Elven Postman(二叉树)
Elven Postman
Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1091 Accepted Submission(s): 617
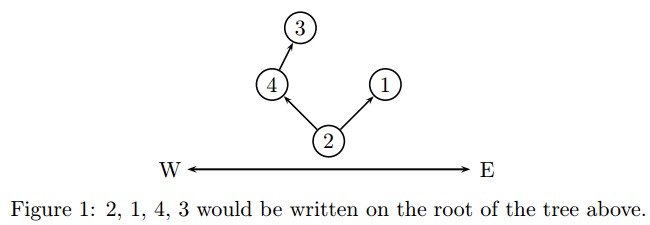
So, as a elven postman, it is crucial to understand how to deliver the mail to the correct room of the tree. The elven tree always branches into no more than two paths upon intersection, either in the east direction or the west. It coincidentally looks awfully like a binary tree we human computer scientist know. Not only that, when numbering the rooms, they always number the room number from the east-most position to the west. For rooms in the east are usually more preferable and more expensive due to they having the privilege to see the sunrise, which matters a lot in elven culture.
Anyways, the elves usually wrote down all the rooms in a sequence at the root of the tree so that the postman may know how to deliver the mail. The sequence is written as follows, it will go straight to visit the east-most room and write down every room it encountered along the way. After the first room is reached, it will then go to the next unvisited east-most room, writing down every unvisited room on the way as well until all rooms are visited.
Your task is to determine how to reach a certain room given the sequence written on the root.
For instance, the sequence 2, 1, 4, 3 would be written on the root of the following tree.
For each test case, there is a number n(n≤1000) on a line representing the number of rooms in this tree. n integers representing the sequence written at the root follow, respectively a1,...,an where a1,...,an∈{1,...,n}.
On the next line, there is a number q representing the number of mails to be sent. After that, there will be q integers x1,...,xq indicating the destination room number of each mail.
Note that for simplicity, we assume the postman always starts from the root regardless of the room he had just visited.
4
2 1 4 3
3
1 2 3
6
6 5 4 3 2 1
1
1
题解:精灵族住在一颗倒着的二叉树上,这棵二叉树是从东到西编号,最东边是1,依次类推,邮递员要给精灵送信,每次邮递员都在最底下的点上,让输出邮递员的路径,思想就是建一颗倒着的二叉树,如果编号小就在东边建,也就是右边,大了就建在左边,每次建图直接把路径存上就妥了;
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define mem(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
const int MAXN=1010;
vector<char>path[MAXN];
struct Node{
Node *L,*R;
int nu;
Node(int x=0):nu(x){
L=NULL;R=NULL;
}
}*rot;
void inst(int x){
Node *p=rot;
while(1){
if(x>p->nu){
path[x].push_back('W');
if(p->L==NULL){
p->L=new Node(x);
break;
}
else p=p->L;
}
else{
path[x].push_back('E');
if(p->R==NULL){
p->R=new Node(x);
break;
}
else p=p->R;
}
}
}
int main(){
int T,n,q;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
for(int i=0;i<MAXN;i++)path[i].clear();
scanf("%d",&n);
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
rot=new Node(x);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&x);
inst(x);
}
scanf("%d",&q);
while(q--){
scanf("%d",&x);
for(int i=0;i<path[x].size();i++)
printf("%c",path[x][i]);
puts("");
}
}
return 0;
}
java:注意java的对象传递是引用类型, 但是tree = new Tree()会给tree重新分配一个jvm地址,这时候tree的改变不会使原值改变,此时变成了值传递,所以想了个思路,就是在类里面对属性复制,也就是newL(),newR()方法;
代码:
package com.lanqiao.week1; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner; public class hdu5444 {
private static Scanner cin = null;
static{
cin = new Scanner(System.in);
}
static class Tree{
public Tree l;
public Tree r;
public int value; public void newL(int v){
l = new Tree(null, null, v);
} public void newR(int v){
r = new Tree(null, null, v);
}
public static void insert(Tree t, int v){
if(v > t.value){
if(t.r != null)
insert(t.r, v);
else
t.newR(v);
}else{
if(t.l != null)
insert(t.l, v);
else
t.newL(v);
}
}
public static void visit(Tree t, int v){
if(t == null)
return;
if(v == t.value){
return;
}
if(v > t.value){
System.out.print("W");
visit(t.r, v);
}else{
System.out.print("E");
visit(t.l, v);
}
}
public Tree() {
super();
}
public Tree(Tree l, Tree r, int value) {
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
this.value = value;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int T, n, q, a, v;
T = cin.nextInt();
while(T-- > 0){
n = cin.nextInt();
a = cin.nextInt();
Tree t = new Tree(null, null, a); for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
a = cin.nextInt();
Tree.insert(t, a);
}
q = cin.nextInt();
//System.out.println(t);
while(q-- > 0){
v = cin.nextInt();
Tree.visit(t, v);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
Elven Postman(二叉树)的更多相关文章
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman 二叉树
Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others) Problem Descrip ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(二叉树)——2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
Problem Description Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long ...
