.println("if objB");
}
}
}else{
synchronized(MyLock.objB){
System.out.println("else objB");
Synchronized(MyLock.objA){
System.out.println("else objA");
}
}
}
}
}
public class DieDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
DieLock dl1=new DieLock(true);
DieLock dl2=new DieLock(false);
dl1.start();
dl2.start();
}
}3)线程间的通信
不同种类的线程间针对同一个资源的操作,设置线程(生产者),获取线程(消费者)
//学生类(资源类)
public class Student{
String name;
int age;
}
//设置线程
public class SetThread implements Runnable{
private Student s;
private int x=0;
public SetThread(Student s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
synchronized(s){while(true){
if(x%2==0){
s.name="cc";
s.age=18;
}else{
s.name="dd";
s.age=13;
}
x++;
}
}
}}
//消费线程
public class GetThread implements Runnable{
implements Runnable{
private Student s;
public SetThread(Student s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
synchronized(s){while(true){
System,out,println(s.name);
}}
}
}
//测试类
public class StudentDemo{
//创建资源
Student s=new Student{};
//设置和获取的类
pubic static void main {String args[]){
SetThread st=new SetThread(s);
GetThread gt=new GetThread(s);
//线程类
Thread t1=new Thread(st);
Thread t1=new Thread(gt);
//启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}4)等待唤醒机制
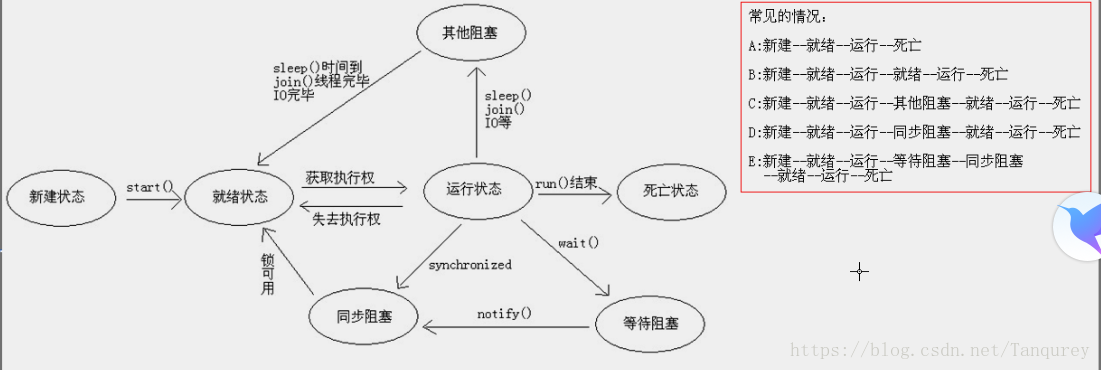
图解:
void wait();
在其他线程调用此对象的notify()或notifyAll()方法前,导致该线程等待
void notify()
唤醒在此对象监视器等待的单个线程
void notifyAll()
唤醒在此对象监视器等待的所有线程
//学生类(资源类)
public class Student{
String name;
int age;
boolean flag;
}
//设置线程
public class SetThread implements Runnable{
private Student s;
private int x=0;
public SetThread(Student s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
while(true){synchronized(s){
if(s.flag){
s.wait();}
if(x%2==0){
s.name="cc";
s.age=18;
}else{
s.name="dd";
s.age=13;
}
x++;
s.flag=true;
s.notify();
}
}
}}
//消费线程
public class GetThread implements Runnable{
implements Runnable{
private Student s;
public SetThread(Student s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
synchronized(s){
if(!s.flag){
s.wait();
}
while(true){
System,out,println(s.name);
s.flag=false;
s.notify();
}}
}
}
//测试类
public class StudentDemo{
//创建资源
Student s=new Student{};
//设置和获取的类
pubic static void main {String args[]){
SetThread st=new SetThread(s);
GetThread gt=new GetThread(s);
//线程类
Thread t1=new Thread(st);
Thread t1=new Thread(gt);
//启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}线程的状态转换图:
3、线程组
1)java使用ThreadGroup来表示线程组,它可以对一批线程进行分类管理,java允许程序直接对线程组进行控制
默认情况下,所有的线程都属于主线程组
public final ThreadGroup getThreadGroup()
也可以给线程设置分组
Thread(ThreadGroup group,Runnable target,String name)
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int x=0;x<0;x++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+x);
}
}
public class void ThreadGroupDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
MyRunnable my=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(my,"cc");
Thread t2=new Thread(my,"dd");
ThreadGruop tg1=t1.getThreadGruop();
ThreadGruop tg2=t2.getThreadGruop();
//获取线程组名
String name1=tg1.getName();//main
String name2=tg2.getName();//main
//修改线程所在组
method1();
}
}
private static void method1(){
ThreadGroup tg=new ThreadGroup("这是新的组");
MyRunnable my=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(tg,my,"cc");
Thread t1=new Thread(tg,my,"dd");
}//生产者消费者案例优化
//学生类(资源类)
public class Student{
private private String name;
int age;
private boolean flag;
public synchronized void set(String name,int age){
if(this.flag){
this.wait();
}
}
//设置数据
this.name=name;
this.age;
//修改标记
this.flag=true;
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void get(){
if(!this.flag){
this.wait();
}
}
System.out,println(this.name);
this.flag=false;
this.notify();
}
//设置线程
public class SetThread implements Runnable{
private Student s;
private int x=0;
public SetThread(Student s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
if(x%2==0){
s.set("cc",23);
}else{
s.set("dd",23);
}
x++;
}
}
}}
//消费线程
public class GetThread implements Runnable{
