【集训笔记】计算几何【HDOJ2036【HDOJ1086【HDOJ1115【HDOJ1147【HDOJ1392 【ZOJ2976
改革春风吹满地 Time Limit: / MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: / K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): Accepted Submission(s): Problem Description
“ 改革春风吹满地,
不会AC没关系;
实在不行回老家,
还有一亩三分地。
谢谢!(乐队奏乐)” 话说部分学生心态极好,每天就知道游戏,这次考试如此简单的题目,也是云里雾里,而且,还竟然来这么几句打油诗。
好呀,老师的责任就是帮你解决问题,既然想种田,那就分你一块。
这块田位于浙江省温州市苍南县灵溪镇林家铺子村,多边形形状的一块地,原本是linle 的,现在就准备送给你了。不过,任何事情都没有那么简单,你必须首先告诉我这块地到底有多少面积,如果回答正确才能真正得到这块地。
发愁了吧?就是要让你知道,种地也是需要AC知识的!以后还是好好练吧... Input
输入数据包含多个测试实例,每个测试实例占一行,每行的开始是一个整数n(<=n<=),它表示多边形的边数(当然也是顶点数),然后是按照逆时针顺序给出的n个顶点的坐标(x1, y1, x2, y2... xn, yn),为了简化问题,这里的所有坐标都用整数表示。
输入数据中所有的整数都在32位整数范围内,n=0表示数据的结束,不做处理。 Output
对于每个测试实例,请输出对应的多边形面积,结果精确到小数点后一位小数。
每个实例的输出占一行。 Sample Input - - Sample Output
0.5
2.0
HDOJ2036
有关叉积相关:http://www.cnblogs.com/wushuaiyi/p/3458659.html
#include <stdio.h>
struct node{
double x,y;
}a[],p1,p2;
int main(){
int i,j,t;
double ans;
while(scanf("%d",&t)!=EOF){
if(t == )
break;
ans = 0.00000;
for(i=;i<t;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&a[i].x,&a[i].y);
for(i=;i<t-;i++){
ans += ((a[i].x * a[i+].y) - (a[i+].x * a[i].y))/;
}
ans+=((a[t-].x * a[].y) - (a[].x * a[t-].y))/;
printf("%.1lf\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
Lifting the Stone Time Limit: / MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: / K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): Accepted Submission(s): Problem Description
There are many secret openings in the floor which are covered by a big heavy stone. When the stone is lifted up, a special mechanism detects this and activates poisoned arrows that are shot near the opening. The only possibility is to lift the stone very slowly and carefully. The ACM team must connect a rope to the stone and then lift it using a pulley. Moreover, the stone must be lifted all at once; no side can rise before another. So it is very important to find the centre of gravity and connect the rope exactly to that point. The stone has a polygonal shape and its height is the same throughout the whole polygonal area. Your task is to find the centre of gravity for the given polygon. Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of them (T) is given on the first line of the input file. Each test case begins with a line containing a single integer N ( <= N <= ) indicating the number of points that form the polygon. This is followed by N lines, each containing two integers Xi and Yi (|Xi|, |Yi| <= ). These numbers are the coordinates of the i-th point. When we connect the points in the given order, we get a polygon. You may assume that the edges never touch each other (except the neighboring ones) and that they never cross. The area of the polygon is never zero, i.e. it cannot collapse into a single line. Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain exactly two numbers separated by one space. These numbers are the coordinates of the centre of gravity. Round the coordinates to the nearest number with exactly two digits after the decimal point (0.005 rounds up to 0.01). Note that the centre of gravity may be outside the polygon, if its shape is not convex. If there is such a case in the input data, print the centre anyway. Sample Input -
- Sample Output
0.00 0.00
6.00 6.00
HDOJ1115
求任意多边形的重心(from:http://www.cnblogs.com/bo-tao/archive/2011/08/16/2141395.html)
已知一多边形没有边相交,质量分布均匀。顺序给出多边形的顶点坐标,求其重心。
分析:
求多边形重心的题目大致有这么几种:
1,质量集中在顶点上。n个顶点坐标为(xi,yi),质量为mi,则重心
X = ∑( xi×mi ) / ∑mi
Y = ∑( yi×mi ) / ∑mi
特殊地,若每个点的质量相同,则
X = ∑xi / n
Y = ∑yi / n
2,质量分布均匀。这个题就是这一类型,算法和上面的不同。
特殊地,质量均匀的三角形重心:
X = ( x0 + x1 + x2 ) / 3
Y = ( y0 + y1 + y2 ) / 3
3,质量分布不均匀。只能用积分来算,不会……
求任意多边形的重心
已知一多边形没有边相交,质量分布均匀。顺序给出多边形的顶点坐标,求其重心。
分析:
求多边形重心的题目大致有这么几种:
1,质量集中在顶点上。n个顶点坐标为(xi,yi),质量为mi,则重心
X = ∑( xi×mi ) / ∑mi
Y = ∑( yi×mi ) / ∑mi
特殊地,若每个点的质量相同,则
