Spring入门第十七课
AOP编程
问题:
代码混乱:
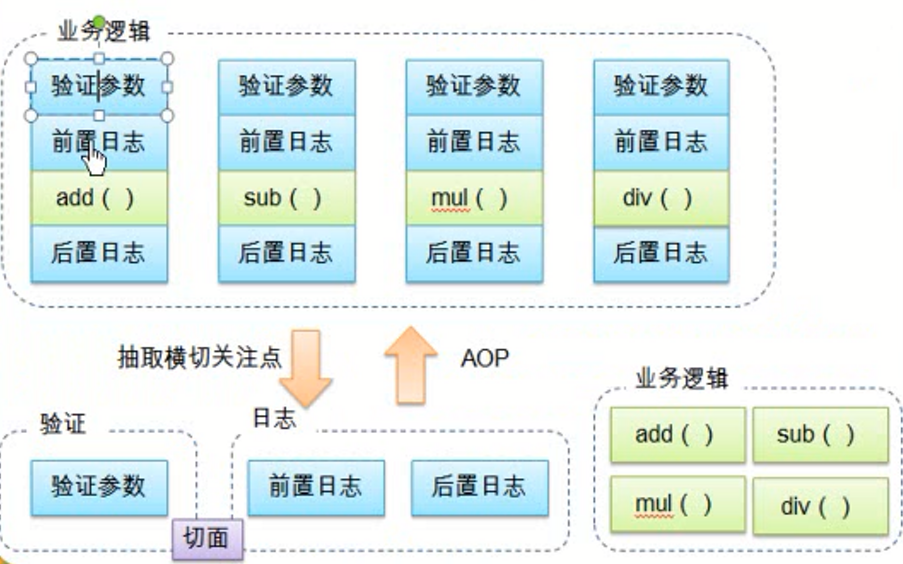
越来越多的非业务需求(日志和验证等)加入后,原有的业务方法急剧膨胀,每个方法在处理核心逻辑的同事还必须兼顾其他多个关注点。
代码分散:以日志需求为例,只是为了满足这个单一需求,就不得不在多个模块(方法)里面多次重复相同的日志代码,如果日志需求发生变化,必须修改所有模块。
先看使用动态代理:
package logan.study.aop.helloworld;
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}
package logan.study.aop.helloworld;
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int result = i + j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int result = i - j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int result = i * j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int result = i / j;
return result;
}
}
package logan.study.aop.helloworld; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays; public class ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy { //要代理的对象
private ArithmeticCalculator target; public ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(ArithmeticCalculator target){
this.target = target;
} public ArithmeticCalculator getLoggingProxy(){
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = null;
//代理对象由哪一个类加载器加载
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
//代理对象的类型,即其中有哪些方法
Class [] interfaces = new Class[]{ArithmeticCalculator.class};
//当调用代理对象其中的方法时,该执行的代码。
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* proxy:正在返回的那个对象,一般情况下,在invok方法中都不使用该对象
* method:正在被调用的方法
* args:调用方法时传入的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String methodName = method.getName();
//日志
System.out.println("The method "+ methodName + "begin with " + Arrays.asList(args));
//执行方法
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
//日志
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + "end with result = " + result);
//返回
return result;
}
};
proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h); return proxy;
} }
package logan.study.aop.helloworld;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArithmeticCalculator target = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl();
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = new ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(target).getLoggingProxy();
int result = proxy.add(1, 2);
System.out.println("-->"+result);
result = proxy.div(8, 2);
System.out.println("-->"+result);
}
}
返回的结果:
The method addbegin with [1, 2]
The method addend with result = 3
-->3
The method divbegin with [8, 2]
The method divend with result = 4
-->4
但是使用动态代理比较麻烦,有没有更简单的方法来实现呢?
AOP(Aspect-Oriented-Programming,面向切面编程)是一种新的方法论,是对传统OOP(Object-Oriented-Programming,面向对象编程)的补充。
AOP的主要编程对象是切面(Aspect),而切面是模块化横切关注点。
在应用AOP编程时,仍然需要定义公共功能,但是可以明确地定义这个功能在哪里,以什么方式应用,并且不必修改受影响的类,这样一来,横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的对象(切面)里。
AOP好处:
-每个事物逻辑错位与一个位置,代码不分散,便于维护和升级
-业务模块更简洁,只包含核心的业务代码
AOP术语
切面(Aspect):横切关注点(跨越应用程序多个模块的功能)被模块化的特殊对象。
通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作。
目标(Target):被通知的对象。
代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
连接点(Joinpoint):程序执行的每个特定位置:如类某个方法调用前,调用后,方法抛出异常等等,连接点由两个信息确定:方法表示的程序的执行点,相对点表示的方位,例如ArithmeticCalculator#add()方法执行前的连接点执行点为ArithmeticCalculator#add();方位为该方法执行前的位置。
切点(pointcut):每个类都拥有多个连接点,例如:ArithmethicCalculator的所有方法实际上都是连接点,即连接点是程序类中客观存在的事务,AOP通过切点定位到特定的连接点。类比:连接点相当于数据库中的记录,切点相当于查询条件,切点和连接点不是一对一关系,一个切点匹配多个连接点,切点通过org.springframework.aop.Pointcut接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件。
Spring入门第十七课的更多相关文章
- Spring入门第六课
XML配置里的Bean自动装配 Spring IOC容器可以自动装配Bean.需要做的仅仅是在<bean>的autowire属性里指定自动装配的模式 ByType(根据类型自动装配):若I ...