implements Runnable{
private Student s;
public SetThread(Student s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
synchronized(s){
if(!s.flag){
s.wait();
}
while(true){
s.get();
}}
}
}
//测试类
public class StudentDemo{
//创建资源
Student s=new Student{};
//设置和获取的类
pubic static void main {String args[]){
SetThread st=new SetThread(s);
GetThread gt=new GetThread(s);
//线程类
Thread t1=new Thread(st);
Thread t1=new Thread(gt);
//启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}4、线程池
1)程序启动一个新线程的成本是比较高的,因为它涉及到要与操作系统进行交互。而使用线程池可以很好地提高性能,尤其是当程序中要创建大量生存期很短的线程时,更应该考虑使用线程池。线程池里的每一个线程代码结束后,并不会死亡,而是再次回到线程池中成为空闲状态,等待下一个对象来使用。
在JDK5之前,必须手动实现自己的线程池,从JDK5开始,Java支持内置线程池。
JDK5新增了一个Exexutors工厂类来产生线程池,有如下几个方法:
public static ExecutorsService newCacheThreadPool()
开启具有缓存功能的线程池
public static ExecutorsService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
创建指定个线程的线程池
public static ExecutorsService newSingleThreadExecutor()
创建1个线程池
这些方法的返回值是ExecutorsService对象。该对象表示一个线程池,可以执行Runnable对象或者Callable对象代表的线程。
public class ExecutorsDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
//创建一个线程池对象,控制要创建2个线程对象
ExecutorService pool=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//可以执行Runnable对象或者Callable对象代表的线程
pool.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool.submit(new MyRunnable());
//结束线程池
pool.shutdown();
}
}
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int x=0;x<100;x++){
System.out.println(Thread.currenThread().getName()+":"+x);
}
}
}
}
}//多线程方式3的实现方式
可以有返回值,可以做出异常,但代码过于复杂一般不用
接口Callable
public class CallableDemo{
ExecutorService pool=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
pool.submit(new MyCallable());
pool.submit(new MyCallable());
}
public class MyCallable implements Callable{
for(int x=0;x<100;x++){
System.out.println(Thread.currenThread().getName()+":"+x);}
public Object call() throws Exception{
return null;
}
}5、匿名内部类实现多线程
new Thread(){代码…}.start();
New Thread (new Runnable(){代码…}}.start();
//
public class ThreadDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
//继承Thread实现多线程
new Thread(){
//重写run()方法
public void run(){
for(int x=0;x<100;x++){
System.out.println(Thread.currenThread().getName()+":"+x);
}
}
}.start();
//实现Runnable接口来实现多线程
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
for(int x=0;x<100;x++){
System.out.println(Thread.currenThread().getName()+":"+x);
}
}
}).start();
}
//走子类对象
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
for(int x=0;x<100;x++){
System.out.println("Hello"+":"+x);
}
}
}){
public void run(){
for(int x=0;x<100;x++){
System.out.println("World"+":"+x);
}
}
}.start();
}
}6、定时器
1)定时器是一个应用十分广泛的线程工具,可用于调度多个定时任务以后线程的方式执行,在java中,可以通过Timer和TimerTask类来实现定义调度的功能
2)Timer
public Timer()
//创建一个新的计时器
public void schedule(TimerTask task,long delay)
安排在指定延迟后执行指定的任务
public void schedule(TimerTask task,long period)
安排指定的任务从指定的延迟后开始进行重复的固定延迟执行
3)TimerTask
public abstract void run()
此计时器任务要执行的操作
public boolean cancel()
//终止此计时器,丢弃所有当前已安排的任务
public class TimerDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
//创建定时器对象
Timer t=new Timer();
t.schedule(new MyTask(t),3000);
}
}
class MyTask extends TimerTask{
private Timer t;
public MyTask(){}
public MyTask(Timer t){
this.t=t;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("爆炸");
t.cancel();
}
}//定时删除指定的带内容目录
class DeleteFolder extends TimerTask{
public void run(){
File file=new File("demo");
deleteFolder(srcFolder);
}
public void deleteFolder(File srcFolder){
File[] fileArray=srcFolder.listFiles();
if(fileArray!=null){
for(File file:fileArray){
if(file.isDirectory()){
deleteFolder(file);
}else{
file.delete();
}
}
srcFolder.delete();
}
}
}
public class TimerTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
Timer t=new Timer();
String s="2018-8-23 15:52:24";
SimpleDateFormat sdf =new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d=sdf.parse(s);
t.schdule(new DeleteFolder(),d);
}
}7、多线程常见面试题回顾
1)多线程有几种实现方案,分别是哪几种。
两(三)种。继承Thread类,实现Runnable接口,(实现Callable接口)
2)同步有几种方式,分别是什么?