X = ∑xi / n
Y = ∑yi / n
2,质量分布均匀。这个题就是这一类型,算法和上面的不同。
特殊地,质量均匀的三角形重心:
X = ( x0 + x1 + x2 ) / 3
Y = ( y0 + y1 + y2 ) / 3
3,质量分布不均匀。只能用积分来算,不会……
2.7.2 猜想n边形的重心
猜想由n个点(x1,y1), (x2,y2), ……, (xn,yn)
构成的多边形的重心的坐标是:( ( x1+x2...+xn )/n,( y1+y2+...+yn )/n );

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
double x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2;
int n,m;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){
for(int i=; i<=n; i++){
double sx,sy,s;
sx = sy = s =0.00000;
scanf("%d",&m);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x0,&y0,&x1,&y1);
for(int j=;j<m; j++){
scanf("%lf%lf",&x2,&y2);
double area=0.50000*((x1-x0)*(y2-y0)-(x2-x0)*(y1-y0));
sx+=area*(x0+x1+x2);//wait to divilded 3
sy+=area*(y0+y1+y2);
s+=area;
x1=x2;
y1=y2;
}
printf("%.2lf %.2lf\n",sx/(*s),sy/(*s));
}
}
return ;
}
You can Solve a Geometry Problem too Time Limit: / MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: / K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): Accepted Submission(s): Problem Description
Many geometry(几何)problems were designed in the ACM/ICPC. And now, I also prepare a geometry problem for this final exam. According to the experience of many ACMers, geometry problems are always much trouble, but this problem is very easy, after all we are now attending an exam, not a contest :)
Give you N (<=N<=) segments(线段), please output the number of all intersections(交点). You should count repeatedly if M (M>) segments intersect at the same point. Note:
You can assume that two segments would not intersect at more than one point. Input
Input contains multiple test cases. Each test case contains a integer N (=N<=) in a line first, and then N lines follow. Each line describes one segment with four float values x1, y1, x2, y2 which are coordinates of the segment’s ending.
A test case starting with terminates the input and this test case is not to be processed. Output
For each case, print the number of intersections, and one line one case. Sample Input 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
0.00 1.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
0.00 1.00 1.00 0.000
0.00 0.00 1.00 0.00 Sample Output
HDOJ1086
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath> using namespace std; const int maxv = ;
struct point { // 点
double x; // x 坐标
double y; // y 坐标
} first[maxv], final[maxv]; double intersect(point p1, point q1, point p2){
point tmp1, tmp2;
tmp1.x = q1.x - p1.x, tmp1.y = q1.y - p1.y; // tmp1 = q1-p1 是向量
tmp2.x = p2.x - p1.x, tmp2.y = p2.y - p1.y; // tmp2 = p2-p1 是向量
return tmp1.x * tmp2.y - tmp2.x * tmp1.y; // ans = (q1-p1) x (p2-p1) (向量叉积)
} int main(){
int n, i, j;
double ans1, ans2, ans3, ans4;
int cnt; //相交次数
while(cin >> n && n) {
cnt = ;
memset(first, , sizeof(first));
memset(final, , sizeof(final));
for(i = ; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> first[i].x >> first[i].y >> final[i].x >> final[i].y;
}
for(i = ; i < n; ++i) {
for(j = i+; j < n; ++j) {
ans1 = intersect(first[i], final[i], first[j]);
ans2 = intersect(first[i], final[i], final[j]);
double t1 = ans1 * ans2;
ans3 = intersect(first[j], final[j], first[i]);
ans4 = intersect(first[j], final[j], final[i]);
double t2 = ans3 * ans4;
if(t1 <= && t2 <= )
cnt++;
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
return ;
}
HDOJ1147
Pick-up sticks
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1858 Accepted Submission(s): 701
has n sticks of various length. He throws them one at a time on the
floor in a random way. After finishing throwing, Stan tries to find the
top sticks, that is these sticks such that there is no stick on top of
them. Stan has noticed that the last thrown stick is always on top but
he wants to know all the sticks that are on top. Stan sticks are very,
very thin such that their thickness can be neglected.
