lecture-9-hashmap
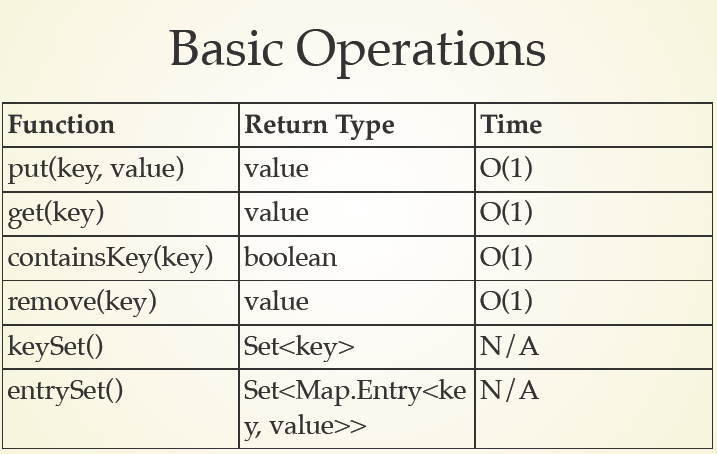
1、hashmap基本操作
2、hash function,equals函数,hashCode
3、练习题
1)Two Sum
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such
that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution,
and you may not use the same element twice.
1、Two pointers
2、If return the two numbers, then HashSet will be enough
3、HashMap is needed to keep the mapping from
number to index
方法一
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int targer) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i], i);//key:num[i], value:i
}
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(complement) && map.get(complement) != i) {
return new int[] {i, map.get(complement)};
}
}
return result;
}
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int targer) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i], i);//key:num[i], value:i
}
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(complement) && map.get(complement) != i) {
result[0] = i;
result[1] = map.get(complement);
break;
}
}
return result;
}
方法二
1 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
2 HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
4 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
5 int complement = target - nums[i];
6 if (map.containsKey(complement && map.get(complement) != i)) {
7 return new int[] {i, map.get(complement)};
8 }
9 map.put(nums[i], i);//假设result = {1,8},在找到1时,8还没有放进去,但是找到8时,1在hashmap里面,就找到了
10 }
11 return null;
12 }
1)Word Pattern
Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same
pattern. Here follow means a full match, such that there is a
bijection between a letter in pattern and a non-empty word in str.
Examples:
1. pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return true.
2. pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat fish" should return false.
3. pattern = "aaaa", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return false.
4. pattern = "abba", str = "dog dog dog dog" should return false.
Notes:
You may assume pattern contains only lowercase letters, and str
contains lowercase letters separated by a single space.
方法一
Keep a 1:1 mapping relationship
HashMap is A->B, so two HashMaps are needed for
A <-> B
public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String str) {
HashMap<Character, String> map = new HaspMap<>();
HashMap<String, Character> map_reverse = new HashMap<>();
String[] words = str.split(" ");
if (pattern.length() != words.length) {//length()
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) {
char a = pattern.chatAt(i);
String b = words[i];
if (!map.containsKey(a)) {
map.put(a, b);
} else if (!map.get(a).equals(b)) {
return false;
}
if (!map_reverse.containsKey(b)) {
map_reverse.put(b, a);
} else if (!map_reverse.get(b) != a) {//a is base type, can not use equals
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
方法二
Keep a 1:1 mapping relationship
HashMap is A->B, so two HashMaps are needed for A <-> B
Keep two A->B mappings at the same time
pattern -> index
string -> index
public boolean worPattern(String pattern, String str) {
HashMap<Character, Integer> mapPattern = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, Integer> mapStr = new HashMap<>();
String[] words = str.spilt(" ");
if (patterh.length() != words.length) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) {
int indexP = -1;
int indexS = -1;
Character a = pattern.charAt(i);
String b = word[i];
if (mapPattern.containsKey(a)) {
indexP = mapPattern.get(a);
} else {
mapPattern.put(a, i);
}
if (mapStr.containsKey(b)) {
indexS = mapStr.get(b);
} else {
mapStr.put(b, i);
}
if (indexP != indexS) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
方法三
public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String str) {
Map<Character, Integer> mappingPattern = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Integer> mappingStr = new HashMap<>();
String[] words = str.split(" ");
if (pattern.length() != words.length) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) {
if (!Objects.equals(mappingPattern.put(pattern.charAt(i), i),
mappingStr.put(words[i], i))) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
习题三Group Anagrams
Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
For example, given: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
Return:
[
["ate", "eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
public ArrayList<String> anagrams(String[] strs) {
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> mapping = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
char[] array = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(array);
String newStr = new String(array);//排序后生成一个新字符串,作为key
if (!mapping.containsKey(newStr)) {
ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<>();
strList.add(str);
mapping.put(array, strList);
} else {
mapping.get(newStr).add(str);
}
}
ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : mapping.keySet() { result.addAll(mapping.get(str)); }
return result;
}
lecture-9-hashmap的更多相关文章
- [C2P3] Andrew Ng - Machine Learning
##Advice for Applying Machine Learning Applying machine learning in practice is not always straightf ...