- (二叉树)Elven Postman -- HDU -- 54444(2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Description Elves are very peculia ...
- 2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online HDU 5444 Elven Postman【二叉排序树的建树和遍历查找】
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(长春网路赛——平衡二叉树遍历)
题目链接:pid=5444http://">http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Time Limi ...
- Elven Postman(BST )
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- Hdu 5444 Elven Postman dfs
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid= ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman (2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online)
Elven Postman Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long time ...
随机推荐
- A Brief Introduction to Multiset[STL]
基础 multiset是<set>库中一个非常有用的类型,它可以看成一个序列,插入一个数,删除一个数都能够在O(logn)的时间内完成,而且他能时刻保证序列中的数是有序的,而且序列中可以存 ...
- C++头文件的包含顺序研究
一.<Google C++ 编程风格指南>里的观点 公司在推行编码规范,领导提议基本上使用<Google C++ 编程风格指南>.其中<Google C++ 编程风格指南 ...
- BZOJ 1739: [Usaco2005 mar]Space Elevator 太空电梯
题目 1739: [Usaco2005 mar]Space Elevator 太空电梯 Time Limit: 5 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MB Description The c ...
- Java中String、StringBuilder以及StringBuffer
原文出处: 海子 相信String这个类是Java中使用得最频繁的类之一,并且又是各大公司面试喜欢问到的地方,今天就来和大家一起学习一下String.StringBuilder和StringBuffe ...
- nginx服务器屏蔽上游错误码
平时的开发工作中,有时会遇到脚本权限不对导致403,文件被删除导致404,甚至后端业务异常导致5xx等情况,其实我们可以在服务器加上判断,检测当后端服务出现异常的时候前端返回一个指定的静态文件(也可以 ...
- 柯里化函数之Javascript
柯里化函数之Javascript 定义 依据定义来说,柯里化就是将一个接收"多个"參数的函数拆分成一个或者很多个接收"单一"參数的函数.定义看起来是比較抽象的. ...
- Android UI 之一步步教你自定义控件(自定义属性、合理设计onMeasure、合理设计onDraw等)
Android开发做到了一定程度,多少都会用到自定义控件,一方面是更加灵活,另一方面在大数据量的情况下自定义控件的效率比写布局文件更高. 一个相对完善的自定义控件在布局文件中和java ...
- android api 中文 (74)—— AdapterView.AdapterContextMenuInfo
前言 本章内容是android.widget.AdapterView.AdapterContextMenuInfo,版本为Android 2.3 r1,翻译来自"cnmahj",欢 ...
- hdu4725 The Shortest Path in Nya Graph【最短路+建图】
转载请注明出处,谢谢:http://www.cnblogs.com/KirisameMarisa/p/4297574.html ---by 墨染之樱花 题目链接:http://acm.hdu ...
- 精通Activity
在平时开发中,Activity我们每个人应用的都滚瓜烂熟,回忆起来没有太难的地方,但是我们学习知识不应该只知其一不知其二,这样才能在学习的道理上越走越远,今天我要给大家分享的内容会让大家明白一些And ...