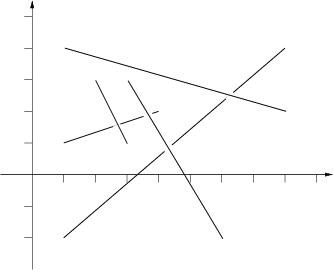
consists of a number of cases. The data for each case start with 1 ≤ n ≤
100000, the number of sticks for this case. The following n lines
contain four numbers each, these numbers are the planar coordinates of
the endpoints of one stick. The sticks are listed in the order in which
Stan has thrown them. You may assume that there are no more than 1000
top sticks. The input is ended by the case with n=0. This case should
not be processed.
each input case, print one line of output listing the top sticks in the
format given in the sample. The top sticks should be listed in order in
which they were thrown.
The picture to the right below illustrates the first case from input.
1 1 4 2
2 3 3 1
1 -2.0 8 4
1 4 8 2
3 3 6 -2.0
3
0 0 1 1
1 0 2 1
2 0 3 1
0
Top sticks: 1, 2, 3.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<stdio.h> using namespace std; const int maxv = ;
struct point { // 点
double x; // x 坐标
double y; // y 坐标
} first[maxv], final[maxv]; double intersect(point p1, point q1, point p2){
point tmp1, tmp2;
tmp1.x = q1.x - p1.x, tmp1.y = q1.y - p1.y; // tmp1 = q1-p1 是向量
tmp2.x = p2.x - p1.x, tmp2.y = p2.y - p1.y; // tmp2 = p2-p1 是向量
return tmp1.x * tmp2.y - tmp2.x * tmp1.y; // ans = (q1-p1) x (p2-p1) (向量叉积)
} int main(){
int n, i, j, flag[];
double ans1, ans2, ans3, ans4;
while(cin >> n && n) {
memset(flag, -, sizeof(flag));
memset(first, , sizeof(first));
memset(final, , sizeof(final));
for(i = ; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> first[i].x >> first[i].y >> final[i].x >> final[i].y;
}
for(i = ; i < n; i++) {
for(j = i+; j < n; j++) {
ans1 = intersect(first[i], final[i], first[j]);
ans2 = intersect(first[i], final[i], final[j]);
double t1 = ans1 * ans2;
ans3 = intersect(first[j], final[j], first[i]);
ans4 = intersect(first[j], final[j], final[i]);
double t2 = ans3 * ans4;
if(t1 <= && t2 <= ){
flag[i] = ;
break;
}
}
if(flag[i] == -)
flag[i] = ;
}
printf("Top sticks:");
for(i=;i<n-;i++){
if(flag[i] == )
printf(" %d,",i+);
}
printf(" %d.\n",n);
}
return ;
}
Surround the Trees
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 6758 Accepted Submission(s): 2567
are a lot of trees in an area. A peasant wants to buy a rope to
surround all these trees. So at first he must know the minimal required
length of the rope. However, he does not know how to calculate it. Can
you help him?
The diameter and length of the trees are omitted,
which means a tree can be seen as a point. The thickness of the rope is
also omitted which means a rope can be seen as a line.
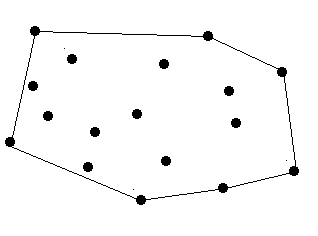
There are no more than 100 trees.
input contains one or more data sets. At first line of each input data
set is number of trees in this data set, it is followed by series of
coordinates of the trees. Each coordinate is a positive integer pair,
and each integer is less than 32767. Each pair is separated by blank.
Zero at line for number of trees terminates the input for your program.