同步代码块
同步方法
3)
8、面向对象思想设计原则及常见设计模式
1)面向对象思想设计原则

2)设计模式
设计模式是一套被反复使用,多数人知晓的,经过分类编目的代码设计经验总结。使用设计模式是为了可重用代码,让代码更容易被他人理解,保证代码的可靠性。
JAVA自学笔记24的更多相关文章
- JAVA自学笔记14
JAVA自学笔记14 1.正则表达式 1)是指一个用来描述或者匹配一系列符合某个句法规则的字符串的单个字符串.其实就是一种规则.有自己的特殊应用 2)组成规则: 规则字符在java.util.rege ...
- JAVA自学笔记18
JAVA自学笔记18 1.Map接口: 1)功能: 2) Map<String,String>m=new HashMap<String,String>(); //添加元素,元素 ...
- JAVA自学笔记09
JAVA自学笔记09 1.子类的方法会把父类的同名方法覆盖(重写) 2.final: 1)可修饰类.方法.变量 2)修饰类时:此时该类变为最终类,它将无法成为父类而被继承 3)修饰方法时:该方法将无法 ...
- JAVA自学笔记05
JAVA自学笔记05 1.方法 1)方法就是完成特定功能的代码块,类似C语言中的函数. 2)格式: 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型 参数名1,参数类型 参数名2,-){ 函数体; return ...
- JAVA自学笔记06
JAVA自学笔记06 1.二维数组 1)格式: ①数据类型[][]数组名 = new 数据类型[m][n]; 或 数据类型[]数组名[]=new 数据类型[m][n]; m表示这个二维数组有多少个一维 ...
- JAVA自学笔记04
JAVA自学笔记04 1.switch语句 1)格式:switch(表达式){ case 值1: 语句体1; break; case 值2: 语句体2; break; - default: 语句体n+ ...
- JAVA自学笔记07
JAVA自学笔记07 1.构造方法 1) 例如:Student s = new Student();//构造方法 System.out.println(s);// Student@e5bbd6 2)功 ...
- JAVA自学笔记10
JAVA自学笔记10 1.形式参数与返回值 1)类名作为形式参数(基本类型.引用类型) 作形参必须是类的对象 2)抽象类名作形参 需要该抽象类的子类对象,通过多态实现 3)接口名为形参 需要的是该接口 ...
- JAVA自学笔记13
JAVA自学笔记13 1.StringBuffer类 1)线程安全的可变字符序列 线程安全(即同步) 2)StringBuffer与String的区别:一个可变一个不可变 3)构造方法: ①publi ...
随机推荐
- delphi TreeView 从数据库添加节点的四种方法
方法一:delphi中递归算法构建treeView 过程:通过读取数据库中table1的数据,来构建一颗树.table1有两个字段:ID,preID,即当前结点标志和父结点标志.所以整个树的表示为父母 ...
- python之多线程 queue 实践 筛选有效url
0.目录 1.背景 某号码卡申请页面通过省份+城市切换归属地,每次返回10个号码. 通过 Fiddler 抓包确认 url 关键参数规律: provinceCode 两位数字 cityCode 三位数 ...
- ftp弱密码案例
- Codeforces 1111D Destroy the Colony 退背包 (看题解)
第一次知道这种背包还能退的.... 我们用dp[ i ]表示选取若干个物品重量到达 i 的方案数. 如果我们g[ i ]表示不用第 x 个物品的, 然后选若干其他的物品到达 i 的方案数. if(i ...
- 借助CSS Shapes实现元素滚动自动环绕iPhone X的刘海
CSS代码: .box { max-width: 414px; height: 480px; border: solid #000; margin: auto; overflow: auto; } . ...
- Codeforces Gym100783H 最短路 其他
原文链接https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/CF-Gym100783H.html 题目传送门 - CF-Gym100783H 题意 给定一个 $n$ 个节点 ...
- java生成Excel文件,下载
pom引入poi的maven依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId> ...
- Python traceback 模块,追踪错误
Python traceback 模块,追踪错误 import traceback try: your code except: traceback.print_exc()
- C. A Mist of Florescence ----- Codeforces Round #487 (Div. 2)
C. A Mist of Florescence time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- Nginx配置以及域名转发
工程中的nginx配置 #user nobody; worker_processes 24; error_log /home/xxx/opt/nginx/logs/error.log; pid /ho ...