- Spring入门第五课
集合属性 在Spring中可以通过一组内置的xml标签(如:<list>,<set>,<map>)来配置集合属性. 配置java.util.List类型的属性,需要 ...
- Spring入门第四课
注入参数详解:null值和级联属性 可以使用专用的<null/>元素标签为Bean的字符串或其他对象类型的属性注入null值. 和Struts,Hiberante等框架一样,Spring支 ...
- Spring入门第三课
属性注入 属性注入就是通过setter方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象. 属性植入使用<property>元素,使用name属性指定Bean的属性名称,value属性或者<val ...
- Spring入门第十三课
通过FactoryBean来配置Bean package logan.spring.study.factoryBean; public class Car { private String brand ...
- Spring入门第十一课
IOC容器中Bean的生命周期 Spring IOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,Spring允许在Bean生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务. Spring IOC容器对Bean的生命周期进行管理的过 ...
- Spring入门第十课
Spring表达式语言:SpEL Spring表达式语言(简称SpEL)是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言. 语法类似于EL:SpEL使用#{...}作为定界符,所有在大括号中的字符都 ...
- Spring入门第八课
看如下代码 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http:// ...
- Spring入门第七课
Bean之间的关系:继承和依赖. 继承Bean配置 Spring允许继承bean的配置,被继承的bean称为父bean,继承这个父bean的Bean称为子Bean. 子Bean从父Bean中继承配置, ...
随机推荐
- EasyPlayerPro Windows流媒体播放器(RTSP/RTMP/HTTP/HLS/File/TCP/RTP/UDP都能播)发布啦
EasyPlayerPro简介 EasyPlayerPro是一款全功能的流媒体播放器,支持RTSP.RTMP.HTTP.HLS.UDP.RTP.File等多种流媒体协议播放.支持本地文件播放,支持本地 ...
- EasyDSS RTMP流媒体解决方案之Windows服务安装方案
Windows服务安装 EasyDSS_Solution流媒体解决方案,可以通过start一键启动.在实际应用中,我们希望可以设置成系统服务,那么下面我将会介绍,如何在windows中将流媒体解决方案 ...
- JavaScript 原型解析
1.什么是对象? javascript中除了null和undefined之外都是Object的实例. 在Javascript中, 每定义一个函数, 将伴生一个原型对象. 原型就是用来为同一类对 ...
- mysql系列之8.mysql高可用 (mha4mysql)
环境: 三台机器 主服务器: 192.168.1.130 主备机器: 192.168.1.131 监控机器: 192.168.1.132 130和131, 是mysql双主架构 1.在三台机器上安装m ...
- java参数的值传递和引用传递
今天抽了点时间继续啃java核心基础,即使出来做web挺长时间了,始终觉得基础极其重要. 遇到了java参数的传递类型,豁然开朗之时不忘写下记录. java中采用的总是值传递,包括对对象参数的传递,采 ...
- 关于String,StringBuffer与StringBuilder的区别
String是字符串常量对象,对其进行改变时会相当影响效率,特别注意在循环中直接拼接字符串效率非常差. 如果你想改变字符串的值,更加推荐使用StringBuffer与StringBuilder两种可变 ...
- client , offset , scroll 系列 及百度导航栏案例
1. client 系列 示例 : <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- React Native 微信分享闪退的解决办法
Android中编写微信分享功能时出现了闪退的现象,经过几番资料的查找,发现是应用签名的问题,解决办法如下: 1. 进入微信官网的开放平台--->资源中心---->资源下载----& ...
- ios图片瀑布流代码
ios瀑布流,实现简单的瀑布流视图布局,可以显示网络图片,下拉刷新,上拉加载更多. 下载:http://www.huiyi8.com/sc/9087.html
- 迁移学习——使用Tensorflow和VGG16预训模型进行预测
使用Tensorflow和VGG16预训模型进行预测 from:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/28997549 fast.ai的入门教程中使用了kaggle: dogs ...