12 7
24 9
30 5
41 9
80 7
50 87
22 9
45 1
50 7
0
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std; struct node{
int x,y;
};
node a[],stack1[]; double dis(node n1,node n2)//求距离{
return (double)sqrt( (n1.x-n2.x)*(n1.x-n2.x)*1.0 + (n1.y-n2.y)*(n1.y-n2.y)*1.0 );
}
double cross(node a,node n1,node n2)// 为正时 "左转"{
return (n1.x-a.x)*(n2.y-a.y) - (n1.y-a.y)*(n2.x-a.x);
}
bool cmp(node n1,node n2)// 叉乘越小的,越靠前{
double k = cross(a[],n1,n2);
if( k>) return true;
else if( k== && dis(a[],n1)<dis(a[],n2))
return true;
else return false;
}
void Graham(int n){
int i,head;
double r=;
for(i=;i<n;i++)
if(a[i].x<a[].x ||(a[i].x==a[].x&&a[i].y<a[].y ) )
swap(a[],a[i]);
sort(a+,a+n,cmp); //排序
a[n]=a[]; //为了对最后一点的检验是否为满足凸包。cross(stack1[head-1],stack1[head],stack[i]);
stack1[]=a[];
stack1[]=a[];
stack1[]=a[];// 放入3个先
head=;
for(i=;i<=n;i++)
{
while( head>= && cross(stack1[head-],stack1[head],a[i])<= )head--;
// == 包含了重点和共线的情况。此题求周长,并没有关系。所以不加==,也是可以的。
stack1[++head]=a[i];
}
for(i=;i<head;i++) //不是<=. 因为 a[0]在 0 和 head 两个位置都出现了。
{
r=r+dis(stack1[i],stack1[i+]);
}
printf("%.2lf\n",r);
}
int main(){
int i,n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)>)
{
if(n==)break;
for(i=;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y);//end input
if(n==)//特判
{
printf("0.00\n");
continue;
}
if(n==)//此题的特判
{
printf("%.2lf\n",dis(a[],a[]));
continue;
}
Graham(n);
}
return ;
}
Light Bulbs
Time Limit: Seconds Memory Limit: KB Wildleopard had fallen in love with his girlfriend for years. He wanted to end the long match for their love and get married this year. He bought a new house for his family and hired a company to decorate his house. Wildleopard and his fiancee were very satisfied with the postmodern design, except the light bulbs. Varieties of light bulbs were used so that the light in the house differed a lot in different places. Now he asks you, one of his best friends, to help him find out the point of maximum illumination. To simplify the problem, we can assume each bulb is a point light source and we only need to consider the grid points of the flat floor of the house. A grid point is a point whose coordinates are both integers. The length and the width of house can be considered infinite. Illumination means the amount of light that go through in one unit area. The illumination of a point can be calculated by simply adding the illumination from each source. The illumination from a source can be calculated by the following equation: , where E is the illumination of the point, I is the luminous intensity of the source, R is the distance between the source and the point and i is the angle between the normal of the plane and the light to the point. Given the position and the luminous intensity of the light bulbs, you are asked to find the maximum illumination on the floor at the grid points. Input Standard input will contain multiple test cases. The first line of the input is a single integer T ( <= T <= ) which is the number of test cases. And it will be followed by T consecutive test cases. The first line of each test case contains one integer n( <= n <= ), indicating the number of bulbs of the lamps in the house. The next n lines will contain integers each, Xi, Yi, Zi, Ii, separated by one space, indicating the coordinates and the luminous intensity of the i-th bulb of the lamp. The absolute values of the coordinates do not exceed and Zi is always positive. Ii is a positive integer less than . Output Results should be directed to standard output. The output of each test case should be a real number rounded to 0.01, which is the maximum illumination on the floor at the grid points. Sample Input -
- -
- Sample Output 100.00
147.43
4.00
ZOJ 2976
注意读懂意即可
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
struct node{
double x,y,z,I;
}a[]; double distance(struct node a,int i,int j){
return (a.x-(double)i)*(a.x-(double)i) + (a.y-(double)j)*(a.y-(double)j) + a.z*a.z;
} int main()
{
int t,n,i,j,k;
double ans,Maxs,temp;
while(scanf("%d",&t)!=EOF){
while(t--){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a[i].x,&a[i].y,&a[i].z,&a[i].I);
}
Maxs = 0.0000;
for(i=-;i<=;i++){
for(j=-;j<=;j++){
ans = 0.0000;
for(k=;k<=n;k++){
temp = distance(a[k],i,j);
ans += a[k].I / temp * a[k].z / sqrt(temp);
}
if(ans > Maxs)
Maxs = ans;
}
}
printf("%.2lf\n",Maxs);
}
}
return ;
}
【集训笔记】计算几何【HDOJ2036【HDOJ1086【HDOJ1115【HDOJ1147【HDOJ1392 【ZOJ2976的更多相关文章
- 2019暑期金华集训 Day6 计算几何
自闭集训 Day6 计算几何 内积 内积不等式: \[ (A,B)^2\le (A,A)(B,B) \] 其中\((A,B)\)表示\(A\cdot B\). (好像是废话?) 叉积 \[ A\tim ...