- HashMap与TreeMap源码分析
1. 引言 在红黑树--算法导论(15)中学习了红黑树的原理.本来打算自己来试着实现一下,然而在看了JDK(1.8.0)TreeMap的源码后恍然发现原来它就是利用红黑树实现的(很惭愧学了Ja ...
- HashMap的工作原理
HashMap的工作原理 HashMap的工作原理是近年来常见的Java面试题.几乎每个Java程序员都知道HashMap,都知道哪里要用HashMap,知道HashTable和HashMap之间 ...
- 计算机程序的思维逻辑 (40) - 剖析HashMap
前面两节介绍了ArrayList和LinkedList,它们的一个共同特点是,查找元素的效率都比较低,都需要逐个进行比较,本节介绍HashMap,它的查找效率则要高的多,HashMap是什么?怎么用? ...
- Java集合专题总结(1):HashMap 和 HashTable 源码学习和面试总结
2017年的秋招彻底结束了,感觉Java上面的最常见的集合相关的问题就是hash--系列和一些常用并发集合和队列,堆等结合算法一起考察,不完全统计,本人经历:先后百度.唯品会.58同城.新浪微博.趣分 ...
- 学习Redis你必须了解的数据结构——HashMap实现
本文版权归博客园和作者吴双本人共同所有,转载和爬虫请注明原文链接博客园蜗牛 cnblogs.com\tdws . 首先提供一种获取hashCode的方法,是一种比较受欢迎的方式,该方法参照了一位园友的 ...
- HashMap与HashTable的区别
HashMap和HashSet的区别是Java面试中最常被问到的问题.如果没有涉及到Collection框架以及多线程的面试,可以说是不完整.而Collection框架的问题不涉及到HashSet和H ...
- JDK1.8 HashMap 源码分析
一.概述 以键值对的形式存储,是基于Map接口的实现,可以接收null的键值,不保证有序(比如插入顺序),存储着Entry(hash, key, value, next)对象. 二.示例 public ...
- HashMap 源码解析
HashMap简介: HashMap在日常的开发中应用的非常之广泛,它是基于Hash表,实现了Map接口,以键值对(key-value)形式进行数据存储,HashMap在数据结构上使用的是数组+链表. ...
- java面试题——HashMap和Hashtable 的区别
一.HashMap 和Hashtable 的区别 我们先看2个类的定义 public class Hashtable extends Dictionary implements Map, Clonea ...
随机推荐
- 找工作--volatile
在Java编写的程序中,有时为了提高程序的运行效率,编译器会自动对其进行优化,把经常访问的变量缓存起来,程序在读取这个变量时有可能会直接从缓存(例如寄存器)中来读取这个值,而不会从内存中读取.这样做的 ...
- spring扩展点之四:Spring Aware容器感知技术,BeanNameAware和BeanFactoryAware接口,springboot中的EnvironmentAware
aware:英 [əˈweə(r)] 美 [əˈwer] adj.意识到的;知道的;觉察到的 XXXAware在spring里表示对XXX感知,实现XXXAware接口,并通过实现对应的set-XXX ...
- canvas变换(移动,缩放等)
代码: 1 /** 2 * Created by Administrator on 2016/1/30. 3 */ 4 function draw (id){ 5 var canvas = docum ...
- HttpApplication 对象的创建过程及HttpModule过滤器的内部实现过程
最近通过Reflector学习了一下asp.net内部的原理,做做笔记,方便以后查阅. 先看下HttpApplication 对象的创建过程 从IHttpHandler applicationInst ...
- linux日常管理-rsync后台服务方式-1
rsync的另外一种方式,写一个配置文件,放在etc下,通过一个命令启动他,它会监听一个端口,在客户端和服务端进行通信. 远程机器的配置文件 IP是192.168.1.117 配置文件的名字,写成这个 ...
- linux日常管理-rsync常用选项详解
-av 同步目录 写法 123/ /tmp/333/ 意思是把123下的文件同步到/tmp/333/下 结尾不加/ 只同步目录 两个目录一样的. //////////////////////// ...
- jquery.html5uploader.js 上传控件
插件地址:http://blog.csdn.net/never_say_goodbye/article/details/8598521 先上个效果图: 相比来说,效果还是很不错的 使用MVC3做服务器 ...
- 韩顺平循序渐进学JAVA从入门到精通 视频全套,需要的联系我
0讲-开山篇.avi 10讲-访问修饰符.重载.覆盖.avi 11讲-约瑟夫问题.avi 12讲-多态.avi 13讲-抽象类.接口.avi 14讲-final.作业评讲.avi 15讲-作业.测试题 ...
- .clearfix:after
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 面试题: Spring 框架 Bean的生命周期
[Java面试五]Spring总结以及在面试中的一些问题. 1.谈谈你对spring IOC和DI的理解,它们有什么区别? IoC Inverse of Control 反转控制的概念,就是将原本 ...