- QDEZ集训笔记【更新中】
这是一个绝妙的比喻,如果青岛二中的台阶上每级站一只平度一中的猫,差不多站满了吧 自己的理解 [2016-12-31] [主席树] http://www.cnblogs.com/candy99/p/61 ...
- 2017清北学堂(提高组精英班)集训笔记——动态规划Part3
现在是晚上十二点半,好累(无奈脸),接着给各位——也是给自己,更新笔记吧~ 序列型状态划分: 经典例题:乘积最大(Luogu 1018) * 设有一个长度为 N 的数字串,要求选手使用 K 个乘号将它 ...
- [英语学习]微软面试前英语集训笔记-day 1
最近有机会参加微软面试前的英语集训. 第一天是由wendy老师主讲.热场题目是介绍你自己.包括你的姓名,家庭hobby,爱好,专业,学校,工作经历等等. 接下来的主题是friendship.给我印象较 ...
- zhengrui集训笔记2
Day_6 计算几何 点积\Large 点积点积 叉积\Large 叉积叉积 极角\Large 极角极角 < π\piπ :叉积判断 else :atan2 旋转\Large 旋转旋转 左乘第一 ...
- 【集训笔记】博弈论相关知识【HDOJ 1850【HDOJ2147
以下资料来自:http://blog.csdn.net/Dinosoft/article/details/6795700 http://qianmacao.blog.163.com/blog/stat ...
- 【集训笔记】母函数【母函数模板】【HDOJ1028【HDOJ1085
以下资料摘自 http://www.cnblogs.com/wally/archive/2012/07/13/hdu1028_1085_1171_.html 生成函数是说,构造这么一个多项式函数g(x ...
- 【集训笔记】【大数模板】特殊的数 【Catalan数】【HDOJ1133【HDOJ1134【HDOJ1130
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=3324 http://blog.csdn.net/xymscau/artic ...
- 【集训笔记】动态规划背包问题【HDOJ1421【HDOJ1058【HDOJ2546
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2546 http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showContestProblem. ...
随机推荐
- 利用python进行数据分析之pandas库的应用(二)
本节介绍Series和DataFrame中的数据的基本手段 重新索引 pandas对象的一个重要方法就是reindex,作用是创建一个适应新索引的新对象 >>> from panda ...
- 神奇的魔法数字0x61c88647
来源JDK源码,产生的数字分布很均匀 用法代码如下. # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647 def magic_hash(n): fo ...
- 字符串匹配算法1-KMP
前面介绍过,字符串搜索一般来说有三种方式,前缀搜索,后缀搜索,子串搜索.KMP使用的是前缀搜索. 假设p的偏移是i,也就是窗口的位置是i,匹配到位置j+1时发现了不匹配.现在的问题是向前移动窗口到什么 ...
- LintCode-比较字符串
题目描述: 比较两个字符串A和B,确定A中是否包含B中所有的字符.字符串A和B中的字符都是 大写字母 注意事项 在 A 中出现的 B 字符串里的字符不需要连续或者有序. 样例 给出 A = " ...
- Qt实战之开发CSDN下载助手 (2)
现在,我们正式开工啦.这一篇主要学习下基本的抓包分析.学会协议登录CSDN并制作登陆界面. 准备工具: 一款http抓包工具. 可以是FireBug或者fiddler.这里我们用httpWatch. ...
- java线程学习——汉堡销售问题
汉堡店中有一个负责做汉堡的厨师,一个负责销售的营业员,用java线程表示他们的营业过程: 问题原型就是生产者与消费者的问题. 首先定义一个汉堡包箱子类与几个相关的变量类: public class H ...
- Linux下shell编程实例
1. 推断一文件是不是块或字符设备文件.假设是将其复制到 /dev 文件夹下 read -p "input a file:" filename if [ -b $filename ...
- Android API 中文(77)——AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener
前言 本章内容是android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener,版本为Android 2.3 r1,翻译来自"cnmahj",欢 ...
- Ext JS学习第八天 Ext基础之 认识Ext.js 和Ext-more.js
此文来记录学习笔记: •认识Ext.js 和Ext-more.js •首先,我们要知道这2个js文件的作用,这俩个文件包含了Ext的一些基础定义.基本的属性和方法,我们要重点学习和深入底层代码进行研究 ...
- View中的onTouchEvent()与setOnTouchListener()中的ontouch()方法的事件处理先后顺序
Touch事件的两种情况 1.覆写View.class中定义的onTouchEvent-->基于事件回调监听方式 @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(Mo ...
